Btree2pcode-machine
Evolution of previous approaches of pcode utilization
Compiling
gcc -o btree2pcode main.c btree2rpn.c rpn2pci.c pcode.c
Running
./btree2pcode filename numValues
- filename: Name of file (Must be in same folder of btree2pcode.c)
- numValues: Number of values in input file (include 0, see next section)
Input
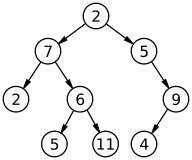
This program accepts as input a comma-separated text file that represents the nodes of a binary tree. The root is the first value, left nodes (2 * pos + 1) and right nodes (2 * pos+2), where pos is the position of father in array.
Examples:
The input file for tree above is: 2,7,5,2,6,0,9,0,0,5,11,0,0,4 (Note 0's to fill the empty nodes)
The input file for tree above is: *,~,6,+,0,0,0,10,5 (Note 0's to fill the empty nodes)
Assumptions
- Your tree has nodes on right position
- A postorder search on that tree will return a valid Reverse Polish Notation.
Glossary
- Inst: Instruction's name;
- Level: Instruction's level (nesting in recursive calls) field;
- Arg: Instruction's argument (address or data) field;
- Top: Stack's top pointer;
- Counter: Program counter (current instruction in instructions array);
- Base: Points to the base address in the stack for the current invocation of a given procedure;
- Stack: A vector used as a datastore for mutable data. All values are integers.
Example
Running: ./btree2pcode input.txt 9
Input: *,~,6,+,0,0,0,10,5
Reverse Polish Notation: 10 5 + ~ 6 *
Output:
Inst Level Arg Top Counter Base Stack
INT 0 9 9 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
LIT 0 10 10 2 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 10
STO 0 0 9 3 1 10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
LIT 0 5 10 4 1 10 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5
STO 0 1 9 5 1 10 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
LOD 0 1 10 6 1 10 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5
LOD 0 0 11 7 1 10 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 5 10
OPR 0 2 10 8 1 10 5 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 15
STO 0 2 9 9 1 10 5 15 0 0 0 0 0 0
LOD 0 2 10 10 1 10 5 15 0 0 0 0 0 0 15
OPR 0 1 10 11 1 10 5 15 0 0 0 0 0 0 -15
STO 0 2 9 12 1 10 5 -15 0 0 0 0 0 0
LIT 0 6 10 13 1 10 5 -15 0 0 0 0 0 0 6
STO 0 3 9 14 1 10 5 -15 6 0 0 0 0 0
LOD 0 3 10 15 1 10 5 -15 6 0 0 0 0 0 6
LOD 0 2 11 16 1 10 5 -15 6 0 0 0 0 0 6 -15
OPR 0 4 10 17 1 10 5 -15 6 0 0 0 0 0 -90
STO 0 4 9 18 1 10 5 -15 6 -90 0 0 0 0
OPR 0 0 0 -15 5