There are currently few datasets appropriate for training and evaluating models for non-goal-oriented dialogue systems (chatbots); and equally problematic, there is currently no standard procedure for evaluating such models beyond the classic Turing test.
The aim of our competition is therefore to establish a concrete scenario for testing chatbots that aim to engage humans, and become a standard evaluation tool in order to make such systems directly comparable.
This is the second Conversational Intelligence (ConvAI) Challenge. The previous one was conducted under the scope of NIPS 2017 Competitions track. This year we aim to improve over last year:
- providing a dataset from the beginning, Persona-Chat
- making the conversations more engaging for humans
- simpler evaluation process (automatic evaluation, followed then by human evaluation)
The winning entry in human evaluations will receive $20,000 in Mechanical Turk funding -- in order to encourage further data collection for dialogue research. The winner in the automatic metrics also receives $5000 in AWS compute.
-
Jan 31: Paper online summarizing the results of the competition. Thanks to everyone for taking part!
-
December 9: And the winner has been announced: "Lost in Conversation"! See the presentation slides for all details: intro, results, top team presentations, and future work.
-
November 20: Schedule for the presentations and awards for the competition at NeurIPS are up here.
-
November 12: 🙋 Call for chat volunteers. ConvAI2 competition is now at the final stage and we kindly invite community to volunteer in evaluating submitted solutions. Even 2-3 evaluated dialogues from you will contribute significantly to the success of the competition. Importantly, all the dialogues collected during competition will be published open source to promote future dialogue system research. Final results will be presented at NeurIPS 2018 Competition track. Evaluation system is available at FB Messenger via link https://m.me/convai.io
-
September 30: The submissions are locked, automatic evals are final on the leaderboard, and the final stage of human evaluation is almost here. We invite successful teams from the first round (🍐 teams) to prepare and test their solutions for MTurk and the 'wild' evaluation part of the challenge. For wild evaluation more details can be found at here. For MTurk evaluation, teams should provide an interactive script, e.g. like this one.
-
July 20: Additional dataset published: This dataset was collected during DeepHack.Chat hackathon as a part of ConvAI2 competition. The dataset contains more than 2000 dialogues for PersonaChat task where human evaluators recruited via the crowd sourcing platform Yandex.Toloka chatted with bots submitted by teams. This human-bot data has a different distribution from the human-human PersonaChat data, but may be useful!
-
July 10: 'Wild' evaluation started: Evaluation by human volunteers is open. Chat with competing bots! Bots are available in Messenger m.me/convai.io and Telegram t.me/Convai_chat_bot.
-
May 9: Hackathon: We will be organizing a non-compulsory hackathon around the competition: DeepHack.Chat Hackathon. The most promising team attending will receive a travel grant to attend NeurIPS 2018!!
-
April 21: Leaderboard and baselines: Leaderboard, baseline numbers and code for training and evaluating them are up!
Dialogues collected during DeepHack.Chat hackathon and `wild' evaluation round are available online.
| Rank | Creator | Rating | Persona detect |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 🍐🍌 | Lost in Conversation [code] | 3.11🍌 | 0.9 |
| 2 🍐🍎 🍎 🍎 | 🤗 (Hugging Face) | 2.68 | 0.98 |
| 3 🍐 | Little Baby(AI小奶娃) | 2.44 | 0.79 |
| 4 🍐 | Mohd Shadab Alam | 2.33 | 0.93 |
| 5 🍐 | Happy Minions | 1.92 | 0.46 |
| 6 🍐 | ADAPT Centre | 1.6 | 0.93 |
| KV Profile Memory | ParlAI team | 2.44 | 0.76 |
| Human | MTurk | 3.48 | 0.96 |
Automatic Evaluation Leaderboard (hidden test set)
| Rank | Creator | PPL | Hits@1 | F1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 🍐 | 🤗 (Hugging Face) | 16.28🍎 | 80.7🍎 | 19.5🍎 |
| 2 🍐 | ADAPT Centre | 31.4 | - | 18.39 |
| 3 🍐 | Happy Minions | 29.01 | - | 16.01 |
| 4 🍐 | High Five | - | 65.9 | - |
| 5 🍐 | Mohd Shadab Alam | 29.94 | 13.8 | 16.91 |
| 6 🍐 | Lost in Conversation | - | 17.1 | 17.77 |
| 7 🍐 | Little Baby(AI小奶娃) | - | 64.8 | - |
| 8 | Sweet Fish | - | 45.7 | - |
| 9 | 1st-contact | 31.98 | 13.2 | 16.42 |
| 10 | NEUROBOTICS | 35.47 | - | 16.68 |
| 11 | Cats'team | - | 35.9 | - |
| 12 | Sonic | 33.46 | - | 16.67 |
| 13 | Pinta | 32.49 | - | 16.39 |
| 14 | Khai Mai Alt | - | 34.6 | 13.03 |
| 15 | loopAI | - | 25.6 | - |
| 16 | Salty Fish | 34.32 | - | - |
| 17 | Team Pat | - | - | 16.11 |
| 18 | Tensorborne | 38.24 | 12.0 | 15.94 |
| 19 | Team Dialog 6 | 40.35 | 10.9 | 7.27 |
| 20 | Roboy | - | - | 15.83 |
| 21 | IamNotAdele | 66.47 | - | 13.09 |
| 22 | flooders | - | - | 15.47 |
| 23 | Clova Xiaodong Gu | - | - | 14.37 |
| Seq2Seq + Attention | ParlAI team | 29.8 | 12.6 | 16.18 |
| Language Model | ParlAI team | 46.0 | - | 15.02 |
| KV Profile Memory | ParlAI team | - | 55.2 | 11.9 |
🍎 denotes the best performing model for each metric on the hidden test set. The rank is determined by sorting by the minimum rank of the score in any of the three metrics, where ties are broken by considering the second (and then third) smallest ranks. The 🍐 teams have made it to the next round (top 3 in each metric). For these teams: please make sure your GitHub repo contains an interactive script (see here for example) that allows your model to function in interactive mode. (To be clear, this must be the same model that we evaluated for the leaderboard above.)
Models by ParlAI team are baselines, and not entries into the competition; code is included for those models.
Note that the scripts that you can run locally will give metrics on the validation set, not the hidden test set which is reported here (for that, you need to submit your code, see below).
Validation Leaderboard We also provide an additional validation set leaderboard here.
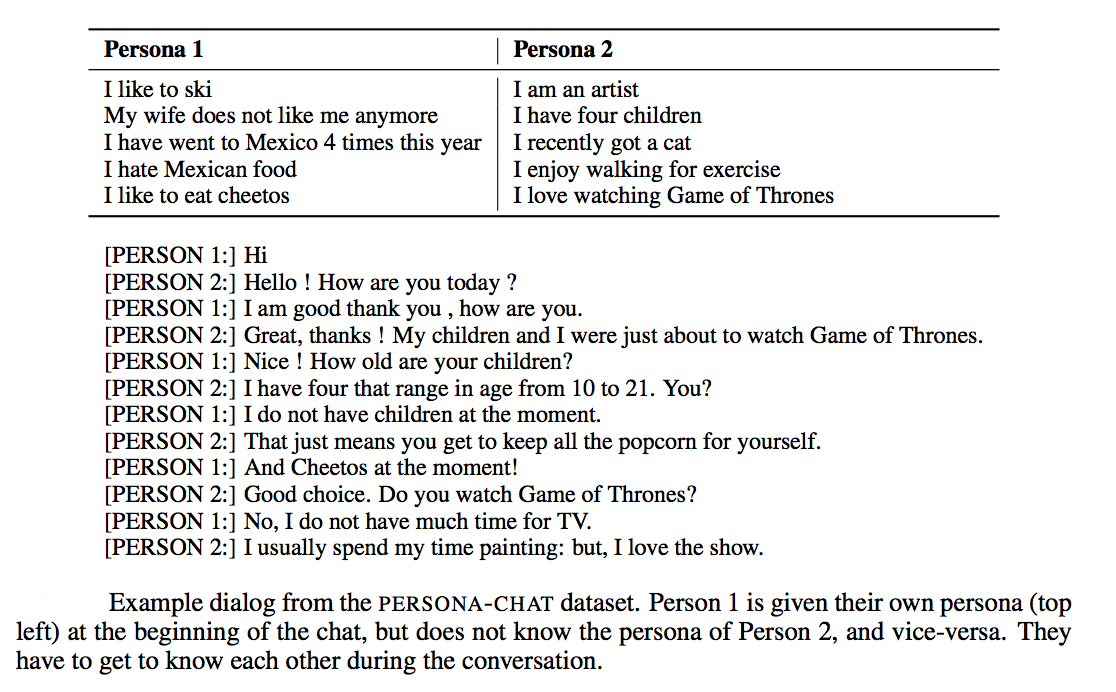
Persona-Chat training set consists of conversations between crowdworkers who were randomly paired and asked to act the part of a given provided persona (randomly assigned, and created by another set of crowdworkers). The paired workers were asked to chat naturally and to get to know each other during the conversation. This produces interesting and engaging conversations that learning agents can try to mimic.
The Persona-Chat task aims to model normal conversation when two interlocutors first meet, and get to know each other. Their aim is to be engaging, to learn about the other's interests, discuss their own interests and find common ground. The task is technically challenging as it involves both asking and answering questions, and maintaining a persistent persona, which is provided.
Conversing with current chit-chat models for even a short amount of time quickly exposes their weaknesses. Common issues with chit-chat models include:
- (i) the lack of a consistent personality (Li et al., 2016) as they are typically trained over many dialogs each with different speakers,
- (ii) the lack of an explicit long-term memory as they are typically trained to produce an utterance given only the recent dialogue history (Vinyals et al., 2015); and
- (iii) a tendency to produce non-specific answers like ``I don't know'' (Li et al., 2015).
This competition aims to find models that address those specific issues. The baseline systems we have already run indicate that there is hope we can make steps in that direction.
The dataset consists of 164,356 utterances in over 10,981 dialogs, some of which are set aside for validation. The speaker pairs each have assigned profiles coming from a set of 1155 possible personas, each consisting of at least 4 profile sentences, setting aside 200 never seen before personas for validation. To avoid modeling that takes advantage of trivial word overlap, we crowdsourced additional rewritten sets of the same personas, with related sentences that are rephrases, generalizations or specializations, rendering the task much more challenging.
More details can be found in the paper describing the dataset.
The competition dataset is available in our open source system ParlAI, more specifically here. That is, install ParlAI and then do:
python examples/display_data.py --task convai2 --datatype trainto look at the data.
Source code for baseline methods for the competition are also already provided in ParlAI here, including training loop and evaluation code for the automatic evaluation metrics. Baseline results are provided in the paper, although the dataset is now larger. (We have hence run new baselines that appear on the leaderboard above.)
As the original test set was released, we have crowdsourced further data for a hidden test set unseen by the competitors for automatic evaluation.
Competitors' models will then be compared in three ways:
- (i) automated evaluation metrics on a new test set hidden from the competitors;
- (ii) evaluation on Amazon Mechanical Turk; and
- (iii) `wild' live evaluation by volunteers having conversations with the bots.
The winning dialogue systems will be chosen based on these scores.
There are three types of metrics we will evaluate:
-
Automated metrics - Perplexity, F1 and hits@k. These will be computed on the hidden test set. Competitors will provide their code, and we will run the final evaluation (a validation set will be provided for their own local tests). Perplexity is only scored for probabilistic generative models, F1 can be computed for any model that produces a response, and hits@k is computed for any model that can rank a set of candidate responses that we provide (either retrieval based models, or generative models capable of assigning a probability to a candidate response). As some methods are not applicable to some metrics, we will have a separate leaderboard for each. The top performing methods for each metric will be evaluated in the live experiments.
-
Amazon Mechanical Turk - given the entrant's model code, we will run live experiments where Turkers chat to their model given instructions identical to the creation of the original dataset, but with new profiles, and then score its performance. Turkers will score the models between 1-5 with three metrics: fluency, consistency and engagingness. Finally the Turker will try to guess the persona being used by the bot (which was provided) as another measure of the ability of the bot to stick to its given persona. See (Zhang et al., 2018) for more details of these metrics and collected scores of baseline systems.
-
`Wild' Live Chat with Volunteers - Finally, we will solicit volunteers to also chat to the models in a similar way to the Mechanical Turk setup. As volunteers, unlike Turkers, are not paid and will likely not follow the instructions as closely, the distribution will likely be different, hence serving as a test of the robustness of the models. This setup will be hosted through the Messenger and Telegram APIs.
We will run live volunteer chat throughout the competition so that competitors can try out their bots talking to humans and to collect live data, if they so wish (however, they are also free to only use the fixed train/test format at this stage).
The automated metrics will be used to obtain a shortlist of best performing systems, likely the top 3 scoring systems from each of the three metrics (Perplexity, F1 and hits@k). If those three leaderboards feature the same models at the top we will take systems further down the leaderboards, up to a maximum of 10. These systems will be evaluated in the final live experiments on Mechanical Turk and via volunteers using the same scoring protocols, already described.
During NeurIPS the `wild' live conversation can continue, and the best performing systems will be showcased and conversed with.
We will declare winners in both the automated metrics tracks, and in the live evaluations (which will be considered the grand prize, being more important). The latter will consist of the weighted average of the Turk and wild (volunteer) scores. Finally, the solutions and any data collected will be made open source to the community.
- Competitors should indicate which training sources are used to build their models, and whether (and how) ensembling is used (we may place these in separate tracks in an attempt to deemphasize the use of ensembles).
- Competitors must provide their source code so that the hidden test set evaluation and live experiments can be computed without the team's influence, and so that the competition has further impact as those models can be released for future research to build off them. Code can be in any language but a thin python wrapper must be provided in order to work with our evaluation and live experiment code via ParlAI's interface.
- We will require that the winning systems also release their training code so that their work is reproducible (although we also encourage that for all systems).
- Competitors are free to augment training with other datasets as long as they are publicly released (and hence, reproducible). Hence, all entrants are expected to work on publicly available data or release the data they use to train.
To submit an entry, create a private repo with your model that works with our evaluation code, and share it with the following github accounts: emilydinan, klshuster, jaseweston, JackUrb, varvara-l, madrugado.
See this directory for example baseline submissions.
You are free to use any system (e.g. PyTorch, Tensorflow, C++,..) as long as you can wrap your model with ParlAI for the evaluation. If you use PyTorch your models should work with PyTorch 0.4. The top level README should tell us your team name, model name, and where the eval_ppl.py, eval_hits.py etc. files are so we can run them. Those should give the numbers on the validation set. Please also include those numbers in the README so we can check we get the same. We will then run the automatic evaluations on the hidden test set and update the leaderboard. You can submit a maximum of once per month. We will use the same submitted code for the top performing models for computing human evaluations when the submission system is locked on September 30th.
Up until September 30th competitors will be able to submit models (source code) to be evaluated on the hidden test set using automated metrics (which we will run on our servers).
Ability to submit a model for evaluation by automatic metrics to be displayed on the leaderboard will be available by April 6th. The current leaderboards will be visible to all competitors.
`Wild' live evaluation can also be performed at this time to obtain evaluation metrics and data, although those metrics will not be used for final judgement of the systems, but more for tuning systems if the competitors so wish.
On September 30th the source code submission system will be locked, and the best performing systems will be evaluated over the next month using Mechanical Turk and the `wild' live evaluation.
Winners will be announced at NeurIPS 2018.
-
Why does the eval_ppl.py script report different perplexity than my model training/testing logs? The eval_ppl script will give different performance than the perplexity reported by our baseline model training scripts. For instance, the model reported perplexity for the seq2seq model includes “easier” tokens such as predicting the “end” token which the model appends to each target. The separate eval_ppl script does a more careful job of evaluating (comparable across models) and doesn't include these extra special tokens from the model.
-
Which personas (self:original, self:revised, etc.) will my model be evaluated on? All submissions for the leaderboard will be evaluated using the “self:original” personas.
-
How do I view the data? The competition dataset is available in our open source system ParlAI, more specifically here. That is, install ParlAI and then run
python examples/display_data.py --task convai2 --datatype trainto look at the data. -
What is the best way to store my model file for submission to the competition? We recommend storing your model files and any other large files you are using with Git-LFS. Please see more information here.
-
Can I submit different models for different metrics? No. This is supposed to measure the performance of a single model in varying ways.
This is not a compulsory part of the competition, but you may also be interested in the following hackathon:
If you submit your solution before the 15th of June, you can participate in the qualification round of DeepHack.Chat hackathon which will take place in Moscow on July 2-8. We will select 10 to 12 teams whose systems score best in terms of automatic metrics, and invite them to participate in the final round of the hackathon. At the hackathon teams will further improve their systems and listen to lectures from the top researchers in the field. Participants will also take part in live human evaluation of dialogue systems of other teams. The winning team will get a travel grant to NeurIPS to ConvAI finals.
If you want to participate in the hackathon, please include a file ``TEAM'' in your repository when you submit your models. The file should contain names and emails of the members of your team. The team should consist of no more than 5 people.
The organizing team comes from multiple groups --- Moscow Institute of Physics and Technology, Facebook AI Research, University of Montreal, McGill and Carnegie Mellon University.
The Team consists of: Mikhail Burtsev, Varvara Logacheva, Valentin Malykh, Ryan Lowe, Iulian Serban, Shrimai Prabhumoye, Emily Dinan, Douwe Kiela, Alexander Miller, Kurt Shuster, Arthur Szlam, Jack Urbanek and Jason Weston.
Advisory board: Yoshua Bengio, Alan W. Black, Joelle Pineau, Alexander Rudnicky, Jason Williams.
Webpage of the 1st NIPS Conversational Intelligence Challenge is available at convai.io/2017