What is Maiter?
The Maiter project started at University of Massachusetts Amherst in 2012. Maiter is a message-passing framework that supports delta-based accumulative iterative computations (DAIC). The DAIC computation model is a new concept of iterative computation that supports asynchronous execution, which is very important for large-scale distributed iterative computation. Based on DAIC: * We can process vertex state updates in delta manner, which means only state changes are considered for computation. The non-change vertex (delta is zero) is skipped for processing. * We can build asynchronous dataflow model. Every worker is processing a data partition totally independent from each other worker. There is no synchronization barrier in the traditional iterative computation. Fast workers perform more computations, while slow workers perform less computations. * We can perform flexible scheduling policies under the asynchronous processing engine, including round robin scheduling, priority scheduling, filter scheduling, and so on.
Maiter is a C++ framework, which runs on hundreds of distributed commodity PCs or in the cloud. It is implemented by modifying Piccolo. Maiter's idea comes from PrIter, which supports prioritized iteration. Maiter is * more general, providing general computation model and flexible scheduling policies including round robin, priority, and filtering. * more efficient, providing asynchronous updates with efficient computations by using the most recent results * more scalable, holding up to 2 billion nodes for PageRank on Amazon EC2 Cloud with 100 instances * faster, 2x-10x faster than PrIter and Piccolo
Why Maiter?
Myriad of machine learning and data mining algorithms require parsing data sets iteratively. The distributed computing frameworks proposed so far either do not support iterative computation or support iterative computation assuming that synchronizations have to be performed. Eliminating synchronization barriers in iterative computation can significantly improve efficiency, especially under a large-scale heterogeneous environment. In addition, asynchronous iteration allows to use the most recent result to perform iterative updates, which helps improve computation efficiency.
Maiter is such a framework that supports asynchronous delta-based accumulative iterative computation. Delta-based Accumulative Iterative Computation is a new technique to perform iterative computations with more efficient computation and avoiding synchronization barriers.
How is Maiter?
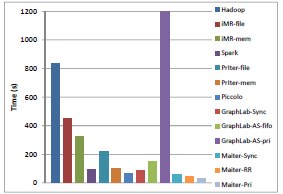
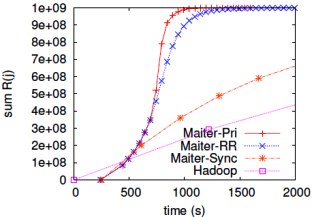
The experimental results performed on 100-node EC2 cloud show
2x-10x faster than synchronous implementation, 60x faster than Hadoop, for Pagerank benchmark.
high-utilized workers near-optimal scaling performance (scaling of PageRank)
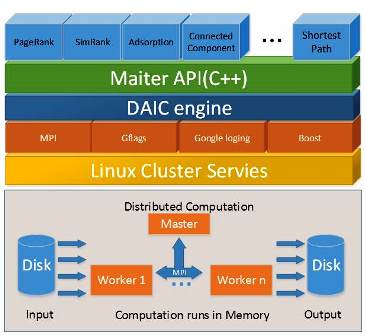
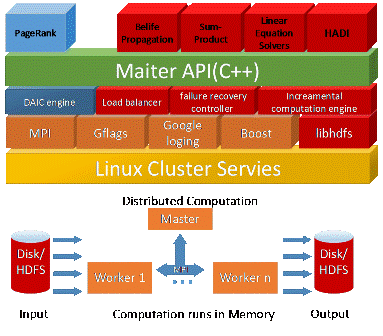
The software stack of Maiter
Download http://faculty.neu.edu.cn/cc/zhangyf/download/maiter-0.1-ubuntu.tar.gz'>maiter-0.1-utunbu.tar.gz. For more usage details, please refer to the wiki page Guidance. For more technical details, please read maiter's http://faculty.neu.edu.cn/cc/zhangyf/papers/maiter.pdf'>technical reports . Published Papers For any usage problem, please contact with us: * Yanfeng Zhang (zhangyf@cc.neu.edu.cn) * Chunlei Wang (wangchunlei.neu@foxmail.com)
Current Work
Maiter with SSD support Looking for more DAIC algorithms (HADI algorithm, Affinity Propagation algorithm, ...) Incremental Computation Load balance processing fault tolerant processing the futrue software of Maiter
Note
Our paper about Maiter with SSD support has been accepted by 2nd DASFAA workshop on Big Data Management and Analytics (BDMA 2014). (Feb. 21 2014) Our paper about asynchronous SimRank algorithm has been accepted by 1st CCF BigData 2013. (Sep. 25 2013) Maiter paper's journal version has been accepted by TPDS. (Sep. 3 2013) A detailed usage instruction is provided here. (Aug. 24 2013) A new sample application, SimRank, is developed. It is 75x faster than SimRank on Hadoop. (Jul. 10 2013) A data partition and distribution tool is developed. (Jun. 1 2013) Fixed a bug, which might lead to memory overflow for real graph. The number of vertices cannot be divisible by number of workers. (Jan. 14 2013) Fixed a bug, which might lead to an inaccurate result when running on a single machine and with output buffer. (Mar. 22 2012) Surprisingly, total asynchronous without dependency check works well. Only a good scheduler is desirable, trying filtering scheduler. (Mar. 12 2012) File-based implementation of PrIter has been implemented, will apply it to Maiter in the future. file-based PrIter. (Feb. 28 2012) Dependency check implemented (Feb. 3 2012) API is changed (Jan. 10 2012) Add an additional field in state table to store priority value, update it only when necessary (Jan. 9 2012) Shared dependency buffer is implemented, for reducing the redundant messages (Dec. 26 2011) Maiter with new API is implemented (Dec. 15 2011)