Symphony
Symphony is a Golang library to allow devs to declare dependencies of tasks/functions,
and symphony automatically resolves run all tasks based on the dependencies.
This library significantly eases the flow-based/graph-based data fetching for Machine Learning prediction, used inside Grab where models require 200+ data in some cases.
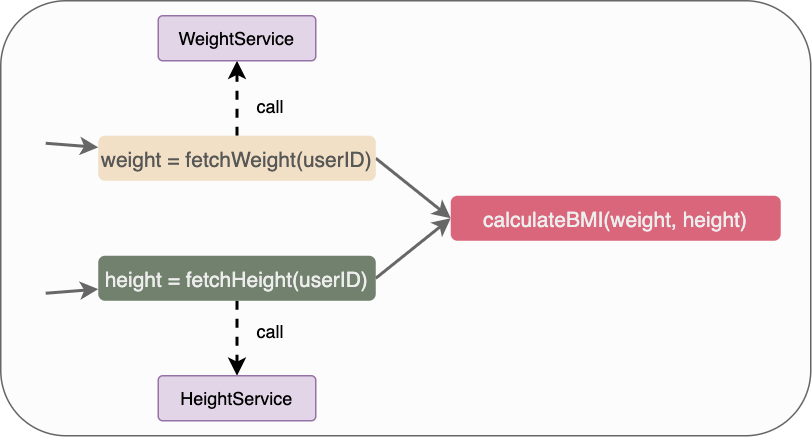
Traditionally, when different data comes with dependency(e.g. phone number based features requires calling user service to get phone number first), developers need to explicitly allocate dependent data fetching (usually different service/DB call) at different layers (layer-1: calling user-service to get phone number, layer-2: calling phone-number feature DB by phone number in layer-1). With Symphony, Developers can declare the direct dependency between different data, and Symphony will build a DAG internally and fetch data based on it, so no need for a developer to specify the global layers.
Quick Usage
package main
import (
"context"
"errors"
"fmt"
"github.com/grab/symphony"
)
type User struct {
ID int64
Weight float64
Height float64
BMI float64
}
func main() {
// create a dummy user with ID=1
u := &User{ID: 1}
// init symphony
s := symphony.New()
// Define Task fetchWeight, fetchHeight, calculateBMI
// Task can be declare in any order
s.Add("fetchWeight", nil, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error)){
// assume a remote WeightService call
u.Weight = callWeightService(u.ID)
return "weight fetched ", nil
}).Add("fetchHeight", nil, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error){
// assume a remote HeightService call
u.Height = callHeightService(u.ID)
return "height fetched", nil
}).Add("calculateBMI", []string{"fetchWeight", "fetchHeight"}, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error) {
// Note that we declare the dependency in the above line, so this block will be called only after fetchWeight and fetchHeight tasks are done
u.BMI = callBMICalculator(u.Weight, u.Height)
return "BMI calculated", nil
})
// shutdown the call if it exceeds 1500ms
result, err := s.Do(context.Background(), 1500)
BMI := result["calculateBMI"]
fmt.Printf("BMI: %d, err: %s", BMI, err)
}Basic Usage with Latency measure
The task depency graph is the same with Quick usage. This Usage just adds the way to log the latency of tasks. To add the latency check, you just need to create a func like func(statRecord *symphony.TaskRunTimeStat), and then call SetTaskRuntimeStatFunc with the Symphony object. BTW, it is optional.
package main
import (
"context"
"errors"
"fmt"
"github.com/grab/symphony"
)
// an example func to log the latency. This is just to print the latency in console, but you can call other log utils too.
// this function will be called after the symphony finished a task.
var symphonyLatencyFunc = func(statRecord *symphony.TaskRunTimeStat) {
//// add your latency log function here, like replacing the logLatency to the method your system supported.
//// statRecord.StartTime is start time of the task including the time to wait all dependents finishing.
//// statRecord.StartTimeForTaskFn is start time of the task's fun, after all dependencies finish.
//// statRecord.EndTime is end time of the task's fun, after all dependencies finish.
taskName := statRecord.Name
startTime := *statRecord.StartTime
startTimeForTaskFn := *statRecord.StartTimeForTaskFn
endTime := *statRecord.EndTime
fmt.Printf("taskName:%v, task begin time with depency waiting time: %v, end time: %v, latency: %v\n", taskName, startTime, endTime, endTime.Sub(startTime).Milliseconds())
fmt.Printf("taskName:%v, task begin time without depency waiting time: %v, end time: %v, latency: %v\n", taskName, startTimeForTaskFn, endTime, endTime.Sub(startTimeForTaskFn).Milliseconds())
}
func main() {
// create a dummy user with ID=1
u := &User{ID: 1}
s := symphony.New()
// Define Task fetchWeight, fetchHeight, calculateBMI
// Task can be declare in any order
s.Add("fetchWeight", nil, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error)){
// assume a remote WeightService call
u.Weight = callWeightService(u.ID)
return "weight fetched ", nil
}).Add("fetchHeight", nil, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error){
// assume a remote HeightService call
u.Height = callHeightService(u.ID)
return "height fetched", nil
}).Add("calculateBMI", []string{"fetchWeight", "fetchHeight"}, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error) {
// Note that we declare the dependency in the above line, so this block will be called only after fetchWeight and fetchHeight tasks are done
u.BMI = callBMICalculator(u.Weight, u.Height)
return "BMI calculated", nil
})
// you could set the latency check func here, and it is optional.
// the function will be called after the symphony finished a task.
s.SetTaskRuntimeStatFunc(symphonyLatencyFunc)
// shutdown the call if it exceeds 1500ms
result, err := s.Do(context.Background(), 1500)
BMI := result["calculateBMI"]
fmt.Printf("BMI: %d, err: %s", BMI, err)
}Advanced Usage
Assuming the task dependency graph is the above one, the following code will resolve and run based on this
package main
import (
"context"
"errors"
"fmt"
"github.com/grab/symphony"
)
func main() {
s := symphony.New()
// Define Task f1, f2, f3, f4, f5, f6, f7
// Task can be declare in any order
s.Add("f2", []string{"f1", "f4"}, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error) {
fmt.Println("==starting f2==")
return "f2 result", nil
}).Add("f3", []string{"f2", "f4"}, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error) {
fmt.Println("==starting f3==")
return fmt.Sprintf("%s|%s|%s", res["f2"].R, res["f4"].R, "f3 result"), nil
}).Add("f4", []string{"f5"}, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error) {
fmt.Println("==starting f4==")
return "f4 result", nil
}).Add("f5", nil, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error) {
fmt.Println("==starting f5==")
return "f5 result", nil
}).Add("f6", []string{"f3"}, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error) {
fmt.Println("==starting f6==")
return "f6 result", nil
}).Add("f7", []string{"f4"}, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error) {
fmt.Println("==starting f7==")
return "f7 result", nil
}).Add("f1", nil, func(res map[string]*symphony.TaskState) (interface{}, error) {
fmt.Println("==starting f1==")
return "f1 result", nil
})
// wait up to 1500ms
res, err := s.Do(context.Background(), 1500)
f3r, _ := res["f3"]
f6r, _ := res["f6"]
fmt.Printf("err=%s", err) // err=nil
fmt.Printf("f3=%s", f3r.R) // f3=f2 result|f4 result|f3 result
fmt.Printf("f6=%s", f6r.R) // f6=f2 result|f4 result|f3 result|f6 result
}Features
-
Automatic trigger dependent task
- once all dependencies of a task are solved, the task would start running immediately
-
Dependency Safety check
- Self Dependency
- Non-existent dependency
- Cyclic Dependency
-
Short-circuit
- If any task returns error, will short-circuit all dependent tasks
- In the above code, if
f3returns error, f6 will not run (and return same error to all its dependencies if any)
-
Timeout
- at
s.Do(context.Background(), 1500),1500defines the max running time in millisecond for, and will timeout by returning error if it exceeds this
- at
Please see symphony_test.go for more use cases