Install GIT Windows
Install Anaconda
Install Github Desktop, if you do not like to use the terminal so much.
Install Atom
Start by cloning this repository, this can either be done with Github Desktop
or with a terminal. When we say terminal, in Windows we mean Anaconda prompt.
However, all code that starts with git can be done with Github Desktop.
With the terminal run
git clone https://github.com/CINPLA/cinpla-base.git
Windows: Search for anaconda and open Anaconda prompt Mac: open a terminal
In order to use phy (a spikesorter) we have to
conda install python=3.5 pyqt=4
Navigate to where you have cloned cinpla-base, then install the cinpla-base
requirements
cd cinpla-base
pip install -r requirements.txt
- Contact Mikkel, Alessio or Svenn-Arne
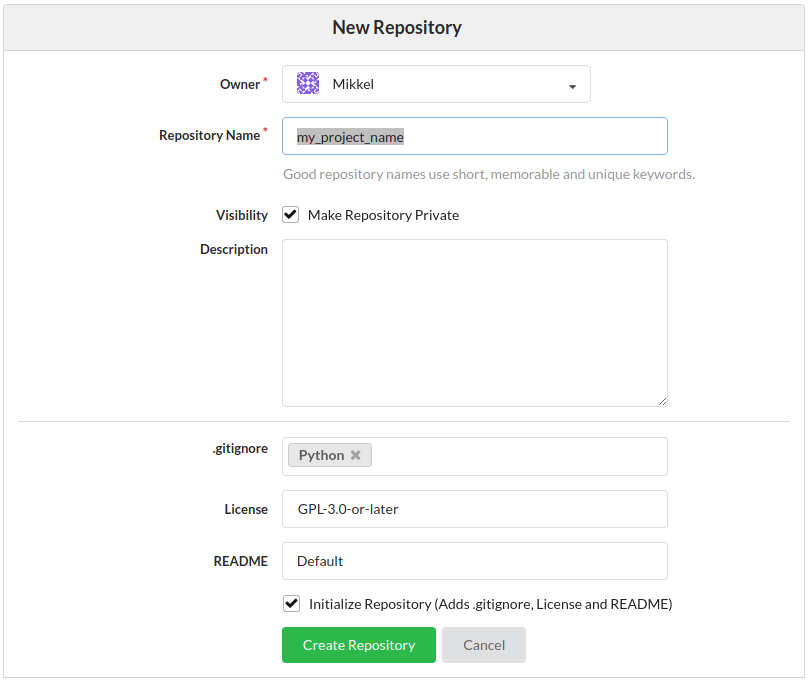
- Navigate to Gitea and expipe on NIRD
- Initialize with .gitignore, licence and README
- from notebook (see example below)
- with git desktop
git clone https://gitea.expipe.sigma2.no/user_name/my_project_name.git
Navigate to my_project_name and write in the terminal
jupyter notebook
In stead of using the terminal from now on, commands can be run from within the
notebook if it is begun with an exclamation mark. That is, if you would write
expipe init in the terminal, you would write in the notebook
expipe init
This command adds actions, entities and templates folders together with an
expipe.yaml, this is necesarry so that my_project_name will be recognized as
a expipe project.
Next, we need to add some information to git LFS which is helping us handling
large files (LFS stands for Large File Storage)
expipe init-lfs
This command adds two files, .gitattributes and .lfsconfig, the latter is not
so interesting but the former deserves some explanation. Inside it says
actions/*/data/**/* filter=lfs diff=lfs merge=lfs -text
*.yaml !filter !diff !merge
The first line says that all the contents in all data directories whithin every
action should be handeled by git LFS. The second line says that even though all
the data directories should be handeled by LFS, all files ending with .yaml
should not be handeled by LFS.
In short, these lines ensures that all file except .yaml files will be downloaded
as LFS files when the repository is cloned or pulled if nothing else is specified.
This means that all files in data except .yaml files will be text files
pointing to the real data files on NIRD.
git add -A
git commit -am "init expipe and LFS"
Navigate to cinpla-base/src/expipe-templates-cinpla/templates, where you'll
find a bunch of example templates, copy some you want to use or write your own.
If you want to write your own template the filename must on the form
filename.yaml and at a minimum contain
name: filename
identifier: filename
It is probably wise to commit after you add the templates.
git add -A
git commit -am "added some templates"
Now you are ready to start using expipe
from expipe_plugin_cinpla.widgets import browser
browser.display('workshop')
import expipe
expipe.Browser('workshop').display()