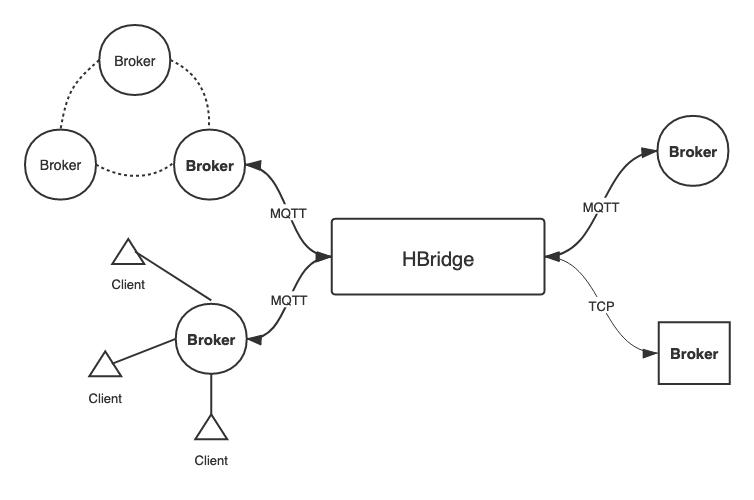
HBridge is a MQTT bridge for forwarding messages of certain topics from one broker to another one, written in Haskell.
It is under development and is really simple now. Everything including structure can vary at any time.
HBridge supports two types of connection:
-
MQTT connection: MQTT connection is the most-used type of connection for performing inter-broker MQTT message forwarding. It supports standard MQTT publishing messages.
-
Bare TCP connection: Although MQTT is (mostly) based on TCP connection, the bridge also supports bare TCP connection. For convenience, the one who connects to the bridge by TCP is also called "broker" no matter what it does. Messages from bare TCP connections can only be forwarded to other TCP ones. It supports following types of message:
- A simple type of message
PlainMsgcontaining only a payload field in plain text and a topic. It is mostly used for testing purposes. - Several types of controll message, for controlling the internal state of the bridge.
- A simple type of message
Both types of connection supports multi-broker work mode. It means that a bridge can connect to multiple brokers at the same time, and these connections can be different types. By proper configuration which will be talked later, a message from a broker can be forwarded to many other brokers.
The concept of the bridge is shown below:
HBridge also provides some extra features:
- Message processing: It means that HBridge can do some processing on the message. It currently provides following functions:
saveMsg: Save all messages to disk.modifyTopic: Modify matched topic to a new one.modifyField: Modify certain field of payload in a message to a new value (if the field exists).
To build from source, haskell build tool stack is required. Type
$ stack build
There is a very simple test program in test/Spec.hs. To run the test with default configuration, it requires several MQTT brokers at running status. We recommend EMQ X broker:
$ docker run -d --name emqx -p 1883:1883 -p 8083:8083 -p 8883:8883 -p 8084:8084 -p 18083:18083 emqx/emqx
$ docker run -d --name emqx -p 1884:1883 -p 8084:8083 -p 8884:8883 -p 8085:8084 -p 18084:18083 emqx/emqx
$ stack test
(in another console)
$ stack exec -- HBridge-exe etc/config.json +RTS -T
In this example, there exists two MQTT brokers B1 and B2 and a TCP one B3 that connects to the bridge. The bridge forwards messages from B1 to B2 and vice versa. B3 sends plain messages and a request for listing processing functions in bridge to the bridge periodically.
The running status can be found at localhost:22333.
CAUTION: This part is currently at very early stage and is quite difficult to use. It will be improved soon.
The configuration file is at etc/config.json. It contains the following fields:
logFile: Log file path.logLevel: Log level, it can be one ofDEBUG,INFO,WARNINGandERROR. Logs whose level is lower than it will not be recorded.logToStdErr: It decides whether to log to console. It can be one oftrueandfalse.brokers: A list of configurations of all brokers to connect to. It will be discussed later.
The brokers field in configuration is a list of configurations of all brokers. Each of it contains:
brokerName: Name of the broker.brokerURI: URI of the broker to connect to. Due to some reasons, it is shown in a more complex form.connectType: Type of the connection. It can be one ofMQTTConnectionandTCPConnection.brokerMount: Mountpoint of the broker. It will be added to the topic of messages it forwards.brokerFwds: Topics this broker forwards. It is a list of strings (topics).brokerSubs: Topics this broker subscribes. It is a list of strings (topics).
A recommended way to write a configuration currently is to write several lines of code in test/Spec.hs. Then run
$ stack repl
...
*Main Environment Extra Types> :l test/Spec.hs
*Main> writeConfig
The configuration file will be written at etc/config.json.
To use message processing features, there are two ways but both are not easy to use currently:
- Hard code the functions in
newEnv1function insrc/Environment.hs. And there are some ones in it by default. - Send insertion request to the bridge by TCP connection. But it is required that the request is correctly encoded to plain text. You can refer to
runTCPinapp/Main.hsandMessagedefinition insrc/Types.hs.
This will be improved soon.