remoteAudio is an audio streaming application, built for Amateur Radio purposes, written in Go. The most typical use case for this software is the remote operation of an amateur radio station.
ADVICE: This project is under development. The parameters, ICD and the behaviour is still not stable and subject to change.
- OPUS (default)
- PCM (variable samplerate and 8/12/16/24 bit depth)
- MQTT
- P2P protocol (UDP/TCP/ZEROMQ) will be added later
RemoteAudio has been tested on the following platforms:
- AMD64
- i386
- ARMv6
- ARMv8
and the following operating Systems:
- Linux (Ubuntu, Raspian)
- MacOS (Sierra)
You can download compiled binaries for MacOS, Linux (ARM/AMD64) from the releases page.
- Make sure you have the latest Go version installed
- Download and install the latest version of the Protocol buffers compiler
- Install ````pkg-config
,libsamplerate``` and ```libopus```
$ sudo apt install pkg-config libsamplerate0 libsamplerate0-dev libopusfile-dev libopus-dev libportaudio2 portaudio19-dev
- Install the gogo protocol buffers plugin
$ go get github.com/gogo/protobuf/protoc-gen-gofast
- Download and install rice command line tool
$ go get github.com/GeertJohan/go.rice/rice
- Download the remoteAudio sources and the packages it depends on
$ go get -d github.com/dh1tw/remoteAudio
as an alternative you can build the protocol buffers compiler also from
source. This repository contains a build script install-protobuf.sh
- Build remoteAudio
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/dh1tw/remoteAudio
$ make build
- Install remoteAudio on your Systems
$ make install
In order to operate remoteAudio you need to either run your own MQTT Broker
(Mosquitto is a good choice) or connect to a public broker, like
iot.eclipse.org or test.mosquitto.org. The load of these brokers
and their ping to your place obviously will influence the latency. These public
brokers are good for inital tests, however they are sometimes overloaded.
$ remoteAudio server mqtt
$ remoteAudio client mqtt
If you are not sure about the name of your audio devices and their parameters, you can easily list that information:
$ remoteAudio enumerate
Both, the server and the client provide extensive configuration possibilities,
either through a configuration file (TOML|YAML|JSON), typically located in
your home directory /home/your_user/.remoteAudio.toml. or through pflags.
An example configuration file is included in the repository.
All parameters can be set through pflags. The following example shows the
options for $ remoteAudio server mqtt --help:
MQTT Server for bi-directional audio streaming
Usage:
remoteAudio server mqtt [flags]
Flags:
-p, --broker-port int Broker Port (default 1883)
-u, --broker-url string Broker URL (default "localhost")
-Y, --radio string Radio ID (default "myradio")
-X, --station string Your station callsign (default "mystation")
Global Flags:
-f, --audio-frame-length int Amount of audio samples in one frame (default 480)
-C, --codec string Audio codec (default "opus")
--config string config file (default is $HOME/.remoteAudio.yaml)
--input-device-channels string Input Channels (default "mono")
--input-device-latency duration Input latency (default 5ms)
-i, --input-device-name string Input device (default "default")
--input-device-samplingrate float Input device sampling rate (default 48000)
--opus-application string profile for opus encoder (default "restricted_lowdelay")
--opus-bitrate int Bitrate (bits/sec) generated by the opus encoder (default 32000)
--opus-complexity int Computational complexity of opus encoder (default 9)
--opus-max-bandwidth string maximum bandwidth of opus encoder (default "wideband")
--output-device-channels string Output Channels (default "stereo")
--output-device-latency duration Output latency (default 5ms)
-o, --output-device-name string Output device (default "default")
--output-device-samplingrate float Output device sampling rate (default 48000)
--pcm-bitdepth int pcm audio bit depth (8, 12, 16, 24 bit) (default 16)
--pcm-channels string pcm audio Channels (default "stereo")
--pcm-resampling-quality int pcm resampling quality (default 1)
--pcm-samplingrate float pcm sampling rate (default 16000)
-R, --rx-buffer-length int Buffer length (in frames) for incoming Audio packets (default 10)
-U, --user-id string Your User ID - required for TX
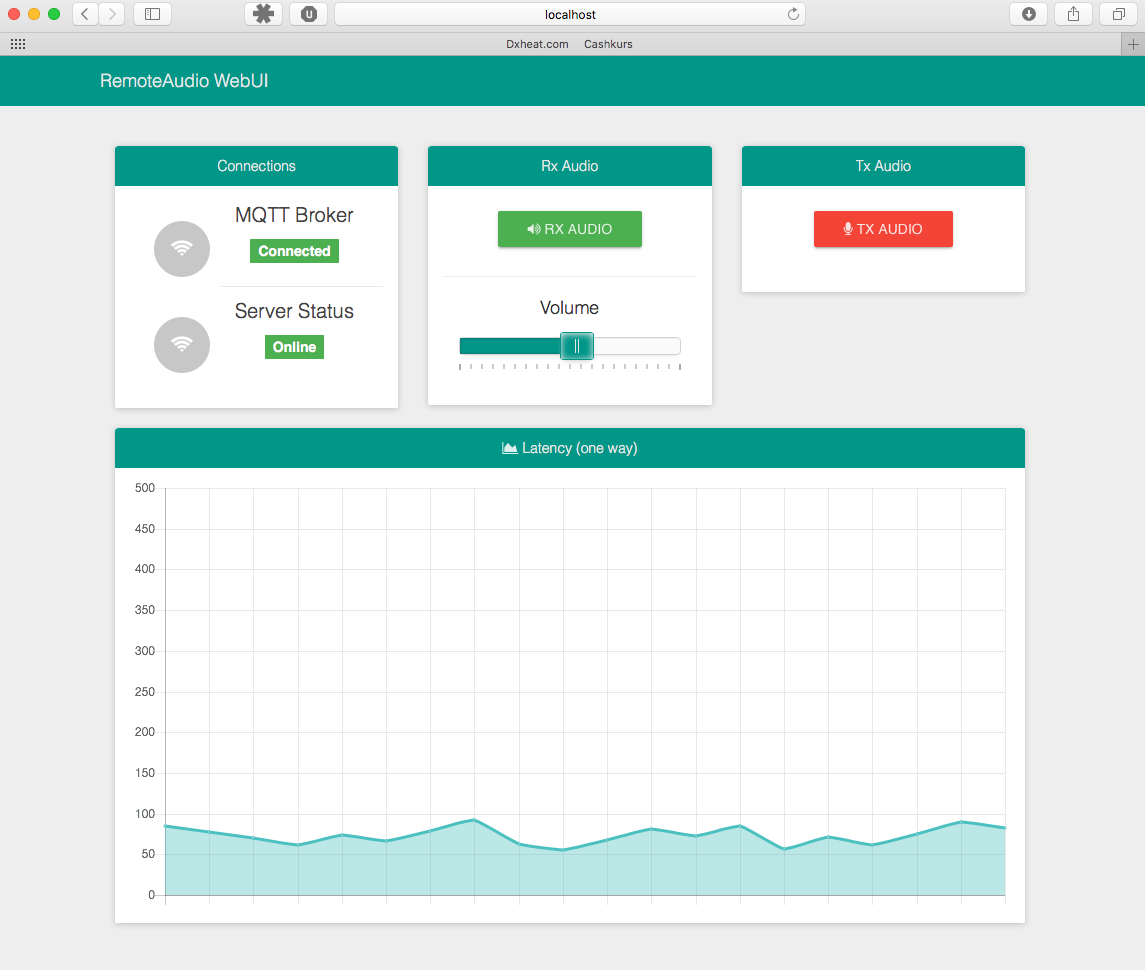
The Client provides a minimal Web Interface for basic control of the client and server side audio streams. Open a Webbrowser at: http://localhost:6060 to access the WebUI.
In any case, the client and server will accept almost any kind of audio frames without any configuration. Internally remoteAudio picks the right codec, resamples and adjust to the local audio output device.
However if the buffer size does not correspond to the internal buffer size, the stream has to be restarted which might result in a small delay.
remoteAudio does it's best to check if your sound hardware is compatible with the parameters you have set. However it's not entirely possible to check all the Settings.
Inexpensive (USB) Soundcards usually operate at 48kHz. They play the audio in Stereo and Record the Audio in MONO.
Feel free to open an issue if you encounter problems.