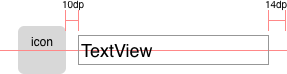
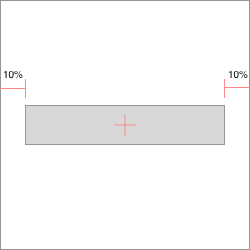
The idea is simple, use java expressions in layout params like layout_left="view1.right+10dp". It is helpful when LinearLayout and RelativeLayout is not enough for you.
<TextView
app:layout_left="icon.right+10dp"
app:layout_right="100%-14dp"
app:layout_centerY="icon.centerY"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
.../>
Try the sample apk: FlexLayout.apk
Add dependencies in your build.gradle:
dependencies {
compile 'com.github.mmin18:flexlayout:1.2.0'
}Or if you are using Eclipse, just copy FlexLayout.java and attrs.xml to your project.
| Horizontal | Vertical |
|---|---|
| layout_left | layout_top |
| layout_right | layout_bottom |
| layout_centerX | layout_centerY |
| layout_width | layout_height |
Remember the app:layout_width is different from android:layout_width
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
<Button
app:layout_left="10%"
app:layout_right="10%"
app:centerY="50%"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
../>
or
<Button
app:layout_width="80%"
app:centerX="50%"
app:centerY="50%"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
../>
Reference previous view using prev, next view using next (Position in the XML layout file)
<View ../> // prev = Previous view in xml layout file
<View
app:layout_left="prev.right"
app:layout_right="next.left"
app:layout_top="prev.top"
app:layout_bottom="next.bottom" />
<View ../> // next = Next view in xml layout file
Reference a specific view using view's id
<View
app:layout_left="view1.right"
app:layout_right="android:text1.left"
app:layout_top="view1.top"
app:layout_bottom="android:text1.bottom" />
<View android:id="@+id/view1"
../>
<View android:id="@android:id/text1"
../>
You can also use parent to reference the FlexLayout and this to reference the child view itself. Use screen to reference screen size.
| Properties | |
|---|---|
| left | top |
| right | bottom |
| centerX | centerY |
| width | height |
| visible | gone |
| *tag |
(screen, parent, this only support width and height property.)
view.visible: view.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE
view.gone: view.getVisibility() == View.GONE
view.tag: view.getTag(). Use View.setTag() to set a Number or Boolean and call View.requestLayout() to trigger layout. Types other than Number and Boolean returns 0.
The syntax is the same as Java or C. Numbers can have units like 10dp, 15sp
(parent.height-view1.centerY)/2
100%-80dp
max(view1.right, view2.right)
screen.width<screen.height ? 64dp : 48dp
view1.visible && view2.visible ? max(view1.bottom, view2.bottom) : 0px
Operators (Order in precedence)
| Operator | Associativity |
|---|---|
| () sp dp dip px pt mm in | Right |
| ! | Right |
| * / % | Left |
| + - | Left |
| <= < >= > | Left |
| == != | Left |
| && | Left |
| ll | Left |
| ?= | Right |
Functions
| Name |
|---|
| max(a,b) |
| min(a,b) |
| round(a) |
| ceil(a) |
| floor(a) |
| abs(a) |
| mod(a) |
| pow(a) |
Show source code position in XML when throw Exceptions. (Syntax exception, Circular dependency, etc.)
Initial release to jcenter. Including percentage, view reference, ?= expressions, logic operators.