- MySQL 쿼리 튜닝 최적화
Day 1
- 오픈소스 DBMS, 1995.03 첫 버전 발표
- LAMP 의 중심 요소
- 대용량 DB에 사용가능(테이블 기본 값은
256TB) - 하나의 테이블에
64개의 index 설정 가능. - 하나의 index에
16개의 칼럼 지정가능
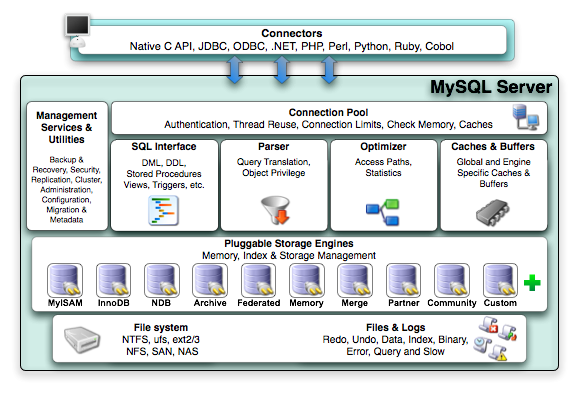
- SQL interface, Parser, Optimizer, Cache & Buffer 로 구성
- 쿼리 재구성, 데이터 처리
- 스토리지 엔진에 데이터 요청
- Join, Group by, Order by 처리
- 함수, 트리거, 프로시저 처리
show engines;| Engine | Support | Comment | Transactions | XA | Savepoints |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| InnoDB | DEFAULT | Supports transactions, row-level locking, and foreign keys | YES | YES | YES |
| MRG_MYISAM | YES | Collection of identical MyISAM tables | NO | NO | NO |
| MEMORY | YES | Hash based, stored in memory, useful for temporary tables | NO | NO | NO |
| BLACKHOLE | YES | /dev/null storage engine (anything you write to it disappears) | NO | NO | NO |
| MyISAM | YES | MyISAM storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| CSV | YES | CSV storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| ARCHIVE | YES | Archive storage engine | NO | NO | NO |
| PERFORMANCE_SCHEMA | YES | Performance Schema | NO | NO | NO |
| FEDERATED | NO | Federated MySQL storage engine | NULL | NULL | NULL |
- MyISAM
- File 기반
- 디스크에 직접 접근, 메모리에 저장하지 않는다.
- 트랜잭션 X, 테이블 단위 Lock
- InnoDB
- 트랜잭션 O
- 행단위 Lock
- 데이터와 인덱스를 메모리에 저장
- InnoDB_buffer_pool_size 크기가 성능에 영향
- archive
- index X
- 데이터 압축 저장
hr-schema-mysql.sql 의 내용을 실행해서 새로운 hr 스키마 생성 (복사 후 쿼리 실행)
Menu - Database - Reverse Enginner(Ctrl + R) - hr 선택
- 애플리케이션 로직
- 테이터 모델링, 테이블 구조
- 쿼리 튜닝
- 하드웨어 성능 튜닝
- 서버 환경 튜닝
- 테이블의 구조
- 칼럼의 타입이 적절한지 살펴봐야 한다.
- 인덱스
- 적절한 칼럼에 인덱스가 정해져 있는지 확인
- 스토리지 엔진 선택
- Lock 전략
- 메모리 캐시량
- 캐시 메모리의 사이즈가 적절한지 확인
- 디스크 검색 시간
- 디스크 I/O 속도
- CPU 사이클
- DBMS에서 쿼리가 실행되는 구조를 알아야 함
- 로그 분석을 통해
느린 쿼리를 찾는 방법을 알아야 함 - 프로파일링
- 쿼리문 최적화 방법
- 실제 쿼리문 실행 후 결과 확인
- 프로파일링
select @@profilinig;
- 실행 계획 분석 explain
- 현재 세션에서 퀴리가 실행될 때 리소스 사용량 확인
- 프로파일 환경 변수 설정
set profiling = 1;- 디폴트
0,1로 설정하면 쿼리 실행 로그가 기록 됨
- 프로파일 목록 보기
show profile;show profiles;show profile for query 4;
- 쿼리 실행 과정에서 어떠한 작업의 조합으로 쿼리가 실행되는 지 알려줌
- 반드시 실행 계획에 따라 수행되지는 않는다.
- 쿼리문 앞에
explain을 붙인다 - 5.7 버전부터
SELECT이외 쿼리도 가능
| item | contents |
|---|---|
| id | select 번호 |
| select_type | select 종류 |
| table | 참조 테이블 명 |
| type | 조인이나 조회 종류 |
| possible_keys | 사용가능한 index 목록 |
| key | 사용된 index |
| key_len | index 길이 |
| ref | key 와 함께 사용된 칼럼 혹은 상수 값 |
| rows | 조회 행 수 |
| filtered | 조회 예정행 추정비(조회행 수 / 전체행 수) |
| Extra | 추가 정보 |
| select_type | description |
|---|---|
| SIMPLE | 단순한 select union이나 sub query가 없다 |
| PRIMARY | 제일 외곽의 select(sub query 가 있는 경우) |
| DERIVED | from 절 내부의 sub query |
| DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | 상호 연관된 sub query |
| UNION | union 에서 두번째 혹인 나중 select |
| SUBQUERY | sub query의 첫 번째 select |
| type | description |
|---|---|
| system | table 에 데이터가 1개인 경우 |
| const | PK 나 Unique key 를 상수와 비교하는 경우. 데이터가 한 개 존재 |
| eq_ref | 조인에서 PK 혹은 Unique key 가 사용된 경우 |
| ref | where 에서 사용된 컬럼이 index로 참조되거나 조인에서 PK Unique key 이외 칼럼이 사용된 경우 |
| ref_or_null | ref 와 동일. Null이 추가되어 사용된 경우 |
| index_merge | 두개의 index 사용된 경우 |
| unique_subquery | 서브쿼리에서 in 내부에 PK 가 사용된 경우 |
| index_subquery | unique_subquery 와 유사. 일반 index 사용된 경우 |
| range | 범위 스캔 |
| index | 인덱스를 Full scan. 커버링 index. 테이블 조회 없이 index로만 데이터 가져온 경우 |
| all | 테이블 Full scan |
| Extra | description |
|---|---|
| Using Index | 커버링 index. Index로만 결과를 추출한 경우 |
| Using Where | where 조건으로 데이터 추출 |
| Using Filesort | 데이터 정렬이 필요한 경우 |
| Using Temporary | 임시 테이블 사용. group by, order by 가 포함된 경우 주로 발생 |
./day1.sql
# 현재 폴더의 sql 파일을 모두 합쳐 all.sql로 만듬
copy *.sql all.sql# all.sql 을 myhr 스키마에 넣으면서 DB 접속
# 사전에 myhr 이라는 스키마가 있어야 함
# worckbench Navigator 에서 오른쪽 클릭으로 생성
mysql -u root -p myhr < all.sql./myhr.sql
hr 스키마를 이용하여 Seattle 에 근무하는 사원들의 성, 이름, 부서명, 급여, 입사일을 출력하고 실행계획을 설명.
select e.last_name, e.first_name, d.department_name, e.salary, e.hire_date
from departments d
join locations l using(location_id)
join employees e using(department_id)
where l.city = 'Seattle';- table
l에 type 이ALL인 이유는where l.city = 'Seattle'쿼리에city칼럼이 PK, index 모두 아니기 때문에 Full scan 했기 때문이다. - table
d,e는 type 이ref인 이유는 join 의 칼럼이 PK, index, unique 중 하나였기 때문이다. - Full scan을 방지하려면 locations
city칼럼을 index에 추가한다.
create index location_city_idx on locations(city);- SELECT 성능 향상을 위해 생성된 별도 데이터
- Table 과는 별도로 존재
- CUD 시 index도 변경
- SELECT 빠름
- 정렬 빠름
- Table 이외의 저장공간 필요
- 데이터 변경시 index 도 변경되서 overhead
- B-Tree
- R-Tree
- Hash Index
- Full-Text Index
- 단일 컬럼 Index
- 복합 컬럼 Index
- 부분 Index
- 커버링 Index
- Root, Branch, Leaf 로 구성
- 어떠한 데이터도 일정한 시간이 소요
- 데이터 변경 시 재구성 필요
PK,Unique,Key로 구분InnoDB에선 PK 에 따라 클러스터화 됨- 보조 Index 는 내부적으로 PK 를 포함하여 생성
- index(email) 은 index(email, id) 와 같다.
- PK 로 지정되는 칼럼의 길이가 길어지는 것을 지양할 것
Day 2
- InnoDB는
Clustered Index와Secondary Index가 있다. - Clustered Index
- PK 시 자동으로
Clustered생성 - 데이터가 순서대로 정렬
- 테이블 당 하나의 Clustered Index
- Unique, Not null 조건 부여시 Clustered Index 생성, PK가 있으면 Clustered Index는 생성되지 않는다. (테이블 다 하나이기 때문)
- 검색 속도 빠름. 입력, 수정, 삭제 느림
- PK 시 자동으로
- Secondary Index
- 입력, 수정, 삭제 빠름
- 검색은
Clustered에 비해 느림 - 테이블에 여러개 생성 가능 < br>
- PK 지정시 index 자동 생성
- FK 지정시 index 자동 생성
CREAE [UNIQUE | FULLTEXT | SPATIAL] INDEX index_name
[index_type]
ON table_name(column_names)
[index_option]
[algorithm_option | lock_option]show indexes from table_name;
# 통계 정보
select * from information_schema.STATISTICS where table_name = 'employees';- index는 수정 불가
- 수정하려면 삭제 후 다시 생성
- Index를 삭제해야 하는 경우
- 대용량 데이터를 넣는 경우
- 데이터 insert 마다 index를 update 해야하기 때문에 일단 지우고 데이터 넣고 index를 다시 생성한다.
- 사용하지 않는 index 있는 경우
- 대용량 데이터를 넣는 경우
drop index index_name on table_name;
# or
alter table table_name drop index index_name;- Unique Index, = 검색
explain
select last_name, first_name, salary, hire_date
from employees where employee_id = 100;- Unique Index, 범위
explain
select last_name, first_name, salary, hire_date
from employees where employee_id >= 100;- Non-Unique Index, = 검색
explain
select last_name, first_name, salary, hire_date
from employees where salary = 8000;- Non-Unique Index, 범위
explain
select last_name, first_name, salary, hire_date
from employees where salary between 8000 and 9000;- OR & IN 조건
explain
select last_name, first_name, salary, hire_date
from employees where employee_id in (100, 200);alter table employees add index(last_name, first_name);
explain
select last_name, first_name, salary, hire_date
from employees where last_name like 'K%';- Index 만으로 데이터를 조회. 테이블에 저장된 데이터를 조회하지 않는다.
- 실행 계획 type 이
index
- 컬럼의 일부분으로 index 생성
- index크기 줄임
- 커버링 index 사용 불가
- BLOB / TEXT 타입 컬럼 적용
- 적절한 길이 필요
Selectivity(선택도) 로 길이 판단
alter table emp add index(last_name(4));MySQL에는 Oracle의 Function based index 는 없으나, 자동 생성 칼럼을 이용해 이와 비슷한 효과를 낼 수 있다.
create table some_table(
id varchar(10),
sub_id varchar(8) as (substring(id, 1, 8)),
index(sub_id)
);
insert some_table(id) values('sub_id_001');
select * from some_table;- use index
- Index 사용
... from employee use index(name_idx) ...
- ignore index
- Index 사용 X
-
... from employee ignore index(name_idx) ...
- force index
- index 강제 사용
-
... from employee force index(name_idx) ...
not연산자is not null연산자- 컬럼을 변형하여 비교
# salary 에는 index가 있지만, * 12 때문에 컬럼 변형됨
explain
select * from employees where salary*12 >= 120000;
# 해결책 - 컬럼 변형 X, 조건식을 변형!
explain
select * from employees where salary >= (120000/12);- 칼럼 타입이 자동 변형되는 경우
create table my_internal(
t_no varchar(10) primary key, # PK를 varchar로
t_name varchar(20)
);
insert into my_internal(t_no, t_name) values(1234, 'hong'); # 자동 형변환
explain select * from my_internal where t_no = 1234; # type: All, index 사용 X, 성능 이슈 야기
explain select * from my_internal where t_no = '1234'; # type: const- 복합 칼럼에서 AND, OR 에 따라
# index 사용 O
explain
select * from employees where last_name = 'King' and first_name = 'Steven';
explain
# index 사용 X
select * from employees where last_name = 'King' or first_name = 'Steven';t_emp 테이블 생성 id: int, name: varchar(200), hire_date: varchar(8)
employees 테이블의 데이터를 t_emp 에 삽입
t_emp hire_date index 생성
t_emp 에서 hire_date 가 19930113, '1993013' 으로 각각 조회하고 실행계획 확인
- t_emp 테이블 생성
create table t_emp(
id int,
name varchar(200),
hire_date varchar(8)
);- t_emp 에 employees 데이터 삽입
insert into t_emp(id, name, hire_date)
select employee_id as id, concat(first_name, ', ', last_name) as name, replace(hire_date,'-','') from employees;- hire_date index 생성
create index hire_date_idx on t_emp(hire_date);- 실행계획
explain
select id, name, hire_date from t_emp where hire_date = 19930113;explain
select id, name, hire_date from t_emp where hire_date = '19930113';- 전체 테이블의 10 ~15% 조회되는 경우
- Index로만 조회시. 커버링 index
- Join 시 연결되는 칼럼인 경우
- MySQL은 nested join 이기 때문에 연결 칼럼의
index는 필수적
- MySQL은 nested join 이기 때문에 연결 칼럼의
- 단순 저장용 table
Full scan경우CUD의 비율이R보다 현저히 높은 경우
컬럼 내부의 저장되 데이터 값들의 종류와 전체 값의 비율
- select 시 where, group by, order by 에 쓰는 컬럼 위주로 선택
- 선택도
- 길이가 짧은 컬럼
- Index의 통계정보를 update할 필요가 있다.
- optimize table_name 명령어 사용
- 테이블 데이터와 index 를 재구조화
- 저장 공간 줄이고 I / O 효율 증가
optimize table employee;- optimize 하는 경우
- 대용량 데이터를
CUD한 경우 - FULLTEXT index를
CUD한 경우
- 대용량 데이터를
- 둘 이상의 테이블에 테이터를 연결하여 조회
- 필요성 방법
- 테이블을 정규화하면 데이터 중복이 최소화 되지만 각 데이터가 흩어지게된다. 이 데이터를 다시 합치기 위해 join 필요
- 주로
FK이용
- 조건이
=인 경우
# 사원 성, 명, 급여, 입사일, 부서번호, 부서명 부서장명 출력
select e.last_name, e.first_name, e.salary, e.salary, d.department_id, concat(m.last_name, ', ', m.first_name) as manager_name
from employees e, departments d, employees m
where e.department_id = d.department_id
and d.manager_id = m.employee_id;- Left outer join
왼쪽테이블에서 join 만족시키지 못하는 null 경우도 포함
- Right outer join
오른쪽테이블에서 null 포함
- Full outer join
- 양쪽 모두 join 만족시키지 못하는 경우도 조회
# 사원 성,명,급여,입사일, 관지자 사번, 관리자 입사일 출력
# 관리자 없는 경우 관리자 없음 출력
select e.last_name, e.first_name, e.salary, e.hire_date, ifnull(m.employee_id, '관리자 없음') as '관리자 사번', ifnull(m.hire_date, '관리자 없음') as '관리자 입사일'
from employees e
left outer join employees m on e.manager_id = m.employee_id;# 자신의 관리자보다 많은 급여를 받는 사원을 조회
select * from employees e join employees m on e.manager_id = m.employee_id
where e.salary > m.salary;
# 자신의 관리자보다 입사일이 빠른 사원을 조회
select * from employees e join employees m on e.manager_id = m.employee_id
where e.hire_date < m.hire_date;hr.employees 도시명을 그 도시에 배치된 부서번호와 부서명도 함께 출력하시오. 단, 배치된 부서가 없는 경우도 출력 도시가 위치한 나라명도 함께 출력
select l.city 도시명, d.department_id 부서, d.department_name 부서명, c.country_name 나라명
from locations l
left join departments d on l.location_id = d.location_id
join countries c on l.country_id = c.country_id;- Nested Loop Join
- 하나의 테이블을 기준으로 순차적으로 join
- Sort Merge Join
- 양 테이블의 처리 범위를 access 해서 정렬한 결과를 합쳐 join
- 배치 작업에 사용
- Hash Join
- hash 함수 사용
- Block Nested Loop
- v5.6 이상부터 MySQL join 방법
MySQL(v5.7)에선 Nested Loop 만 사용
Oracle은 다양한 알고리즘 사용
- MySQL 은
Nested Loop이기 때문에 기준 테이블이 중요하다- 기준 테이블에서 조회되는 데이터양에 따라 연관 테이블의 데이터양이 결정되기 때문에 기준 테이블(왼쪽)의 데이터양을 줄이는 것이 관건
- Outer join 은 지양한다. 꼭 필요한 경우만 쓴다.
- join 시 조합 경우의 수를 줄이기 위해 복합 칼럼 index를 사용한다
100004 ~ 100014 사번의 성, 이름, 입사일, 현재급여 및 현재직급을 출력 employee 테이블을 먼저 조회 관련 제약조건 생성 필요에 따라 index 생성 실행계획 제출
use myhr;
#explain
select straight_join e.emp_no, e.last_name, e.first_name, e.hire_date, es.salary, et.title
from employee e
left join emp_salary es using(emp_no)
left join emp_title et using(emp_no)
where e.emp_no between 100004 and 100014
and es.to_date = (select max(to_date) from emp_salary where emp_no = e.emp_no)
and et.to_date = (select max(to_date) from emp_salary where emp_no = e.emp_no);- where 절에
'9999-01-01'로 비교하면 퇴사자는 나오지 않는다. 퇴사자는 to_date 가 '9999-01-01' 가 아니기 때문에 - 문제에서 퇴사자에 대한 설명 없이 100004 ~ 100014 에 대한 결과를 요구했기 때문에 다음과 같이 작성했다.
- Inline View
FROM절에 사용된 쿼리
- Nested 서브 쿼리
WHERE절에 사용된 쿼리
- Correlated 서브 쿼리(상호연관)
- 서브 쿼리에서 메인 쿼리 참조
- Scalar 서브 쿼리
- 하나의 값만을 출력하는 서브 쿼리
day3
- Inline view 로 최소화 후 join 하는 것이 좋다
# p52 인라인 뷰의 사용으로 join 수 감소
# 일반 join -> 1:n
#explain
select d.department_id, d.department_name, avg(e.salary) dept_salary
from employees e join departments d using(department_id)
group by e.department_id;
# 인라인 뷰 -> 1:1
#explain
select d.department_id, d.department_name, da.dept_salary
from departments d join (
select department_id, avg(salary) dept_salary from employees group by department_id
) da using(department_id);사원 데이터 8만, 부서 100 이라고 가정하면, 첫번째 쿼리는 8만 번의 join 이 필요하고 두번째 쿼리는 100 번의 join 이 필요하다. ( 책 내용)
그러나, 실행 계획은 아래와 같이 두번째 쿼리가 더 많은 실행 계획이 필요하다고 보여진다.
- 서브 쿼리 결과 집합이 소량일 때 사용
- Join 을 많이 할 것으로 예상되는 경우 사용
- 서브 쿼리 내에 메인 쿼리의 컬럼들이 사용됨
- 매번 서브 쿼리가 사용됨
# 부서 평균보다 많은 급여 받는 사원 조회 (전체 사원은 10만)
use hr;
# 상호 연관 쿼리
explain
select * from employees e
where salary > (
# 수행 10만번. 동일 데이터 중복 접근
select avg(salary) from employees where department_id = e.department_id
);
# 인라인 뷰
explain
select * from employees e
join (
# 10만건을 1번 Full Scan
select department_id, avg(salary) avg_salary from employees group by department_id
) da using(department_id)
where e.salary > da.avg_salary;- create 에 서브 쿼리 사용하면 이미 존재하는 테이블에 필요한 데이터만 복사해서 테이블 생성 가능
- 무결성 규칙은 복사되지 않는다.
Not Null은 복사 됨
- 이미 존재하는 테이블에서 필요한 데이터만 복사
- 다른 테이블의 값을 기반으로 테이블 행 변경 가능
- 다른 테이블의 값을 기반으로 테이블 행 삭제 가능
- MySQL v5.5 이하에선
IN절에서 서브 쿼리를 비효율적으로 처리했다.- v5.5 이전에선 메인 쿼리에서 조회된 각 row 에 대해
in조건 내부의 서브 쿼리를 매번 실행 - v5.6 이후에선 서브쿼리를 메인 쿼리 이전에 한번만 실행하여 메인 쿼리와 비교하는 방식으로 실행
- v5.5 이전에선 메인 쿼리에서 조회된 각 row 에 대해
# 부서장의 정보를 출력
explain
select * from employees e # exists 사용
where exists ( select 'x' from departments where manager_id = e.employee_id);
explain
select * from employees e # in 사용
where employee_id in ( select manager_id from departments);| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PRIMARY | e | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 107 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | departments | NULL | ref | manager_id | manager_id | 5 | hr.e.employee_id | 2 | 100.00 | Using index |
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | SIMPLE | departments | NULL | index | manager_id | manager_id | 5 | NULL | 27 | 44.44 | Using where; Using index; LooseScan |
| 1 | SIMPLE | e | NULL | eq_ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | hr.departments.manager_id | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
- 서브 쿼리 사용할 때, COALESCE() & IF() 함수를 이용하면 효율적인 쿼리 생성이 가능하다.
부서(department_id), 직무(job_id) 별 지원수와 급여 총액 출력
- 부서별/직무별, 천체 총 직원 수와 급여 총액 출력
- 부서번호/ 직무번호 순 정렬 null 은 나중에
- MySQL 은 Lock 과 트랜잭션으로 동시성을 제어
- MySQL Lock 매커니즘
- 쓰레드가 데이터 집합을 요청할 때 Lock 설정
- 데이터 집합은 테이블, 행, 페이지, 메타데이타
- 쓰레드가 데이터 집합 처리 완료하면 Lock 해제
- MySQL 트랜잭션
- 신뢰성 있게 처리되는 일의 단위
- 읽기 Lock
R만 가능CUD불가
- 쓰기 Lock
CRUD불가
- Table Lock
- 테이블 전체에 Lock을 걸기 때문에 다른 트랜잭션이 해당 테이블에 접근 불가
- Row Lock
- 하나 이상의 개별적인 행에 Lock
- Lock이 걸리지 않은 행에 접근 가능
- Page Lock
BDB라는 스토리지 엔진에 적용.- 거의 사용되지 않음
- Metadata Lock
- 쓰레드가 테이블을 사용할 때 테이블의 모든 메타데이터에 Lock
- 메타테이터란,
DDL 에 의해 변경되는 정보
MyISAM스토리지 엔진에서 사용- 스토리지 엔진과 무관하게
LOCK TABLE명령으로 Lock 가능 - v5.5 이상에서
DDL실행 시 Lock 발생
- 테이블 전체가 아닌 일부 행에 lock
InnoDB는 행 lock
# 행 lock
create table my_inno_t(
id int auto_increment primary key,
name varchar(10)
);
insert into my_inno_t(name) values('a');
insert into my_inno_t(name) values('b');
insert into my_inno_t(name) values('c');
select * from my_inno_t;
update my_inno_t set name = sleep(200) where id = 1; # 200초 걸림다른 세션 열고
select * from my_inno_t; 하면 가능
update my_inno_t set name='aaa' where id=1; 하면 불가능 행에 lock 이 걸려서
- MySQL 은 스토리지 엔지 레벨으로 트랜잭션
select @@autocommit;으로 트랜재션 사용 여부 확인
- MySQL 트랜잭션
start transaction;orbegin;으로 트랜잭션 시작commit;으로 수행 완료rollback으로 수행 취소
- 두 개 이상의 트랜잭션이 각기
Lock을 풀지 않고 서로의Lock이 풀리길 기다리는 상황 - 행 Lock 을 사용하면 데드 Lock을 피할 수 없다.
- InnoDB에는 데드 Lock 탐지기가 있다.
- 만능 셋팅은 없다.
- 스토리지 엔진을 적절히 선택하는 것이 중요
- H/W OS 의 영향을 받는다.
- 쿼리 튜닝이 최우선
my.ini설정- C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.7
- /etc/my.cnf or /etc/mysql/my.cnf
- 서버 실행 시 명령어 입력
- 실행 중 세션이나 글로벌 변수 설정
show status;show global status;show session status;show status like 'Key%';
- 서버가 기동될 때
설정 파일을 통해 MySQL 서버 셋팅 my.iniormy.inf- 서버 기동 중에도
SET GLOBAL명령으로 변경 가능. 서버 재시작 하면 리셋됨- 변경 후, cmd(관리자)에서
net stop MYSQL57net start MYSQL57restart 명령어 없음
- 변경 후, cmd(관리자)에서
- general-log=0
- 일반 로그는 남기지 않음
- slow-query-log=1
- 느린 쿼리는 로그 남김
- long_query_time=10
- 느린 쿼리는 10초 이상 걸리는 쿼리
- innodb_buffer_pool_size
- 테이블, 인덱스 등을 저장하는 위한 공간
- InnoDB 성능에 가장 중요
- 테이블 데이터가
pool에cache되면 DB I/O 없이 캐싱된 데이터에 접근할 수 있다 - buffer_pool_size 계산 쿼리
- innodb_autoinc_lock_mode
- innodb_lock_wait_timeout
# buffer_pool_size 계산 쿼리
SELECT
CEILING(Total_InnoDB_Bytes*1.6/POWER(1024,3)) AS RIBPS
FROM
(
SELECT SUM(data_length+index_length) Total_InnoDB_Bytes
FROM information_schema.tables WHERE engine='InnoDB'
) AS T;mysqladmin ping -u root -p
-> mysqld is alive- MySQL 은 기본적으로
data폴더에 로깅- C:\ProgramData\MySQL\MySQL Server 5.7\Data
- 로그 기록은
비활성화가 디폴트 - 로그 종류
- 에러
- 일반 쿼리
- 느린 쿼리
- DDL
# 로그 남기기 디폴트는 비활성화(0) 이기 때문에 다음과 같이 변경
select @@general_log;
set global general_log=1;analyze table table_name;check table table_name;- 두 테이블의 내용이 일치하는지 확인
CHECKSUM TABLE table_name [, table_name ...]
create table my_emp
select * from employees;
select * from my_emp;
checksum table employees, my_emp;- 대량 데이터
CUD후 index 재구축 과정
optimize table table_name;- 물리적으로 여러 테이블로 구성되는 하나의 논리적 테이블
- 이력 / 로그 데이터 테이블에 주로 사용
- MySQL v5.0 부터 지원
- 메모리 적재에 너무 큰 테이블에 사용
- 일반 테이블보다 관리 용이
- 물리적 배포 용이, 여러 Disk 분산 배치 가능
FK사용 불가Full Text index불가- 하나의 테이블의
1024개 까지만 생성 가능
- Range
- 범위로 지정
- List
- 파티션 key 값으로 key들의 목록 지정
- Hash
- Range 와 List 로 분할하기 어려운 경우 Hash 함수 사용
- Key
- Hash 와 동일 key 값 결정 가능
- Sub
- 파티션 내부에 하위 파티션 생성 가능
- 범위로 지정
- 날짜 값을 기준으로 나눌 수 있는 데이터에 적합
- Key 로 데이터를 검색할 때 유용
create table my_member(
first_name varchar(25) not null,
last_name varchar(25) not null,
email varchar(25) not null,
joined_date date
)
partition by range columns(joined_date) (
partition lessthan1990 values less than('1990-12-31'),
partition p2000 values less than('2000-12-31'),
partition p2020 values less than maxvalue
);
show table status where name='my_member';
select * from information_schema.PARTITIONS where table_name = 'my_member';- Range 와 유사
- Range 와 다른점은 순서대로 정렬될 필요는 없다.
- emp_salary를 파티션으로 분할
- 테이블 = partitioned_emp_salary
- from_date를 조사하여 파티션 수 정하기
- emp_salary에 저장된 데이터를 파티션으로 저장
- 각 파티션에 저장된 row 수 현황 조회
- 파티션 현황 조회 캡처
- 통계 정보 생성 캡처
- 두 테이블의 데이터 일치 여부 체크
use myhr;
create table partitioned_emp_salary
select * from emp_salary; # 2844047 개
select from_date from partitioned_emp_salary order by from_date;
select DATE_FORMAT(from_date,'%Y-%m') m from partitioned_emp_salary group by m; # 월별 분류 시 212 개
select DATE_FORMAT(from_date,'%Y') y from partitioned_emp_salary group by y; # 년별 분류 시 18 개
select count(*), DATE_FORMAT(from_date,'%Y') y from partitioned_emp_salary group by y; # 년별 분류 시 각 행 수
select min(from_date) from partitioned_emp_salary; # 1985-01-01
select max(from_date) from partitioned_emp_salary; # 2002-08-01
# 1년 단위
alter table partitioned_emp_salary partition by range(YEAR(from_date)) (
partition p1985 values less than(1985),
partition p1986 values less than(1986),
partition p1987 values less than(1987),
partition p1988 values less than(1988),
partition p1989 values less than(1989),
partition p1990 values less than(1990),
partition p1991 values less than(1991),
partition p1992 values less than(1992),
partition p1993 values less than(1993),
partition p1994 values less than(1994),
partition p1995 values less than(1995),
partition p1996 values less than(1996),
partition p1997 values less than(1997),
partition p1998 values less than(1998),
partition p1999 values less than(1999),
partition p2000 values less than(2000),
partition p2001 values less than(2001),
partition p2002 values less than(2002),
partition pmax values less than maxvalue
);
select PARTITION_NAME, PARTITION_ORDINAL_POSITION, PARTITION_DESCRIPTION, TABLE_ROWS, AVG_ROW_LENGTH, DATA_LENGTH
from information_schema.PARTITIONS where table_name = 'partitioned_emp_salary'; #파티션 주요 현황
analyze table partitioned_emp_salary; # 통계 정보
checksum table emp_salary, partitioned_emp_salary; # 체크 섬- 테이블 row 는 PK 에 따라 클러스터화 된다.
- row 가 추가될 때마다 페이징 현상을 줄이는 것이 좋다
- PK를 임의의 값으로 하는 것은 좋지 않다.
int타입이 적절
- 보조 index 는 PK 와 함께 저장
index(name)은index(name, id)와 동일- PK 길이는 작을수록 좋다.
oracle의merge처럼, 존재하면 update 없으면 insert- 해당 기능을 application 단에서 수행하면 network 양이 증가하고 불필요한 로직이 늘어난다.
- MySQL 에서는
INSERT ... ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE로 해결
oracle의Top N Query와 유사
# 사원의 급여 등급별 인원 수
select
case
when salary <= 4000 then '초급'
when salary <= 7000 then '중급'
when salary <= 10000 then '고급'
else '특급'
end sal_grade,
count(*) 인원수
from employees
group by
case
when salary <= 4000 then '초급'
when salary <= 7000 then '중급'
when salary <= 10000 then '고급'
else '특급'
end
order by
case
when salary <= 4000 then 1
when salary <= 7000 then 2
when salary <= 10000 then 3
else 4
end
;- MySQL 스토리지 엔진을 적재적소에 사용해야 한다
- 트랜잭션이 필요할 땐,
InnoDBinnodb-buffer-pool-size가 성능에 큰 영향을 미친다.
- 원시 로그 데이터 저장시엔
Archive스토리지가 적절- 데이터가 압축된 상태로 저장
- 저장된 데이터는
UD불가 - 파티션 지원
Created by leesanghak@gabia.com 2017.03.31