Build your Slack apps by reacting to messages, emojis, files, and many more types of interesting events in the Events API. This package will help you start with sensible and secure defaults.
The adapter gives you a simple and highly configurable Node-style EventEmitter to attach functions to handle events.
$ npm install --save @slack/events-api
Get started by creating a Slack App if you haven't already. On the Basic Information page, in the section for App Credentials, note the Signing Secret. You will need it to initialize the adapter.
⚠️ As ofv2.0.0, the Events API adapter no longer accepts legacy verification tokens. You must pass a signing secret to verify requests from Slack.
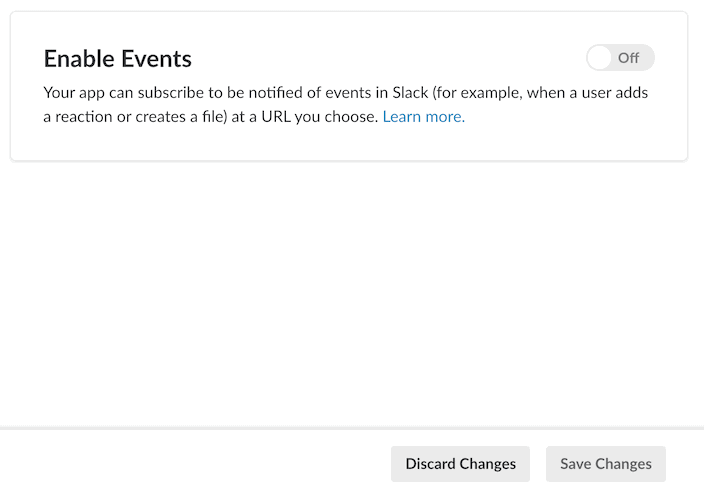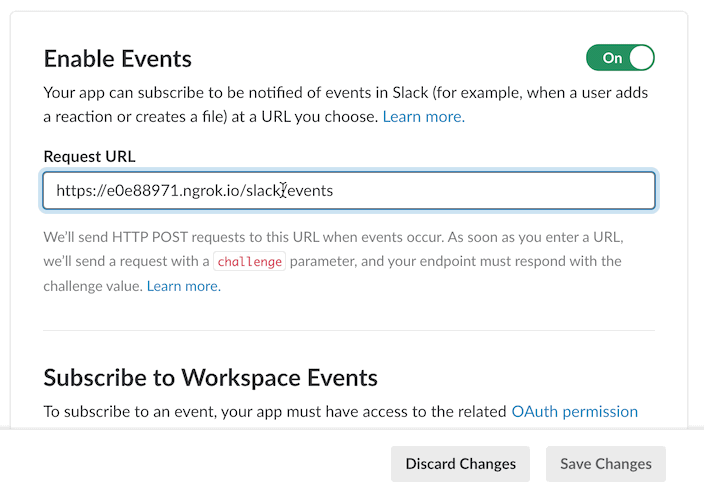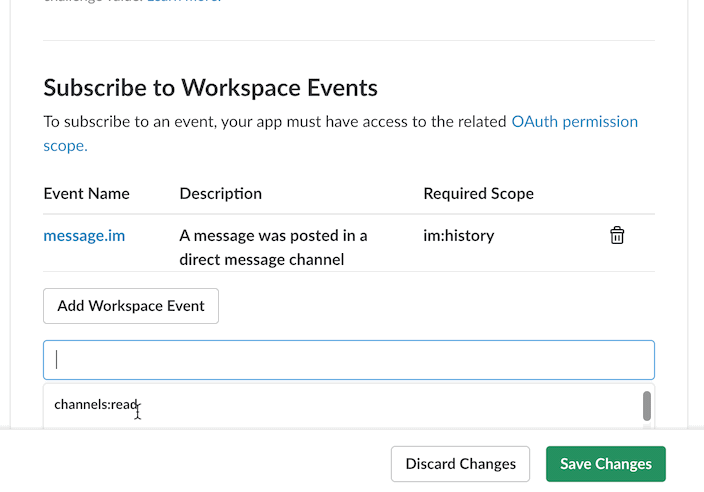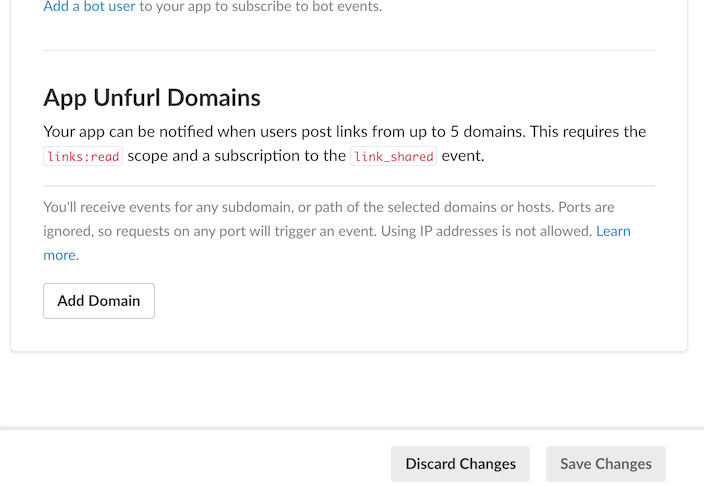
Select the Event Subscriptions feature, and enable it. Input a Request URL.
What's a request URL? How can I get one for development?
Slack will send requests to your app server each time an event from a subscription is triggered. In order to reach your server, you have to tell Slack where your app is listening for those requests. This location is the request URL.
If you're just getting started with development, you may not have a publicly accessible URL for your app. We recommend using a development proxy, such as ngrok or localtunnel, to generate a URL that can forward requests to your local machine. Once you've installed the development proxy of your choice, run it to begin forwarding requests to a specific port (for example, 3000).
ngrok:
ngrok http 3000
localtunnel:
lt --port 3000
The output should show you a newly generated URL that you can use (ngrok will actually show you two
and we recommend the one that begins with "https"). Let's call this the base URL (for example,
https://e0e88971.ngrok.io)
To create the request URL, we add the path where our app listens for events onto the end of
the base URL. If you are using the built-in HTTP server it is set to /slack/events. In this
example the request URL would be https://e0e88971.ngrok.io/slack/events. If you are using the
Express middlware, you can set whichever path you like, just remember to make the path you mount the
middleware into the application the same as the one you configure in Slack.
I'm getting an error about the `challenge` parameter. Help?
Before you can save the subscription, your app will need to respond to a challenge at your chosen request URL. I know what you're thinking: 🤔 How can I respond if I haven't written my app yet? This package comes with a command line tool which starts a server that can properly respond to the challenge. If you're using the development proxy as described above, you can run the tool from inside your project directory (after this package has been installed) with the following command:
./node_modules/.bin/slack-verify --secret <signing_secret> [--path=/slack/events] [--port=3000]You'll need to substitute your own signing secret for <signing_secret>. The path and port values
are optional. If your request URL includes a different path, you should specify it with
--path=/my/path/here (no brackets). Similarly, if your development proxy is forwarding requests to
a different port, you should specify it with --port=8888 (no brackets). If you're using the
defaults, you can ignore everything after <signing_secret>. You should only use the command line
tool in development. If your app is up and running, the adapter will automatically respond to
challenges.
You might need to click "Retry" in the Request URL input to ask Slack to send the challenge again. Once the request URL is verified, you can terminate the two processes (command line tool and development server) with Ctrl+C.
Add each event type your app requires. In the tables below, you may add Workspace events and Bot events. Once you've selected all the event types, be sure to Save Changes.
Lastly, if you've added event types that require scopes your app did not previously have, you'll need to reinstall the app into the workspace(s) from where you'd like Slack to send your app new events. To quickly install the app to your Development Workspace, visit the Install App page.
The easiest way to start using the Events API is by using the built-in HTTP server.
// Initialize using signing secret from environment variables
const { createEventAdapter } = require('@slack/events-api');
const slackEvents = createEventAdapter(process.env.SLACK_SIGNING_SECRET);
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000;
// Attach listeners to events by Slack Event "type". See: https://api.slack.com/events/message.im
slackEvents.on('message', (event) => {
console.log(`Received a message event: user ${event.user} in channel ${event.channel} says ${event.text}`);
});
// Handle errors (see `errorCodes` export)
slackEvents.on('error', console.error);
// Start a basic HTTP server
slackEvents.start(port).then(() => {
console.log(`server listening on port ${port}`);
});NOTE: To use the example above, you need to add a Workspace Event such as message.im in the Event
Subscriptions section of your Slack App configuration settings.
For usage within an existing Express application, you can route requests to the adapter's express
middleware by calling the expressMiddleware() method;
const http = require('http');
// Initialize using signing secret from environment variables
const { createEventAdapter } = require('@slack/events-api');
const slackEvents = createEventAdapter(process.env.SLACK_SIGNING_SECRET);
const port = process.env.PORT || 3000;
// Initialize an Express application
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
// Mount the event handler on a route
// NOTE: you must mount to a path that matches the Request URL that was configured earlier
app.use('/slack/events', slackEvents.expressMiddleware());
// Attach listeners to events by Slack Event "type". See: https://api.slack.com/events/message.im
slackEvents.on('message', (event)=> {
console.log(`Received a message event: user ${event.user} in channel ${event.channel} says ${event.text}`);
});
// Handle errors (see `errorCodes` export)
slackEvents.on('error', console.error);
// Start the express application
http.createServer(app).listen(port, () => {
console.log(`server listening on port ${port}`);
});
⚠️ As ofv2.0.0, the Events API adapter parses raw request bodies while performing request signing verification. This means apps no longer need to usebody-parsermiddleware to parse JSON-encoded requests.
NOTE: To use the example above, you need to add a Team Event such as message.im in the Event
Subscriptions section of your Slack App configuration settings.
- Greet And React - A ready to run sample app that listens for messages and emoji reactions, and responds to them. It is built on top of the Express web framework. It also implements OAuth to demonstate how an app can handle installation to additional workspaces and be structured to handle events from multiple workspaces.
To learn more, see the reference documentation.
Need help? Join the Bot Developer Hangout team and talk to us in #slack-api.
You can also create an Issue right here on GitHub.