To make use of functions from this package, you need to clone this
repository, install the devtools R package, navigate to the directory
of this package and use the load_all() function.
# install.packages("devtools")
library(devtools)
load_all()
Install the development version from GitHub:
# Currently, documentation is missing. Hence, installation may fail
# remotes::install_github("giuseppec/customtrees")
- This package is not intended to be fast. It serves as a modular framework and playground to explore/study the splitting of features by custom objectives.
- Currently only trees of depth 1 are fitted with
split_parent_node. If you want a tree, you need to call this function recursively on the generated child nodes. You can usegenerate_node_indexto get the split indices of the observations from the current node. - Splits for categorical variables currently not implemented and tested. Try to handle categoricals as numerics as workaround.
- The
perform_splitfunction computes (and aggregates) the objective in the generated nodes after splitting w.r.t. specific split points. - Binary splits generate two nodes and are implemented in
find_best_binary_split. The implementation does exhaustive search of split point candidates to find the best split point for a given feature. - Multiple splits generate multiple nodes and are implemented in
find_best_multiway_split. The implementation currently uses a slow simulated annealing optimization to find the best split point for a given feature (might be improved and replaced with other, faster optimization procedures).
library(tidyverse)
library(Rmalschains)
library(dfoptim)
library(iml)
library(ranger)
library(kmlShape)
library(dtw)
# objective that fits a constant in the nodes (CART)
SS = function(y, x, requires.x = FALSE, ...) {
ypred = mean(y)
sum((y - ypred)^2)
}
# objective that fits a linear model in the nodes (mob)
SS_lm = function(y, x, requires.x = TRUE, ...) {
ypred = predict(lm(y ~ x))
sum((y - ypred)^2)
}
# point-wise L1 distance (is this frechet distance if grids are the same?)
SS_L1 = function(y, x, requires.x = FALSE, ...) {
require(Rfast)
ypred = Rfast::colMedians(as.matrix(y))
sum(t(abs(t(y) - ypred)))
}
# point-wise L2 distance
SS_L2 = function(y, x, requires.x = FALSE, ...) {
ypred = colMeans(y)
sum(t((t(y) - ypred)^2))
}
# # point-wise L1 distance = frechet distance if grids are the same
# SS_L1 = function(y, x, requires.x = FALSE, ...) {
# n = nrow(y)
# center = colMeans(y)
# centermat = t(replicate(n, center))
# sum(abs(y - centermat))
# }
# Frechet distance FDA measure
SS_fre = function(y, x, requires.x = FALSE, ...) { # slow
# using only y-axis of curves is enough as x-axis is always the same for all curves
require(kmlShape)
center = colMeans(y)
grid.x = as.numeric(names(center))
pdp.y = unname(center)
dist = apply(y, 1, function(ice) distFrechet(grid.x, pdp.y, grid.x, ice, FrechetSumOrMax = "sum"))
sum(dist)
}
# Dynamic time warping FDA measure
SS_dtw = function(y, x, requires.x = FALSE, ...) {
require(dtw)
pdp = colMeans(y) # this is the pdp
dist = apply(y, 1, function(ice) dtw(ice, pdp, distance.only = TRUE)$normalizedDistance)
sum(dist)
}
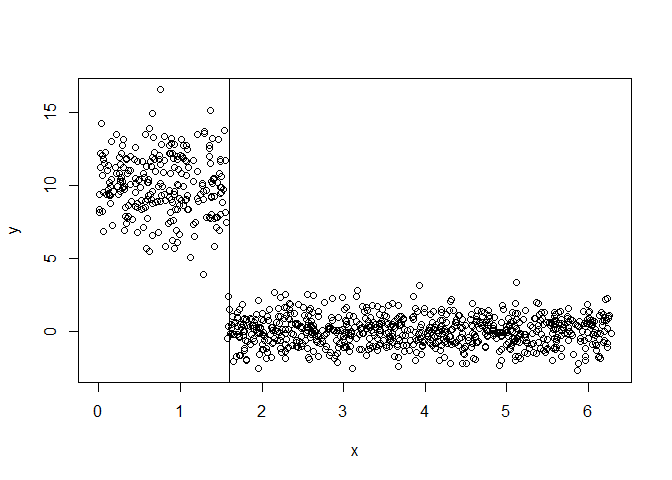
nsim = 1000L
x = x = sort(runif(n = nsim, min = 0, max = 2*pi))
q = quantile(x, seq(0, 1, length.out = 100), type = 1)
y = ifelse(x > pi/2, rnorm(nsim, mean = 0), rnorm(nsim, mean = 10, sd = 2))
X = data.frame(x = x)
split = split_parent_node(y, X, objective = SS, optimizer = find_best_binary_split)
split
## feature objective.value runtime split.points best.split
## 1: x 2113.473 0.16 1.605472 TRUE
# plot result
plot(x, y)
abline(v = unlist(split$split.points))
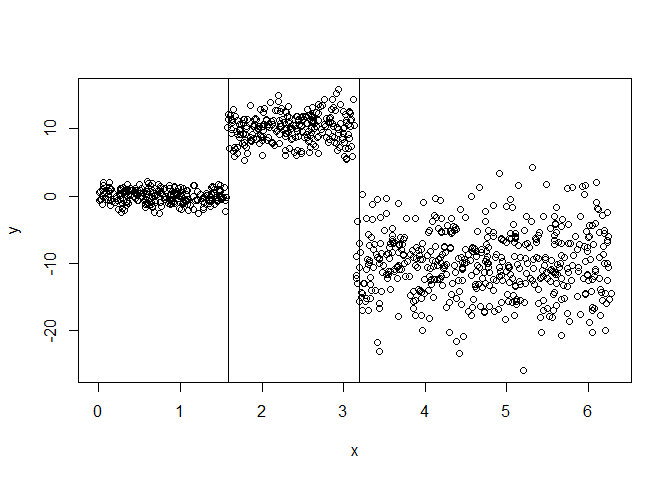
y = ifelse(x < pi/2, rnorm(nsim, mean = 0),
ifelse(x < pi, rnorm(nsim, mean = 10, sd = 2),
rnorm(nsim, mean = -10, sd = 5)))
# MA-LS Chains
split = split_parent_node(y, X, objective = SS,
optimizer = find_best_multiway_split_mals, n.splits = 2)
split
## feature objective.value runtime split.points best.split
## 1: x 14884.64 0.94 1.592668,3.188205 TRUE
plot(x, y)
abline(v = unlist(split$split.points))
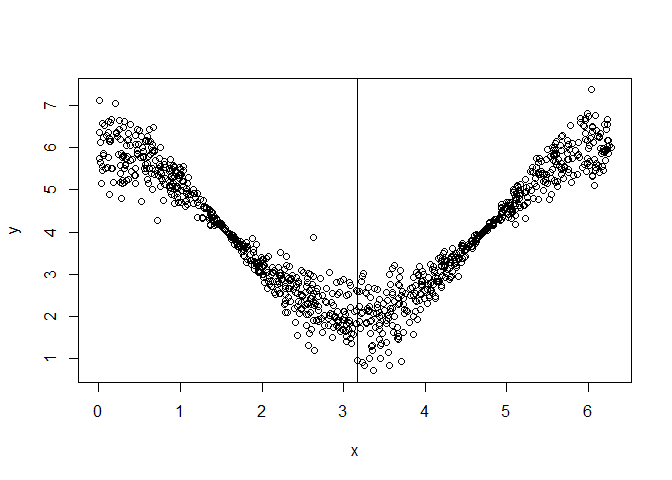
y = 4 + 2 * cos(x) + rnorm(nsim, mean = 0, sd = abs(cos(x)) / 2)
split = split_parent_node(y, X, objective = SS_lm, optimizer = find_best_binary_split, n.splits = 1)
split
## feature objective.value runtime split.points best.split
## 1: x 157.5399 0.51 3.167946 TRUE
plot(x, y)
abline(v = unlist(split$split.points))
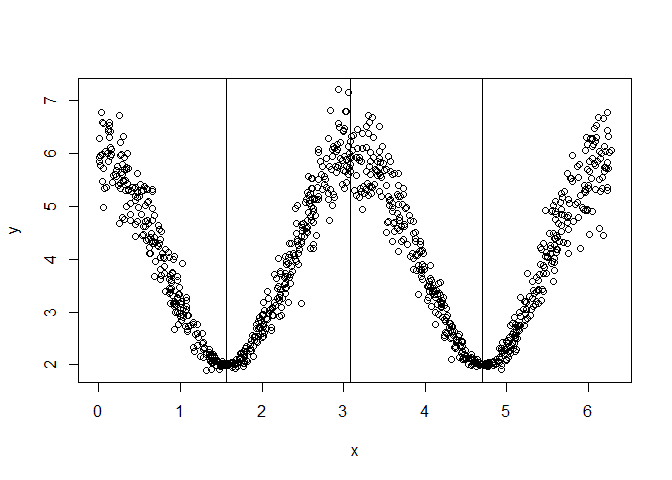
y = 4 + 2 * cos(x*2) + rnorm(nsim, mean = 0, sd = abs(cos(x)) / 2)
# MA-LS Chains
split = split_parent_node(y, X, objective = SS_lm, optimizer = find_best_multiway_split_mals,
n.splits = 3)
split
## feature objective.value runtime split.points best.split
## 1: x 142.1684 4 1.567564,3.077776,4.699875 TRUE
plot(x, y)
abline(v = unlist(split$split.points))
We first generate some functional data:
# Simulate Data
n = 500
x1 = round(runif(n, -1, 1), 1)
x2 = round(runif(n, -1, 1), 3)
x3 = sample(c(0, 1), size = n, replace = TRUE, prob = c(0.5, 0.5))
x4 = sample(c(0, 1), size = n, replace = TRUE, prob = c(0.7, 0.3))
# noisy vars
x5 = sample(c(0, 1), size = n, replace = TRUE, prob = c(0.5, 0.5))
x6 = rnorm(n, mean = 1, sd = 5)
y = 0.2*x1 - 8*x2 + ifelse(x1 < quantile(x1, 0.25), 8*x2, ifelse(x1 > quantile(x1, 0.75), 16*x2, 0))
#y = 0.2*x1 - 8*x2 + ifelse(x3 == 0, I(16*x2),0) + ifelse(x1 > mean(x1), I(8*x2),0)
# We also get interesting results using a 2-way interaction of numeric features
#y = 0.2*x1 - 8*x2 + 8*x6*x2
#y = 0.2*x1 - 8*x2^2 + 5*cos(x2*5)*x6 + ifelse(x3 == 0, I(8*x2),0)
eps = rnorm(n, 0, 0.1*sd(y))
y = y + eps
dat = data.frame(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, y)
X = dat[, setdiff(colnames(dat), "y")]
# Fit model and compute ICE for x2
mod = ranger(y ~ ., data = dat, num.trees = 500)
pred = function(model, newdata) predict(model, newdata)$predictions
model = Predictor$new(mod, data = X, y = dat$y, predict.function = pred)
effect = FeatureEffect$new(model, method = "ice", grid.size = 20, feature = "x2")
eff = as.data.table(effect$results)
# Center ICE curves
eff = as.data.frame(eff[, .value := (.value - mean(.value)), by = c(".type", ".id")])
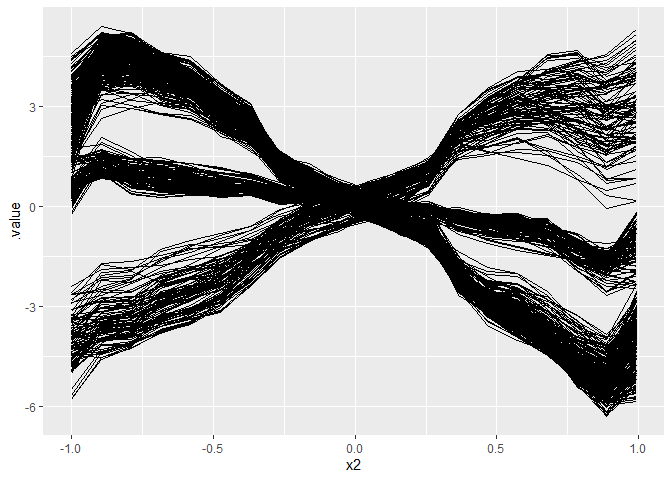
# Plot ICE curves: WE WANT TO FIND SUBGROUPS SUCH THAT ICE KURVES ARE HOMOGENOUS
ggplot(eff, aes(x = x2, y = .value)) +
geom_line(aes(group = .id))
Formulate curves above by multivariate target and find feature that splits the curves such that they are more homogenous in the nodes:
# Get ICE values and arrange them in a horizontal matrix
Y = spread(eff, x2, .value)
Y = Y[, setdiff(colnames(Y), c(".type", ".id"))]
str(X) # contains our feature values
## 'data.frame': 500 obs. of 6 variables:
## $ x1: num -0.8 1 -0.4 -0.6 -0.2 0.5 0.4 0.5 0.5 -0.6 ...
## $ x2: num 0.473 0.935 0.944 0.154 -0.602 -0.266 -0.912 0.958 -0.777 -0.846 ...
## $ x3: num 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 ...
## $ x4: num 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 ...
## $ x5: num 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 ...
## $ x6: num -4.686 2.749 -0.433 -11.956 -0.84 ...
str(Y) # contains ICE values for each grid point
## 'data.frame': 500 obs. of 20 variables:
## $ -1 : num 0.601 -4.296 3.036 0.59 3.474 ...
## $ -0.895157894736842: num 1.47 -4.05 4.76 1.1 4.82 ...
## $ -0.790315789473684: num 1.249 -3.913 4.662 0.834 4.699 ...
## $ -0.685473684210526: num 1.208 -3.597 4.192 0.841 4.394 ...
## $ -0.580631578947368: num 1.16 -3.36 3.97 0.85 4.04 ...
## $ -0.475789473684211: num 1.034 -3.167 3.308 0.812 2.923 ...
## $ -0.370947368421053: num 0.867 -2.395 2.654 0.766 2.506 ...
## $ -0.266105263157895: num 0.624 -1.564 1.475 0.561 1.206 ...
## $ -0.161263157894737: num 0.403 -1.064 0.794 0.411 0.702 ...
## $ -0.056421052631579: num 0.239 -0.666 0.438 0.274 0.239 ...
## $ 0.0484210526315789: num 0.0664 -0.2706 -0.078 0.1342 -0.121 ...
## $ 0.153263157894737 : num -0.0732 0.0267 -0.651 0.0282 -0.546 ...
## $ 0.258105263157895 : num -0.06416 0.76146 -0.91594 -0.00355 -0.94999 ...
## $ 0.362947368421052 : num -0.278 2.513 -2.062 -0.371 -2.211 ...
## $ 0.467789473684211 : num -0.405 3.156 -2.73 -0.533 -3.177 ...
## $ 0.572631578947368 : num -0.473 3.681 -2.898 -0.554 -3.771 ...
## $ 0.677473684210526 : num -1.12 4.01 -3.89 -1.02 -4.3 ...
## $ 0.782315789473684 : num -1.83 4.33 -5 -1.64 -4.8 ...
## $ 0.887157894736842 : num -2.3 4.56 -5.93 -1.77 -5.1 ...
## $ 0.992 : num -2.38 5.31 -5.14 -1.31 -4.02 ...
sp = split_parent_node(Y = Y, X = X, objective = SS_L2,
n.splits = 1, optimizer = find_best_binary_split)
sp
## feature objective.value runtime split.points best.split
## 1: x1 20615.92 0.05 0.55 TRUE
## 2: x2 49944.31 0.13 -0.899 FALSE
## 3: x3 50389.03 0.01 0.5 FALSE
## 4: x4 50439.39 0.00 0.5 FALSE
## 5: x5 50353.81 0.00 0.5 FALSE
## 6: x6 49231.41 0.22 -0.5898811 FALSE
node_index = generate_node_index(Y, X, result = sp)
str(node_index)
## List of 2
## $ class: Factor w/ 2 levels "[-1,0.55]","(0.55,1]": 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ...
## $ index:List of 2
## ..$ [-1,0.55]: int [1:397] 1 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ...
## ..$ (0.55,1] : int [1:103] 2 17 27 32 36 37 38 46 51 60 ...
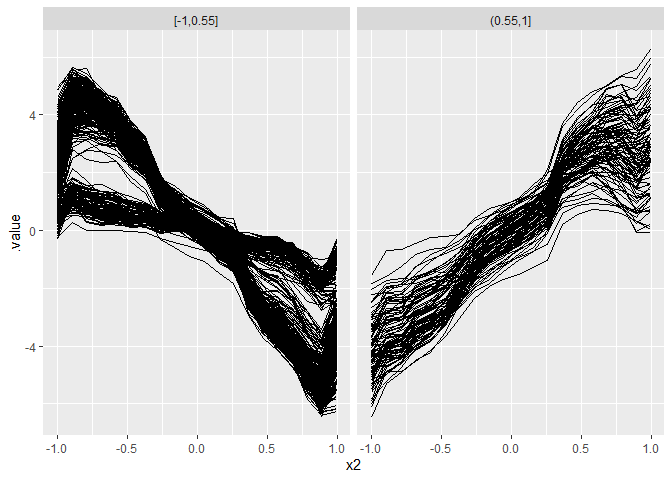
Visualize the results:
plot.data = effect$results
plot.data$.split = node_index$class[plot.data$.id]
ggplot(plot.data, aes(x = x2, y = .value)) +
geom_line(aes(group = .id)) + facet_grid(~ .split)
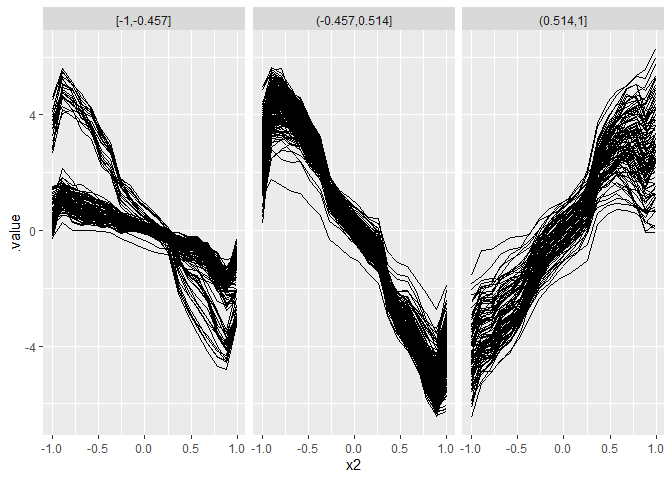
Multiway splits using a distance measure suited for curves:
sp_multiway = split_parent_node(Y = Y, X = X, objective = SS_L2,
n.splits = 2, optimizer = find_best_multiway_split_mals)
sp_multiway
## feature objective.value runtime split.points best.split
## 1: x1 1807.511 1.95 -0.4570238, 0.5144859 TRUE
## 2: x2 49569.425 1.48 -0.7704058,-0.5325179 FALSE
## 3: x3 50389.034 0.00 0.5 FALSE
## 4: x4 50439.387 0.02 0.5 FALSE
## 5: x5 50353.813 0.00 0.5 FALSE
## 6: x6 48944.352 1.59 -0.6257652, 0.2943695 FALSE
node_index_multiway = generate_node_index(Y, X, result = sp_multiway)
str(node_index_multiway)
## List of 2
## $ class: Factor w/ 3 levels "[-1,-0.457]",..: 1 3 2 1 2 2 2 2 2 1 ...
## $ index:List of 3
## ..$ [-1,-0.457] : int [1:126] 1 4 10 12 14 15 24 25 28 29 ...
## ..$ (-0.457,0.514]: int [1:271] 3 5 6 7 8 9 11 13 16 18 ...
## ..$ (0.514,1] : int [1:103] 2 17 27 32 36 37 38 46 51 60 ...
plot.data$.split = node_index_multiway$class[plot.data$.id]
ggplot(plot.data, aes(x = x2, y = .value)) +
geom_line(aes(group = .id)) + facet_grid(~ .split)
Now, we try a non-linear effect with a continuous interaction effect.
y = 0.2*x1 - 8*x2^2 + 5*cos(x2*5)*x6 + eps
dat = data.frame(x1, x2, x3, x4, x5, x6, y)
X = dat[, setdiff(colnames(dat), "y")]
# Fit model and compute ICE for x2
mod = ranger(y ~ ., data = dat, num.trees = 1000)
pred = function(model, newdata) predict(model, newdata)$predictions
model = Predictor$new(mod, data = X, y = dat$y, predict.function = pred)
effect = FeatureEffect$new(model, method = "ice", grid.size = 20, feature = "x2")
eff = as.data.table(effect$results)
# Center ICE curves
eff = as.data.frame(eff[, .value := (.value - mean(.value)), by = c(".type", ".id")])
Y = spread(eff, x2, .value)
Y = Y[, setdiff(colnames(Y), c(".type", ".id"))]
#Y = as.data.frame(t(apply(Y, MARGIN = 1, function(x) x - mean(x))))
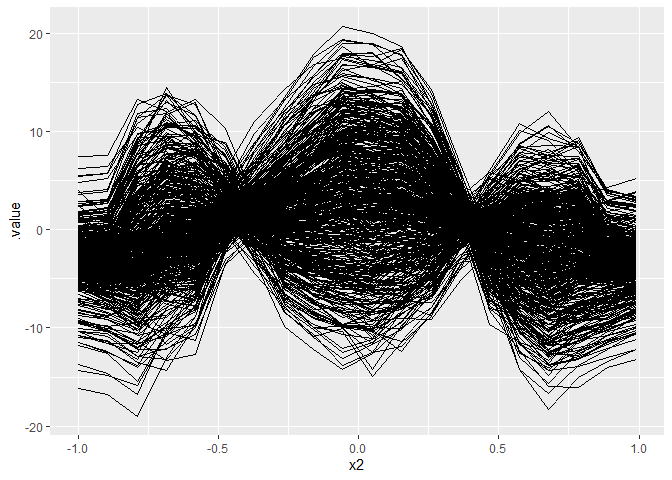
# Plot ICE curves: WE WANT TO FIND SUBGROUPS SUCH THAT ICE KURVES ARE HOMOGENOUS
ggplot(eff, aes(x = x2, y = .value)) +
geom_line(aes(group = .id))
sp_multi = lapply(1:4, function(i) {
split_parent_node(Y = Y, X = X, objective = SS_L2,
n.splits = i, optimizer = find_best_multiway_split_mals, min.node.size = 10)
})
results = rbindlist(sp_multi, idcol = "n.splits")
results[results$best.split, ]
## n.splits feature objective.value runtime split.points best.split
## 1: 1 x6 88235.54 0.12 0.6014337 TRUE
## 2: 2 x6 54962.54 1.59 -2.444091, 2.989396 TRUE
## 3: 3 x6 48116.97 1.83 -2.583962, 1.019968, 4.609502 TRUE
## 4: 4 x6 43256.47 2.03 -4.519632,-2.042282, 1.369073, 5.015983 TRUE
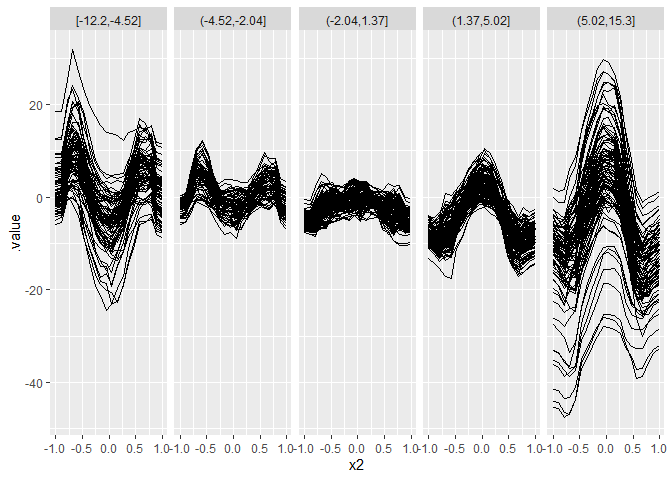
node_index_multiway = generate_node_index(Y, X, result = sp_multi[[length(sp_multi)]])
str(node_index_multiway)
## List of 2
## $ class: Factor w/ 5 levels "[-12.2,-4.52]",..: 1 4 3 1 3 5 3 5 2 4 ...
## $ index:List of 5
## ..$ [-12.2,-4.52]: int [1:85] 1 4 13 20 22 23 25 30 31 36 ...
## ..$ (-4.52,-2.04]: int [1:72] 9 16 26 38 41 42 58 71 75 89 ...
## ..$ (-2.04,1.37] : int [1:124] 3 5 7 11 18 19 24 28 39 43 ...
## ..$ (1.37,5.02] : int [1:125] 2 10 14 21 33 40 44 53 56 65 ...
## ..$ (5.02,15.3] : int [1:94] 6 8 12 15 17 27 29 32 34 35 ...
plot.data = effect$results
plot.data$.split = node_index_multiway$class[plot.data$.id]
ggplot(plot.data, aes(x = x2, y = .value)) +
geom_line(aes(group = .id)) + facet_grid(~ .split)