This notebook will be used to prepare the capstone project 'Eye for Blind'
#Import all the required libraries
#Import all the required libraries
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import os
import PIL
import random
import collections
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import string
import glob
from PIL import Image
from matplotlib.pyplot import figure
import tensorflow as tf
from operator import itemgetter
from tensorflow import keras
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from tensorflow.keras import layers, Model
from tqdm import tqdm
import time
from nltk.translate.bleu_score import sentence_bleu
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')Let's read the dataset
from google.colab import drive
drive.mount('/content/drive')Mounted at /content/drive
1.Import the dataset and read image & captions into two seperate variables
2.Visualise both the images & text present in the dataset
3.Create a dataframe which summarizes the image, path & captions as a dataframe
4.Create a list which contains all the captions & path
5.Visualise the top 30 occuring words in the captions
#Import the dataset and read the image into a seperate variable
# Loading The text Data
text_path = '/content/drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/captions.txt'
text = open(text_path).readlines()
# Loading the images data
img_path = "drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/Flickr8k_Dataset/Flicker8k_Dataset"
images = os.listdir(img_path)
all_imgs = glob.glob(img_path + '/*.jpg',recursive=True)
print("The total images present in the dataset: {}".format(len(all_imgs)))The total images present in the dataset: 8091
#Visualise both the images & text present in the dataset
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 4)
fig.set_figwidth(20)
for _ in range(len(axes)):
axes[_].imshow(Image.open(random.choice(all_imgs)))
for _ in range(4):
print(random.choice(text))3626689571_5817f99c0e.jpg,Tall man in red and black stands outside holding basketball .
2486364531_b482d7f521.jpg,Boy wearing a red shirt standing on a plastic object and holding a yellow toy shovel .
2992808092_5f677085b7.jpg,Two boys fight for the ball .
3419238351_ac18b440c0.jpg,A bunch of people watching a child in the bathtub .
#Import the dataset and read the text file into a seperate variable
def load_doc(filename):
text = pd.read_csv(filename)
return text
text_file = text_path
doc = load_doc(text_file)
print(doc.shape[0])
doc[:10]40455
.dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| image | caption | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | A child in a pink dress is climbing up a set o... |
| 1 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | A girl going into a wooden building . |
| 2 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | A little girl climbing into a wooden playhouse . |
| 3 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | A little girl climbing the stairs to her playh... |
| 4 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | A little girl in a pink dress going into a woo... |
| 5 | 1001773457_577c3a7d70.jpg | A black dog and a spotted dog are fighting |
| 6 | 1001773457_577c3a7d70.jpg | A black dog and a tri-colored dog playing with... |
| 7 | 1001773457_577c3a7d70.jpg | A black dog and a white dog with brown spots a... |
| 8 | 1001773457_577c3a7d70.jpg | Two dogs of different breeds looking at each o... |
| 9 | 1001773457_577c3a7d70.jpg | Two dogs on pavement moving toward each other . |
Create a dataframe which summarizes the image, path & captions as a dataframe
Each image id has 5 captions associated with it therefore the total dataset should have 40455 samples.
all_img_id= doc['image']
all_img_vector= [img_path+'/'+_ for _ in all_img_id]
annotations= doc['caption']
df = pd.DataFrame(list(zip(all_img_id, all_img_vector,annotations)),columns =['ID','Path', 'Captions'])
df.dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| ID | Path | Captions | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/Flickr8k_Data... | A child in a pink dress is climbing up a set o... |
| 1 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/Flickr8k_Data... | A girl going into a wooden building . |
| 2 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/Flickr8k_Data... | A little girl climbing into a wooden playhouse . |
| 3 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/Flickr8k_Data... | A little girl climbing the stairs to her playh... |
| 4 | 1000268201_693b08cb0e.jpg | drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/Flickr8k_Data... | A little girl in a pink dress going into a woo... |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 40450 | 997722733_0cb5439472.jpg | drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/Flickr8k_Data... | A man in a pink shirt climbs a rock face |
| 40451 | 997722733_0cb5439472.jpg | drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/Flickr8k_Data... | A man is rock climbing high in the air . |
| 40452 | 997722733_0cb5439472.jpg | drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/Flickr8k_Data... | A person in a red shirt climbing up a rock fac... |
| 40453 | 997722733_0cb5439472.jpg | drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/Flickr8k_Data... | A rock climber in a red shirt . |
| 40454 | 997722733_0cb5439472.jpg | drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/Flickr8k_Data... | A rock climber practices on a rock climbing wa... |
40455 rows × 3 columns
#Create a list which contains all the captions
annotations= list(df['Captions'])
#add the <start> & <end> token to all those captions as well
annotations = ['<start> '+_+' <end>' for _ in annotations]
#Create a list which contains all the path to the images
all_img_path= [img_path+'/'+_ for _ in os.listdir(img_path)]
print("Total captions present in the dataset: "+ str(len(annotations)))
print("Total images present in the dataset: " + str(len(all_img_path)))Total captions present in the dataset: 40455
Total images present in the dataset: 8091
#Create the vocabulary & the counter for the captions
def Counter(vocab):
frequency = collections.Counter(vocab)
return frequency
def Vocab(text):
text = text.split(' ')
text = [_.strip().lower() for _ in text if _ not in string.punctuation]
return text
vocabulary= Vocab(' '.join(annotations))
val_count = Counter(vocabulary)
df_word = pd.DataFrame.from_dict(val_count, orient='index')
df_word = df_word.sort_values(by=[0],ascending=False).reset_index()
df_word =df_word.rename(columns={'index':'word', 0:'count'})
df_word[0:5].dataframe tbody tr th {
vertical-align: top;
}
.dataframe thead th {
text-align: right;
}
| word | count | |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | a | 62986 |
| 1 | <start> | 40455 |
| 2 | <end> | 40455 |
| 3 | in | 18974 |
| 4 | the | 18418 |
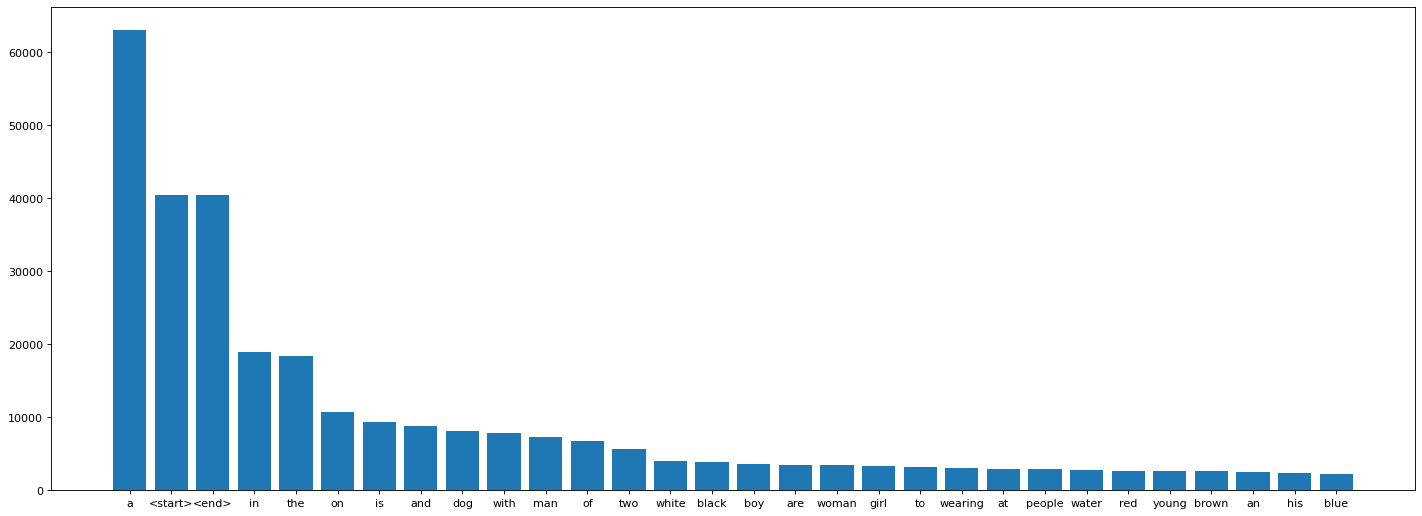
#Visualise the top 30 occuring words in the captions
figure(figsize=(22, 8), dpi=80)
plt.bar(df_word[:30]['word'],df_word[:30]['count'])
#write your code here<BarContainer object of 30 artists>
1.Create the tokenized vectors by tokenizing the captions fore ex :split them using spaces & other filters. This gives us a vocabulary of all of the unique words in the data. Keep the total vocaublary to top 5,000 words for saving memory.
2.Replace all other words with the unknown token "UNK" .
3.Create word-to-index and index-to-word mappings.
4.Pad all sequences to be the same length as the longest one.
# create the tokenizer
top_freq_words = 5001
tokenizer = tf.keras.preprocessing.text.Tokenizer(
num_words = top_freq_words,
filters = string.punctuation.replace('<','').replace('>',''),
lower=True, split=' ', char_level=False, oov_token="UNK"
)
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(annotations)
# Create the tokenized vectors
cap_sequences = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(annotations)
print(cap_sequences[:3]) [[3, 2, 44, 5, 2, 91, 173, 8, 120, 52, 2, 394, 13, 395, 5, 29, 1, 671, 4], [3, 2, 20, 317, 65, 2, 197, 118, 4], [3, 2, 41, 20, 120, 65, 2, 197, 2438, 4]]
# Create word-to-index and index-to-word mappings.
def word_to_index(word):
return tokenizer.word_index[word]
def index_to_word(index):
return tokenizer.index_word[index]
print("index of 'the' is " + str(word_to_index('the')))
print("word of index 7 is '" + str(index_to_word(7)) + "'")index of 'the' is 6
word of index 7 is 'on'
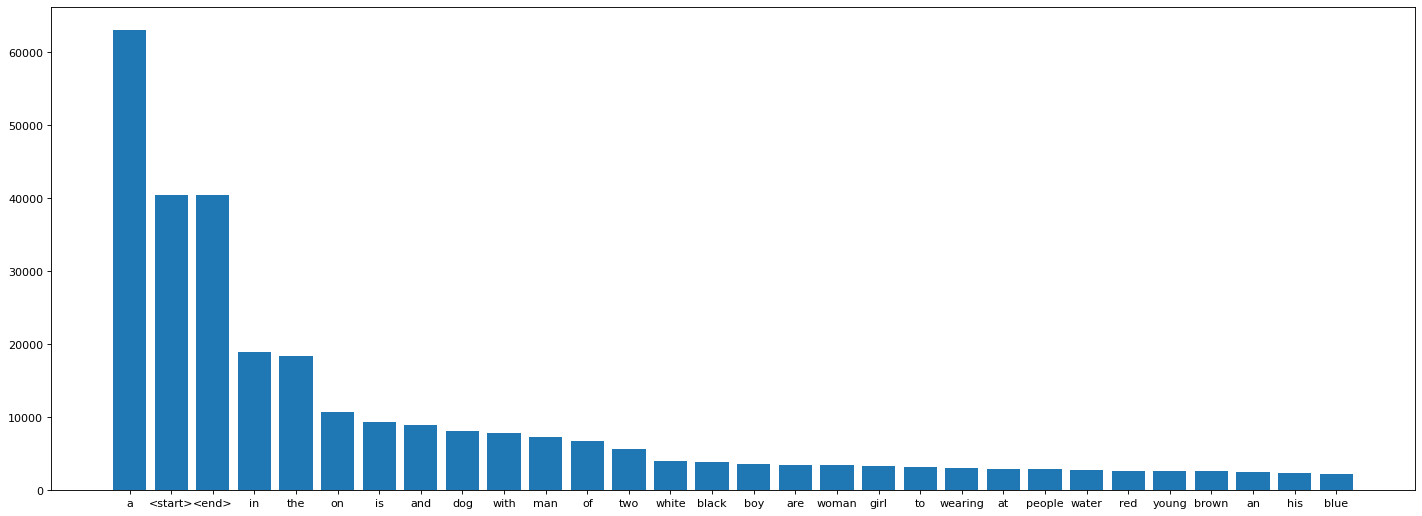
# Create a word count of your tokenizer to visulize the Top 30 occuring words after text processing
word_count = tokenizer.word_counts
word_count = sorted(word_count.items(), key=itemgetter(1), reverse = True)
figure(figsize=(22, 8), dpi=80)
x = [_[0] for _ in word_count[:30]]
y = [_[1] for _ in word_count[:30]]
plt.bar(x,y)<BarContainer object of 30 artists>
# Pad each vector to the max_length of the captions ^ store it to a vairable
max_length = max([len(cap) for cap in cap_sequences])
cap_vector = tf.keras.preprocessing.sequence.pad_sequences(cap_sequences, padding='post')
tokenizer.word_index['PAD'] = 0
tokenizer.index_word[0] = 'PAD'
print("The shape of Caption vector is :" + str(cap_vector.shape))
print(cap_vector[:5])
word_to_index('PAD')The shape of Caption vector is :(40455, 39)
[[ 3 2 44 5 2 91 173 8 120 52 2 394 13 395
5 29 1 671 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 3 2 20 317 65 2 197 118 4 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 3 2 41 20 120 65 2 197 2438 4 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 3 2 41 20 120 6 395 21 61 2438 4 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
[ 3 2 41 20 5 2 91 173 317 65 2 197 2982 4
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]]
0
1.Resize them into the shape of (299, 299)
3.Normalize the image within the range of -1 to 1, such that it is in correct format for InceptionV3.
- Since you have a list which contains all the image path, you need to first convert them to a dataset using tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices. Once you have created a dataset consisting of image paths, you need to apply a function to the dataset which will apply the necessary preprocessing to each image.
- This function should resize them and also should do the necessary preprocessing that it is in correct format for InceptionV3.
#write your code here to create the dataset consisting of image paths
all_img_path = sorted(set(all_imgs))#write your code here for creating the function. This function should return images & their path
def load_image(images):
#write your pre-processing steps here
shape = (299, 299)
img = tf.io.read_file(images)
img = tf.image.decode_jpeg(img,channels=3)
img = tf.image.resize(img,shape)
img = tf.keras.applications.inception_v3.preprocess_input(img)
return img, images1.To save the memory(RAM) from getting exhausted, extract the features of the images using the last layer of pre-trained model. Including this as part of training will lead to higher computational time.
2.The shape of the output of this layer is 8x8x2048.
3.Use a function to extract the features of each image in the train & test dataset such that the shape of each image should be (batch_size, 8*8, 2048)
Iv3 = tf.keras.applications.InceptionV3(include_top=False,weights='imagenet')
new_input = Iv3.input
hidden_layer = Iv3.layers[-1].output
feature_extractor = keras.Model(new_input,hidden_layer)Downloading data from https://storage.googleapis.com/tensorflow/keras-applications/inception_v3/inception_v3_weights_tf_dim_ordering_tf_kernels_notop.h5
87916544/87910968 [==============================] - 1s 0us/step
87924736/87910968 [==============================] - 1s 0us/step
# write the code to apply the feature_extraction model to your earlier created dataset which contained images & their respective paths
# Once the features are created, you need to reshape them such that feature shape is in order of (batch_size, 8*8, 2048)
feature_dict = {}
for img,path in img_data:
fv = Iv3(img)
fv = tf.reshape(fv,(fv.shape[0], -1, fv.shape[3]))
for bf, pat in zip(fv, path):
feature_path = pat.numpy().decode("utf-8")
feature_dict[feature_path] = bf.numpy()- You can store the features using a dictionary with the path as the key and values as the feature extracted by the inception net v3 model OR
- You can store using numpy(np.save) to store the resulting vector.
1.Apply train_test_split on both image path & captions to create the train & test list. Create the train-test spliit using 80-20 ratio & random state = 42
2.Create a function which maps the image path to their feature.
3.Create a builder function to create train & test dataset & apply the function created earlier to transform the dataset
2.Make sure you have done Shuffle and batch while building the dataset
3.The shape of each image in the dataset after building should be (batch_size, 8*8, 2048)
4.The shape of each caption in the dataset after building should be(batch_size, max_len)
#write your code here
path_train, path_test, cap_train, cap_test = train_test_split( all_img_vector,cap_vector,random_state=50,test_size=0.2)print("Training data for images: " + str(len(path_train)))
print("Testing data for images: " + str(len(path_test)))
print("Training data for Captions: " + str(len(cap_train)))
print("Testing data for Captions: " + str(len(cap_test)))Training data for images: 32364
Testing data for images: 8091
Training data for Captions: 32364
Testing data for Captions: 8091
# Create a function which maps the image path to their feature.
# This function will take the image_path & caption and return it's feature & respective caption.
def map_func(img_path,cap):# your input variable goes here)
img_tensor = feature_dict[img_path.decode('utf-8')]
return img_tensor,cap- You can load the features using the dictionary created earlier OR
- You can store using numpy(np.load) to load the feature vector.
# create a builder function to create dataset which takes in the image path & captions as input
# This function should transform the created dataset(img_path,cap) to (features,cap) using the map_func created earlier
def gen_dataset(img_data,cap_data,BUFFER_SIZE=1000):
dataset = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((img_data,cap_data))
dataset = dataset.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE)
dataset = dataset.map(lambda item1, item2: tf.numpy_function(
map_func, [item1, item2], [tf.float32, tf.int32]),
num_parallel_calls=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE).batch(32)
dataset = dataset.prefetch(buffer_size=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
return dataset
train_dataset = gen_dataset(path_train,cap_train)
test_dataset = gen_dataset(path_test,cap_test)sample_img_batch, sample_cap_batch = next(iter(train_dataset))
print(sample_img_batch.shape) #(batch_size, 8*8, 2048)
print(sample_cap_batch.shape) #(batch_size,max_len)(32, 64, 2048)
(32, 39)
1.Set the parameters
2.Build the Encoder, Attention model & Decoder
embedding_dim = 256
units = 512
BATCH_SIZE = 32
vocab_size = 5001 #top 5,000 words +1
train_num_steps = len(path_train) // BATCH_SIZE
test_num_steps = len(path_test) // BATCH_SIZEclass Encoder(Model):
def __init__(self,embed_dim):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.dense = tf.keras.layers.Dense(embed_dim)#build your Dense layer with relu activation #embedding_dim
def call(self, features):
# extract the features from the image shape: (batch, 8*8, embed_dim)
features = self.dense(features)
features = tf.nn.relu(features)
return featuresencoder=Encoder(embedding_dim)class Attention_model(Model):
def __init__(self, units):
super(Attention_model, self).__init__()
self.W1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units)
self.W2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(units)
self.V = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)
self.units=units
def call(self, features, hidden):
#features shape: (batch_size, 8*8, embedding_dim)
# hidden shape: (batch_size, hidden_size)
hidden_with_time_axis = tf.expand_dims(hidden, 1)
score = tf.keras.activations.tanh(self.W1(features) + self.W2(hidden_with_time_axis))
attention_weights = tf.keras.activations.softmax(self.V(score), axis=1)
context_vector = attention_weights * features
context_vector = tf.reduce_sum(context_vector, axis = 1)
return context_vector, attention_weightsclass Decoder(Model):
def __init__(self, embed_dim, units, vocab_size):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.units=units
self.attention = Attention_model(self.units)
self.embed = tf.keras.layers.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_dim)
self.gru = tf.keras.layers.GRU(self.units,return_sequences=True,return_state=True,recurrent_initializer='glorot_uniform')
self.d1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(self.units)
self.d2 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(vocab_size)
def call(self,x ,features ,hidden):
context_vector, attention_weights = self.attention(features, hidden)
embed = self.embed(x)
embed = tf.concat([tf.expand_dims(context_vector, 1), embed], axis=-1)
output,state = self.gru(embed)
output = self.d1(output)
output = tf.reshape(output, (-1, output.shape[2]))
output = self.d2(output)
return output,state, attention_weights
def init_state(self, batch_size):
return tf.zeros((batch_size, self.units))decoder=Decoder(embedding_dim, units, vocab_size)features = encoder(sample_img_batch)
hidden = decoder.init_state(batch_size=sample_cap_batch.shape[0])
dec_input = tf.expand_dims([tokenizer.word_index['<start>']] * sample_cap_batch.shape[0], 1)
predictions, hidden_out, attention_weights= decoder(dec_input, features, hidden)
print('Feature shape from Encoder: {}'.format(features.shape)) #(batch, 8*8, embed_dim)
print('Predcitions shape from Decoder: {}'.format(predictions.shape)) #(batch,vocab_size)
print('Attention weights shape from Decoder: {}'.format(attention_weights.shape)) #(batch, 8*8, embed_dim)Feature shape from Encoder: (32, 64, 256)
Predcitions shape from Decoder: (32, 5001)
Attention weights shape from Decoder: (32, 64, 1)
1.Set the optimizer & loss object
2.Create your checkpoint path
3.Create your training & testing step functions
4.Create your loss function for the test dataset
optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam()
loss_object = tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True, reduction='none')def loss_function(real, pred):
mask = tf.math.logical_not(tf.math.equal(real, 0))
loss_ = loss_object(real, pred)
mask = tf.cast(mask, dtype=loss_.dtype)
loss_ *= mask
return tf.reduce_mean(loss_)checkpoint_path = "/content/drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/checkpoints"
ckpt = tf.train.Checkpoint(encoder=encoder,
decoder=decoder,
optimizer = optimizer)
ckpt_manager = tf.train.CheckpointManager(ckpt, checkpoint_path, max_to_keep=5)start_epoch = 0
if ckpt_manager.latest_checkpoint:
start_epoch = int(ckpt_manager.latest_checkpoint.split('-')[-1])- While creating the training step for your model, you will apply Teacher forcing.
- Teacher forcing is a technique where the target/real word is passed as the next input to the decoder instead of previous prediciton.
@tf.function
def train_step(img_tensor, target):
loss = 0
hidden = decoder.init_state(batch_size=target.shape[0])
dec_input = tf.expand_dims([tokenizer.word_index['<start>']] * target.shape[0], 1)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
features = encoder(img_tensor)
for i in range(1, target.shape[1]):
predictions, hidden, _ = decoder(dec_input, features, hidden)
loss += loss_function(target[:, i], predictions)
dec_input = tf.expand_dims(target[:, i], 1)
avg_loss = (loss/int(target.shape[1]))
trainable_variables = encoder.trainable_variables + decoder.trainable_variables
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, trainable_variables))
return loss, avg_loss- While creating the test step for your model, you will pass your previous prediciton as the next input to the decoder.
@tf.function
def test_step(img_tensor, target):
loss = 0
hidden = decoder.init_state(batch_size=target.shape[0])
dec_input = tf.expand_dims([tokenizer.word_index['<start>']] * target.shape[0], 1)
with tf.GradientTape() as tape:
features = encoder(img_tensor)
for i in range(1, target.shape[1]):
predictions, hidden, _ = decoder(dec_input, features, hidden)
loss += loss_function(target[:, i], predictions)
dec_input = tf.expand_dims(target[:, i], 1)
avg_loss = (loss / int(target.shape[1]))
trainable_variables = encoder.trainable_variables + decoder.trainable_variables
gradients = tape.gradient(loss, trainable_variables)
optimizer.apply_gradients(zip(gradients, trainable_variables))
return loss, avg_lossdef test_loss_cal(test_dataset):
total_loss = 0
for (batch, (img_tensor, target)) in enumerate(test_dataset):
batch_loss, t_loss = test_step(img_tensor, target)
total_loss += t_loss
avg_test_loss=total_loss/test_num_steps
return avg_test_lossloss_plot = []
test_loss_plot = []
EPOCHS = 15
best_test_loss=100
for epoch in tqdm(range(0, EPOCHS)):
start = time.time()
total_loss = 0
for (batch, (img_tensor, target)) in enumerate(train_dataset):
batch_loss, t_loss = train_step(img_tensor, target)
total_loss += t_loss
avg_train_loss=total_loss / train_num_steps
loss_plot.append(avg_train_loss)
test_loss = test_loss_cal(test_dataset)
test_loss_plot.append(test_loss)
print ('For epoch: {}, the train loss is {:.3f}, & test loss is {:.3f}'.format(epoch+1,avg_train_loss,test_loss))
print ('Time taken for 1 epoch {} sec\n'.format(time.time() - start))
if test_loss < best_test_loss:
print('Test loss has been reduced from %.3f to %.3f' % (best_test_loss, test_loss))
best_test_loss = test_loss
ckpt_manager.save() 0%| | 0/15 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
For epoch: 1, the train loss is 1.200, & test loss is 1.016
Time taken for 1 epoch 513.0347232818604 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 100.000 to 1.016
7%|▋ | 1/15 [08:33<1:59:50, 513.61s/it]
For epoch: 2, the train loss is 0.941, & test loss is 0.903
Time taken for 1 epoch 350.524614572525 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 1.016 to 0.903
13%|█▎ | 2/15 [14:24<1:30:35, 418.11s/it]
For epoch: 3, the train loss is 0.859, & test loss is 0.836
Time taken for 1 epoch 351.74618792533875 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.903 to 0.836
20%|██ | 3/15 [20:17<1:17:36, 388.02s/it]
For epoch: 4, the train loss is 0.799, & test loss is 0.782
Time taken for 1 epoch 351.5722801685333 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.836 to 0.782
27%|██▋ | 4/15 [26:09<1:08:31, 373.81s/it]
For epoch: 5, the train loss is 0.750, & test loss is 0.737
Time taken for 1 epoch 351.46406054496765 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.782 to 0.737
33%|███▎ | 5/15 [32:01<1:00:59, 365.95s/it]
For epoch: 6, the train loss is 0.708, & test loss is 0.696
Time taken for 1 epoch 351.97780752182007 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.737 to 0.696
40%|████ | 6/15 [37:53<54:12, 361.36s/it]
For epoch: 7, the train loss is 0.672, & test loss is 0.660
Time taken for 1 epoch 351.8647634983063 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.696 to 0.660
47%|████▋ | 7/15 [43:45<47:47, 358.39s/it]
For epoch: 8, the train loss is 0.635, & test loss is 0.627
Time taken for 1 epoch 351.74872183799744 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.660 to 0.627
53%|█████▎ | 8/15 [49:38<41:35, 356.44s/it]
For epoch: 9, the train loss is 0.605, & test loss is 0.597
Time taken for 1 epoch 350.48855805397034 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.627 to 0.597
60%|██████ | 9/15 [55:29<35:28, 354.73s/it]
For epoch: 10, the train loss is 0.576, & test loss is 0.569
Time taken for 1 epoch 351.46787428855896 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.597 to 0.569
67%|██████▋ | 10/15 [1:01:21<29:29, 353.94s/it]
For epoch: 11, the train loss is 0.550, & test loss is 0.544
Time taken for 1 epoch 351.7448718547821 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.569 to 0.544
73%|███████▎ | 11/15 [1:07:13<23:33, 353.41s/it]
For epoch: 12, the train loss is 0.526, & test loss is 0.521
Time taken for 1 epoch 351.6812627315521 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.544 to 0.521
80%|████████ | 12/15 [1:13:05<17:39, 353.08s/it]
For epoch: 13, the train loss is 0.503, & test loss is 0.499
Time taken for 1 epoch 350.5990266799927 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.521 to 0.499
87%|████████▋ | 13/15 [1:18:56<11:44, 352.46s/it]
For epoch: 14, the train loss is 0.485, & test loss is 0.478
Time taken for 1 epoch 351.2602620124817 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.499 to 0.478
93%|█████████▎| 14/15 [1:24:48<05:52, 352.28s/it]
For epoch: 15, the train loss is 0.478, & test loss is 0.460
Time taken for 1 epoch 351.0725197792053 sec
Test loss has been reduced from 0.478 to 0.460
100%|██████████| 15/15 [1:30:40<00:00, 362.68s/it]
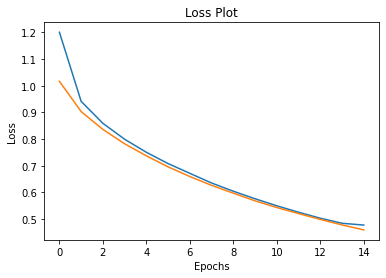
plt.plot(loss_plot)
plt.plot(test_loss_plot)
plt.xlabel('Epochs')
plt.ylabel('Loss')
plt.title('Loss Plot')
plt.show()- Since there is a difference between the train & test steps ( Presence of teacher forcing), you may observe that the train loss is decreasing while your test loss is not.
- This doesn't mean that the model is overfitting, as we can't compare the train & test results here, as both approach is different.
- Also, if you want to achieve better results you can run it more epochs, but the intent of this capstone is to give you an idea on how to integrate attention mechanism with E-D architecture for images. The intent is not to create the state of art model.
1.Define your evaluation function using greedy search
2.Define your evaluation function using beam search ( optional)
3.Test it on a sample data using BLEU score
def plot_attmap(caption, weights, image):
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
temp_img = np.array(Image.open(image))
len_cap = len(caption)
for cap in range(len_cap):
weights_img = np.reshape(weights[cap], (8,8))
weights_img = np.array(Image.fromarray(weights_img).resize((224, 224), Image.LANCZOS))
ax = fig.add_subplot(len_cap//2, len_cap//2, cap+1)
ax.set_title(caption[cap], fontsize=15)
img=ax.imshow(temp_img)
ax.imshow(weights_img, cmap='gist_heat', alpha=0.6,extent=img.get_extent())
ax.axis('off')
plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.2, wspace=0.2)
plt.show()def evaluate(image):
attention_plot = np.zeros((max_length, attention_features_shape))
hidden = decoder.init_state(batch_size=1)
temp_input = tf.expand_dims(load_image(image)[0], 0) #process the input image to desired format before extracting features
img_tensor_val = Iv3(temp_input)# Extract features using our feature extraction model
img_tensor_val = tf.reshape(img_tensor_val, (img_tensor_val.shape[0], -1, img_tensor_val.shape[3]))
features = encoder(img_tensor_val)# extract the features by passing the input to encoder
dec_input = tf.expand_dims([tokenizer.word_index['<start>']], 0)
result = []
for i in range(max_length):
predictions, hidden, attention_weights = decoder(dec_input, features, hidden)# get the output from decoder
attention_plot[i] = tf.reshape(attention_weights, (-1, )).numpy()
predicted_id = tf.argmax(predictions[0]).numpy()#extract the predicted id(embedded value) which carries the max value
result.append(tokenizer.index_word[predicted_id])#map the id to the word from tokenizer and append the value to the result list
if tokenizer.index_word[predicted_id] == '<end>':
return result, attention_plot, predictions
dec_input = tf.expand_dims([predicted_id], 0)
attention_plot = attention_plot[:len(result), :]
return result, attention_plot,predictions
attention_features_shape = 64
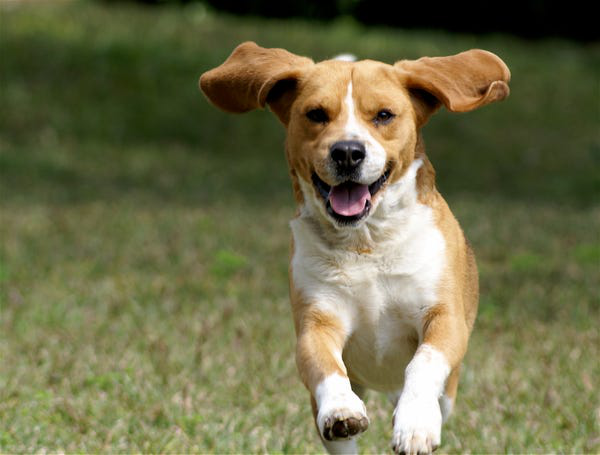
test_image = '/content/drive/MyDrive/eye_for_blind_data/test.jpg'
result, attention_plot,pred_test = evaluate(test_image)
real_caption= 'a dog running on grass'
pred_caption=' '.join(result).rsplit(' ', 1)[0]
real_appn = []
real_appn.append(real_caption.split())
reference = real_appn
candidate = pred_caption.split()
score = sentence_bleu(reference, candidate, weights=(0.35, 0.45, 0.1, 0.1))
print(f"BELU score: {score*100}")
print ('Real Caption:', real_caption)
print ('Prediction Caption:', pred_caption)
plot_attmap(result, attention_plot, test_image)
Image.open(test_image)BELU score: 72.56396362752623
Real Caption: a dog running on grass
Prediction Caption: a brown and white dog runs on the green grass