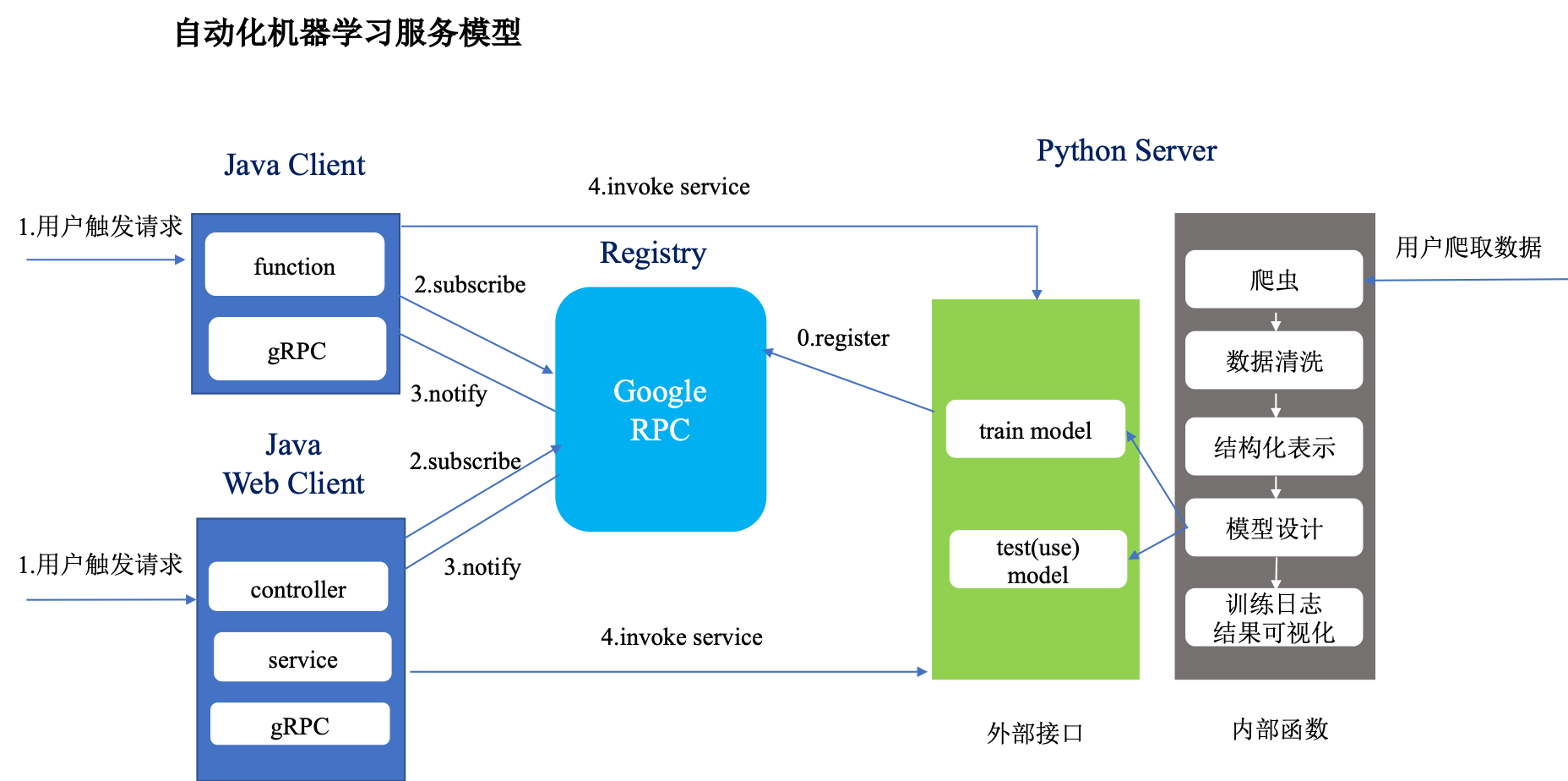
客户端采用Java语言编写,服务端采用Python语言编写,服务端直接将Python服务注册到gRPC, Java客户端根据端口号通过gRPC注册中心调用服务端服务。具体过程如下:
Python服务端将服务直接注册到gRPC注册中心,Java客户端通过端口号映射请求相关的服务,gRPC协议层接受服务之后,由应用层对服务进行处理,可以直接调用注册的服务实例,服务计算完成之后返回结果给gRPC,响应回调通知线程,Java客户端接收返回的结果。
- 安装依赖
Python依赖: pip install grpcio / pip install grpcio-tls
Java Project在maven中加入相关的依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-netty-shaded</artifactId>
<version>1.15.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-protobuf</artifactId>
<version>1.15.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.grpc</groupId>
<artifactId>grpc-stub</artifactId>
<version>1.15.0</version>
</dependency>Python客户端:
- 编写MachineLearning.proto,并执行
syntax = "proto3";
package example;
// The machine learning service definition.
service MachineLearning {
// Sends a machine learning result
rpc StartLearn (SendRequest) returns (GetReply) {}
}
// The request message containing the params.
message SendRequest {
string param = 1;
}
// The response message containing the results
message GetReply {
string result = 1;
}在根目录下创建example目录,用于存放上述proto文件已经生成的rpc服务端代码,然后在当前目录下执行python -m grpc_tools.protoc -I. --python_out=. --grpc_python_out=. ./MachineLearning.proto 进行编译执行,即可在example目录下生成MachineLearning_pb2.py和MachineLearning_pb2_grpc.py代码
- 编写Python服务端代码
# python服务端代码
class MachineLearning(MachineLearning_pb2_grpc.MachineLearningServicer):
def StartLearn(self, request, context):
return MachineLearning_pb2.GetReply(message='The model is %sing!' % request.name)
def serve():
server = grpc.server(futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=10))
MachineLearning_pb2_grpc.add_MachineLearningServicer_to_server(MachineLearning(), server)
server.add_insecure_port('[::]:50051') # 设置端口号
server.start() # 启动服务
try:
while True:
time.sleep(_ONE_DAY_IN_SECONDS)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
server.stop(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
serve()Java服务端:
- resources/proto目录下编写MachineLearning.proto参数与步骤1保持一致,然后通过maven proto插件进行编译(注意参数名称与python服务端代码一致,否则无法调用)
syntax = "proto3";
package example;
option java_package = "com.shgx.grpc";
option java_outer_classname = "MachineLearningServiceProto";
option java_multiple_files = true;
// The machine learning service definition.
service MachineLearning {
// Sends a request
rpc StartLearn (SendRequest) returns (GetReply) {}
}
// The request message containing the params.
message SendRequest {
string param = 1;
}
// The response message containing the results.
message GetReply {
string result = 1;
}- Java客户端代码,用于grpc调用Python服务端服务
public class MachineLearningClient {
private static final Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(MachineLearningClient.class.getName());
private final ManagedChannel channel;
private final MachineLearningGrpc.MachineLearningBlockingStub blockingStub;
/**
* Construct client connecting to MachineLearning server at {@code host:port}.
*/
public MachineLearningClient(String host, int port) {
channel = ManagedChannelBuilder.forAddress(host, port)
.usePlaintext(true)
.build();
blockingStub = MachineLearningGrpc.newBlockingStub(channel);
}
public void shutdown() throws InterruptedException {
channel.shutdown().awaitTermination(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* Send params to server.
*/
public void connect(String params) {
logger.info("Will try to connect " + params + " ...");
SendRequest request = SendRequest.newBuilder().setName(params).build();
GetReply response;
try {
response = blockingStub.startLearn(request);
} catch (StatusRuntimeException e) {
logger.log(Level.WARNING, "RPC failed: {0}", e.getStatus());
return;
}
logger.info("Response Result: " + response.getMessage());
}
/**
* Machine Learning server. If provided, the first element of {@code args} is the param to send to server.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MachineLearningClient client = new MachineLearningClient("localhost", 50051);
try {
String param = "train";
if (args.length > 0) {
param = args[0];
}
client.connect(param);
} finally {
client.shutdown();
}
}
}- 先启动Python服务端代码,然后启动Java客户端,输出结果
The model is training!
采用gRPC,有了服务的注册中心,服务切换更新更加轻量化,并且遵循 Netty 的线程分工原则,协议层消息的接收和编解码由Netty 的 I/O(NioEventLoop)线程负责;后续应用层的处理由应用线程负责,防止由于应用处理耗时而阻塞 Netty 的 I/O 线程, 可以通过服务名和方法名调用,直接调用启动的时候注册的服务实例,不需要反射或者JSON编码解码进行调用,性能更优; 不过因为有Netty的线程分工原则,gRPC之间会做频繁的线程切换,如果在一次gRPC调用过程中,做了多次I/O线程到应用线程之间的切换,会导致性能的下降。