SmartCar is a project which aims to navigate readers in the library to help find the book they want. The car can autonomously drive to the right bookshelf after you input the name of the book.
The major work of our project is to achieve accurate indoor localization. To solve this, we combine the traditional inertial navigation technology with image processing.
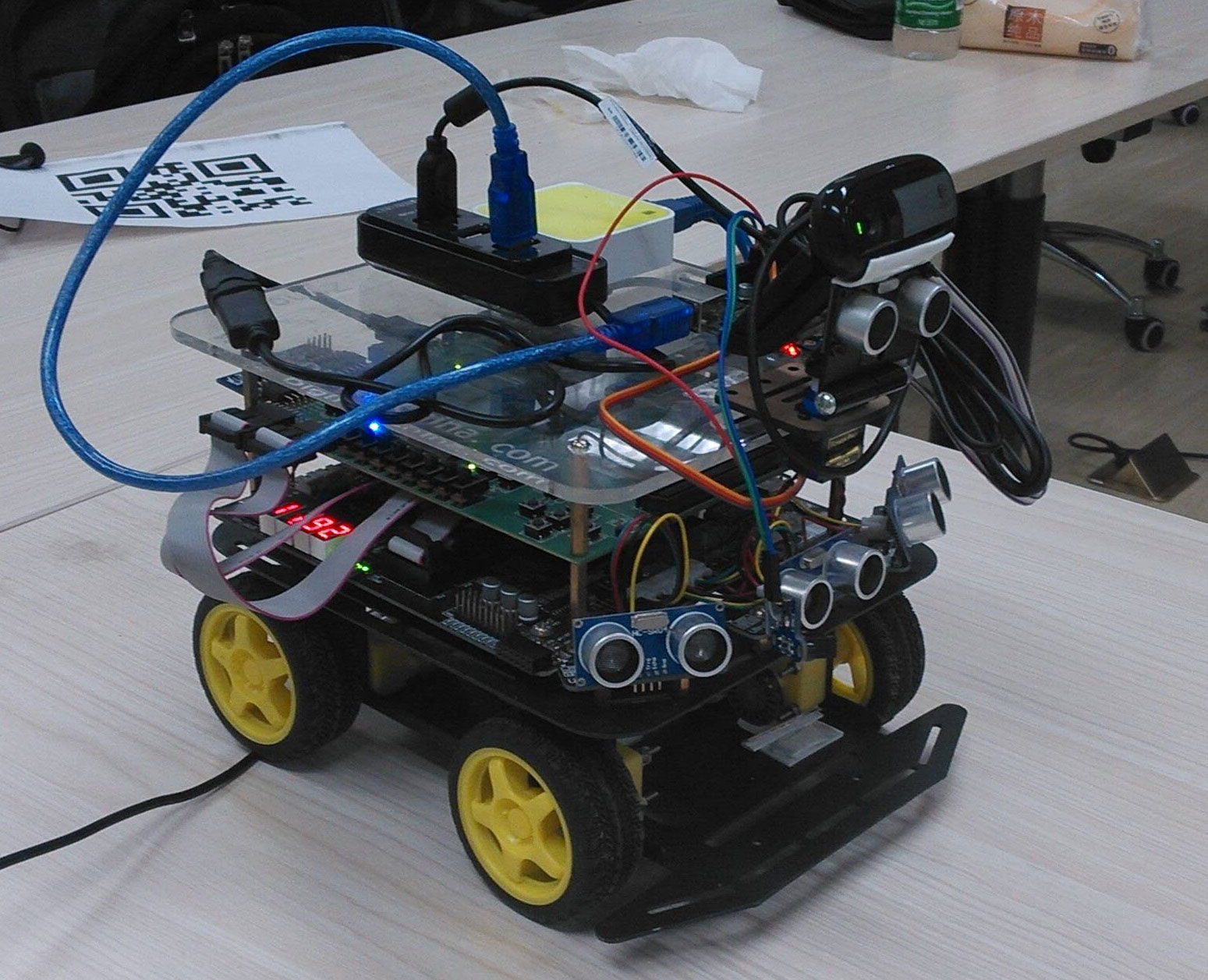
We use the platform ZRobot which is an all programmable robot with motors, camera, ultrasonic sensors and wireless AP. And it is capable of finishing tasks requiring fast movement, obstruction avoidance, computer vision and remote control.
The car consists of two layer boards, one is for control and the other for power supply. The heart of the control board is a Zynq®-7000 chip, which is the newest FPGA chip integrating FPGA resources with ARM-A9 hard core. We run the software on the hard core and take advantage of FPGA resources as middleware between the software and exterior sensors or devices.
The picture above is the original ZRobot. We have made some changes to the car, as shown in image below.
###1. Hardware ### The chart below shows the sensors or devices we add to the car and their corresponding usage.
| device | measured data | usage |
|---|---|---|
| accelerator sensor | acceleration | get the displacement by double integral of speed |
| gyroscope | angular speed | get the angle by integral of angular speed |
| Hall sensor | number of rotations of the wheel | get the distance |
| ultrasonic sensors | distance | detecting and avoiding obstruction |
| digital Pan-Tilt | providing accurate positioning of cameras and ultrasonic sensor | |
| USB Camera | image | localization by image recognition |
| Wireless AP | communication between the car and the computer or smart phone |
###2. Software ### We have used C, Java and Verilog in our project. Verilog code is to implement the controllers of various sensors on FPGA. And the these controllers are connected to CPU via AXI4 bus and corresponding Linux drivers are written in C. Java code is used on the top layer of software hierarchy, achieving the functions of autonomous driving, path planning and obstruction avoidance.
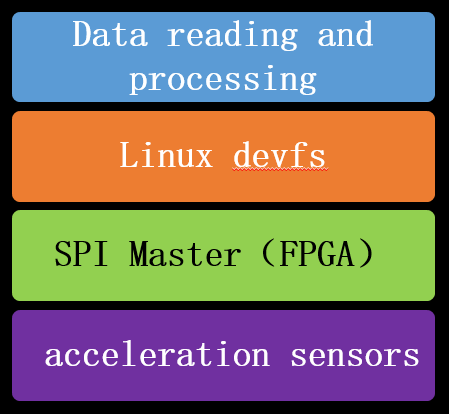
The picture below is the software hierarchy of acceleration sensor.
###1. Kalman filter ### For the inevitable noises of the measured data, we cannot carry out the integral of original data directly. And thus we adopt the Kalman filter to smooth the data and get relatively stable results. The code for Kalman filter comes from the library OpenCV.
###2. QR Code ### The paper with QR Code image is stuck on the wall. And the car could recognize the QR Code image from the camera by using image processing algorithm. After decoding the image we could get the location of the car.
###3. Path planning ### First, we insert the map data into the car and it shall rasterize data. Then we will use Dijkstra algorithm to get both optimal and the shortest path from the car's current location to the destination dynamically.