pgrServer
Introduction
pgrServer is a routing service that is able to use pgRouting topologies to load data into a JGraphT graph for very fast searches even with dense networks.
The graph is created at startup when the topology is read from a PostgreSQL database. This graph though can be re-created at regular intervals by making a service request, for networks that have dynamic costs.
And similar to pgRouting, this application is not road navigation centric. This application can be used for a wide variety of networks: i.e. utilities (fiber optic lines), water systems, etc.
As of this version, the following search algorithms are included as a service:
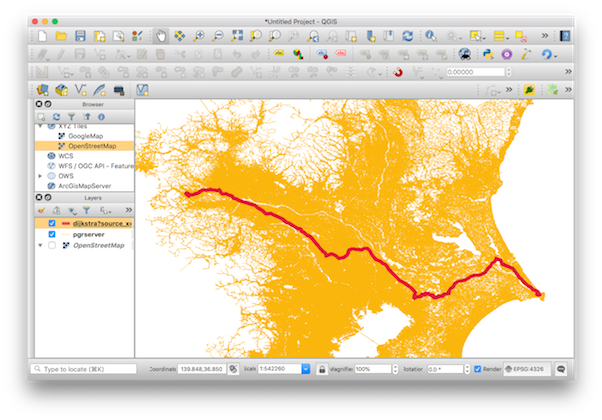
- Dijkstra ( for dense networks )
- A-Star ( for dense networks )
- ContractionHierarchyBidirectionalDijkstra ( for dense networks * )
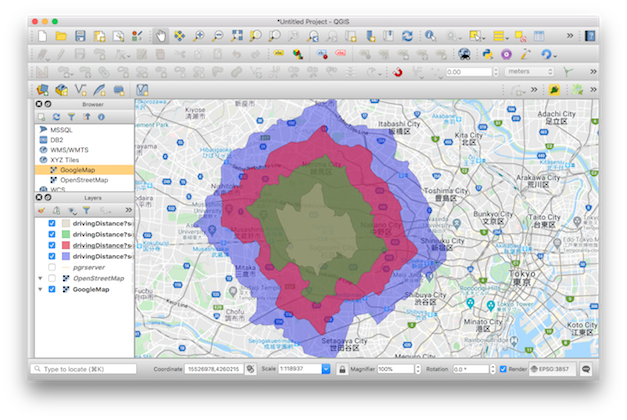
- ClosestFirstIterator ( for Driving Distance Isochrone creation )
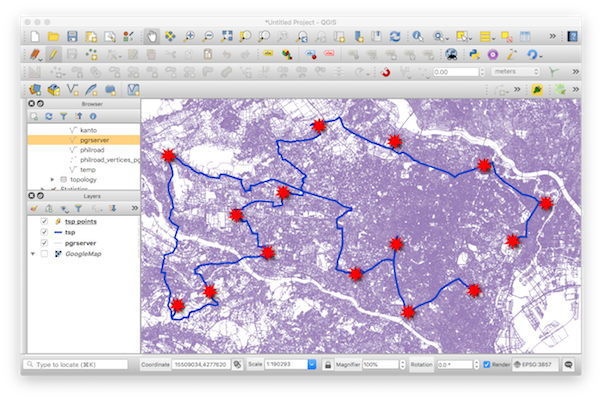
- NearestNeighborHeuristicTSP ( for Traveling Salesperson Problem )
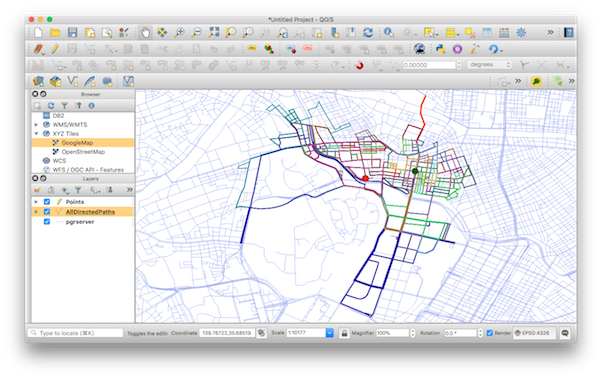
- All Directed Paths ( for sparse networks or short distance search)
- Bellman-Ford ( for sparse networks )
- BFS ( for sparse networks )
- Johnson ( for sparse networks )
- Floyd-Warshall ( for sparse networks )
(*Note: Initial call to a ContractionHierarchyBidirectionalDijkstra request will take time since a contraction graph will be created first. Subsequent calls will result in a much faster response.)
When to use pgrServer
-
When a web service is required to serve route data. pgrServer can be used to easily serve data to a variety of web or mobile application clients.
-
When the network is very dense and pgRouting struggles with long distance searches. pgrServer stores the entire graph into memory at start and can do route searches within the entire graph.
-
When performance is paramount. pgrServer can return routes within ~50 kilometer searches in milliseconds even in very dense networks.
-
When the cost (weight) of the graph is not dynamic. pgrServer can be used when the cost does not have to be computed at each request, since pgrServer only reads the cost whenever the graph is loaded. pgrServer can be forced to re-read the graph for routes that have semi-dynamic costs.
Requirements
- PostgreSQL > 9.4
- PostGIS
- PgRouting (to create a topology)
- Maven
- Tomcat Application Server for deployment
Preparing the Topology
-
Create a topology table. Refer to pgRouting's Documentations on the pgr_createTopology function.
-
Ensure that there is an index on an unique id field, an index on the source field, an index on the target field, and a spatial index on the geometry field of the topology table.
-
Create a View Table pgrserver based on the topology table that will contain the following fields: id, source, target, cost, geom.
CREATE VIEW pgrserver AS SELECT id,node_from AS source,node_to AS target,cost,wkb_geometry AS geom FROM kanto ; Building the Application
-
Edit src/main/resources/application.properties and modify the PostgreSQL Database URL and login parameters.
-
Create a WAR file that can be deployed to a Tomcat Server.
mvn clean install -DskipTests
- Or run and test the application with the built-in Tomcat container.
mvn spring-boot:run
Display the List of APIs
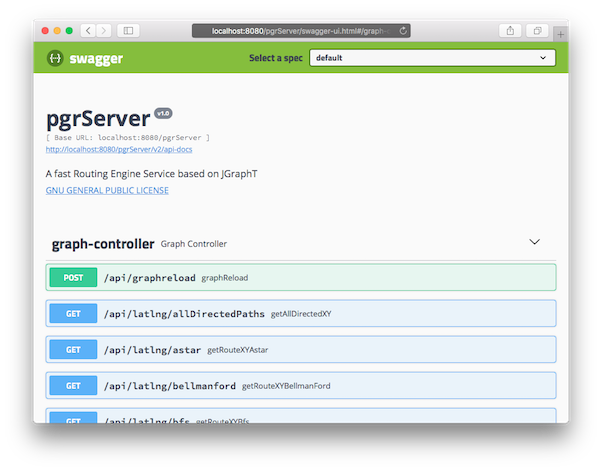
The list of APIs can be viewed by displaying the Swagger page:
http://localhost:8080/pgrServer/swagger-ui.htmlReload the Graph
To reload the graph if the cost has changed, send a POST request with the authcode parameter value. The authcode value can be set by updating the installed pgrs_auth table in the PostgreSQL database.
curl -X POST -F "authcode=abc12345" "http://localhost:8080/pgrServer/api/graphreload"Viewing the Data
pgrServer returns a GeoJSON object for the created route or driving distance polygon, hence any application that supports GeoJSON can be used to view the results.
To quickly view the results, GeoJSONLint web service can be used:
http://www.geojsonlint.comIt is also possible to use the result as a Vector Layer in QGIS by doing:
Layer -> Add Layer -> Add Vector Layer
and set the protocol to HTTP and add the URL request of pgrServer.