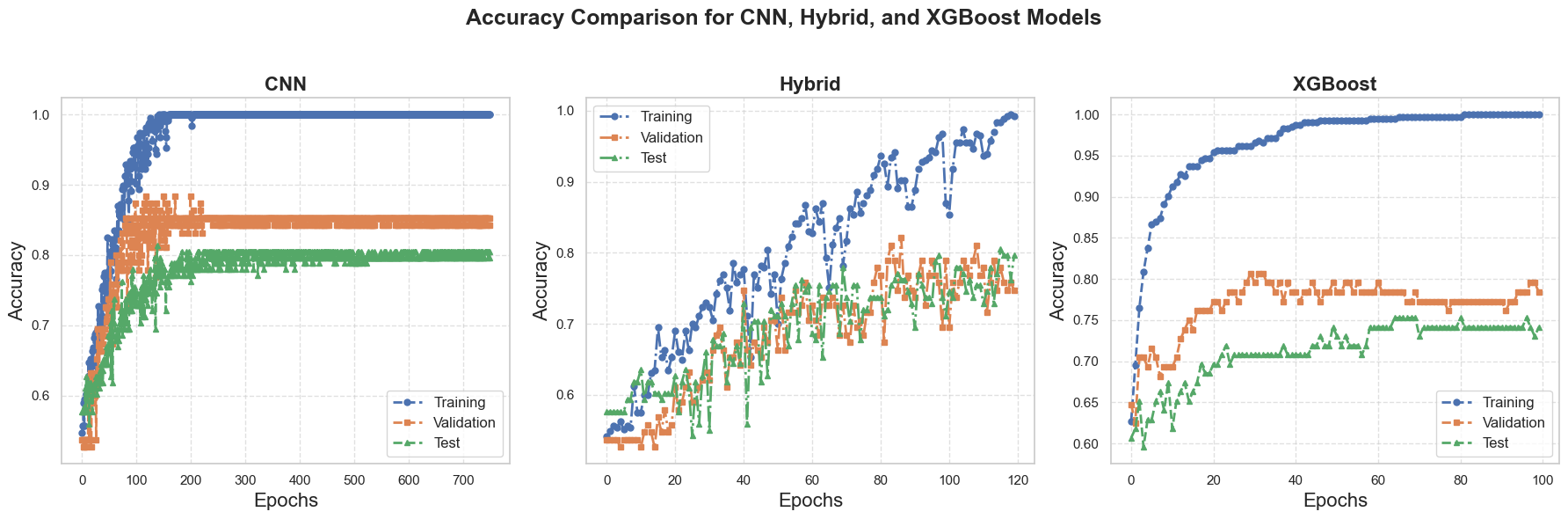
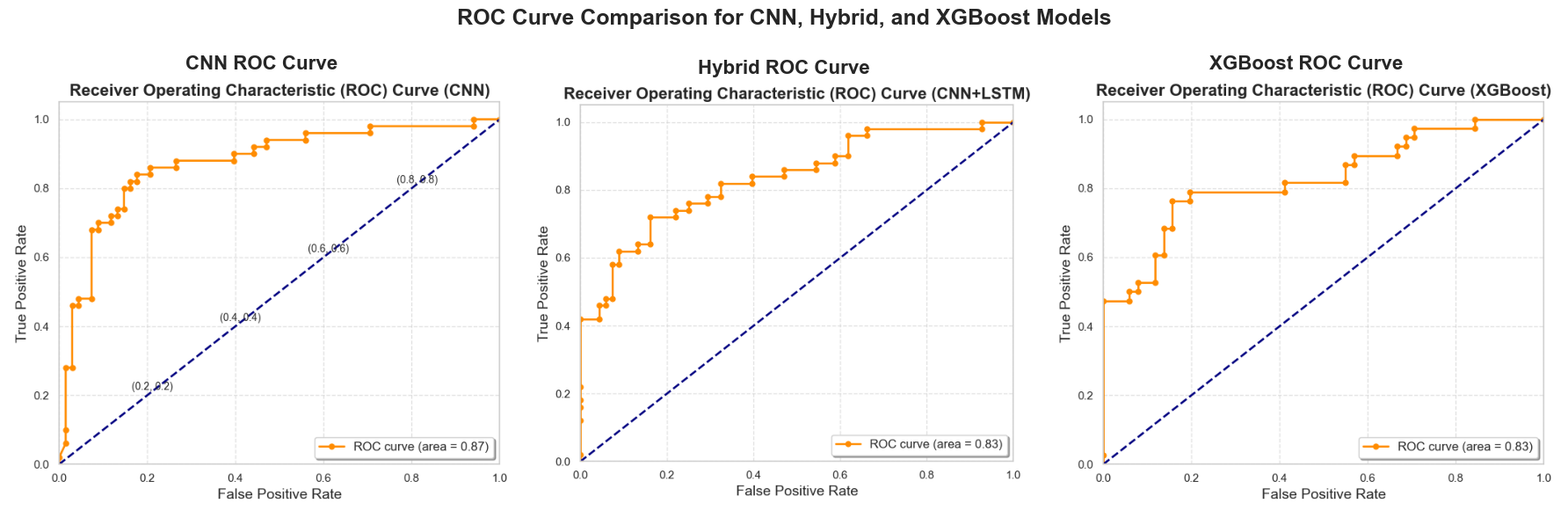
This study investigates the use of machine learning techniques to classify circulating tumor cells (CTCs) based on their movement patterns within a hyperuniform micropost microfluidic device. Utilizing cell-based modeling, a synthetic dataset was created to simulate the behavior of CTCs in blood flow. Three machine learning models were employed to analyze the trajectory data: a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), a hybrid model combining CNNs and Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, and the eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) algorithm. These models achieved an average classification accuracy of 80% in identifying distinct CTC phenotypes, demonstrating the potential of this method for early cancer detection.
Create the virtual environment
pip install virtualenv
virtualenv venv
venv\Scripts\activate
Install Dependencies
pip3 install -r requirements.txt
Run CNN Code/Notebook
python CNN_Model.py
or,
CNN_Model.ipynb
Run Hybrid Model Code/Notebook
python Hybrid_Model.py
or,
Hybrid_Model.ipynb
Run XGBoost Model Code/Notebook
python XGBoost_Model.py
or,
XGBoost_Model.ipynb
Run Final and Merge Model
Final_Models.ipynb
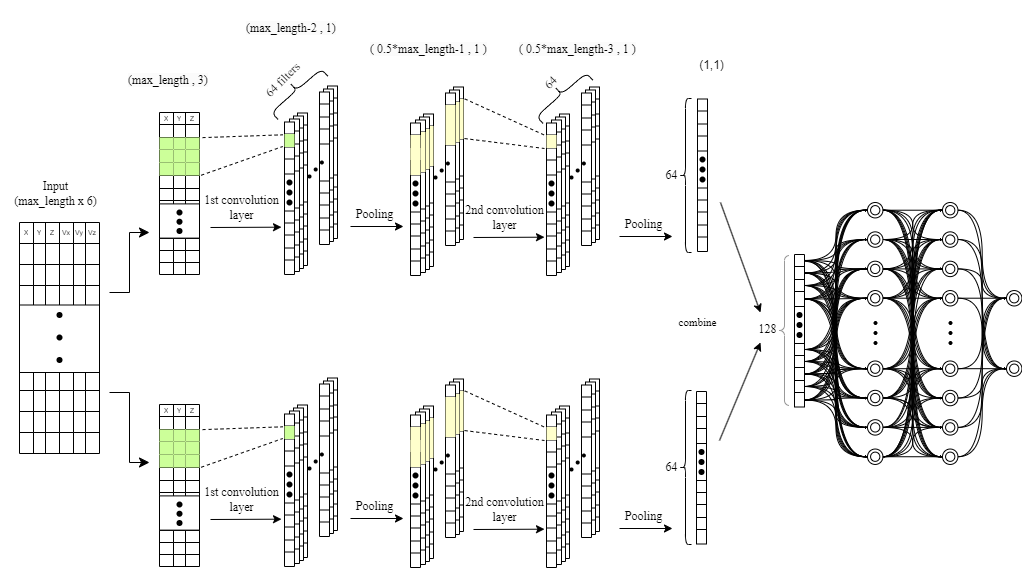
def create_model(input_shape):
# Separate inputs for position and velocity
position_input = Input(shape=input_shape)
velocity_input = Input(shape=input_shape)
# Convolutions for position
x_pos = Conv1D(64, kernel_size=3, activation='relu')(position_input)
x_pos = MaxPooling1D(2)(x_pos)
x_pos = Conv1D(64, kernel_size=3, activation='relu')(x_pos)
x_pos = GlobalAveragePooling1D()(x_pos)
# Convolutions for velocity
x_vel = Conv1D(64, kernel_size=3, activation='relu')(velocity_input)
x_vel = MaxPooling1D(2)(x_vel)
x_vel = Conv1D(64, kernel_size=3, activation='relu')(x_vel)
x_vel = GlobalAveragePooling1D()(x_vel)
# Combine features
combined = concatenate([x_pos, x_vel])
# Dense layers
x = Dense(128, activation='relu')(combined)
x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x)
output = Dense(2, activation='softmax')(x)
# Create model
model = Model(inputs=[position_input, velocity_input], outputs=output)
return model
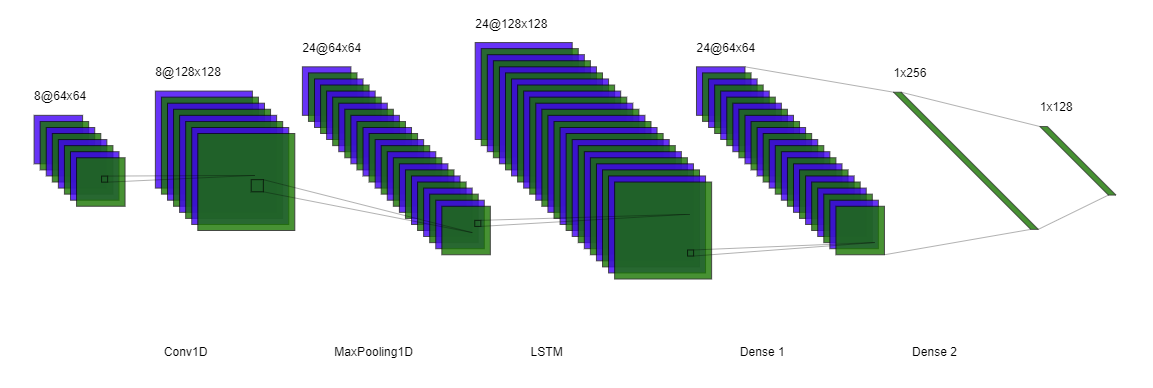
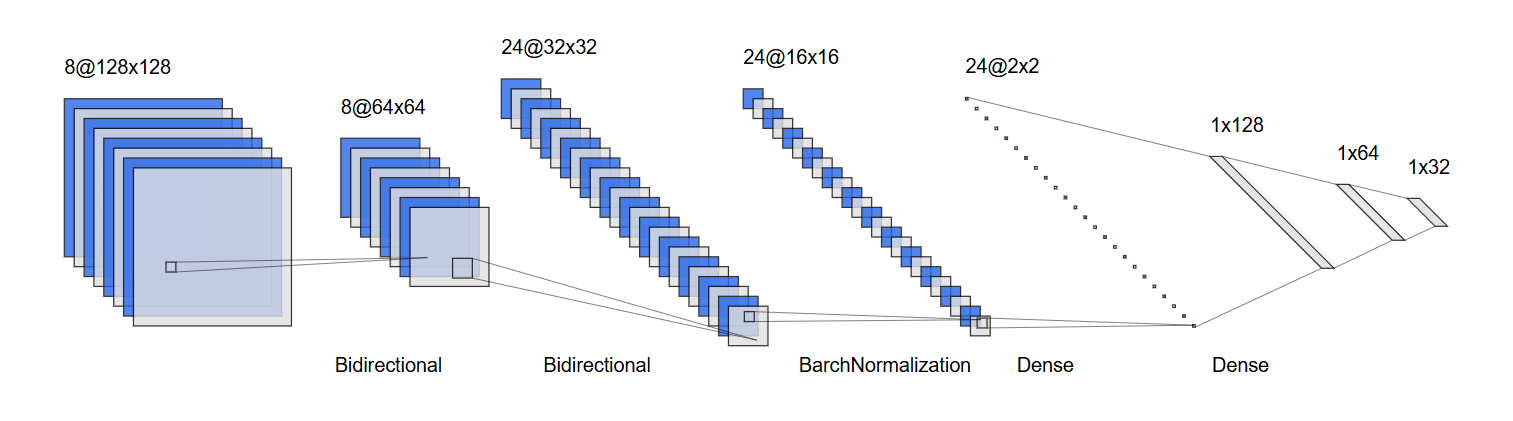
def create_all_outputs_model(model):
return Model(inputs=model.inputs, outputs=[layer.output for layer in model.layers])def create_hybrid_model(input_shape):
# Separate inputs for position and velocity
position_input = Input(shape=input_shape)
velocity_input = Input(shape=input_shape)
# Convolutions for position
x_pos = Conv1D(64, kernel_size=3, activation='relu')(position_input)
x_pos = BatchNormalization()(x_pos)
x_pos = MaxPooling1D(2)(x_pos)
x_pos = Conv1D(64, kernel_size=3, activation='relu')(x_pos)
x_pos = BatchNormalization()(x_pos)
x_pos = LSTM(64, return_sequences=True)(x_pos)
x_pos = GlobalAveragePooling1D()(x_pos)
# Convolutions for velocity
x_vel = Conv1D(64, kernel_size=3, activation='relu')(velocity_input)
x_vel = BatchNormalization()(x_vel)
x_vel = MaxPooling1D(2)(x_vel)
x_vel = Conv1D(64, kernel_size=3, activation='relu')(x_vel)
x_vel = BatchNormalization()(x_vel)
x_vel = LSTM(64, return_sequences=True)(x_vel)
x_vel = GlobalAveragePooling1D()(x_vel)
# Combine features
combined = concatenate([x_pos, x_vel])
# Dense layers
x = Dense(128, activation='relu')(combined)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = Dropout(0.5)(x)
x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x)
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
output = Dense(2, activation='softmax')(x)
# Create model
model = Model(inputs=[position_input, velocity_input], outputs=output)
return model# Convert data to DMatrix for XGBoost
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(X_train, label=y_train)
dval = xgb.DMatrix(X_val, label=y_val)
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(X_test, label=y_test)
params = {
'objective': 'binary:logistic',
'eval_metric': 'logloss',
'max_depth': 6,
'eta': 0.1,
}
# Train the model for multiple epochs
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
model = xgb.train(params, dtrain, num_boost_round=1, xgb_model=model if epoch > 0 else None)
# Predict probabilities
y_train_pred_prob = model.predict(dtrain)
y_val_pred_prob = model.predict(dval)
y_test_pred_prob = model.predict(dtest)
# Convert probabilities to binary predictions (threshold = 0.5)
y_train_pred = (y_train_pred_prob > 0.5).astype(int)
y_val_pred = (y_val_pred_prob > 0.5).astype(int)
y_test_pred = (y_test_pred_prob > 0.5).astype(int)
# Calculate and store accuracy
train_acc.append(accuracy_score(y_train, y_train_pred))
val_acc.append(accuracy_score(y_val, y_val_pred))
test_acc.append(accuracy_score(y_test, y_test_pred))
print("Training complete!")@misc{Microfluidic Data CTC Modeling,
author = {Sanjoy Kumar, Yifan Wang, Huixin Zhan, Karl Gardner, Travis Thompson, and Wei Li},
title = {Classification of Circulating Tumor Cells Using Machine Learning on Microfluidic Trajectory Data},
year = {2024},
publisher = {ICMLC-International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing},
}