Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a scene-photo (for example the text on signs and billboards in a landscape photo) or from subtitle text superimposed on an image. Scene text detection has attracted much attention in the computer vision field because of its numerous applications, such as instant translation, image retrieval, scene parsing, geo-location, and blind-navigation.
So the aim of this project is creating OCR and the web application, where user can upload theirs images, and get images with detected and recognised text by using OCR.
- Clone our repository:
# Clone git repo git clone {} - Install all following requirements from requirements.txt:
After this command, keras-ocr, tenserflow, opencv(v4.2.0.34), flask will be installed in your environment
# With pip pip install -r requirements.txt
The project use keras-ocr, tenserflow, opencv for creating OCR model and flask for creating web-application. So let's talk about this libraries and framework.
Keras is an open-source library that provides a Python interface for artificial neural networks. Keras acts as an interface for the TensorFlow library. Keras contains numerous implementations of commonly used neural-network building blocks such as layers, objectives, activation functions, optimizers, and a host of tools to make working with image and text data easier to simplify the coding necessary for writing deep neural network code.
TenserFlow is a free and open-source software library for machine learning. It can be used across a range of tasks but has a particular focus on training and inference of deep neural networks.
OpenCV or Open Source Computer Vision Library is a library of programming functions mainly aimed at real-time computer vision.
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) is used to process images or scanned documents to produce raw text or other structured output. Before character recognition of the image with the images, it is advisable to extract the words and lines of text. The major trend in scene text detection before the emergence of deep learning was bottom-up, where handcrafted features were mostly used, but recently, deep learningbased text detectors have been proposed by adopting popular object detection/segmentation methods. So by using detector we generate for each training image the ground truth label with characterlevel limited boxes.In this way, the source data is compressed, and images containing the words and lines are extracted from text.
The next step is character recognition. The recognition in images is most successfully performed on the basis of deep machine learning. Neural networks containing many levels are used, which are able to accumulate features and representations in the processed data. In this project the model has been already trained, so it is not essential to prepare data for training.
So the first step will be creating a OCR pipeline, by using keras-ocr. This pipeline transforms images into raw text data with OCR. OCR pipline consists of two parts Detector and Recogniser
Then let's create a an object of class. Weights of model models/craft_mlt_25k.h5 & models/crnn_kurapan.h5 will be downloaded by url (in the keras-ocr code) and cached in parent folder ~/models.
# keras-ocr will automatically download pretrained
# weights for the detector and recognizer.
pipeline = keras_ocr.pipeline.Pipeline()
To cache inside the project, set the following variable:
os.environ["KERAS_OCR_CACHE_DIR"] = 'models'
The model has been already trained, so we use it only for inference stage. At the inference stage, the final output can be delivered in various shapes, such as word boxes or character boxes, and further polygons.
Then we pass the trained model and images to inference function:
def inference(pipeline, images: List[Image.Image]) -> List[Dict]:
if not isinstance(images, list):
# pack in list if single image
images = [images]
for i, image in enumerate(images):
# convert to numpy array.
if isinstance(image, Image.Image):
images[i] = np.array(image)
# # Each list of predictions in prediction_groups is a list of
# # (word, box) tuples.
prediction_groups = pipeline.recognize(images)
results = []
for image, prediction in zip(images, prediction_groups):
result = []
for data in prediction:
result.append({
'name': str(data[0]),
'bbox': data[1].astype(int).tolist()
})
results.append(result)
return results
Since flask is very simple and wroted by python, we build it with only a few lines of code.
This function receive base64 encoded image from front end page, converted it to PIL Image, then do the object detection step.
@app.route('/api/', methods=["POST"])
def main_interface():
response = request.get_json()
data_str = response['image']
point = data_str.find(',')
base64_str = data_str[point:] # remove unused part like this: "data:image/jpeg;base64,"
image = base64.b64decode(base64_str)
img = Image.open(io.BytesIO(image))
if(img.mode!='RGB'):
img = img.convert("RGB")
# convert to numpy array.
img_arr = np.array(img)
# do object detection in inference function.
results = inference(sess, detection_graph, img_arr, conf_thresh=0.5)
print(results)
return jsonify(results)
In front end page, with the help of jQuery ajax, we can send the base64 image to backend, wait for the result, then draw the bounding box on the page.
Core code is:
// handle image files uploaded by user, send it to server, then draw the result.
function parseFiles(files) {
const file = files[0];
const imageType = /image.*/;
if (file.type.match(imageType)) {
warning.innerHTML = '';
const reader = new FileReader();
reader.readAsDataURL(file);
reader.onloadend = () => {
image.src = reader.result;
// send the img to server
communicate(reader.result);
}
} else {
setup();
warning.innerHTML = 'Please drop an image file.';
}
}
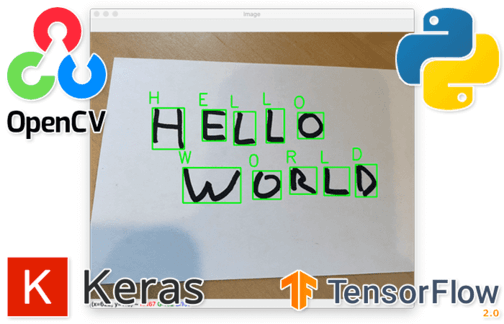
Finally, we get a web aplliction where you can upload your images, and then by using OCR get images with detected and recognised text:
To run project, execute following commands in terminal:
Step 1: Open the server with
python app.py
The server is setup on port 5000.
Step 2: Open the front end page.
If you want to use python.
// python3
python -m http.server
// python2
python -m SimpleHTTPServer
If you prefer Node.js
npm install serve -g // install serve
serve // this will open a mini web serve
// or http-serve
npm install http-server -g
http-server
This project is licensed under the MIT License - see the LICENSE file for details
-
"Keras-ocr" repo: https://github.com/faustomorales/keras-ocr
-
"Flask" repo: https://github.com/pallets/flask