Image compression algorithm, developed for research and educational purposes.
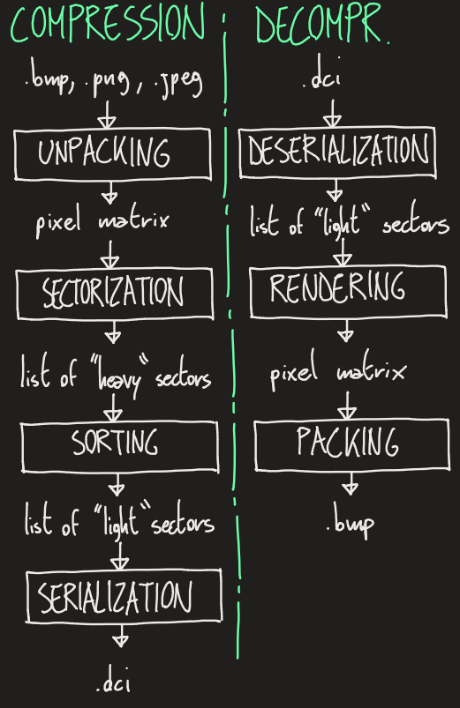
The dichotomic compression aims to minimize the size of a raster image by dinamically reducing the resolution. It is done by aggregating regions of homogeneous pixels into a single sector. The similarity of the region is regulated by the threshold value (in a range between 0-255).
What emerged from early experiments, is that we can see that the algorithm is best when compressing drawings, sketches, signs or car plates. It prioritizes high contrast details, such as lines, dots and texts.

These examples show the compressed file size compared to the original. Custom thresholds have been used.
This workflow doesn't have to implemented strictly: depending on the implementation, some steps can be (or must be) integrated with one another.
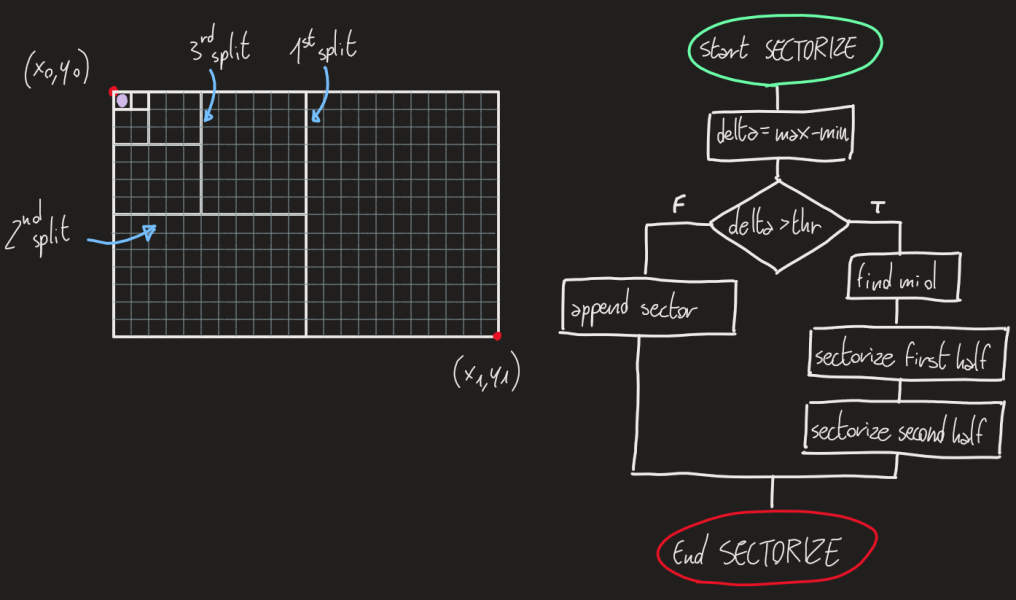
It's the core of the whole process. It's implemented in a recursive function that operates on the pixel matrix. The sectors, when found, are added to a proper list.
The "delta" is a 3-dimensional array, representing the absolute difference between channels of each pixel inside a sector. This mean that "details" (anything that will be preserved as a near original resolution) are usually high contrast regions.
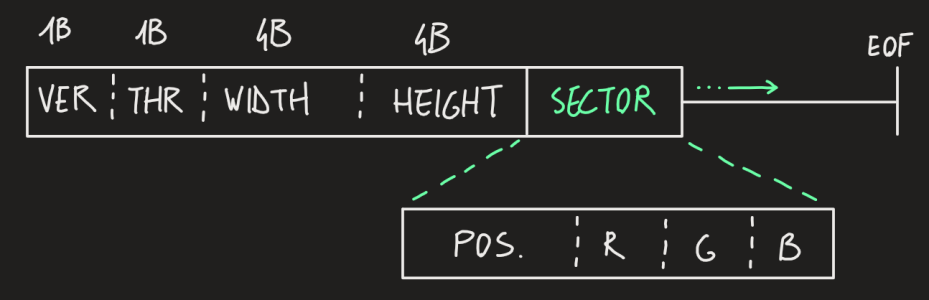
DCI (dichotmic compression image) is the format chosen to store the compressed image.
- Metadata (10 bytes)
- version (1 byte): specifies the version used
- threshold (1 byte): specifies the chosen threshold
- width (4 bytes): width of the original image
- height (4 bytes): height of the original image
- Sectors (variable length depending on sectors count and version)
- size/position: any data that can give information about the position of the sector
- color channels (RGB)
- Version 1
- Size/position: number of sectorizations done before getting to the sector itself (1 byte)
- RGB stored as 3 1-byte channels
- Final sector "weight": 4 bytes (32 bits)
- Version 2
- Applies the sectorization on the three separate color channels as if they were 3 different images.
- Size/position: number of sectorizations done before getting to the sector itself (1 byte)
- Color stored as 8-bit channel.
- Final sector "weight": 2 bytes (16 bits)
- Approximately 3 times more sectors
The repository only includes the source and the compilation script. In order to use it, you must first compile the source code with ./compile.sh.
In order to improve testing and usability of the dichotomic compression, a custom web application can been deployed on a self-hosted server. You can find the code in the ./web folder. The website allows the user to:
- compress any image, select version and threshold, take a look at the program output and download the
.dcifile - decompress any
.dcifile, take a look at the program output and download the decompressed image
Required
-cor-d: specifies compression or decompression-f FILENAME: specifies which file will be processed
Not required
-t THRESHOLD: specifies compression threshold-v VERSION: specifies used version (default 2)-V: verbose
./dc_core -c -f ../examples/lines.png -t 30 -VCompression (verbose, with custom threshold)./dc_core -d -f ../examples/lines.png.dci -VDecompression (verbose)