This repository holds the official code for the paper "Debiasing Deep Chest X-Ray Classifiers using Intra- and Post-processing Methods" presented at the the 7th Machine Learning for Healtcare Conference (MLHC), 2022, and ICLR 2022 Workshop on Socially Responsible Machine Learning. A short explanation of the method is provided in this spotlight talk; poster can be viewed here.
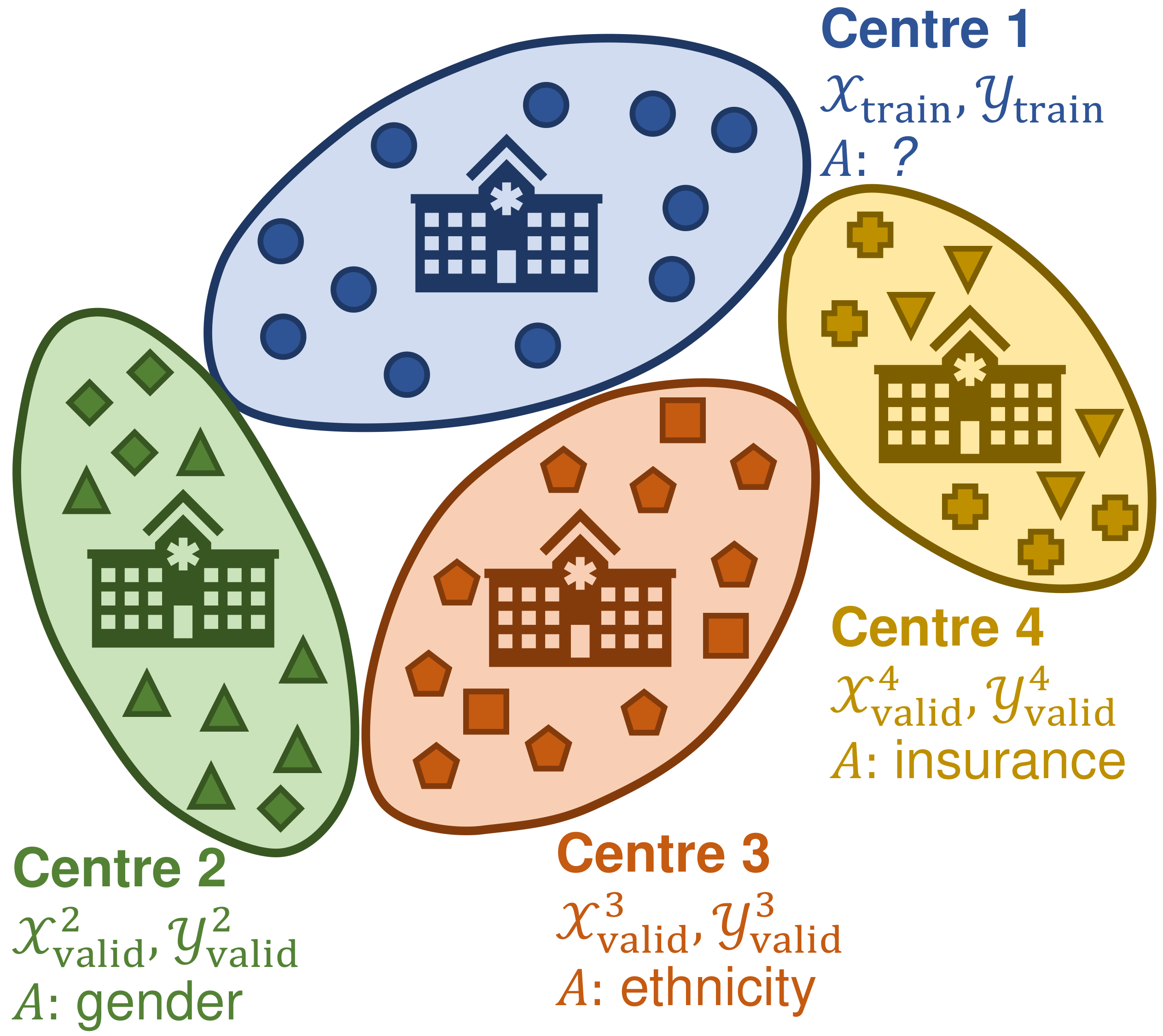
The intra-processing setting: a classification model is trained on centre 1, and debiased on centres 2, 3, and 4 that might have different protected attributes and fairness constraints, denoted by $A$.Deep neural networks for image-based screening and computer-aided diagnosis have achieved expert-level performance on various medical imaging modalities, including chest radiographs. Recently, several works have indicated that these state-of-the-art classifiers can be biased with respect to sensitive patient attributes, such as race or gender, leading to growing concerns about demographic disparities and discrimination resulting from algorithmic and model-based decision-making in healthcare. A practical scenario of mitigating bias w.r.t. protected attributes could be as follows: consider deploying a predictive neural-network-based model in several clinical centres with different demographics (see the figure above). The constraints on the bias and protected attribute of interest might vary across clinical centres due to different population demographics. Therefore, it might be more practical to debias the original model based on the local data, following an intra- or post-processing approach.
This repository implements two novel intra-processing techniques based on fine-tuning and pruning an already-trained neural network. These methods are simple yet effective and can be readily applied post hoc in a setting where the protected attribute valid,
valid, using differentiable proxy functions for the classification parity, and can produce unbiased predictions without the protected attribute
All the libraries required are in the conda environment environment.yml. To install it, follow the instructions below:
conda env create -f environment.yml # install dependencies
conda activate DiffBiasProxies # activate environment
To run the MIMIC-III experiments, you will need to first execute the code by Purushotham et al. (2018) to get the pre-processed data. To prepare MIMIC-CXR data, run this Jupyter notebook.
Scripts main_tabular.py and main_ChestXRay.py run the experiments on the tabular and chest X-ray data, respectively. /bin folder contains example shell scripts for concrete datasets:
- Tabular benchmarks:
run_adult,run_bank,run_compas,run_mimic_iii - MIMIC-CXR:
run_mimic_cxr
For example, to run debiasing on the Bank dataset, from the /bin folder, execute the command
python ../main_tabular.py --config ../configs/bank.yml
Above, file bank.yml specifies a configuration for the experiment.
For the experiments on tabular data, the configuration should contain the following parameters:
seed: [777, 666] # list of seeds for replications
experiment_name: my_experiment # name of the experiment, for logging purposes
dataset: bank # name of the dataset
# {adult, bank, compas, mimic,
# synthetic_loh, synthetic_zafar}
protected: age # name of the protected attribute
metric: eod # bias measure {spd, eod}
accc_metric: balanced_accuracy # performance measure
# {balanced_accuracy, accuracy, f1_score}
modelpath: my_model # name of the trained model, for logging purposes
dataset_alpha: 2.0 # α parameter for the synthetic dataset by Loh et al.
dataset_theta: 0.7 # θ parameter for the sythetic datatset by Zafar et al.
models: # list of models/debiasing procedures to be run
- default
- pruning
- biasGrad
pruning: # pruning parameters
dynamic: true # re-compute neuron influences after every pruning step?
# {true, false}
step_size: 1 # number of units pruned per step
stop_early: true # stop when the performance is close to random or
# the maximum number of steps is reached?
# {true, false}
val_only: true # perform pruning only on the validation set?
# {true, false}
obj_lb: 0.80 # ϱ parameter, a lower bound on the performance
biasGrad: # bias gradient descent/ascent parameters
lr: 0.00001 # learning rate
n_epochs: 200 # number of epochs
batch_size: 256 # batch size
val_only: true # perform fine-tuning only on the validation set?
# {true, false}
obj_lb: 0.70 # ϱ parameter, a lower bound on the performance
n_evals: 3 # number of times to evaluate the model per epoch
For the chest X-ray experiments, additional parameters include:
priv_class: M # name of the privileged class of the prot. attribute
unpriv_class: F # name of the unprivileged class of the prot. attribute
prot_ratio: 0.75 # the ratio between privileged and unprivileged
# class frequencies in the training set
disease: Enlarged Cardiomediastinum # disease label to be predicted
num_workers: 2 # number of loader worker processes for data loaders
default: # original model's parameters
batch_size: 32 # batch size
n_epochs: 20 # number of training epochs
arch: vgg # network's architecture {vgg, resnet}
pretrained: true # initialise the model with pretrained weights?
# {true, false}
pruning: # pruning parameters
max_steps: 10 # the maximum number of steps before early stopping
batch_size: 80 # batch size for approximating neuron influence
For the further details regarding YAML parameters, consult the code by Savani et al. (2020).
Folder /algorithms contains implementation of the debiasing procedures. pruning.py and biasGrad.py hold the code for the pruning and bias gradient descent/ascent. The file structure of the project is as follows:
├── algorithms # debiasing algorithms
├── bin # shell scripts and logs
│ ├── models # trained models are saved here
│ ├── results
│ │ ├── figures # plotting output of the experiments
│ │ └── logs # experiment logs
├── configs # .yml files
├── datasets # data loaders and structures
│ ├── chestxray_dataset.py
│ ├── mimic_iii_dataset.py
│ ├── simulations.py
│ └── tabular.py
├── main_ChestXRay.py # script for the chest X-ray experiments
├── main_tabular.py # script for the experiments on tabular data
├── models # base classifiers
│ ├── networks_ChestXRay.py
│ └── networks_tabular.py
├── notebooks # Jupyter notebooks
└── utils # utility functions
├── data_utils.py
├── evaluation.py
├── misc_utils.py
├── plotting.py
└── sim_utils.py
Further details are documented within the code.
🆘 Feeling lost or want a concrete example? You might find this demo Jupyter notebook useful!
- The code structure is based on the repository by Savani et al. (2020)
- For MIMIC-III, we used the pre-processing based on the code by Purushotham et al. (2018)
- For MIMIC-CXR, we adpated implementation of adversarial in-processing by Shweta Chopra et al.
- One of the synthetic datasets is based on the code by Zafar et al. (2017)
To better understand the background behind this work, we recommend reading the following papers:
- Muhammad Bilal Zafar, Isabel Valera, Manuel Gomez Rogriguez, and Krishna P. Gummadi. Fairness Constraints: Mechanisms for Fair Classification. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics, volume 54, pages 962–970. PMLR, 2017.
- Brian Hu Zhang, Blake Lemoine, and Margaret Mitchell. Mitigating unwanted biases with adversarial learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 AAAI/ACM Conference on AI, Ethics, and Society. ACM, 2018.
- Klas Leino, Shayak Sen, Anupam Datta, Matt Fredrikson, and Linyi Li. Influence-directed explanations for deep convolutional networks. In IEEE International Test Conference (ITC). IEEE, 2018.
- Yash Savani, Colin White, and Naveen Sundar Govindarajulu. Intra-processing methods for debiasing neural networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, volume 33, pages 2798–2810. Curran Associates, Inc., 2020.
- Laleh Seyyed-Kalantari, Haoran Zhang, Matthew B. A. McDermott, Irene Y. Chen, and Marzyeh Ghassemi. Underdiagnosis bias of artificial intelligence algorithms applied to chest radiographs in under-served patient populations. Nature Medicine, 27(12):2176–2182, 2021.
- Chuizheng Meng, Loc Trinh, Nan Xu, James Enouen, and Yan Liu. Interpretability and fairness evaluation of deep learning models on MIMIC-IV dataset. Scientific Reports, 12(1), 2022.
Please cite our paper and repository as
@InProceedings{Marcinkevics2022,
title = {Debiasing Deep Chest {X}-Ray Classifiers using Intra- and Post-processing Methods},
author = {Marcinkevics, Ricards and Ozkan, Ece and Vogt, Julia E.},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 7th Machine Learning for Healthcare Conference},
pages = {504--536},
year = {2022},
editor = {Lipton, Zachary and Ranganath, Rajesh and Sendak, Mark
and Sjoding, Michael and Yeung, Serena},
volume = {182},
series = {Proceedings of Machine Learning Research},
month = {05--06 Aug},
publisher = {PMLR},
pdf = {https://proceedings.mlr.press/v182/marcinkevics22a/marcinkevics22a.pdf},
url = {https://proceedings.mlr.press/v182/marcinkevics22a.html},
}