Creating a Multi-Region Application with AWS Services. Bespoke AWS Cross-Region CI/CD Pipeline (CloudFormation). 📌
AWS CodePipeline includes a number of actions that help you configure build, test, and deploy resources for your automated release process. You can add actions to your pipeline that are in an AWS Region different from your pipeline. When an AWS service is the provider for an action, and this action type/provider type are in a different AWS Region from your pipeline, this is a cross-Region action. [Chapter 3]
Note: Cross-region actions are supported and can only be created in those AWS Regions where CodePipeline is supported. For a list of the supported AWS Regions for CodePipeline, see Quotas in AWS CodePipeline.
You can use the console, AWS CLI, or AWS CloudFormation to add cross-Region actions in pipelines.
Note: Certain action types in CodePipeline may only be available in certain AWS Regions. Also note that there may be AWS Regions where an action type is available, but a specific AWS provider for that action type is not available.
When you create or edit a pipeline, you must have an artifact bucket in the pipeline Region and then you must have one artifact bucket per Region where you plan to execute an action. For more information about the ArtifactStores parameter, see CodePipeline pipeline structure reference.
Note: CodePipeline handles the copying of artifacts from one AWS Region to the other Regions when performing cross-region actions.
If you use the console to create a pipeline or cross-Region actions, default artifact buckets are configured by CodePipeline in the Regions where you have actions. When you use the AWS CLI, AWS CloudFormation, or an SDK to create a pipeline or cross-Region actions, you provide the artifact bucket for each Region where you have actions.
Note: You must create the artifact bucket and encryption key in the same AWS Region as the cross-Region action and in the same account as your pipeline.
You cannot create cross-Region actions for the following action types:
-
Source actions
-
Third-party actions
-
Custom actions
When a pipeline includes a cross-Region action as part of a stage, CodePipeline replicates only the input artifacts of the cross-Region action from the pipeline Region to the action's Region.
Note: The pipeline Region and the Region where your CloudWatch Events change detection resources are maintained remain the same. The Region where your pipeline is hosted does not change.
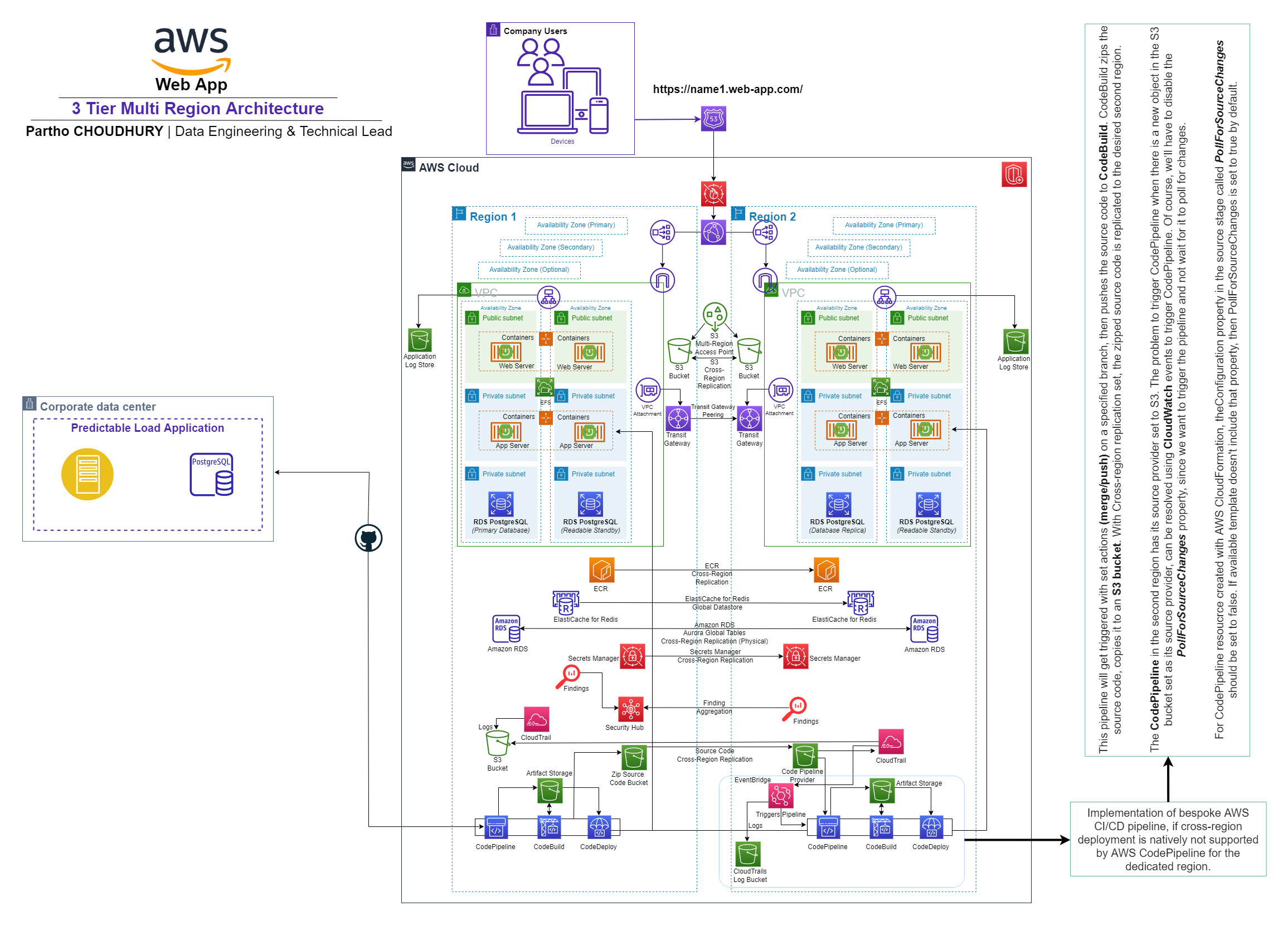
This solution aims at deploying a pipeline, which will get triggered with set actions (merge/push) on a specified branch, then will pushe the source code to CodeBuild. CodeBuild than zips the source code, copies it to an S3 bucket. With Cross-region replication set, the zipped source code is replicated to the desired region.
The project is supported by several managed services including Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2), Route 53, CloudFront, Secrets Manager, CloudTrail, Security Hub, Amazon ECR, Transit Gateway, and required Cross-Region Replications, etc.
Cross-region deployment is natively supported by AWS CodePipeline. At the build stage, builds can be processed by already created CodeBuild projects in supported regions. Native Cross-region deployment with deploy stage providers like CloudFormation, CodeDeploy, and ECS is possible when operating within supported regions.
However, some Regions do not have native support for cross-region deployment. Below explanation provides 2 ways to implement a bespoke AWS CI/CD pipeline in such regions. In regions where AWS natively supports cross-region or multi-region deployments, the default integrated solution should be used to achieve a cleaner solution.
When there is no full support for builtin code connection in a region, a pipeline is set up in an AWS region which already supports this feature.
This pipeline will get triggered with set actions (merge/push) on a specified branch, then pushes the source code to CodeBuild. CodeBuild zips the source code, copies it to an S3 bucket. With Cross-region replication set, the zipped source code is replicated to our desired region.
The CodePipeline in the 1st region region as per the architecture above, has its source provider set to S3. The next problem arises, how can we trigger CodePipeline when there is a new object in the S3 bucket set as its source provider?
This article approaches this problem using CloudWatch events to trigger CodePipeline. Of course, we’ll have to disable the PollForSourceChanges property, since we want to trigger the pipeline and not wait for it to poll for changes.
For CodePipeline resoucrce created with AWS CloudFormation, theConfiguration property in the source stage called PollForSourceChanges should be set to false. If your template doesn't include that property, then PollForSourceChanges is set to true by default.
CodePipelineTrigger:
Type: 'AWS::S3::Bucket'
Properties:
VersioningConfiguration:
Status: Enabled
CodePipeline:
Type: 'AWS::CodePipeline::Pipeline'
Properties:
Name: !Sub 'codepipeline-${AWS::StackName}'
RoleArn: !GetAtt CodePipelineServiceRole.Role.Arn
Stages:
- Name: Source
Actions:
- Name: SourceAction
ActionTypeId:
Version: '1'
Owner: AWS
Category: Source
Provider: S3
Configuration:
S3Bucket: !Ref CodePipelineTrigger
S3ObjectKey: ! Ref PipelineSourceObjectKey
PollForSourceChanges: 'false'
OutputArtifacts:
- Name: SourceCodeThe Amazon S3 source event-based change detection using Cloudwatch Events.
The following CloudFormation resources are required to implement CloudWatch Events, CodePipeline trigger:
- CloudWatch IAM role (with CodePipeline StartPipelineExecution policy attached)
AmazonCloudWatchEventRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Properties:
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
-
Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- events.amazonaws.com
Action: sts:AssumeRole
Path: /
Policies:
-
PolicyName: cwe-pipeline-execution
PolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
-
Effect: Allow
Action: codepipeline:StartPipelineExecution
Resource: "*"- CloudWatch Event Rule
AmazonCloudWatchEventRole:
Type: AWS::Events::Role
Properties:
EventPattern:
source:
- aws.s3
detail-type:
- 'AWS API Call via CloudTrail'
detail:
eventSource:
- s3.amazonwas.com
eventName:
- PutObject
- CompleteMultipartUpload
resources:
ARN:
- !Join [ '', [ !GetAtt CodePipelineTrigger.Arn, '/', !Ref PipelineSourceObjectKey ] ]
Targets:
-
Arn:
!Join [ '', [ 'arn:aws:codepipeline:', !Ref 'AWS::Region', ':', !Ref 'AWS::AccountId', ':', !Ref CodePipeline ] ]
RoleArn: !GetAtt AmazonCloudWatchEventRole.Arn
Id: codepipeline-Rule- CloudTrail trail, S3Bucket (to store CloudTrail event log files) and Bucket policy (Amazon S3 uses to log the events that occur)
#CloudTrail Bucket Policy
AWSCloudTrailBucketPolicy:
Type: AWS::S3::BucketPolicy
Properties:
Bucket: !Ref AWSCloudTrailBucket
PolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
-
Sid: AWSCloudTrailAclCheck
Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- cloudtrail.amazonaws.com
Action: s3.GetBucketAcl
Resource: !GetAtt AWSCloudTrailBucket.Arn
-
Sid: AWSCloudTrailWrite
Effect: Allow
Principal:
Service:
- cloudtrail.amazonaws.com
Action: s3:PutObject
Resource: !Join [ '', [ !GetAtt AWSCloudTrailBucket.Arn, '/AWSLogs/', !Ref 'AWS::AccountId', '/*' ] ]
Condition:
StringEquals:
s3:x-amz-acl: bucket-owner-full-control
#CloudTrail log Bucket
AWSCloudTrailBucket:
Type: AWS::S3::Bucket
#CloudTrail
AWSCloudTrail:
DependsOn:
- AWSCloudTrailBucketPolicy
Type: AWS::CloudTrail::Trail
Properties:
S3BucketName: !Ref AWSCloudTrailBucket
EventSelectors:
-
DataResources:
-
Type: AWS::S3::Object
Values:
- !Join [ '', [ !GetAtt CodePipelineTrigger.Arn, '/', !Ref PipelineSourceObjectKey ] ]
ReadWriteType: WriteOnly
IncludeGlobalServiceEvents: true
IsLogging: true
IsMultiRegionTrail: trueWhen these CloudFormation resources are pieced together, the seond pipeline is triggered when files matching the set object key, are created or updated to the S3 source bucket (this also includes objects created through cross-region replication).
AWS Regions are built with multiple isolated and physically separate Availability Zones (AZs). This approach allows you to create highly available Well-Architected workloads that span AZs to achieve greater fault tolerance. This satisfies the availability goals for most applications, but there are some general reasons that you may be thinking about expanding beyond a single Region:
- Expansion to a global audience as an application grows and its user base becomes more geographically dispersed, there can be a need to reduce latencies for different parts of the world.
- Reducing Recovery Point Objectives (RPO) and Recovery Time Objectives (RTO) as part of a multi-Region disaster recovery (DR) plan.
- Local laws and regulations may have strict data residency and privacy requirements that must be followed.
If you’re building a new multi-Region application, you may want to consider focusing on AWS services that have built-in functionality to assist. Existing applications will need to be further examined to determine the most expandable architecture to support its growth. The following sections review these services, and highlight use cases and best practices.
- Developer tools - Automation that uses infrastructure as code (IaC) removes manual steps to create and configure infrastructure. It offers a repeatable template that can deploy consistent environments in different Regions.
IaC with AWS CloudFormation StackSets uses a single template to create, update, and delete stacks across multiple accounts and Regions in a single operation. When writing an AWS CloudFormation template, you can change the deployment behavior by pairing parameters with conditional logic. For example, you can set a “standby” parameter that, when “true,” limits the number of Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2) instances in an Amazon EC2 Auto Scaling group deployed to a standby Region.
Applications with deployments that span multiple Regions can use cross-Region actions in AWS CodePipeline for a consistent release pipeline. This way you won’t need to set up different actions in each Region. EC2 Image Builder and Amazon Elastic Container Registry (Amazon ECR) have cross-Region copy features to help with consistent AMI and image deployments.
- Event-driven architecture - Decoupled, event-driven applications produce a more extensible and maintainable architecture by having each component perform its specific task independently.
Amazon EventBridge, a serverless event bus, can send events between AWS resources. By utilizing cross-Region event routing, you can share events between workloads in different Regions and accounts. For example, you can share health and utilization events across Regions to determine which Regional workload deployment is best suited for requests.
If your event-driven application relies on pub/sub messaging, Amazon Simple Notification Service (Amazon SNS) can fan out to multiple destinations. When the destination targets are Amazon Simple Queue Service (Amazon SQS) queues or AWS Lambda functions, Amazon SNS can notify recipients in different Regions. For example, you can send messages to a central SQS queue that processes orders for a multi-Region application.
- Monitoring and observability - Observability becomes even more important as the number of resources and deployment locations increases. Being able to quickly identify the impact and root cause of an issue will influence recovery activities, and ensuring your observability stack is resilient to failures will help you make these decisions. When building on AWS, you can pair the health of AWS services with your application metrics to obtain a more complete view of the health of your infrastructure.
To maintain visibility over an application deployed across multiple Regions and accounts, you can create a Trusted Advisor dashboard and an operations dashboard with AWS Systems Manager Explorer. The operations dashboard offers a unified view of resources, such as Amazon EC2, Amazon CloudWatch, and AWS Config data. You can combine the metadata with Amazon Athena to create a multi-Region and multi-account inventory view of resources.
You can view metrics from applications and resources deployed across multiple Regions in the CloudWatch console. This makes it easy to create graphs and dashboards for multi-Region applications. Cross-account functionality is also available in CloudWatch, so you can create a centralized view of dashboards, alarms, and metrics across your organization.
- Management: Governance - Growing an application into a new country means there may be additional data privacy laws and regulations to follow. These will vary depending on the country, and we encourage you to investigate with your legal team to fully understand how this affects your application.
AWS Control Tower supports data compliance by providing guardrails to control and meet data residency requirements. These guardrails are a collection of Service Control Policies (SCPs) and AWS Config rules. You can implement them independently of AWS Control Tower if needed.
-
Management: Operations - Several AWS Systems Manager capabilities allow for easier administration of AWS resources, especially as applications grow. Systems Manager Automation simplifies common maintenance and deployment tasks for AWS resources with automated runbooks. These runbooks automate actions on resources across Regions and accounts. You can pair Systems Manager Automation with Systems Manager Patch Manager to ensure instances maintain the latest patches across accounts and Regions.
-
Bringing it together - At the end of each part of this blog series, I actually built on a sample application based on the services covered. This shows us how to bring these services together to build a multi-Region application with AWS services. I did not use every service mentioned, just those that fit the use case.
I built this example to expand to a global audience. It requires high availability across Regions, and favors performance over strict consistency. I have chosen the following services covered in this post to accomplish our goals:
- CloudFormation StackSets to deploy everything with IaC. This ensures the infrastructure is deployed consistently across Regions.
- AWS Config rules provide a centralized place to monitor, record, and evaluate the configuration of our resources.
- For added observability, we created dashboards with CloudWatch dashboard, Personal Health dashboard, and Trusted Advisor dashboard.
While our primary objective is expanding to a global audience, we note that some of the services such as CloudFormation StackSets rely on Region 1. Each Regional deployment is set up for static stability, but if there were an outage in Region 1 for an extended period of time, our DR playbook would outline how to make CloudFormation changes in Region 2.
The following architecture illustrates the workflow:
Scenario: The Architecture Design - 3 Tier Multi Region with Cross-Region CI/CD Pipeline and Replications.
Many AWS services have features to help you build and manage a multi-Region architecture, but identifying those capabilities across 200+ services can be overwhelming.
It’s important to create a solid foundation when architecting a multi-Region application. These foundations lay the groundwork for you to move fast in a secure, reliable, and elastic way as you build out your application. Many AWS services include native features to help you build a multi-Region architecture. Your architecture will be different depending on the reason for expanding beyond a single Region.
- With 10+ years of industry experience, I have thrived in Data Science, Data Governance, IT, Cloud and Product Management. I have a keen interest and expertise in solving business problems using unique logic and analytics. I bring solutions to the table based on competitive Business Acumen and Human Intelligence.
- Have a look at my portfolio: Helping organization level all their Seeds Business arguments using Data & Technology | Ex_Zalando | Ex_Freecharge | Ex_Myntra Jabong | Ex_Supercell | Ex_Infosys
- I love talking about #cloudarchitecture, #businessanalytics, #datapipelines, #machinelearning, and #artificialintelligence