Multi-Label Annotation of Text Reports from Computed Tomography of the Chest Abdomen and Pelvis Using RBA and Deep Learning
This Repo contains the updated implementation of our paper "Multi-Label Annotation of Text Reports from Computed Tomography of the Chest Abdomen and Pelvis Using Deep Learning" (Will be Submitted to BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making) a pre-print is available: "Multi-Label Annotation of Chest Abdomen Pelvis Computed Tomography Text Reports Using Deep Learning" : https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.02959
@misc{danniballe2021multilabel,
title={Multi-Label Annotation of Chest Abdomen Pelvis Computed Tomography Text Reports Using Deep Learning},
author={Vincent M. D'Anniballe and Fakrul I. Tushar and Khrystyna Faryna and Songyue Han and Maciej A. Mazurowski and Geoffrey D. Rubin and Joseph Y. Lo},
year={2021},
eprint={2102.02959},
archivePrefix={arXiv},
primaryClass={cs.AI}
}D'Anniballe, V.M., Tushar, F.I., Faryna, K., Han, S., Mazurowski, M.A., Rubin, G.D., Lo, J.Y., 2021.
Multi-Label Annotation of Chest Abdomen Pelvis Computed Tomography Text Reports Using Deep Learning, p. arXiv:2102.02959.Purpose: To develop high throughput multi-label annotatorsfor body (chest, abdomen, and pelvis) Computed Tomography (CT) reports that can be applied across a variety of abnormalities, organs, and disease states.
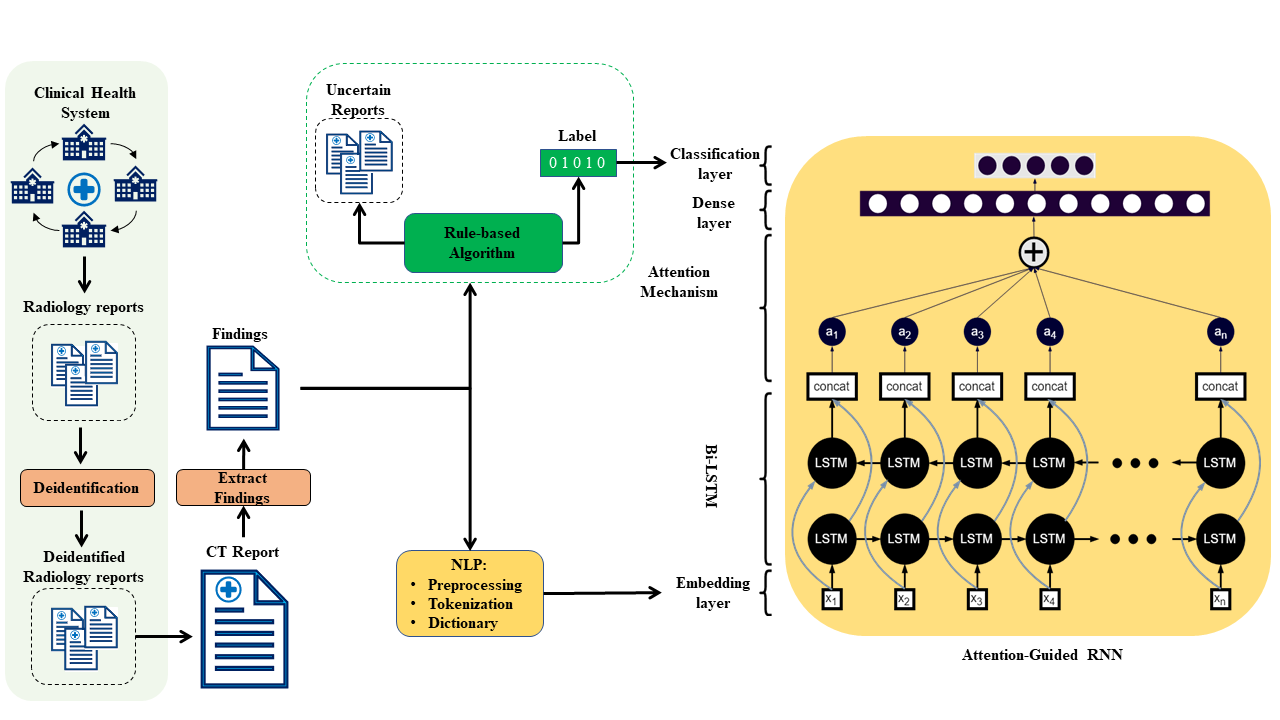
Approach: We used a dictionary approach to develop rule-based algorithms (RBA) for extraction of disease labels from radiology text reports. We targeted three organ systems (lungs/pleura, liver/gallbladder, kidneys/ureters) with four diseases per system based on their prevalence in our dataset. To expand the algorithms beyond pre-defined keywords attention-guided recurrent neural networks (RNN) were trained using the RBA-extracted labels to classify reports as being positive for one or more diseases or normal for each organ system. Confounding effects on model performance were evaluated using random initialization or pre-trained embedding as well as different sizes of training datasets. Performance was evaluated using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) area under the curve (AUC) against 2,158 manually obtained labels.
Results: Our models extracted disease labels from 261,229 radiology reports of 112,501 unique subjects. Pre-trained models outperformed random initialization across all diseases. As the training dataset size was reduced, performance was robust except for a few diseases with relatively small number of cases. Pre-trained classification AUCs achieved > 0.95 for all five disease outcomes across all three organ systems.
Conclusions: Our label-extracting pipeline was able to encompass a variety of cases and diseases by generalizing beyond strict rules with exceptional accuracy. This method can be easily adapted to enable automated labeling of hospital-scale medical data sets for training image-based disease classifiers.
This Study Contains main two parts:
-
- Developed and Used RBA to generate labels from radiology reports.
-
- Using generated label data reained Deep learning model to classify radiology text.
we used a dictionary approach to develop a rule-based algorithm (RBA) for extraction of disease labels from radiology text reports
-
- Use this docker container to run the RBA codes
docker pull ft42/ct_predict_ft42:rba_tf2_gpu_py3
- Use this docker container to run the RBA codes
-
- RBA codes are given in Directory
RBA- i) Lungs_RBA-|->Lungs RBA codes
a) RBA_Lung_Config.py |-- Configuration file of RBA to input data, dictonary and path to save created dictonary. b) RBA_Lungs.py |-- RBA Main.py.
- ii) Liver_RBA-|->Liver RBA codes
a) RBA_Liver_Config.py |-- Configuration file of RBA to input data, dictonary and path to save created dictonary. b) RBA_Liver.py |-- RBA Main.py. c) RBA_Liver_Statistics.py |-- generate Satatistics
- iii) Kidneys_RBA-|->Kidneys RBA codes
a) RBA_Kidneys_Config.py |-- Configuration and RBA are inside the code this is main RBA py for kedney. b) RBA_Kidneys.py |-- RBA Main.py. c) RBA_Kidneys_Statistics.py |-- generate Satatistics
- RBA codes are given in Directory
RBA_Lung_Config.py.py
####0000000000000-----INPUTS----------0000
REPORT_CSV="/path/to/report/csv/report.csv"
LUNG_ORGAN_LIST = ['lung',
['lung','pulmonary'],
['lung', 'pulmonary', '(lower|upper|middle)\s+lobe', 'centrilobular', 'perifissural','(left|right)\s+base\s', 'bases', 'basilar', 'bronch', 'trachea', 'airspace', 'airway']]
COMMON_DIS_LIST = ['mass','opaci', 'calcul', 'stone', 'scar', 'metas', 'malignan', 'cancer', 'tumor', 'neoplasm', 'lithiasis', 'atroph', 'recurren',
'hyperenhanc' , 'hypoenhanc', 'aneurysm', 'lesion', 'nodule', 'nodular', 'calcifi', 'opacit', 'effusion', 'resect', 'thromb', 'infect', 'infarct',
'inflam', 'fluid', 'consolidat', 'degenerative', 'dissect', 'collaps', 'fissure', 'edema', 'cyst', 'focus', 'angioma', 'spiculated', 'architectural\s+distortion',
'lytic', 'pathologic', 'defect', 'hernia', 'biops', 'encasement', 'fibroid', 'hemorrhage', 'multilocul', 'distension','distention', 'stricture', 'obstructi',
'hypodens', 'hyperdens', 'hypoattenuat', 'hyperattenuat', 'necrosis', 'irregular', 'ectasia', 'destructi', 'dilat', 'granuloma', 'enlarged', 'abscess', 'stent',
'fatty\s+infiltr', 'stenosis', 'delay', 'carcinoma', 'adenoma', 'atrophy', 'hemangioma', 'density', 'surgically\s+absent']
LUNG_DIS_LIST=['pneumothorax', 'emphysema', 'pneumoni', 'ground\s+glass', 'aspiration', 'bronchiectasis', 'atelecta', 'embol', 'fibrosis','air\s+trapping','pleural\s+effusion','pneumonectomy']
ABANDON_LIST = ['postsurgical', 'posttreatment', 'postradiation', 'postoperative', 'cholecystectomy', 'resection', 'cholelithiasis','cystectomy']
PATH_TO_SAVE_CSV="/path/to/save/dictonary/and/data/satatistics/Save_Satatistics/"
####-------|Statistics-----inputs-----------------|----###
LIST_FOR_OVERLAP_STATISTICS=['normal','mass','opaci', 'calcul', 'stone', 'scar', 'metas', 'malignan', 'cancer', 'tumor', 'neoplasm', 'lithiasis', 'atroph', 'recurren','pleural\s+effusion',
'hyperenhanc' , 'hypoenhanc', 'aneurysm', 'lesion', 'nodule', 'nodular', 'calcifi', 'opacit', 'effusion', 'resect', 'thromb', 'infect', 'infarct',
'inflam', 'fluid', 'consolidat', 'degenerative', 'dissect', 'collaps', 'fissure', 'edema', 'cyst', 'focus', 'angioma', 'spiculated', 'architectural\s+distortion',
'lytic', 'pathologic', 'defect', 'hernia', 'biops', 'encasement', 'fibroid', 'hemorrhage', 'multilocul', 'distension','distention', 'stricture', 'obstructi',
'hypodens', 'hyperdens', 'hypoattenuat', 'hyperattenuat', 'necrosis', 'irregular', 'ectasia', 'destructi', 'dilat', 'granuloma', 'enlarged', 'abscess', 'stent',
'fatty\s+infiltr', 'stenosis', 'delay', 'carcinoma', 'adenoma', 'atrophy', 'hemangioma', 'density', 'surgically\s+absent','pneumothorax', 'emphysema', 'pneumoni', 'ground\s+glass',
'aspiration', 'bronchiectasis', 'atelecta', 'embol', 'fibrosis','air\s+trapping']
DISEASE_NAME_AND_NUMBERS=PATH_TO_SAVE_CSV+"LungDisease_NameAndNumberDecending.csv"
DISEASE_COUNT_THRESHOLD= 1- Docker container to use is
docker pull ft42/ct_predict_ft42:nlp_tf2_gpu_py3 - NLP directory contains all the data, Training and Deploy codes Folder orientation are as fellowing
* 1) Lung_Classification--|-> |-->Multi_Label--|-> a) config.py |-- Training Configuration |-> b) model.py |-- Attention guided RNN |-> c) Train.py |-- Traing Main py. |-> d) loss_funnction_And_matrics.py |-- loss functions. |-->Multi_Label_Pretrained--|-> a) config.py |-- Training Configuration |-> b) model.py |-- Attention guided RNN |-> c) Train.py |-- Traing Main py. |-> d) loss_funnction_And_matrics.py |-- loss functions. |---> Deploy----|-> a) deploy_config |-- Training Configuration |-> b) model.py |-- Attention guided RNN |-> c) loss_funnction_And_matrics.py |-- loss functions. |-> d) nlp_predict.py |-- Multi-label prediction. |-> e) nlp_predict_Binary.py |-- Binary prediction. |-> f) nlp_predict_save_html.py |-- Generating HTML Heatmaps. |-> g) loss_funnction_And_matrics.py |-- loss functions.
- Pretrained Embadding can be accesed at:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41597-019-0055-0
- To train All you need is to config the config.py based on your data, paths and requeirement, and use the command
python Train.py
config.py
import tensorflow as tf
from loss_funnction_And_matrics import*
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(42) # Define random seed for the reproducability
####---Input-Data---###
TRAIN_CSV="/image_data/Scripts/NLP_Classification_CNN/Lung_Classification/Lung_Train_csv.csv" # Training data-sampled are in folder
VAL_CSV="/image_data/Scripts/NLP_Classification_CNN/Lung_Classification/Lung_Val_csv.csv" #validation data in folder
#-----using which sections you want to train the model define the column name
#choice['text_finding_impression_list','text_impression_only' ,'text_Finding_only']
REPORT_TEXT_COLUMN_NAME='text_Finding_only'
LABELS_COLUMN_NAMES=['lung_atelecta_lbl','lung_nodule_lbl','lung_emphysema_lbl','lung_pleural_effusion_lbl','lung_normal_lbl'] # Label columns name
#=-----Model Configuration----###
NUMBER_OF_CLASSES=5
MAX_WORDS=650
EMBADDING_DIMENTION=200
USING_PRE_TRAINED_EMBADDING=False # (True/False) if True: Will use Pretrained Embading
PRE_TRAINING_EMBADDING="/image_data/Scripts/BioWordVec_PubMed_MIMICIII_d200.vec.bin.gz"
###----Resume-Training----###
RESUME_TRAINING=0
RESUME_TRAIING_MODEL='/image_data/Scripts/NLP_Classification_CNN/Lung_Classification/Multi_Label/Model_Multi_Label/'
TRAINING_INITIAL_EPOCH=0
##--------Training-----Hyperperametter---------
TRAING_EPOCH=50
TRAIN_CLASSIFY_LEARNING_RATE =1e-4
TRAIN_CLASSIFY_LOSS=Weighted_BCTL #tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy() #Weighted_BCTL
OPTIMIZER=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=TRAIN_CLASSIFY_LEARNING_RATE,epsilon=1e-5)
TRAIN_CLASSIFY_METRICS=tf.keras.metrics.AUC()
BATCH_SIZE=512
SHUFFLE=True
###-------SAVING_UTILITY-----########
ModelCheckpoint_MOTITOR='val_loss'
TRAINING_SAVE_MODEL_PATH='/image_data/Scripts/NLP_Classification_CNN/Lung_Classification/Multi_Label/Model_Multi_Label/'
TRAINING_CSV='Lung_Multi.csv'
LOG_NAME="Log_Lung_Multi"
MODEL_SAVING_NAME="nlp_Lung_Multi_label{val_loss:.2f}_{epoch}.h5"- To Deploy All you need is to config the deploy_config.py based on your data, paths and requeirement, and use the command
python nlp_predict.py if predicting only or python nlp_predict_save_html.py to saved attention ot heatmaps by the RNN
- deploy_config
import tensorflow as tf
from loss_funnction_And_matrics import*
import numpy as np
np.random.seed(42)
#---Defining the punctuations to remove
PUNCTUATION=['"', ':', ')', '(', '-', '!', '?', '|', ';', "'", '$', '&', '/', '[', ']', '>', '%', '=', '#', '*', '+', '\\', '•', '~', '@', '£',
'·', '_', '{', '}', '©', '^', '®', '`', '<', '→', '°', '€', '™', '›', '♥', '�', '×', '§', '″', '′', 'Â', '█', '½', 'à ', '…',
'“', '★', '�', '–', '�', 'â', '►', '−', '¢', '²', '¬', '░', '¶', '↑', '±', '¿', '▾', '�', '¦', '║', '―', '¥', '▓', '—', '‹', '─',
'▒', ':', '¼', '⊕', '▼', '▪', '†', '■', '’', '▀', '¨', '▄', '♫', '☆', 'é', '¯', '♦', '¤', '▲', 'è', '¸', '¾', 'Ã', '⋅', '‘', '∞',
'∙', ')', '↓', '�', '│', '(', '»', ',', '♪', '╩', '╚', '³', '・', '╦', '╣', '╔', '╗', '▬', '�', 'ï', 'Ø', '¹', '≤', '‡', '√', ]
#=-----Model Configuration----###
NUMBER_OF_CLASSES=5
MAX_WORDS=650
EMBADDING_DIMENTION=200
USING_PRE_TRAINED_EMBADDING=True # (True/False) if True: Will use Pretrained Embading
PRE_TRAINING_EMBADDING="/image_data/Scripts/BioWordVec_PubMed_MIMICIII_d200.vec.bin.gz"
##---Training--Hyperperametter---###
TRAIN_CLASSIFY_LEARNING_RATE =1e-4
TRAIN_CLASSIFY_LOSS=Weighted_BCTL #tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy() #Weighted_BCTL #tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy() #Weighted_BCTL
OPTIMIZER=tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(lr=TRAIN_CLASSIFY_LEARNING_RATE,epsilon=1e-5)
TRAIN_CLASSIFY_METRICS=tf.keras.metrics.AUC()
####---Input-Data---###---Lungs
TEST_CSV="/image_data/Scripts/NLP_Classification_CNN/Lung_Manual_Test_set_patient.csv"
REPORT_TEXT_COLUMN_NAME='text_Finding_only'
#['text_finding_impression_list','text_impression_only' ,'text_Finding_only']
SUBJECT_ID_COLUMN_NAME='Report_id'
LABELS_COLUMN_NAMES=['lung_atelecta_lbl','lung_nodule_lbl','lung_emphysema_lbl','lung_pleural_effusion_lbl','lung_normal_lbl']
LABELS_COLUMB_BINARY_LABEL_NAME=['lung_normal_lbl']
#-----Multi-label
TOKENIZER_PICKLE="/image_data/Scripts/NLP_Classification_CNN/Lung_Classification/Multi_Label_Pretrained/tokenizer.pickle"
MODEL_WIGHT='nlp_Lung_Multi_Label_Pretrained_weight.h5'
SAVING_CSV="nlp_Lung_Multi_Label_Pretrained_Test_ManualTest_html.csv"
SAVING_HTML_FILE='/path/to/save/html/MultiLabel_Pretrained_ManualTestset_HTML/'