Table of Contents
This demo shows users how to monitor Kafka streaming ETL deployments using Confluent Control Center. All the components in the Confluent platform have security enabled end-to-end. Follow along with the playbook in this README and watch the video tutorials.
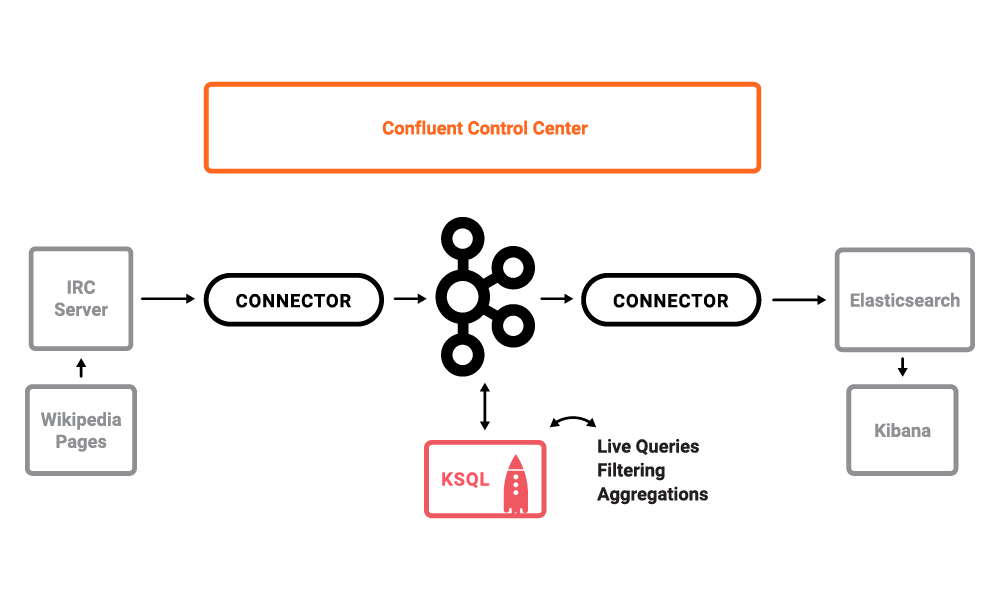
The use case is a stream processing on live edits to real Wikipedia pages. Wikimedia Foundation has IRC channels that publish edits happening to real wiki pages (e.g. #en.wikipedia, #en.wiktionary) in real time. Using Kafka Connect, a Kafka source connector kafka-connect-irc streams raw messages from these IRC channels, and a custom Kafka Connect transform kafka-connect-transform-wikiedit transforms these messages and then the messages are written to a Kafka cluster. This demo uses KSQL for data enrichment, or you can optionally develop and run your own Kafka Streams application. Then a Kafka sink connector kafka-connect-elasticsearch streams the data out of Kafka, applying another custom Kafka Connect transform called NullFilter. The data is materialized into Elasticsearch for analysis by Kibana.
Note: this is a Docker environment and has all services running on one host. Do not use this demo in production. It is meant exclusively to easily demo the Confluent Platform. In production, Confluent Control Center should be deployed with a valid license and with its own dedicated metrics cluster, separate from the cluster with production traffic. Using a dedicated metrics cluster is more resilient because it continues to provide system health monitoring even if the production traffic cluster experiences issues.
This demo has been verified with:
- Docker version 17.06.1-ce
- Docker Compose version 1.14.0 with Docker Compose file format 2.1
- Java version 1.8.0_92
- MacOS 10.12
-
Download the repository with
git clone:$ git clone https://github.com/confluentinc/cp-demo -
In the advanced Docker preferences settings, increase the memory available to Docker to at least 8GB (default is 2GB).
-
From the
cp-demodirectory, generate certs used for security.$ (cd scripts/security && ./certs-create.sh) -
Start the demo. It will take about 2 minutes for all containers to start and for Confluent Control Center GUI to be ready.
$ docker-compose up -d
-
Verify the status of the Docker containers show
Upstate, except for thekafka-clientcontainer which is expected to haveExit 0state. If any containers are not up, verify in the advanced Docker preferences settings that the memory available to Docker is at least 8GB (default is 2GB).$ docker-compose ps Name Command State Ports ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ cpdemo_connect_1 /etc/confluent/docker/run Up 0.0.0.0:8083->8083/tcp, 9092/tcp cpdemo_control-center_1 /etc/confluent/docker/run Up 0.0.0.0:9021->9021/tcp cpdemo_elasticsearch_1 /bin/bash bin/es-docker Up 0.0.0.0:9200->9200/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9300->9300/tcp cpdemo_kafka-client_1 bash -c -a echo Waiting fo ... Exit 0 cpdemo_kafka1_1 /etc/confluent/docker/run Up 0.0.0.0:29091->29091/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9091->9091/tcp, 9092/tcp cpdemo_kafka2_1 /etc/confluent/docker/run Up 0.0.0.0:29092->29092/tcp, 0.0.0.0:9092->9092/tcp cpdemo_kibana_1 /bin/sh -c /usr/local/bin/ ... Up 0.0.0.0:5601->5601/tcp cpdemo_ksql-cli_1 perl -e while(1){ sleep 99 ... Up 0.0.0.0:9098->9098/tcp cpdemo_schemaregistry_1 /etc/confluent/docker/run Up 8081/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8082->8082/tcp cpdemo_zookeeper_1 /etc/confluent/docker/run Up 0.0.0.0:2181->2181/tcp, 2888/tcp, 3888/tcp -
Wait till Confluent Control Center is running fully. Verify it is ready when the logs show the following event:
$ docker-compose logs -f control-center | grep -e "Started NetworkTrafficServerConnector" control-center_1 | [2017-09-06 16:37:33,133] INFO Started NetworkTrafficServerConnector@26a529dc{HTTP/1.1}{0.0.0.0:9021} (org.eclipse.jetty.server.NetworkTrafficServerConnector)
-
Run the setup script which customizes the Kafka cluster, Kafka source and sink connectors, Elasticsearch, and Kibana dashboard.
$ ./scripts/setup.sh
-
Use Google Chrome to view the Confluent Control Center GUI at http://localhost:9021.
Click on the top right button that shows the current date, and change
Last 4 hourstoLast 30 minutes. -
View the data in the Kibana dashboard at http://localhost:5601/app/kibana#/dashboard/Wikipedia
-
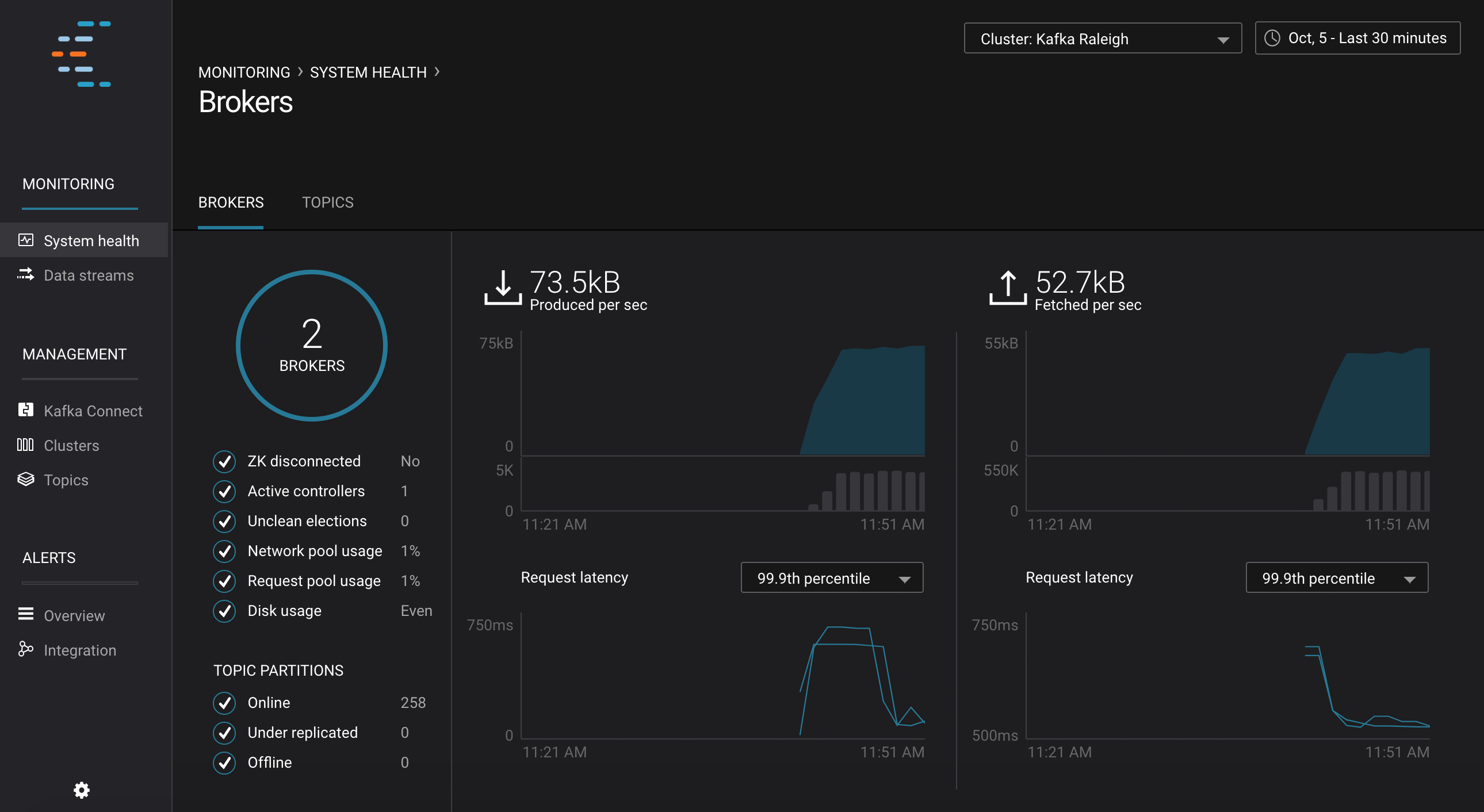
Monitoring --> System Health: Confluent Control Center landing page shows the overall system health of a given Kafka cluster. For capacity planning activities, view cluster utilization:
- CPU: look at network and thread pool usage, produce and fetch request latencies
- Network utilization: look at throughput per broker or per cluster
- Disk utilization: look at disk space used by all log segments, per broker
-
Management --> Kafka Connect: Confluent Control Center uses the Kafka Connect API to manage Kafka connectors.
-
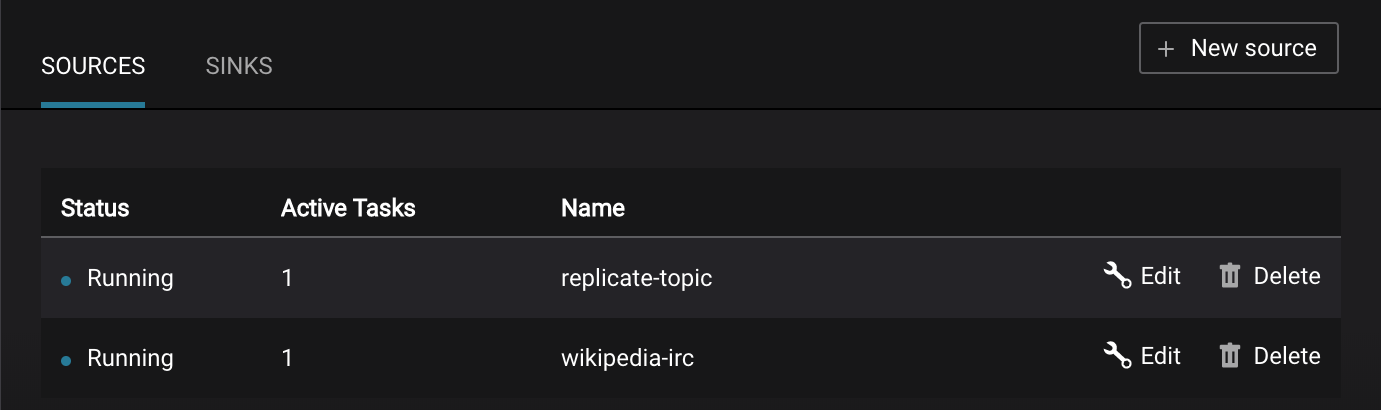
Kafka Connect Sources tab shows the connectors
wikipedia-ircandreplicate-topic. ClickEditto see the details of the connector configuration and custom transforms. -
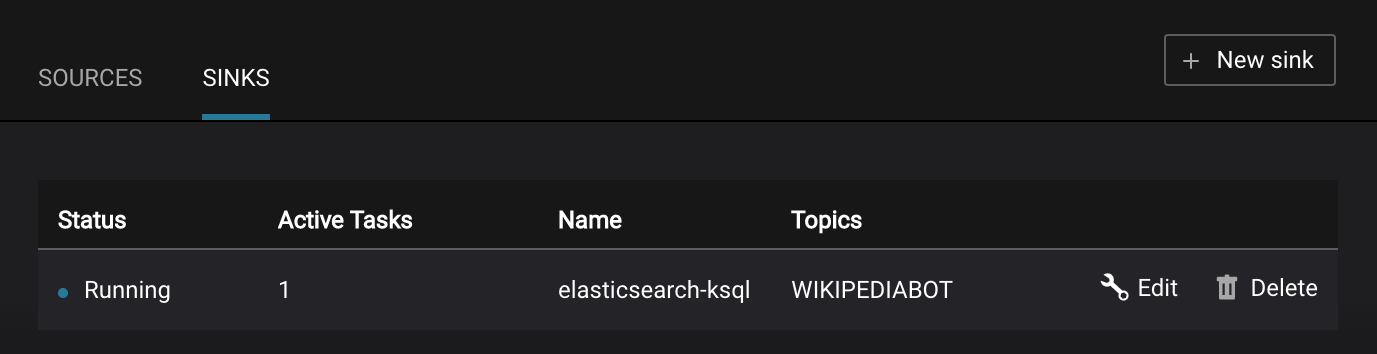
Kafka Connect Sinks tab shows the connector
elasticsearch-ksql. ClickEditto see the details of the connector configuration and custom transforms.
-
-
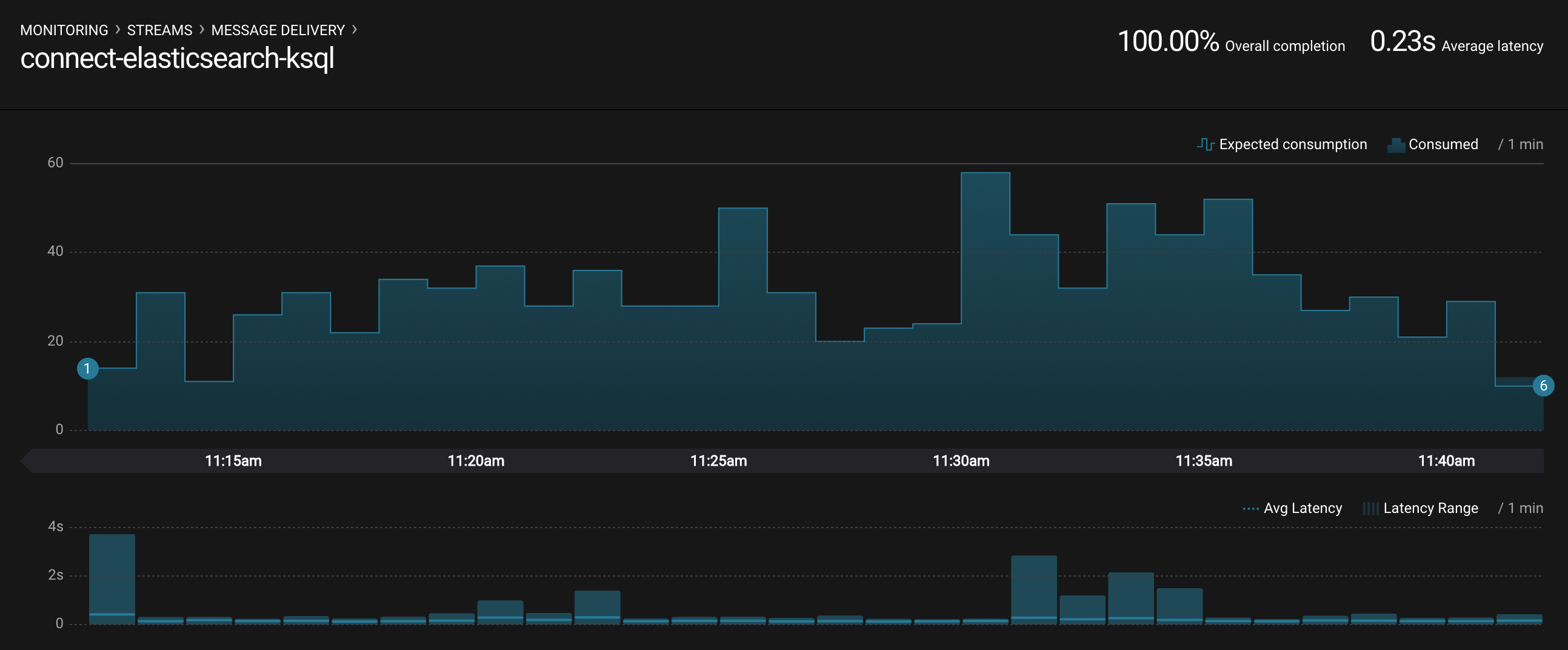
Monitoring --> Data Streams --> Message Delivery: hover over any chart to see number of messages and average latency within a minute time interval.
The Kafka Connect sink connectors have corresponding consumer groups
connect-elasticsearch-ksqlandconnect-replicator. These consumer groups will be in the consumer group statistics in the stream monitoring charts. -
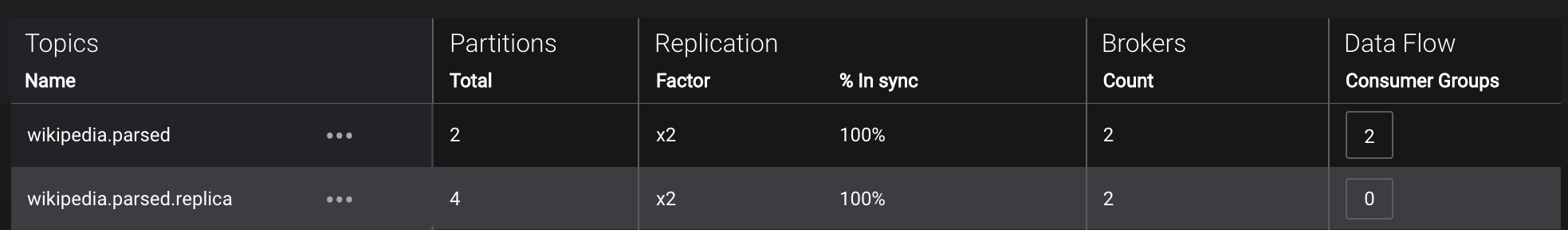
Management --> Topics --> Topic Information: For a given topic, click on the three dots
...next to the topic name and click onView details. View which brokers are leaders for which partitions and the number of consumer groups currently consuming from this topic. Click on the boxed consumer group count to select a consumer group for which to monitor its data streams and jump to it.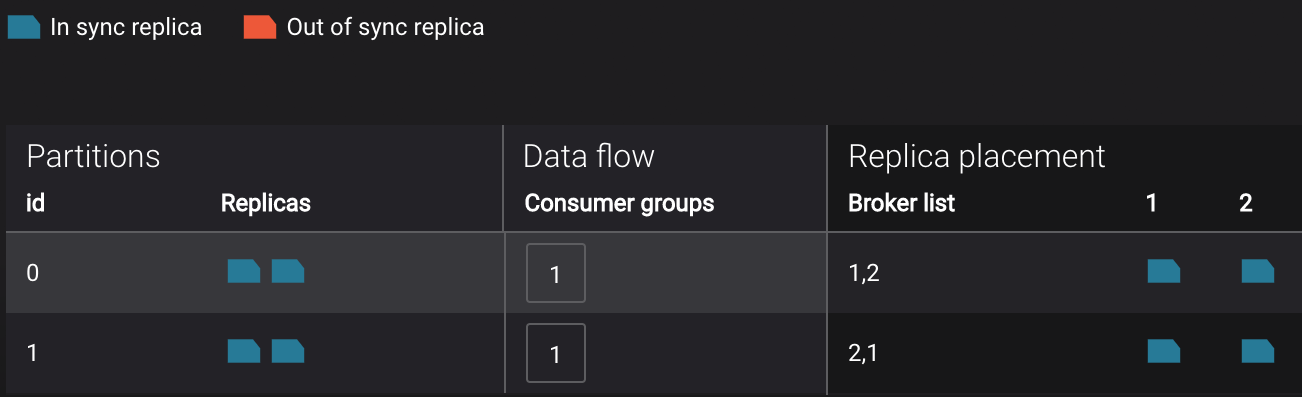
-
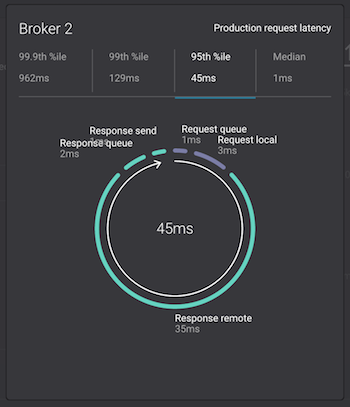
Monitoring --> System Health: to identify bottlenecks, you can see a breakdown of produce and fetch latencies through the entire request lifecycle. Click on the line graph in the
Request latencychart. The request latency values can be shown at the median, 95th, 99th, or 99.9th percentile. Depending on where the bottlenecks are, you can tune your brokers and clients appropriately.
In this demo, KSQL is configured with properties to connect to the secured Kafka cluster and is already running queries.
-
Run the KSQL CLI to get more information on the queries, streams, and tables.
$ docker-compose exec ksql-cli ksql-cli remote http://localhost:8080 ... ksql> SHOW QUERIES; ksql> DESCRIBE WIKIPEDIABOT; ksql> SELECT * FROM WIKIPEDIABOT LIMIT 3; ksql> DESCRIBE EN_WIKIPEDIA_GT_1; ksql> SELECT * FROM EN_WIKIPEDIA_GT_1 LIMIT 3;
By default when you run a
SELECTin KSQL it will return new data that is added. If you want to view data already existing in the topic run this first (once per session):SET 'auto.offset.reset' = 'earliest'; -
Monitoring --> Data Streams --> Message Delivery: KSQL queries are materialized in Confluent Control Center as consumer groups with names
ksql_query_. To correlate these consumer groups to the actual KSQL query, note the query id in the output of:$ docker-compose exec ksql-cli ksql-cli remote http://localhost:8080 --exec "show queries;"
-
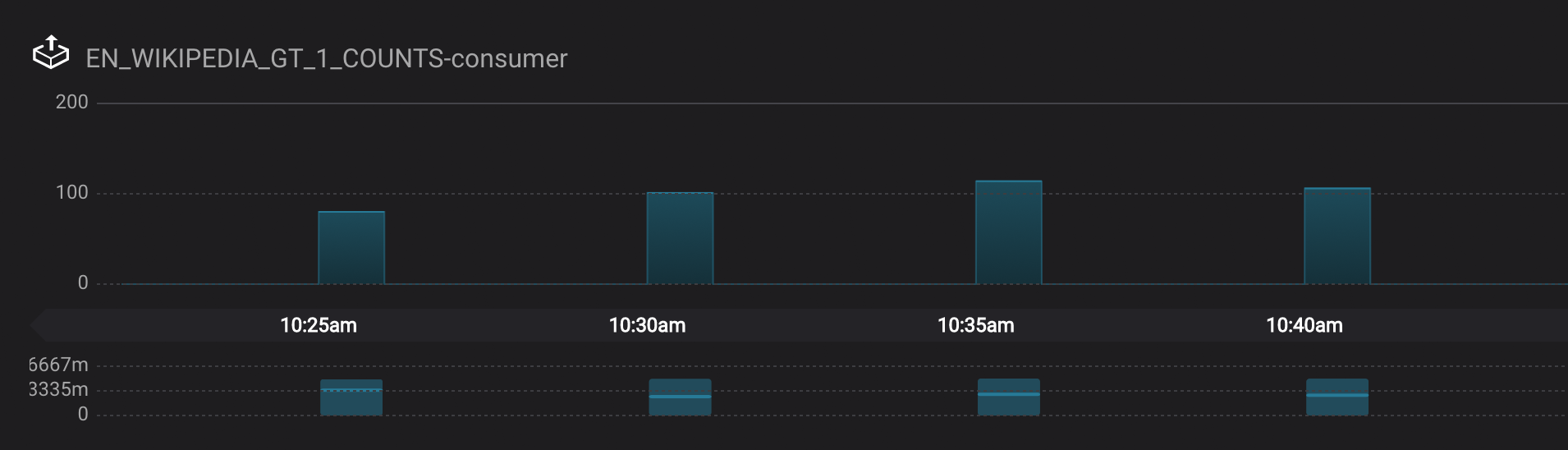
Monitoring --> Data Streams --> Message Delivery: graphs for consumer groups
EN_WIKIPEDIA_GT_1_COUNTS-consumerandksql_query_CSAS_EN_WIKIPEDIA_GT_1_COUNTSare displaying data at intervals instead of smoothly like the other consumer groups. This is because Confluent Control Center displays data based on message timestamps, and this particular stream of a data is a tumbling window with a window size of 5 minutes. Thus all its message timestamps are marked to the beginning of each 5-minute window and this is why the latency for these streams appears to be high. Kafka streaming tumbling windows are working as designed and Confluent Control Center is reporting them accurately.
Control Center shows which consumers in a consumer group are consuming from which partitions and on which brokers those partitions reside. Control Center updates as consumer rebalances occur in a consumer group.
-
Start consuming from topic
wikipedia.parsedwith a new consumer groupappwith one consumerconsumer_app_1. It will run in the background.$ ./scripts/app/start_consumer_app.sh 1
-
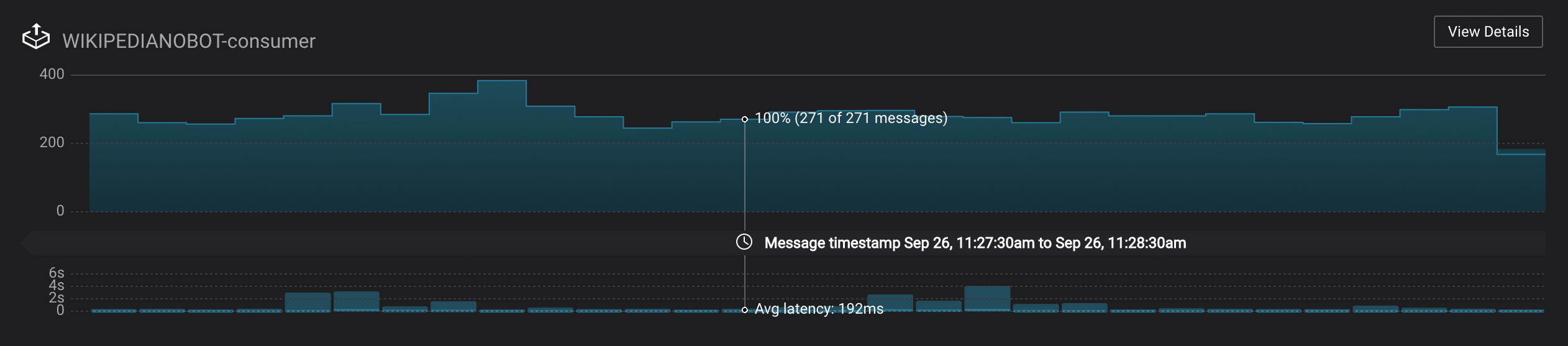
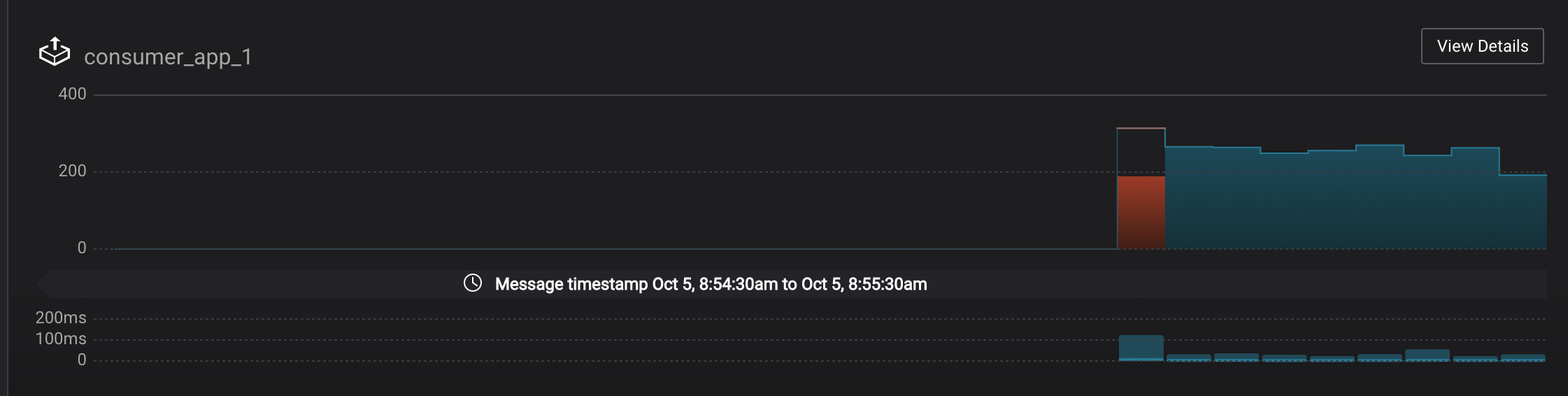
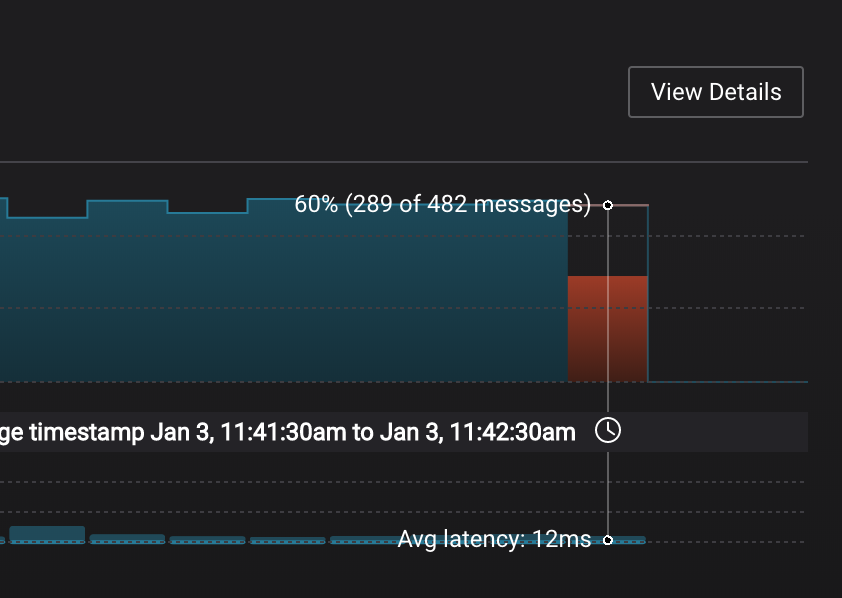
Let this consumer group run for 2 minutes until Control Center stream monitoring shows the consumer group
appwith steady consumption. Click on the boxView Detailsabove the bar graph to drill down into consumer group details. This consumer groupapphas a single consumerconsumer_app_1consuming all of the partitions in the topicwikipedia.parsed. The first bar may be red because the consumer started in the middle of a time window and did not receive all messages produced during that window. This does not mean messages were lost. -
Add a second consumer
consumer_app_2to the existing consumer groupapp.$ ./scripts/app/start_consumer_app.sh 2
-
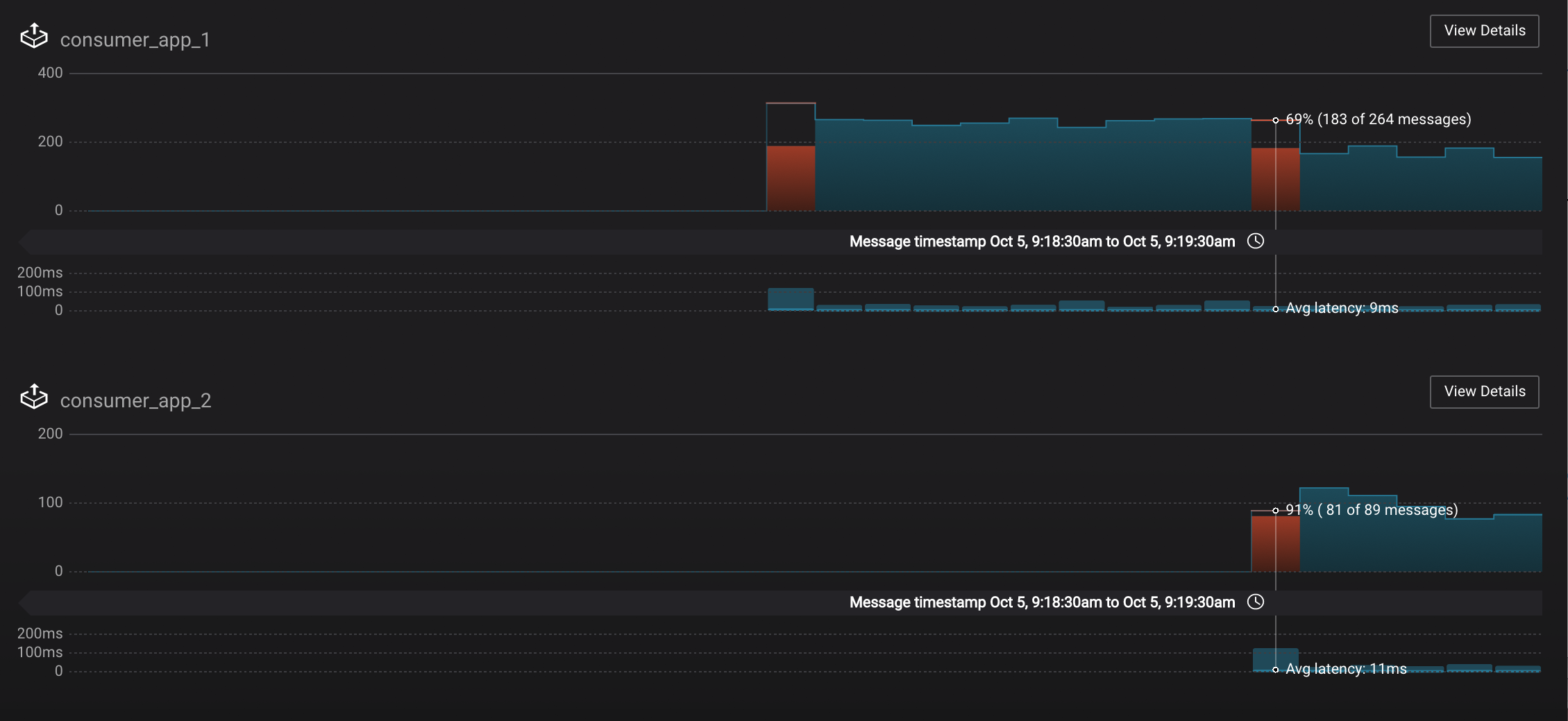
Let this consumer group run for 2 minutes until Control Center stream monitoring shows the consumer group
appwith steady consumption. Notice that the consumersconsumer_app_1andconsumer_app_2now share consumption of the partitions in the topicwikipedia.parsed. When the second consumer was added, that bar may be red for both consumers because a consumer rebalance occurred during that time window. This does not mean messages were lost, as you can confirm at the consumer group level.
Streams monitoring in Control Center can highlight consumers that are slow to keep up with the producers. This is critial to monitor for real-time applications where consumers should consume produced messages with as low latency as possible. To simulate a slow consumer, we will use Kafka's quota feature to rate-limit consumption from the broker side, for just one of two consumers in a consumer group.
-
Click on
Data streams, andView Detailsfor the consumer groupapp. Click on the left-hand blue circle on the consumption line to verify there are two consumersconsumer_app_1andconsumer_app_2, that were created in an earlier section. If these two consumers are not running, start them as described in the section consumer rebalances.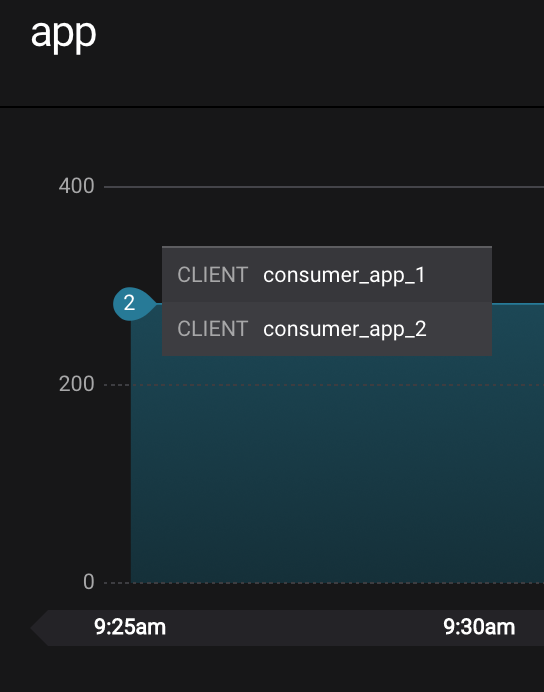
-
Let this consumer group run for 2 minutes until Control Center stream monitoring shows the consumer group
appwith steady consumption. -
Add a consumption quota for one of the consumers in the consumer group
app.$ ./scripts/app/throttle_consumer.sh 1 add
Note: you are running a Docker demo environment with all services running on one host, which you would never do in production. Depending on your system resource availability, sometimes applying the quota may stall the consumer (KAFKA-5871), thus you may need to adjust the quota rate. See the
./scripts/app/throttle_consumer.shscript for syntax on modifying the quota rate.- If consumer group
appdoes not increase latency, decrease the quota rate - If consumer group
appseems to stall, increase the quota rate
- If consumer group
-
View the details of the consumer group
appagain,consumer_app_1now shows high latency, andconsumer_app_2shows normal latency. -
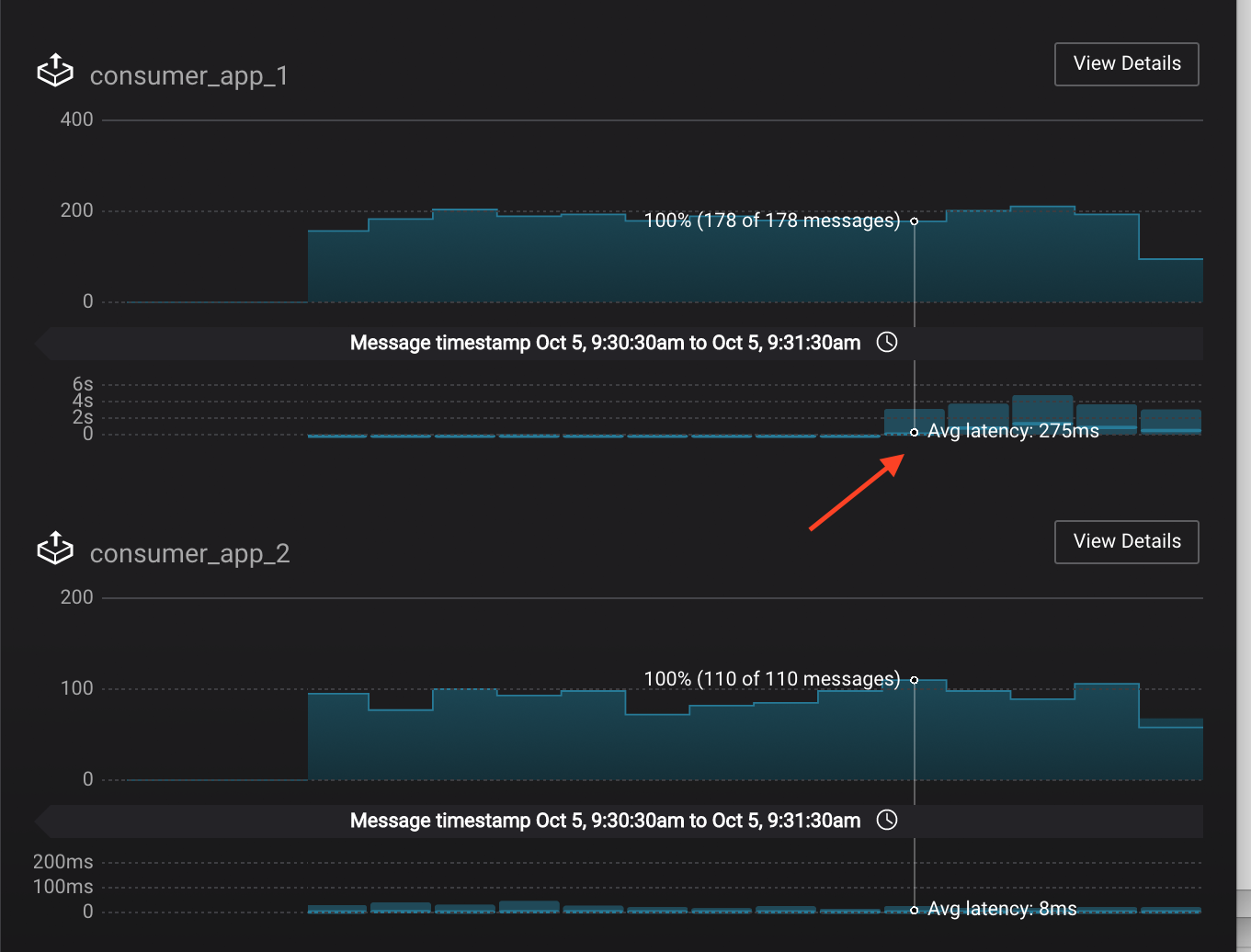
In the System Health dashboard, you see that the fetch request latency has likewise increased. This is the because the broker that has the partition that
consumer_app_1is consuming from is taking longer to service requests.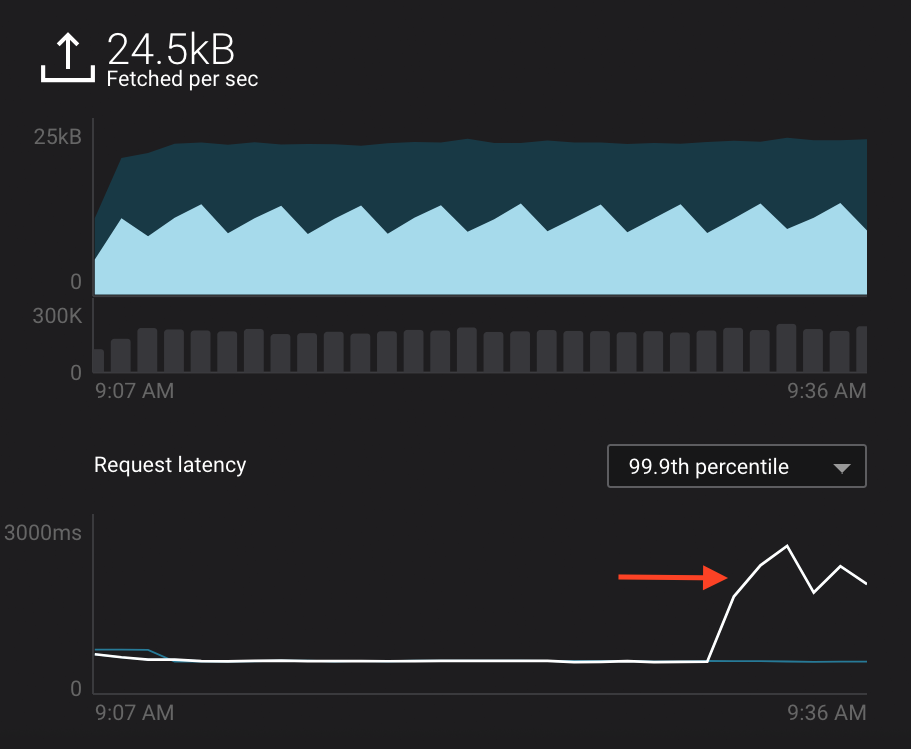
-
Click on the fetch request latency line graph to see a breakdown of produce and fetch latencies through the entire request lifecycle. The middle number does not necessarily equal the sum of the percentiles of individual segments because it is the total percentile latency.
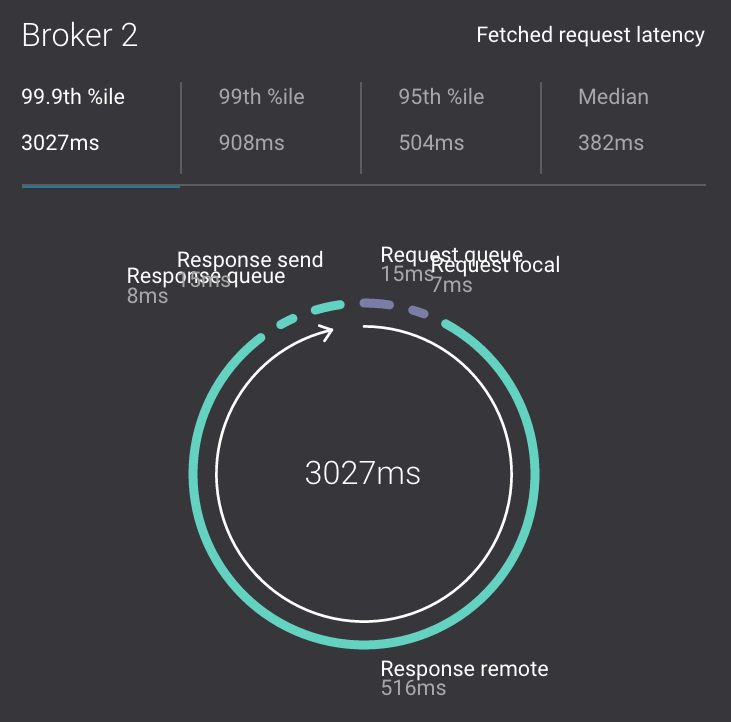
-
Remove the consumption quota for the consumer. Latency for
consumer_app_1recovers to steady state values.$ ./scripts/app/throttle_consumer.sh 1 delete
Streams monitoring in Control Center can highlight consumers that are over consuming some messages, which is an indication that consumers are processing a set of messages more than once. This may happen intentionally, for example an application with a software bug consumed and processed Kafka messages incorrectly, got a fix, and then reprocesses previous messages correctly. This may also happen unintentionally if an application crashes before committing processed messages. To simulate over consumption, we will use Kafka's consumer offset reset tool to set the offset of the consumer group app to an earlier offset, thereby forcing the consumer group to reconsume messages it has previously read.
-
Click on
Data streams, andView Detailsfor the consumer groupapp. Click on the blue circle on the consumption line on the left to verify there are two consumersconsumer_app_1andconsumer_app_2, that were created in an earlier section. If these two consumers are not running and were never started, start them as described in the section consumer rebalances.
-
Let this consumer group run for 2 minutes until Control Center stream monitoring shows the consumer group
appwith steady consumption. -
Stop the consumer group
appto stop consuming from topicwikipedia.parsed. Note that the command below stops the consumers gracefully withkill -15, so the consumers follow the shutdown sequence.$ ./scripts/app/stop_consumer_app_group_graceful.sh
-
Wait for 2 minutes to let messages continue to be written to the topics for a while, without being consumed by the consumer group
app. Notice the red bar which highlights that during the time window when the consumer group was stopped, there were some messages produced but not consumed. These messages are not missing, they are just not consumed because the consumer group stopped.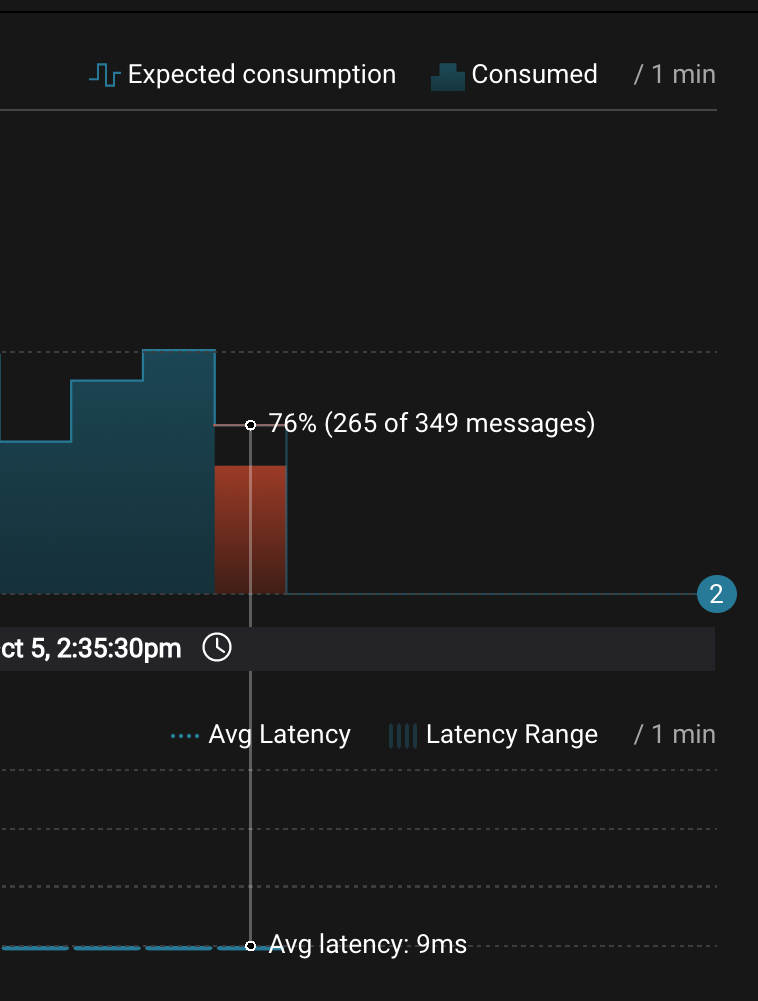
-
Reset the offset of the consumer group
appby shifting 200 offsets backwards. The offset reset tool must be run when the consumer is completely stopped. Offset values in output shown below will vary.$ docker-compose exec kafka1 kafka-consumer-groups --reset-offsets --group app --shift-by -200 --bootstrap-server kafka1:10091 --all-topics --execute TOPIC PARTITION NEW-OFFSET wikipedia.parsed 1 4071 wikipedia.parsed 0 7944 -
Restart consuming from topic
wikipedia.parsedwith the consumer groupappwith two consumers.$ ./scripts/app/start_consumer_app.sh 1 $ ./scripts/app/start_consumer_app.sh 2
-
Let this consumer group run for 2 minutes until Control Center stream monitoring shows the consumer group
appwith steady consumption. Notice several things:- Even though the consumer group
appwas not running for some of this time, all messages are shown as delivered. This is because all bars are time windows relative to produce timestamp. - For some time intervals, the the bars are red and consumption line is above expected consumption because some messages were consumed twice due to rewinding offsets.
- The latency peaks and then gradually decreases, because this is also relative to the produce timestamp.
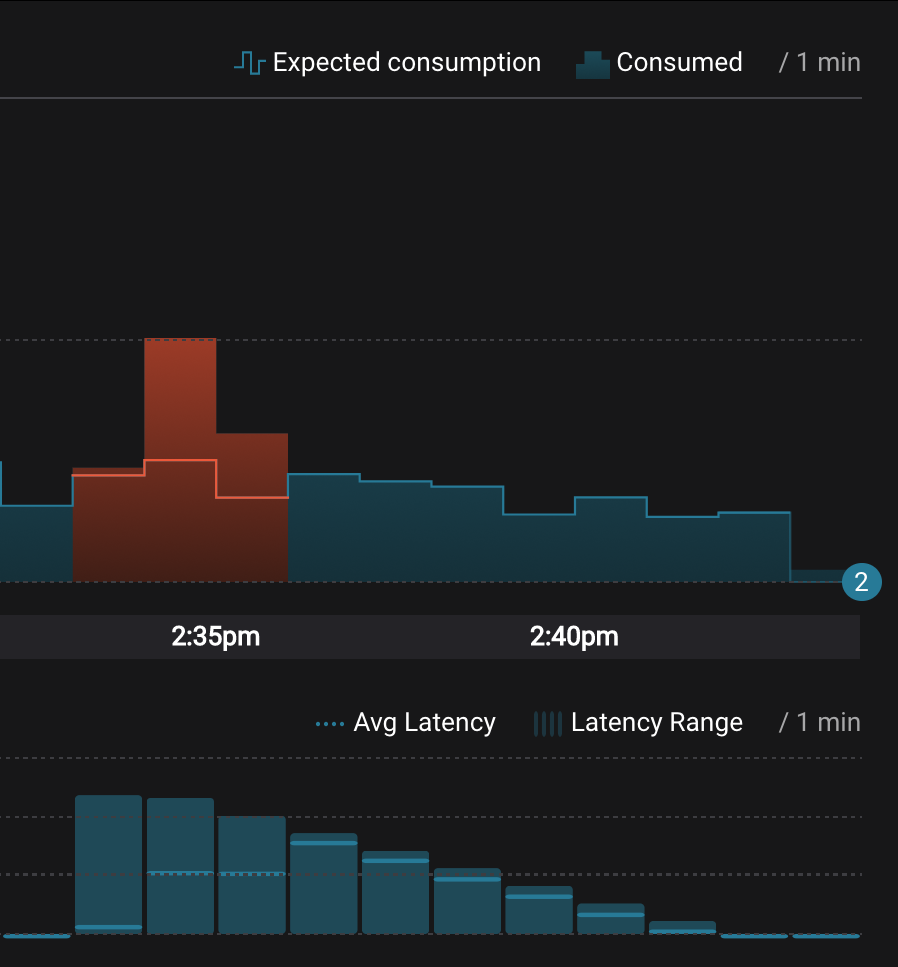
- Even though the consumer group
Streams monitoring in Control Center can highlight consumers that are under consuming some messages. This may happen intentionally when consumers stop and restart and operators change the consumer offsets to the latest offset. This avoids delay processing messages that were produced while the consumers were stopped, especially when they care about real-time. This may also happen unintentionally if a consumer is offline for longer than the log retention period, or if a producer is configured for acks=0 and a broker suddenly fails before having a chance to replicate data to other brokers. To simulate under consumption, we will use Kafka's consumer offset reset tool to set the offset of the consumer group app to the latest offset, thereby skipping messages that will never be read.
-
Click on Data Streams, and
View Detailsfor the consumer groupapp. Click on the blue circle on the consumption line on the left to verify there are two consumersconsumer_app_1andconsumer_app_2, that were created in an earlier section. If these two consumers are not running and were never started, start them as described in the section consumer rebalances.
-
Let this consumer group run for 2 minutes until Control Center stream monitoring shows the consumer group
appwith steady consumption. -
Stop the consumer group
appto stop consuming from topicwikipedia.parsed. Note that the command below stops the consumers ungracefully withkill -9, so the consumers did not follow the shutdown sequence.$ ./scripts/app/stop_consumer_app_group_ungraceful.sh
-
Wait for 2 minutes to let messages continue to be written to the topics for a while, without being consumed by the consumer group
app. Notice the red bar which highlights that during the time window when the consumer group was stopped, there were some messages produced but not consumed. These messages are not missing, they are just not consumed because the consumer group stopped.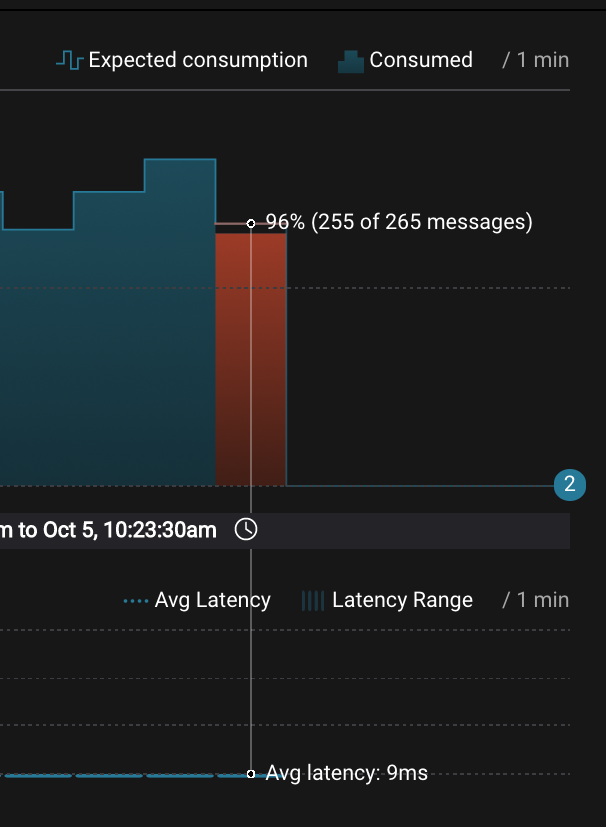
-
Wait for another few minutes and notice that the bar graph changes and there is a herringbone pattern to indicate that perhaps the consumer group stopped ungracefully.
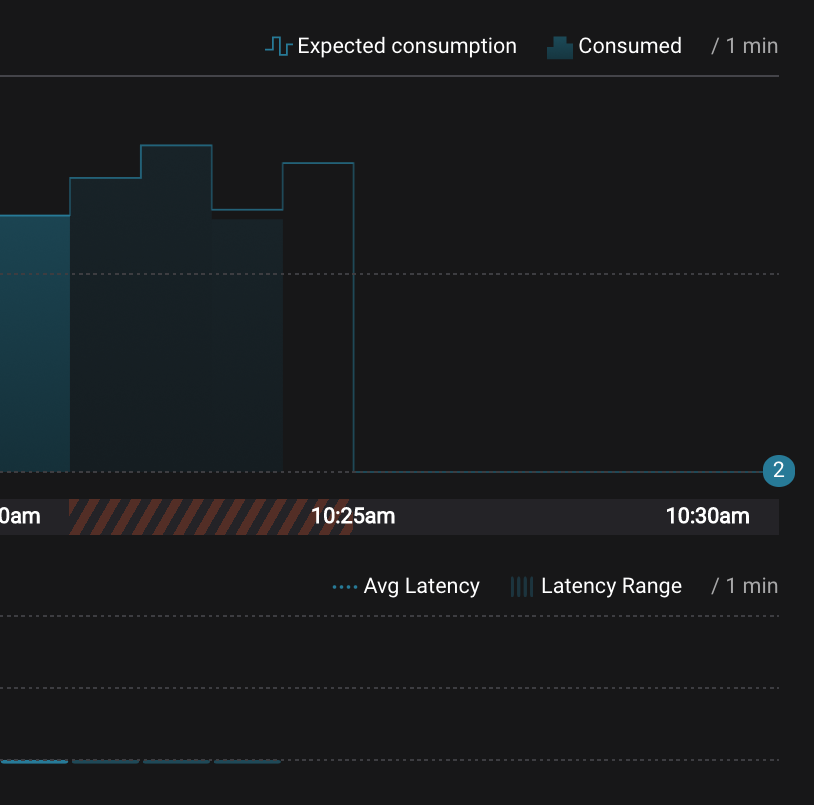
-
Reset the offset of the consumer group
appby setting it to latest offset. The offset reset tool must be run when the consumer is completely stopped. Offset values in output shown below will vary.$ docker-compose exec kafka1 kafka-consumer-groups --reset-offsets --group app --to-latest --bootstrap-server kafka1:10091 --all-topics --execute TOPIC PARTITION NEW-OFFSET wikipedia.parsed 1 8601 wikipedia.parsed 0 15135 -
Restart consuming from topic
wikipedia.parsedwith the consumer groupappwith two consumers.$ ./scripts/app/start_consumer_app.sh 1 $ ./scripts/app/start_consumer_app.sh 2
-
Let this consumer group run for 2 minutes until Control Center stream monitoring shows the consumer group
appwith steady consumption. Notice that during the time period that the consumer groupappwas not running, no produced messages are shown as delivered.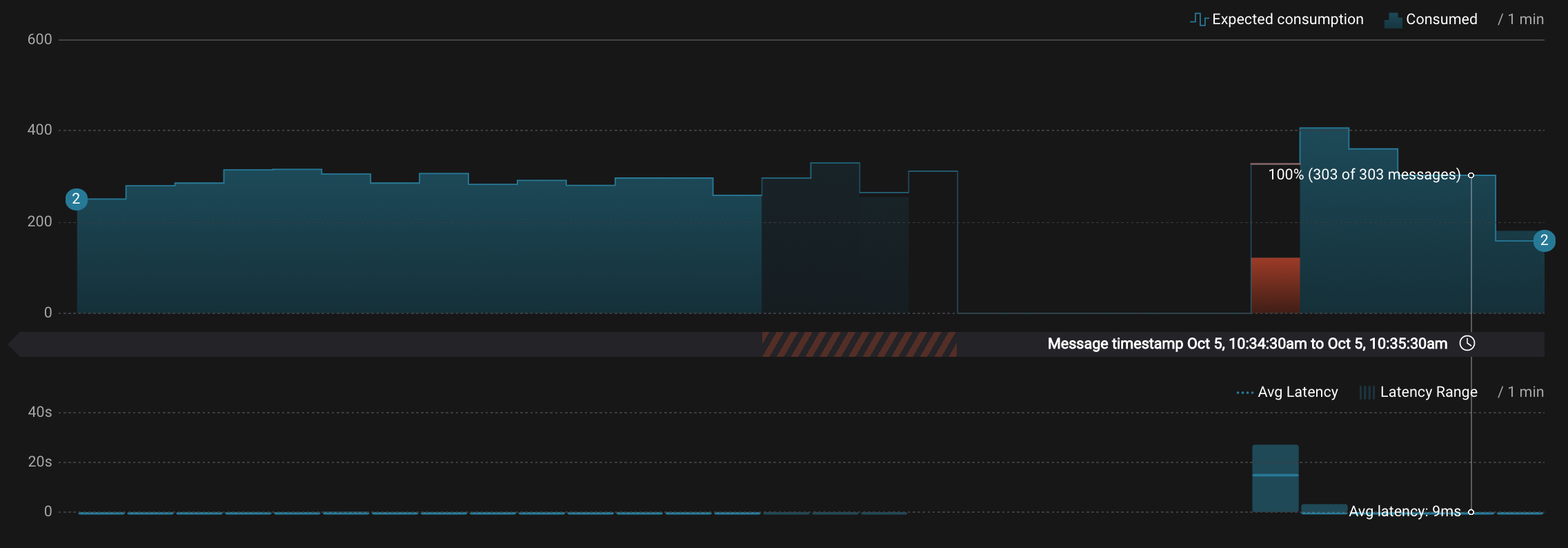
To simulate a failed broker, stop the Docker container running one of the two Kafka brokers.
-
Stop the Docker container running Kafka broker 2.
$ docker-compose stop kafka2
-
After a few minutes, observe the System Health shows the broker count has gone down from 2 to 1, and there are many under replicated partitions.
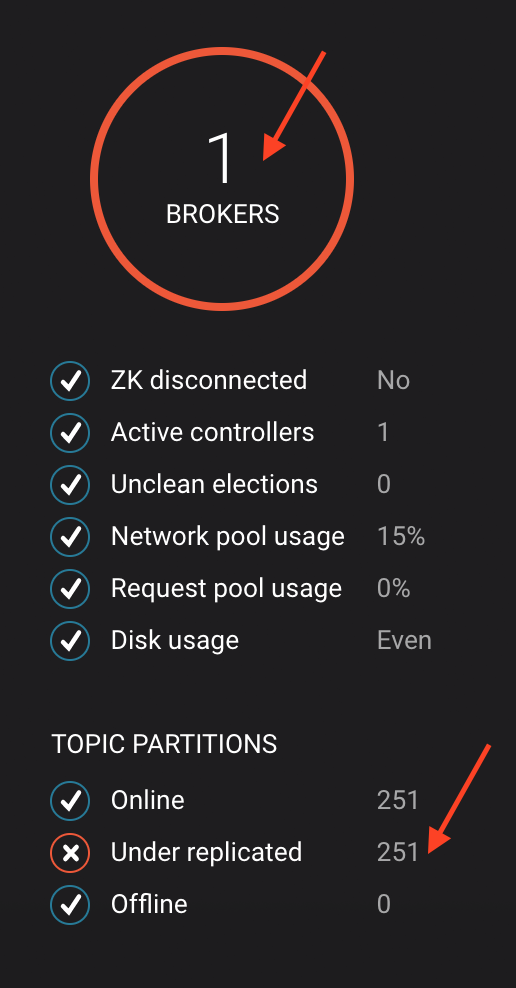
-
View topic details to see that there are out of sync replicas on broker 2.
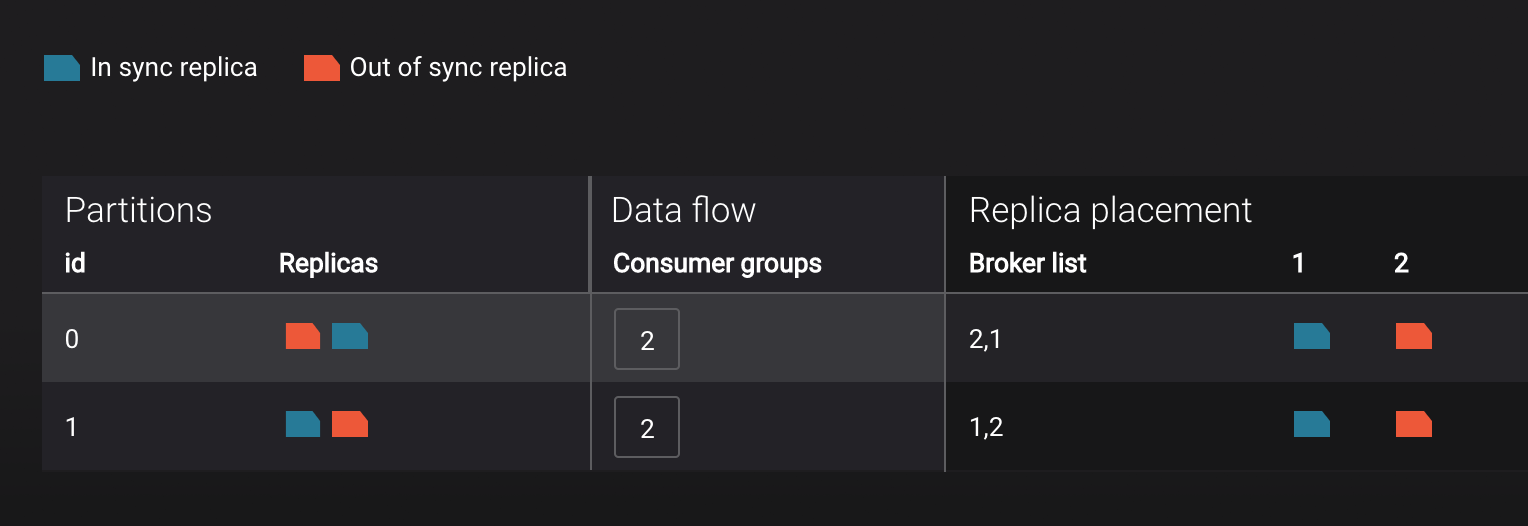
-
Restart the Docker container running Kafka broker 2.
$ docker-compose start kafka2
-
After about a minute, observe the System Health view in Confluent Control Center. The broker count has recovered to 2, and the topic partitions are back to reporting no under replicated partitions.
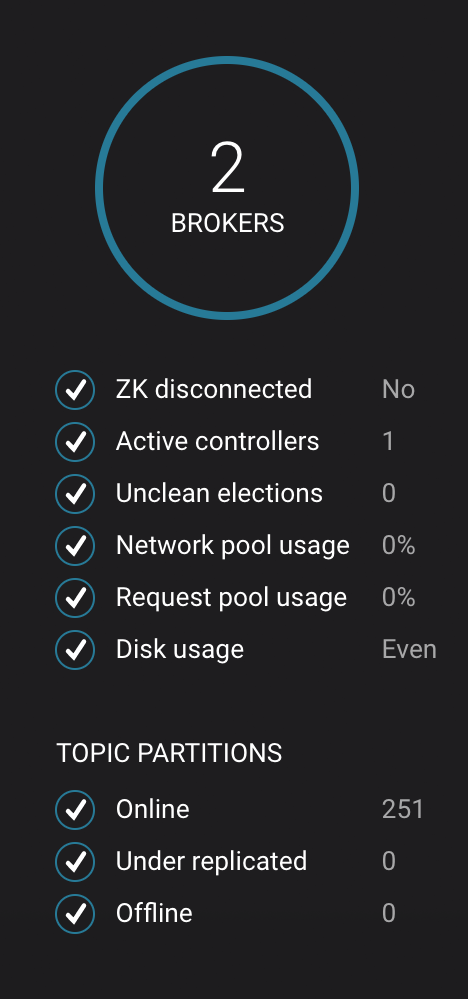
-
Click on the broker count
2inside the circle to view when the broker counts changed.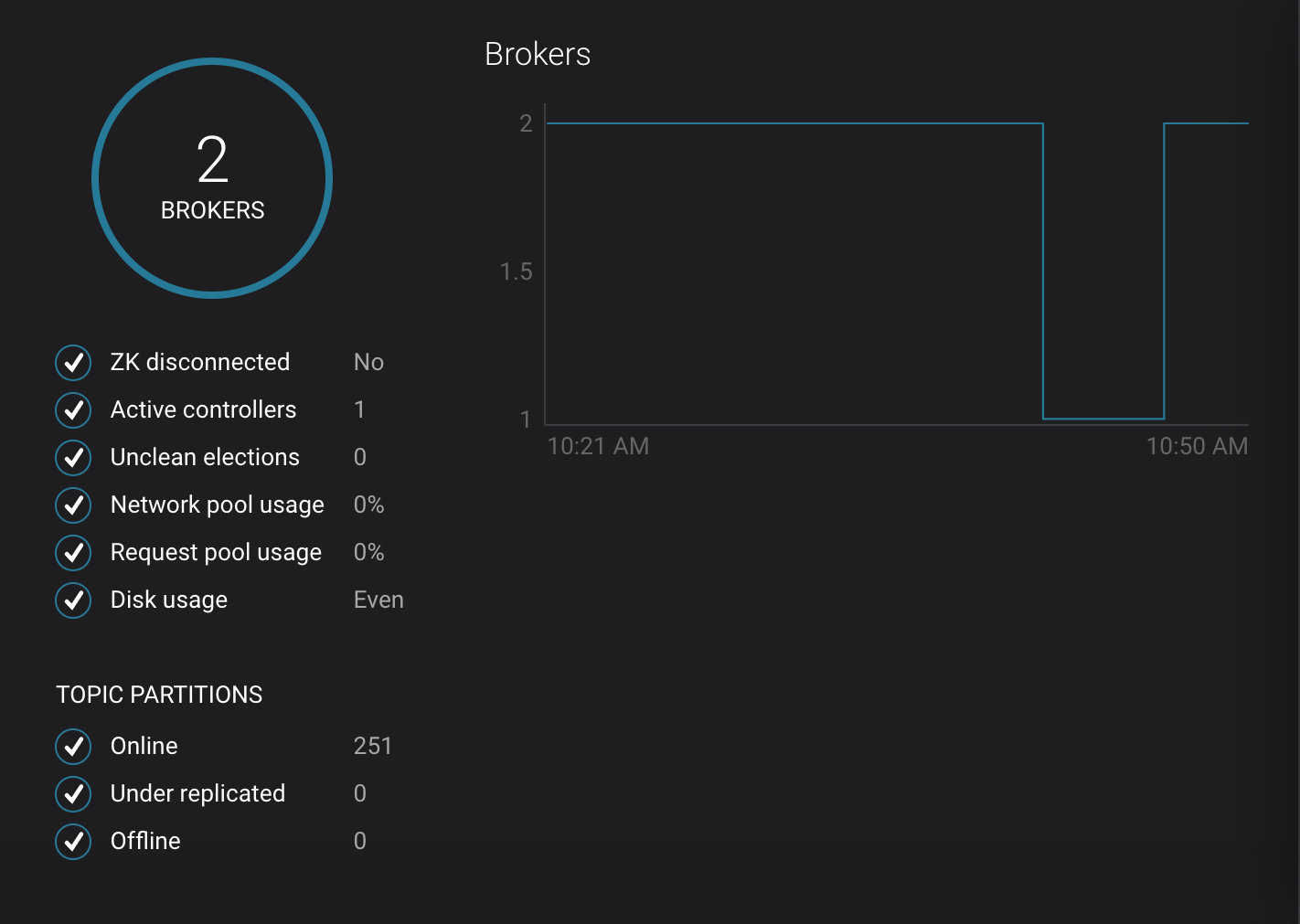
There are many types of Control Center alerts and many ways to configure them. Use the Alerts management page to define triggers and actions, or click on a streams monitoring graph for consumer groups or topics to setup alerts from there.
-
This demo already has pre-configured triggers and actions. View the Alerts
Triggersscreen, and clickEditagainst each trigger to see configuration details.- The trigger
Under Replicated Partitionshappens when a broker reports non-zero under replicated partitions, and it causes an actionEmail Administrator. - The trigger
Consumption Differencehappens when consumption difference for the Elasticsearch connector consumer group is greater than0, and it causes an actionEmail Administrator.
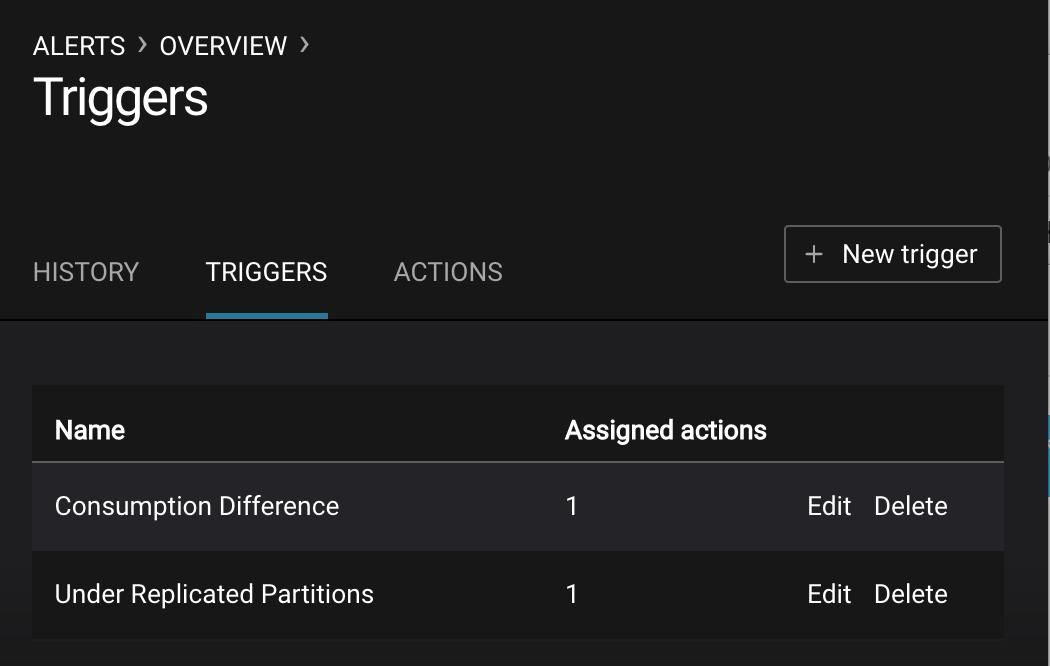
- The trigger
-
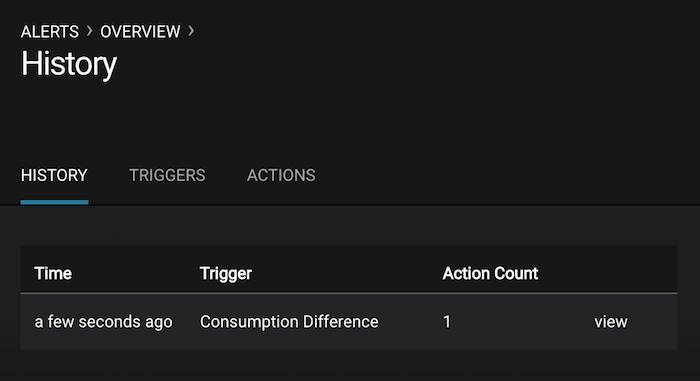
If you followed the steps in the failed broker section, view the Alert history to see that the trigger
Under Replicated Partitionshappened and caused an alert when you stopped broker 2. -
You can also trigger the
Consumption Differencetrigger. In the Kafka Connect -> Sinks screen, edit the running Elasticsearch sink connector. -
In the Kafka Connect view, pause the Elasticsearch sink connector by pressing the pause icon in the top right. This will stop consumption for the related consumer group.

-
View the Alert history to see that this trigger happened and caused an alert.
Confluent Replicator copies data from a source Kafka cluster to a destination Kafka cluster. The source and destination clusters are typically different clusters, but in this demo, Replicator is doing intra-cluster replication, i.e., the source and destination Kafka clusters are the same. As with the rest of the components in the solution, Confluent Replicator is also configured with security.
-
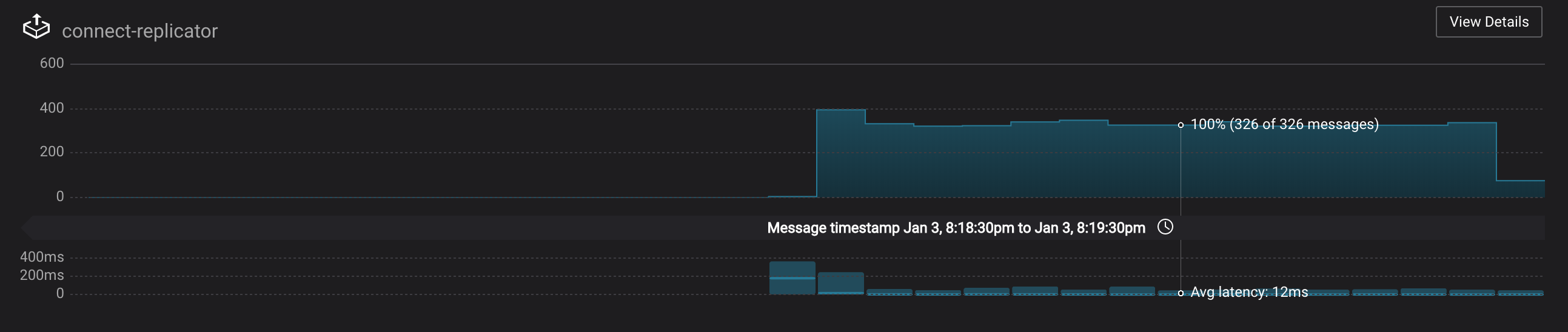
Monitoring --> Data Streams --> Message Delivery: monitor throughput and latency of Confluent Replicator in the Data streams monitoring view. Replicator is a Kafka Connect source connector and has a corresponding consumer group
connect-replicator. -
Management --> Topics: scroll down to view the topics called
wikipedia.parsed(Replicator is consuming data from this topic) andwikipedia.parsed.replica(Replicator is copying data to this topic). Click onConsumer Groupsfor the topicwikipedia.parsedand observe that one of the consumer groups is calledconnect-replicator. -
Management --> Kafka Connect: pause the Replicator connector by pressing the pause icon in the top right. This will stop consumption for the related consumer group.

-
Observe that the
connect-replicatorconsumer group has stopped consumption. -
Restart the Replicator connector.
-
Observe that the
connect-replicatorconsumer group has resumed consumption. Notice several things:* Even though the consumer group `connect-replicator` was not running for some of this time, all messages are shown as delivered. This is because all bars are time windows relative to produce timestamp. * The latency peaks and then gradually decreases, because this is also relative to the produce timestamp.
All the components in this demo are enabled with many security features:
- SSL for encryption, except for ZooKeeper which does not support SSL
- SASL/PLAIN for authentication, except for ZooKeeper
- Authorization. If a resource has no associated ACLs, then users are not allowed to access the resource, except super users
- HTTPS for Schema Registry
Note: this demo showcases a secure Confluent Platform for educational purposes and is not meant to be complete best practices. There are certain differences between what is shown in the demo and what you should do in production:
- Each component should have its own username, instead of authenticating all users as
client - Authorize users only for operations that they need, instead of making all of them super users
- If the
PLAINTEXTsecurity protocol is used, theseANONYMOUSusernames should not be configured as super users - Consider not even opening the
PLAINTEXTport ifSSLorSASL_SSLare configured
Encryption & Authentication:
Each broker has four listener ports:
- PLAINTEXT port called
PLAINTEXTfor users with no security enabled - SSL port port called
SSLfor users with just SSL without SASL - SASL_SSL port called
SASL_SSLfor communication between services inside Docker containers - SASL_SSL port called
SASL_SSL_HOSTfor communication between any potential services outside of Docker that communicate to the Docker containers
| port | kafka1 | kafka2 |
|---|---|---|
| PLAINTEXT | 10091 | 10092 |
| SSL | 11091 | 11092 |
| SASL_SSL | 9091 | 9092 |
| SASL_SSL_HOST | 29091 | 29092 |
Authorization:
All the brokers in this demo authenticate as broker, and all other components authenticate as client. Per the broker configuration parameter super.users, as it is set in this demo, the only users that can communicate with the cluster are those that authenticate as broker or client, or users that connect via the PLAINTEXT port (their username is ANONYMOUS). All other users are not authorized to communicate with the cluster.
-
Verify the ports on which the Kafka brokers are listening with the following command, and they should match the table shown below:
$ docker-compose logs kafka1 | grep "Registered broker 1" $ docker-compose logs kafka2 | grep "Registered broker 2"
-
This demo automatically generates simple SSL certificates and creates keystores, truststores, and secures them with a password. To communicate with the brokers, Kafka clients may use any of the ports on which the brokers are listening. To use a security-enabled port, they must specify security parameters for keystores, truststores, password, or authentication so the Kafka command line client tools pass the security configuration file with interceptors or without interceptors with these security parameters. As an example, to communicate with the Kafka cluster to view all the active consumer groups:
a. Communicate with brokers via the PLAINTEXT port
# PLAINTEXT port
$ docker-compose exec kafka1 kafka-consumer-groups --list --bootstrap-server kafka1:10091
b. Communicate with brokers via the SASL_SSL port, and SASL_SSL parameters configured via the --command-config argument for command line tools or --consumer.config for kafka-console-consumer.
# SASL_SSL port with SASL_SSL parameters
$ docker-compose exec kafka1 kafka-consumer-groups --list --bootstrap-server kafka1:9091 --command-config /etc/kafka/secrets/client_without_interceptors.config
c. If you try to communicate with brokers via the SASL_SSL port but don't specify the SASL_SSL parameters, it will fail
```bash
# SASL_SSL port without SASL_SSL parameters
$ docker-compose exec kafka1 kafka-consumer-groups --list --bootstrap-server kafka1:9091
Error: Executing consumer group command failed due to Request METADATA failed on brokers List(kafka1:9091 (id: -1 rack: null))
```
-
Verify the super users are configured for the authenticated users
broker,client, and unauthenticatedPLAINTEXT.$ docker-compose logs kafka1 | grep SUPER_USERS KAFKA_SUPER_USERS=User:client;User:broker;User:ANONYMOUS
-
Verify that a user
clientwhich authenticates via SASL can consume messages from topicwikipedia.parsed:$ ./scripts/consumers/listen_wikipedia.parsed.sh SASL
-
Verify that a user which authenticates via SSL cannot consume messages from topic
wikipedia.parsed. It fails with an exceptionorg.apache.kafka.common.errors.TopicAuthorizationException: Not authorized to access topics: [wikipedia.parsed].$ ./scripts/consumers/listen_wikipedia.parsed.sh SSL [2018-01-12 21:13:18,481] ERROR Unknown error when running consumer: (kafka.tools.ConsoleConsumer$) org.apache.kafka.common.errors.TopicAuthorizationException: Not authorized to access topics: [wikipedia.parsed]
-
Verify that the broker's Authorizer logger logs the denial event. As shown in the log message, the user which authenticates via SSL has a username
CN=client,OU=TEST,O=CONFLUENT,L=PaloAlto,ST=Ca,C=US, not justclient.# Authorizer logger logs the denied operation $ docker-compose logs kafka1 | grep kafka.authorizer.logger [2018-01-12 21:13:18,454] INFO Principal = User:CN=client,OU=TEST,O=CONFLUENT,L=PaloAlto,ST=Ca,C=US is Denied Operation = Describe from host = 172.23.0.7 on resource = Topic:wikipedia.parsed (kafka.authorizer.logger) [2018-01-12 21:13:18,464] INFO Principal = User:CN=client,OU=TEST,O=CONFLUENT,L=PaloAlto,ST=Ca,C=US is Denied Operation = Describe from host = 172.23.0.7 on resource = Group:test (kafka.authorizer.logger)
-
Add an ACL that authorizes user
CN=client,OU=TEST,O=CONFLUENT,L=PaloAlto,ST=Ca,C=US, and then view the updated ACL configuration.$ docker-compose exec connect /usr/bin/kafka-acls --authorizer-properties zookeeper.connect=zookeeper:2181 \ --add --topic wikipedia.parsed --allow-principal User:CN=client,OU=TEST,O=CONFLUENT,L=PaloAlto,ST=Ca,C=US --operation Read --group test $ docker-compose exec connect /usr/bin/kafka-acls --authorizer-properties zookeeper.connect=zookeeper:2181 \ --list --topic wikipedia.parsed --group test Current ACLs for resource `Topic:wikipedia.parsed`: User:CN=client,OU=TEST,O=CONFLUENT,L=PaloAlto,ST=Ca,C=US has Allow permission for operations: Read from hosts: * Current ACLs for resource `Group:test`: User:CN=client,OU=TEST,O=CONFLUENT,L=PaloAlto,ST=Ca,C=US has Allow permission for operations: Read from hosts: *
-
Verify that the user which authenticates via SSL is now authorized and can successfully consume some messages from topic
wikipedia.parsed.$ ./scripts/consumers/listen_wikipedia.parsed.sh SSL
-
To view sample messages for each topic, including
wikipedia.parsed:$ ./scripts/consumers/listen.sh
-
If the data streams monitoring appears to stop for the Kafka source connector, restart the connect container.
$ docker-compose restart connect
-
Stop the consumer group
appto stop consuming from topicwikipedia.parsed. Note that the command below stops the consumers gracefully withkill -15, so the consumers follow the shutdown sequence.$ ./scripts/app/stop_consumer_app_group_graceful.sh
-
Stop the Docker demo, destroy all components and clear all Docker volumes.
$ ./scripts/reset_demo.sh