Table of contents generated with markdown-toc
GoMark is a tool for system status monitoring and it implements some variables exactly like bvar in brpc, but using go instead of c++.
For more detailed information, see: https://github.com/apache/incubator-brpc/blob/master/docs/en/bvar.md
gomark monitor variable statistics through HTTP web server, so you need call
StartHTTPServer(port int)to start HTTP service before using.
Maybe you have your own HTTP server and you wish to dock gomark to it instead of create a new one. GoMark actually supports this deployment. You need:
GoMark requires the following routers:
r := mux.NewRouter()
r.HandleFunc("/vars/js/{script}", procJs) // Route: js
r.HandleFunc("/vars", procVar) // Route: vars
r.HandleFunc("/vars/{var}", procVar) // Route: vars
r.HandleFunc("/vars/debug", procDebug) // Route: debugHere {xxx} indicates a path variable, like/vars/test_adder or /vars/*adder*.
Note that each router may require additional path parameters in form ?a=b or ?a, like /vars/test_adder?dataonly, here dataonly is a parameter, or /vars/debug?p=1, here p is a parameter.
Both path variables or parameters are stored in gmi.Request along with headers:
type Request struct {
Router Route
Params map[string]string
headers map[string]string
}You need fill them from HTTP request.
Note that for path variable, you need use word inside {} in route definition above as key in Request.Params.
You may note that no URL is required here, that's because Router defines a string to represent above routes, see comments after each definition.
Like gmi.Request, gmi.Response defines all information you need to write into HTTP response, make sure you write them all.
type Response struct {
Status int
headers map[string]string
Body []byte
}In your routing handler, you need convert HTTP request to gmi.Request and call gomark.Request, and write returned gmi.Response to HTTP response.
/vars/js/jquery_minshould deliver params:{"script": "jquery_min"}, route:"js", herescriptcomes from path variable definition in route./vars/debug?p=1should deliver params:{"p": "1"}, route:"debug". DO NOT add parameter{"var": "debug"}./vars/*latency*,*add*?dataonly&v=1should deliver params:{"var": "*latency*,*add*", "dataonly":"", "v": "1"}, route:"var". Note heredataonlytakes no value and SHOULD NOT be ignored, andvaras key comes from path variable definition in route.
A variable is an entity that maintains all information of statistics. There are several variables, and can be created by:
NewLatencyRecorder
NewAdder
NewCounter
NewQPS
NewMaxer
NewWindowMaxer
Each of above will create a variable and returns as gmi.Marker, which is an interface:
// Marker is an interface to provide variable marking.
type Marker interface {
// Mark a number, the number definition is bound to marker itself.
Mark(n int32)
// Stop this marking.
Cancel()
}Call Mark to send a marking point to variable and Cancel to stop using(and never use it).
If you need to use latency recorder and use millisecond as time unit, you may be interested in gmi.Latency. It record a start point of time on creation, and calculate milliseconds since creation on marking. Here is how to use:
// create a latency recorder
lr = gomark.NewLatencyRecorder("test")
// at start point, create a latency with latency recorder
latency = gomark.NewLatency(lr)
// at end point, call Latency.Mark()
latency.Mark()
// Now latency will calculate duration between start point and end point in millisecond
// and call latency recorder to markgomark is designed to work on GO. But it also provide an adapter to work with C/CPP.
adapter provide C interfaces to call variable create/mark/cancel of gomark package. It works along with hook, which is a sub-project of gomark compiling to be a dynamic library libgmhook.so for C/CPP users.
This is how it works:
- gomark user calls
adapter.StartAdapterto enable hook connected with gomark by registering C callbacks to create/mark/cancel variables(register_gm_hook). - C program working with gomark should directly call
gm_var_create/gm_var_mark/gm_var_cancelinlibgmhook.soto use gomark through adapter(adatper will call registered gomark callbacks). - CPP program working with gomark may delcare
GmVariabledefined in gmhookpp to use gomark also through adatper.
To use this feature, gomark user need:
- make hook and install, see readme
- GO program should call
adapter.StartAdapter - add these two CGO flags in environment before building to let adapter found
libgmhook.soandgmhook.h
export CGO_CFLAGS="-I/path_to_install_of_hook/include"
export CGO_LDFLAGS="-L/path_to_install_of_hook/lib -lgmhook"example shows how to use adder and latency recorder. Actually all variables are used in the same way:
- create
- mark int32 values
- cancel
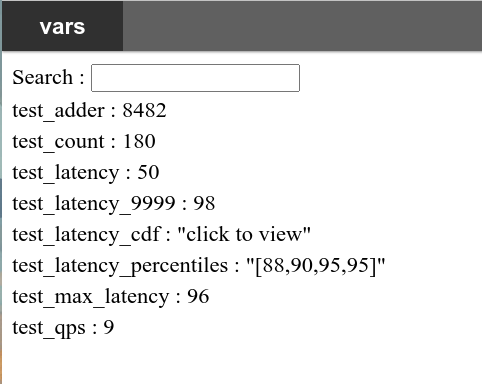
Visit http://ip:port/vars to monitor system statistics.
This is how it looks like:
You may click those clickable records, and you will see:
Test method: in one goroutine, continuouesly marking for 10 million marks, get the time elasped and calculate how many marks can be done in one second(QPS).
updated 2020.11.19
| Variable | QPS |
|---|---|
| MaxWindow | 6214338 |
| Maxer | 6497730 |
| Adder | 6445707 |
| LatencyRecorder | 5411037 |
| QPS | 6837910 |
| Counter | 6163937 |
cmd/main/gomark.go is used run tests. It use glog for logging, so add -stderrthreshold=INFO in command line:
go run gomark.go -stderrthreshold=INFO
Read the usage and run test.
- Provide interface for Prometheus