Tim-Oliver Buchholz*,1,2, Mangal Prakash*,1,2,, Alexander Krull1,2,3, and Florian Jug1,2,^
1 Max Planck Institute of Molecular Cell Biology and Genetics, Dresden, Germany
2 Center for Systems Biology, Dresden, Germany
3 Max Planck Institute for Physics of Complex Systems, Dresden, Germany
^ jug@mpi-cbg.de
* Equal contribution (alphabetical order).
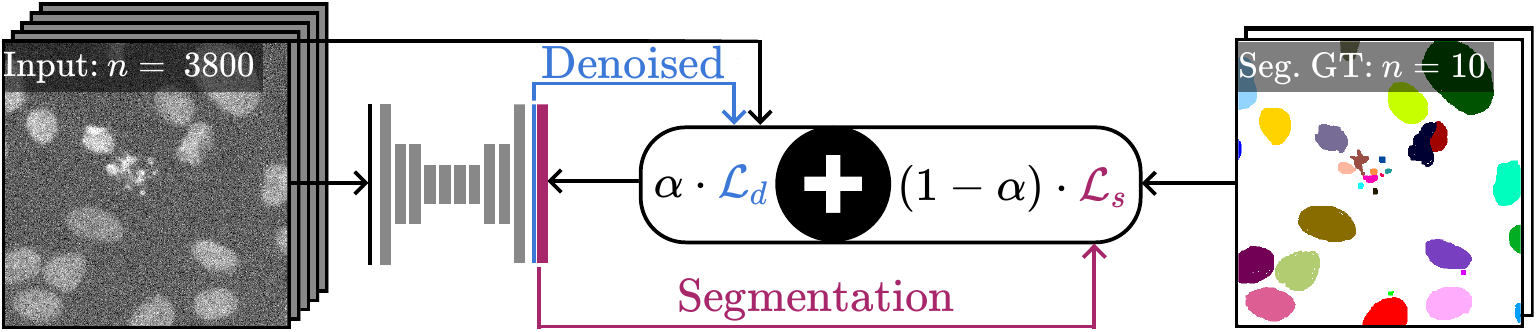
Microscopy image analysis often requires the segmentation of objects, but training data for this task is typically scarce and hard to obtain. Here we propose DenoiSeg, a new method that can be trained end-to-end on only a few annotated ground truth segmentations. We achieve this by extending Noise2Void, a self-supervised denoising scheme that can be trained on noisy images alone, to also predict dense 3-class segmentations. The reason for the success of our method is that segmentation can profit from denoising, especially when performed jointly within the same network. The network becomes a denoising expert by seeing all available raw data, while co-learning to segment, even if only a few segmentation labels are available. This hypothesis is additionally fueled by our observation that the best segmentation results on high quality (very low noise) raw data are obtained when moderate amounts of synthetic noise are added. This renders the denoising-task non-trivial and unleashes the desired co-learning effect. We believe that DenoiSeg offers a viable way to circumvent the tremendous hunger for high quality training data and effectively enables few-shot learning of dense segmentations.
Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2005.02987
This implementation requires Tensorflow. We have tested DenoiSeg on LinuxMint 19 using python 3.6 and 3.7 and tensorflow-gpu 1.15.
We recommend using miniconda. If you do not yet have a strong opinion, just use it too!
After installing Miniconda, the following lines might are likely the easiest way to get Tensorflow and CuDNN installed on your machine (Note: Macs are not supported, and if you sit on a Windows machine all this might also require some modifications.):
$ conda create -n 'denoiSeg' python=3.7
$ source activate denoiSeg
$ conda install cudatoolkit=10.1 cudnn
$ pip install tensorflow==2.3
$ pip install jupyter
$ conda install nb_conda
Note: it is very important that the version of keras be 2.2.4 or 2.2.5, hence the explicit installation above. Once this is done (or you had tensorflow et al. installed already), you can install DenoiSeg with one of the following two options:
$ pip install denoiseg
This option is ideal if you want to edit the code. Clone the repository:
$ git clone https://github.com/juglab/DenoiSeg.git
Change into its directory and install it:
$ cd DenoiSeg
$ pip install -e .
You are now ready to run DenoiSeg.
Have a look at our jupyter notebook:
@inproceedings{BuchholzPrakash2020DenoiSeg,
title={DenoiSeg: Joint Denoising and Segmentation},
author={Tim-Oliver Buchholz and Mangal Prakash and Alexander Krull and Florian Jug},
year={2020}
}
The current release and master is a refactored version of the code used for the paper. This refactored version produces the same number as reported in the paper, but if you wish to use the exact code used in the paper, please continue here.
Further results (qualitative and quantitative) can be found on the wiki.