pip install pyspark-aifrom pyspark_ai import SparkAI
spark_ai = SparkAI()
spark_ai.activate() # active partial functions for Spark DataFrameIf you have set up the Google Python client, you can ingest data via search engine:
auto_df = spark_ai.create_df("2022 USA national auto sales by brand")Otherwise, you can ingest data via URL:
auto_df = spark_ai.create_df("https://www.carpro.com/blog/full-year-2022-national-auto-sales-by-brand")Take a look at the data:
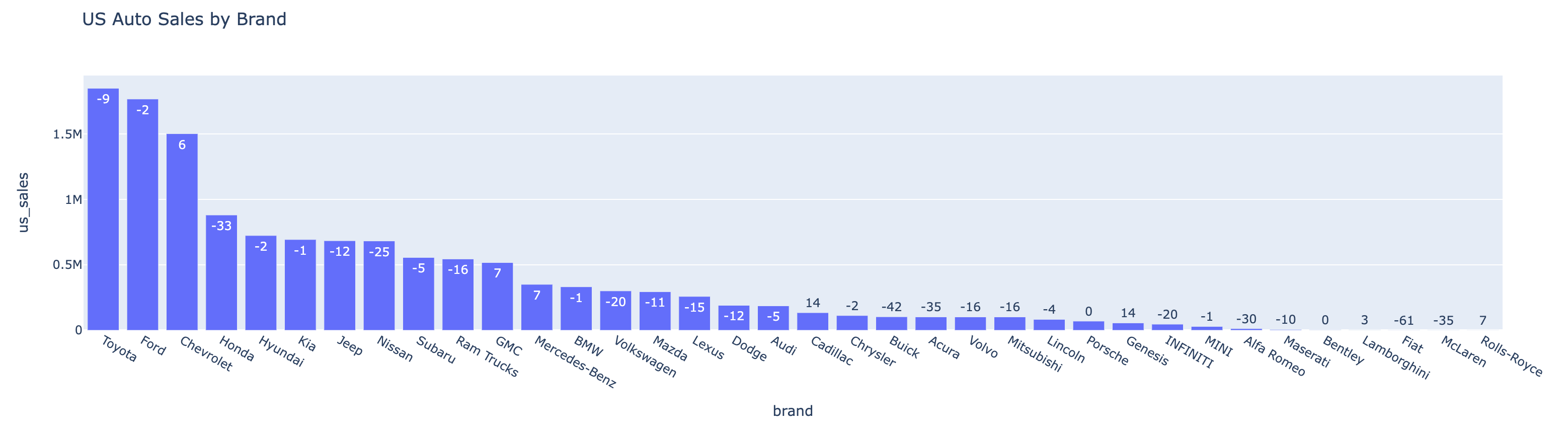
auto_df.show(n=5)| rank | brand | us_sales_2022 | sales_change_vs_2021 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Toyota | 1849751 | -9 |
| 2 | Ford | 1767439 | -2 |
| 3 | Chevrolet | 1502389 | 6 |
| 4 | Honda | 881201 | -33 |
| 5 | Hyundai | 724265 | -2 |
auto_df.ai.plot()To plot with an instruction:
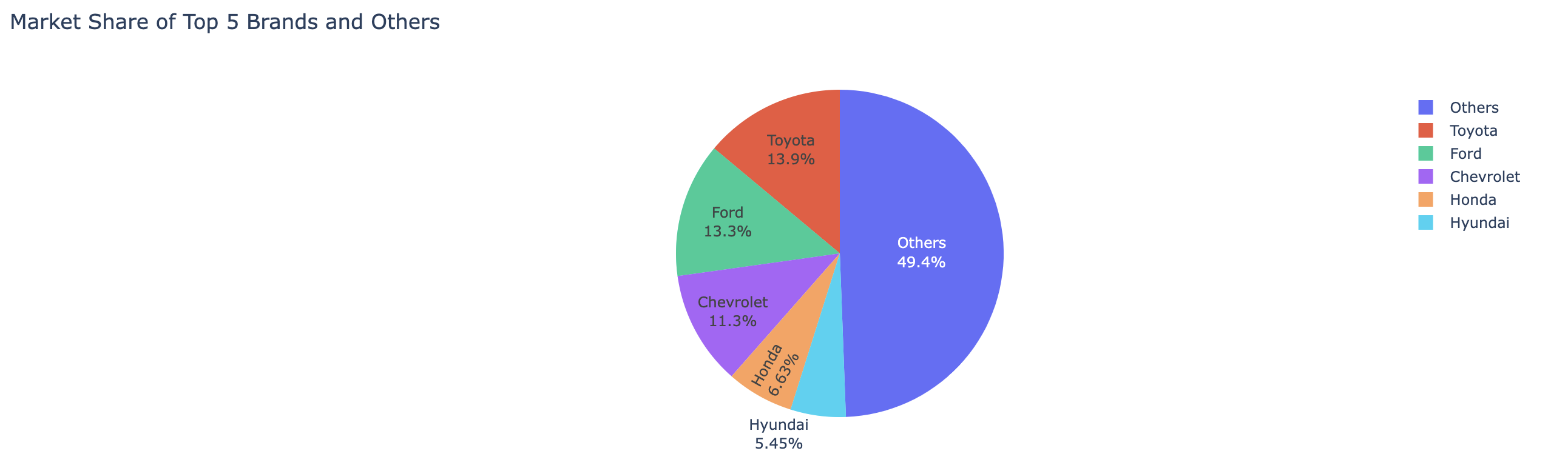
auto_df.ai.plot("pie chart for US sales market shares, show the top 5 brands and the sum of others")auto_top_growth_df=auto_df.ai.transform("brand with the highest growth")
auto_top_growth_df.show()| brand | us_sales_2022 | sales_change_vs_2021 |
|---|---|---|
| Cadillac | 134726 | 14 |
auto_top_growth_df.ai.explain()In summary, this dataframe is retrieving the brand with the highest sales change in 2022 compared to 2021. It presents the results sorted by sales change in descending order and only returns the top result.
auto_top_growth_df.ai.verify("expect sales change percentage to be between -100 to 100")result: True
@spark_ai.udf
def previous_years_sales(brand: str, current_year_sale: int, sales_change_percentage: float) -> int:
"""Calculate previous years sales from sales change percentage"""
...
spark.udf.register("previous_years_sales", previous_years_sales)
auto_df.createOrReplaceTempView("autoDF")
spark.sql("select brand as brand, previous_years_sales(brand, us_sales, sales_change_percentage) as 2021_sales from autoDF").show()| brand | 2021_sales |
|---|---|
| Toyota | 2032693 |
| Ford | 1803509 |
| Chevrolet | 1417348 |
| Honda | 1315225 |
| Hyundai | 739045 |
The SparkAI supports a simple in-memory and persistent cache system. It keeps an in-memory staging cache, which gets updated for LLM and web search results. The staging cache can be persisted through the commit() method. Cache lookup is always performed on both in-memory staging cache and persistent cache.
spark_ai.commit()Refer to example.ipynb for more detailed usage examples.
Pull requests are welcome. For major changes, please open an issue first to discuss what you would like to change.
Licensed under the Apache License 2.0.