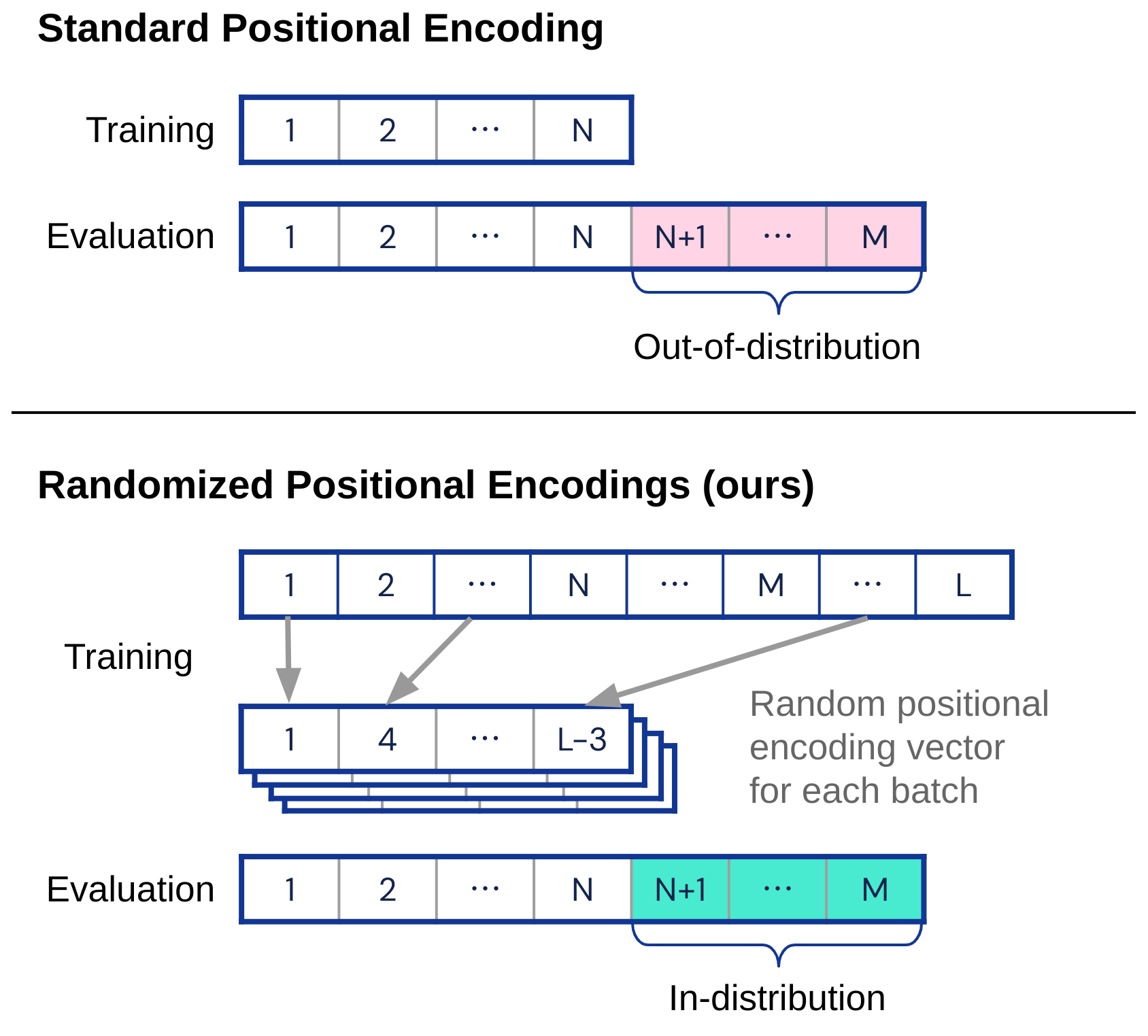
This repository provides an implementation of our ACL 2023 paper Randomized Positional Encodings Boost Length Generalization of Transformers.
Transformers have impressive generalization capabilities on tasks with a fixed context length. However, they fail to generalize to sequences of arbitrary length, even for seemingly simple tasks such as duplicating a string. Moreover, simply training on longer sequences is inefficient due to the quadratic computation complexity of the global attention mechanism. In this work, we demonstrate that this failure mode is linked to positional encodings being out-of-distribution for longer sequences (even for relative encodings) and introduce a novel family of positional encodings that can overcome this problem. Concretely, our randomized positional encoding scheme simulates the positions of longer sequences and randomly selects an ordered subset to fit the sequence's length. Our large-scale empirical evaluation of 6000 models across 15 algorithmic reasoning tasks shows that our method allows Transformers to generalize to sequences of unseen length (increasing test accuracy by 12.0% on average).
It is based on JAX and Haiku and contains all the code, datasets, and models necessary to reproduce the paper's results.
.
├── models
│ ├── positional_encodings.py
│ ├── transformer.py - Transformer (Vaswani et al., 2017)
│ └── transformer_utils.py
├── tasks
│ ├── cs - Context-sensitive tasks
│ ├── dcf - Deterministic context-free tasks
│ ├── regular - Regular tasks
│ └── task.py - Abstract `GeneralizationTask`
├── experiments
| ├── constants.py - Training/Evaluation constants
| ├── curriculum.py - Training curricula (over sequence lengths)
| ├── example.py - Example traning script
| ├── range_evaluation.py - Evaluation loop (test sequences lengths)
| ├── training.py - Training loop
| └── utils.py - Utility functions
├── README.md
└── requirements.txt - Dependencies
Clone the source code into a local directory:
git clone https://github.com/google-deepmind/randomized_positional_encodings.git
cd randomized_positional_encodingspip install -r requirements.txt will install all required dependencies.
This is best done inside a conda environment.
To that end, install Anaconda.
Then, create and activate the conda environment:
conda create --name randomized_positional_encodings
conda activate randomized_positional_encodingsInstall pip and use it to install all the dependencies:
conda install pip
pip install -r requirements.txtIf you have a GPU available (highly recommended for fast training), then you can install JAX with CUDA support.
pip install --upgrade "jax[cuda12_pip]" -f https://storage.googleapis.com/jax-releases/jax_cuda_releases.htmlNote that the jax version must correspond to the existing CUDA installation you wish to use (CUDA 12 in the example above). Please see the JAX documentation for more details.
Before running any code, make sure to activate the conda environment and set the PYTHONPATH:
conda activate randomized_positional_encodings
export PYTHONPATH=$(pwd)/..We provide an example of a training and evaluation run at:
python experiments/example.py@inproceedings{ruoss2023randomized,
author = {Anian Ruoss and
Gr{\'{e}}goire Del{\'{e}}tang and
Tim Genewein and
Jordi Grau{-}Moya and
R{\'{o}}bert Csord{\'{a}}s and
Mehdi Bennani and
Shane Legg and
Joel Veness},
title = {Randomized Positional Encodings Boost Length Generalization of Transformers},
booktitle = {61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics}
year = {2023},
}Copyright 2023 DeepMind Technologies Limited
All software is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (Apache 2.0); you may not use this file except in compliance with the Apache 2.0 license. You may obtain a copy of the Apache 2.0 license at: https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
All other materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC-BY). You may obtain a copy of the CC-BY license at: https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, all software and materials distributed here under the Apache 2.0 or CC-BY licenses are distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the licenses for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under those licenses.
This is not an official Google product.