Lately there has been a growing interest on the microfrontends (MF(s) from now on).
This project is a POC to show how an application can be built with a MFs architecture implementing Module Federation Plugin from Webpack 5.
This repo has 3 submodules, which are the 3 MFs that conform the whole app.
A MFs architecture is one where the Frontend (FE) is divided in spplited modules that work in an autonomous way.
Sometimes, large scale companies face the problem that, when having monolithic FE apps, scaling them becomes extremely difficult. The codebase becomes too large and the coordination between teams sharing a unique codebase becomes really complicated.
The best approach then seems to be to have different teams working on different parts of the entire application, having their own repositories, tests, releases, etc. so they can work independently. That code will be somehow merged afterwards to form the end user application.
The most popular solution to different teams working in spplited codebases was to work on npm packages. But the use of this kind of dependencies has some disadvantages:
- It needs some coordination to have the latest version of a package.
- Package installation increases the size of the app as more packages are added.
- There is no update in the app until another build is done.
Module Federation from Webpack 5 was created to bring a solution to this problems.
Module federation makes it easy to share components and information between many FE applications.
Some advantages of using Module Federation from Webpack 5 are:
- It’s not a framework. It’s a JavaScript architecture and plugin added to Webpack. So there is no dependency on a particular framework.
- It also happens at run time so there is no overhead involved in the build process.
- It allows independent development by teams and dynamically import code from other applications at runtime. End results feels like an SPA.
- It allows independent testing and deployment/release strategies.
- Each of the micro app can choose their own tech stack and are not bound by a particular framework.
Module Federated modules expose and/or consume JavaScript modules. Any JavaScript module to be shared is to be exposed in the webpack.config.js file. There is normally a host app that renders all modules together to make up the application as a whole. This is done in runtime.
If you need further information on Module Federation implementation you can visit the Webpack documentation section on this topic
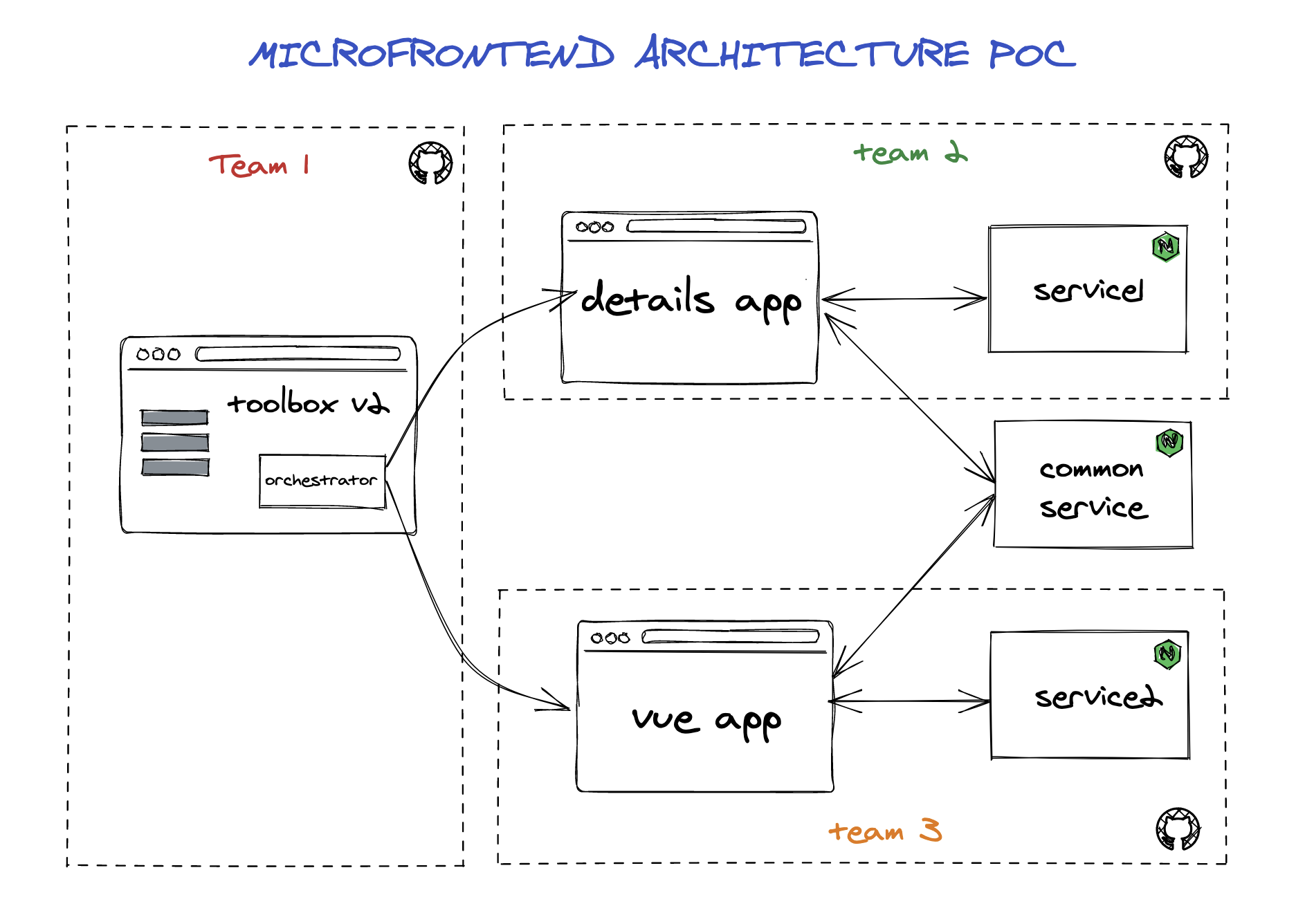
This is the main architecture of this POC:
There are 3 microapps. Each of them has its own repository and could have its own pipeline, tests, environments, connections to servers/db... The aim is to allow developers to work in different teams and handling their own projects.
As mentioned, microapps orchestration is made with Federated Modules Plugin from Webpack 5. There were other options to handle this orchestration, such us using a Framework like Single SPA, but for reasons exposed on a previous section, finally we used Federated Modules.
For now, there are no connections to services or common services in the microapps. But we wanted to show that it is possible to make those integrations.
-
Host App or Toolbox (React):
- Main Layout (Header, Footer, sidebar)
- Basic router config
- Landing page
- Routing
- Renderers for MF from other frameworks
-
Details App (React):
- Router config
- Pages
-
Vue App (Vue):
- Vue page
- Vue component
- Vue mount function
- Build MFs architecture with Modules Federation plugin
- Render a Vue page and a Vue component inside the React host (so find out how different frameworks can work together)
- Dynamically generate routes with a config array exposed in a microapp and rendered in the host app.
- Check basic communication between apps through DOM event bubbling & native events from W3C
- Different frameworks integration is not always possible, and if it is, is not easy.
- There are not many MF architecture examples in production
- Limited documentation
- It is difficult not to share a common state
- A preliminary design is necessary to face this kind of architecture.
- Feeling that the possible time to be won during development is expended in architecture design and configuration.
After cloning this repo:
git submodule update --init --recursive
Go to each submodule and follow installation instructions in Readme
Go to each submodule and follow running instructions in Readme