- Frontend:
- Vue 3, TypeScript
- Supabase.js for user management and realtime data syncing.
- Backend:
- app.supabase.io: hosted Postgres database with restful API for usage with Supabase.js.
Sign up to Supabase - https://app.supabase.io and create a new project. Wait for your database to start.
Once your database has started, run the "Todo List" quickstart.
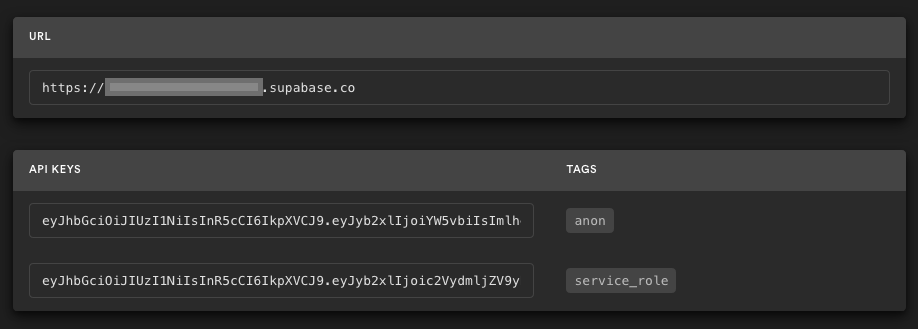
Go to the Project Settings (the cog icon), open the API tab, and find your API URL and anon key, you'll need these in the next step.
The anon key is your client-side API key. It allows "anonymous access" to your database, until the user has logged in. Once they have logged in, the keys will switch to the user's own login token. This enables row level security for your data. Read more about this below.
NOTE: The service_role key has full access to your data, bypassing any security policies. These keys have to be kept secret and are meant to be used in server environments and never on a client or browser.
Here, we recommend forking this repo so you can deploy through Vercel by clicking the button above. When you click the button, replace the repo URL with your fork's URL.
You will be asked for a VUE_APP_SUPABASE_URL and VUE_APP_SUPABASE_KEY. Use the API URL and anon key from step 3.
On app.supabase.io, you can go to Authentication -> Settings to change your auth settings for your project if necessary. Here, you can change the site URL, which is used for determining where to redirect users after they confirm their email addresses or attempt to use a magic link to log in.
Here, you can also enable external oauth providers, such as Google and GitHub.
This project uses very high-level Authorization using Postgres' Role Level Security.
When you start a Postgres database on Supabase, we populate it with an auth schema, and some helper functions.
When a user logs in, they are issued a JWT with the role authenticated and their UUID.
We can use these details to provide fine-grained control over what each user can and cannot do.
This is a trimmed-down schema, with the policies:
create table todos (
id bigint generated by default as identity primary key,
user_id uuid references auth.users not null,
task text check (char_length(task) > 3),
is_complete boolean default false,
inserted_at timestamp with time zone default timezone('utc'::text, now()) not null
);
alter table todos enable row level security;
create policy "Individuals can create todos." on todos for
insert with check (auth.uid() = user_id);
create policy "Individuals can view their own todos. " on todos for
select using (auth.uid() = user_id);
create policy "Individuals can update their own todos." on todos for
update using (auth.uid() = user_id);
create policy "Individuals can delete their own todos." on todos for
delete using (auth.uid() = user_id);Supabase is open source, we'd love for you to follow along and get involved at https://github.com/supabase/supabase
npm install
npm run serve
npm run build
npm run lint