1. 参考资料
- https://hadyang.github.io/interview/docs/basic/algo/hash/
- https://hadyang.github.io/interview/docs/java/collection/HashMap/
- https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Hashtable.html
2. 简述
java.util.HashMap(下文简称为 HashMap) 和 java.util.Hashtable(下文简称为 Hashtable) 都实现了 java.util.Map 接口,
它们的源码有不少相通之处,将两者的源码结合起来看,会有新的收获。
Hashtable 的源文件有一千多行(虽然有很多行是注释,但是总的代码量还是挺大的),如果每一行都细看,则要花费不少时间。本文只涉及如下三部分内容
Hashtable中的重要字段Hashtable的创建以及增删查改的操作Hashtable与HashMap的区别
2.1 Hashtable 中的重要字段
本文只涉及如下5个字段
table字段count字段threshold字段loadFactor字段modCount字段
2.1.1 table 字段
table 字段用于保存 Hashtable 中的桶, table.length 的值就是桶的数量
/**
* The hash table data.
*/
private transient Entry<?,?>[] table;table 是 Entry 类型的数组,而 Entry 是 Hashtable 的静态内部类
/**
* Hashtable bucket collision list entry
*/
private static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
// hash 值
final int hash;
// kv 对的 k
final K key;
// kv 对的 v
V value;
// 下一个元素
Entry<K,V> next;
// 构造函数和方法都略去了
}Entry 实例连接在一起就构成了单链表。
2.1.2 count 字段
count 字段用于保存 Hashtable 中 Entry 实例的数量(也就是 kv 对的数量)
/**
* The total number of entries in the hash table.
*/
private transient int count;2.1.3 threshold 字段
threshold 字段用于保存阈值(判断是否需要扩容的逻辑与阈值有关)
/**
* The table is rehashed when its size exceeds this threshold. (The
* value of this field is (int)(capacity * loadFactor).)
*
* @serial
*/
private int threshold;2.1.4 loadFactor 字段
loadFactor 字段用于保存负载因子,当 Hashtable 中的元素数量超过 table.length * loadFactor 时,就会触发扩容机制(扩容后,桶的数量会变多)。有的构造函数会将 loadFactor 的值设置成 0.75f(下文会看到)
/**
* The load factor for the hashtable.
*
* @serial
*/
private float loadFactor;2.1.5 modCount 字段
modCount 字段用于保存 Hashtable 经历过的结构性变更的次数
/**
* The number of times this Hashtable has been structurally modified
* Structural modifications are those that change the number of entries in
* the Hashtable or otherwise modify its internal structure (e.g.,
* rehash). This field is used to make iterators on Collection-views of
* the Hashtable fail-fast. (See ConcurrentModificationException).
*/
private transient int modCount = 0;2.2 Hashtable 的创建以及增删查改的操作
Hashtable 的 创建 是通过构造函数完成的,相关内容在 2.2.1 小节。
Hashtable 的 增 和 改 是通过 put(...) 方法完成的,相关内容在 2.2.2 小节。
Hashtable 的 查 是通过 get(...) 方法完成的,相关内容在 2.2.3 小节。
Hashtable 的 删 是通过 remove(...) 方法完成的,相关内容在 2.2.4 小节。
Hashtable 的 增删查改 都涉及如下步骤
- 计算
key对应的hash值 - 计算
hash值对应的桶的下标(桶中要么是null,要么就是一个单链表的头元素) - 遍历第2步提到的单链表,查找与
key匹配的Entry
2.2.1 Hashtable 的创建逻辑
Hashtable 的构造函数有4个,具体如下
- 指定
initialCapacity(初始容量) 和loadFactor(负载因子)
initialCapacity 这个参数用于指定初始的桶数(桶的数量等于 table.length),loadFactor 用于计算阈值(阈值用于判定是否需要扩容)
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
// initialCapacity 不能小于 0
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
// 不予许 loadFactor <=0 ,也不允许loadFactor 是 NaN
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Load: "+loadFactor);
// 如果 initialCapacity 为 0, 则替换成 1
if (initialCapacity==0)
initialCapacity = 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
// table.length(也就是桶的数量)刚好等于 initialCapacity
table = new Entry<?,?>[initialCapacity];
// 计算阈值
threshold = (int)Math.min(initialCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
}- 指定
initialCapacity(初始容量)
这个构造函数会调用第一个构造函数(它会将 loadFactor 参数的值指定成 0.75f)
public Hashtable(int initialCapacity) {
this(initialCapacity, 0.75f);
}- 无参构造函数
这个构造函数会调用第一个构造函数(它会将 initialCapacity 和 loadFactor 这两个参数的值分别指定成 11 和 0.75f)
public Hashtable() {
this(11, 0.75f);
}- 将一个
Map作为参数
public Hashtable(Map<? extends K, ? extends V> t) {
// 调用第一个构造函数,并保证 initialCapacity 足够大(这样在 putAll(t) 的时候,不会触发扩容)
this(Math.max(2*t.size(), 11), 0.75f);
// 把 t 中的元素全都 put 一次
putAll(t);
}2.2.2 Hashtable 中的 put(...) 方法
/**
* Maps the specified <code>key</code> to the specified
* <code>value</code> in this hashtable. Neither the key nor the
* value can be <code>null</code>. <p>
*
* The value can be retrieved by calling the <code>get</code> method
* with a key that is equal to the original key.
*
* @param key the hashtable key
* @param value the value
* @return the previous value of the specified key in this hashtable,
* or <code>null</code> if it did not have one
* @exception NullPointerException if the key or value is
* <code>null</code>
* @see Object#equals(Object)
* @see #get(Object)
*/
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
// 1. hash & 0x7FFFFFFF 的作用是保留 hash 的低 31 位(也就是将最高位清零)
// 2. 将 (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length 的值保存在 index 中,index 就是 key 对应的桶的下标
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
// Hashtable 中使用拉链法(不涉及红黑树)来解决冲突。tab[index] 对应的桶是一个单链表的头元素,遍历这个单链表,如果在遍历时找到了匹配的 Entry,则直接替换其 value。
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
// 如果 tab[index] 对应的单链表中没有与 key 匹配的元素,则使用头插法进行处理
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}addEntry(...) 的核心逻辑是使用头插法将新元素放置在某个单链表里
private void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int index) {
// Hashtable 将要发生一次结构性变化(新增一个 Entry),所以 modCount 加一
modCount++;
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = key.hashCode();
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
// 将新生成的 Entry 作为单链表的表头元素
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>) tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
// Hashtable 中的 Entry 实例数加一
count++;
}在调用 addEntry(...) 方法时,有可能会触发扩容操作,扩容操作是通过 rehash() 实现的
/**
* Increases the capacity of and internally reorganizes this
* hashtable, in order to accommodate and access its entries more
* efficiently. This method is called automatically when the
* number of keys in the hashtable exceeds this hashtable's capacity
* and load factor.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected void rehash() {
int oldCapacity = table.length;
Entry<?,?>[] oldMap = table;
// overflow-conscious code
// 新容量=老容量*2 + 1
int newCapacity = (oldCapacity << 1) + 1;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
if (oldCapacity == MAX_ARRAY_SIZE)
// Keep running with MAX_ARRAY_SIZE buckets
return;
newCapacity = MAX_ARRAY_SIZE;
}
// 新 Map 的容量(即桶的数量)=newCapacity
Entry<?,?>[] newMap = new Entry<?,?>[newCapacity];
// Hashtable 将要发生一次结构性变化(各个桶中的 Entry 实例会重新安置一次),所以计数值加一
modCount++;
// 计算新的阈值。除极端情况外,新的阈值=newCapacity * loadFactor
threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAX_ARRAY_SIZE + 1);
// 让 table 指向 newMap
table = newMap;
// 外层循环的作用:对 oldMap 中的所有桶进行遍历
for (int i = oldCapacity ; i-- > 0 ;) {
// 内层循环的作用:对单链表中的元素进行遍历(每个桶都对应一个单链表的表头元素)
for (Entry<K,V> old = (Entry<K,V>)oldMap[i] ; old != null ; ) {
Entry<K,V> e = old;
old = old.next;
// 计算 e 应该放在 newMap 中的哪个桶中
int index = (e.hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % newCapacity;
// 用头插法将 e 放到正确的桶中
e.next = (Entry<K,V>)newMap[index];
newMap[index] = e;
}
}
}2.2.3 Hashtable 中的 remove(...) 方法
删 的逻辑比 增/改 的逻辑简单一点(因为不涉及扩容),其核心步骤如下
- 计算 key 对应的 hash 值
- 计算 hash 值对应的桶的下标(将下标值记为 index)
- 遍历 table[index] 对应的单链表,查找与 key 匹配的
Entry - 如果有与 key 匹配的
Entry,则将那个Entry从Hashtable中删除
完整的代码如下
/**
* Removes the key (and its corresponding value) from this
* hashtable. This method does nothing if the key is not in the hashtable.
*
* @param key the key that needs to be removed
* @return the value to which the key had been mapped in this hashtable,
* or <code>null</code> if the key did not have a mapping
* @throws NullPointerException if the key is <code>null</code>
*/
public synchronized V remove(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
// 获取 key 对应的 hash 值
int hash = key.hashCode();
// 1. hash & 0x7FFFFFFF 的作用是保留 hash 的低 31 位(也就是将最高位清零)
// 2. 将 (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length 的值保存在 index 中,index 就是 key 对应的桶的下标
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
// for 循环的作用:遍历 e 对应的单链表,查找与 key 对应的元素(tab 中的每个元素都是单链表的表头,所以 e 也是一个单链表的表头)
for(Entry<K,V> prev = null ; e != null ; prev = e, e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
// Hashtable 将要发生一次结构性变化(Entry 的数量会减一),所以 modCount 加一
modCount++;
// 如果 if 分支成立,则说明找到与 key 匹配的元素了
if (prev != null) {
// 这个单链表中与 key 对应的元素不是链表的头
prev.next = e.next;
} else {
// prev == null,说明这个单链表中与 key 对应的元素刚好是链表头
tab[index] = e.next;
}
// Hashtable 中的 Entry 实例数减一
count--;
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = null;
return oldValue;
}
}
// 没有找到和 key 匹配的元素
return null;
}2.2.4 Hashtable 中的 get(...) 方法
查 的逻辑,其核心步骤如下
- 计算 key 对应的 hash 值
- 计算 hash 值对应的桶的下标(将下标值记为 index)
- 遍历 table[index] 对应的单链表,查找与 key 匹配的
Entry
/**
* Returns the value to which the specified key is mapped,
* or {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key.
*
* <p>More formally, if this map contains a mapping from a key
* {@code k} to a value {@code v} such that {@code (key.equals(k))},
* then this method returns {@code v}; otherwise it returns
* {@code null}. (There can be at most one such mapping.)
*
* @param key the key whose associated value is to be returned
* @return the value to which the specified key is mapped, or
* {@code null} if this map contains no mapping for the key
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified key is null
* @see #put(Object, Object)
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public synchronized V get(Object key) {
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
// 获取 key 对应的 hash 值
int hash = key.hashCode();
// 1. hash & 0x7FFFFFFF 的作用是保留 hash 的低 31 位(也就是将最高位清零)
// 2. 将 (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length 的值保存在 index 中,index 就是 key 对应的桶的下标
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
// for 循环的作用:遍历 e 对应的单链表,查找与 key 对应的元素(tab 中的每个元素都是单链表的头元素,所以 e 也是一个单链表的头元素)
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
return (V)e.value;
}
}
// 没找到与 key 对应的元素
return null;
}Hashtable 与 HashMap 的区别
- 对
null的支持
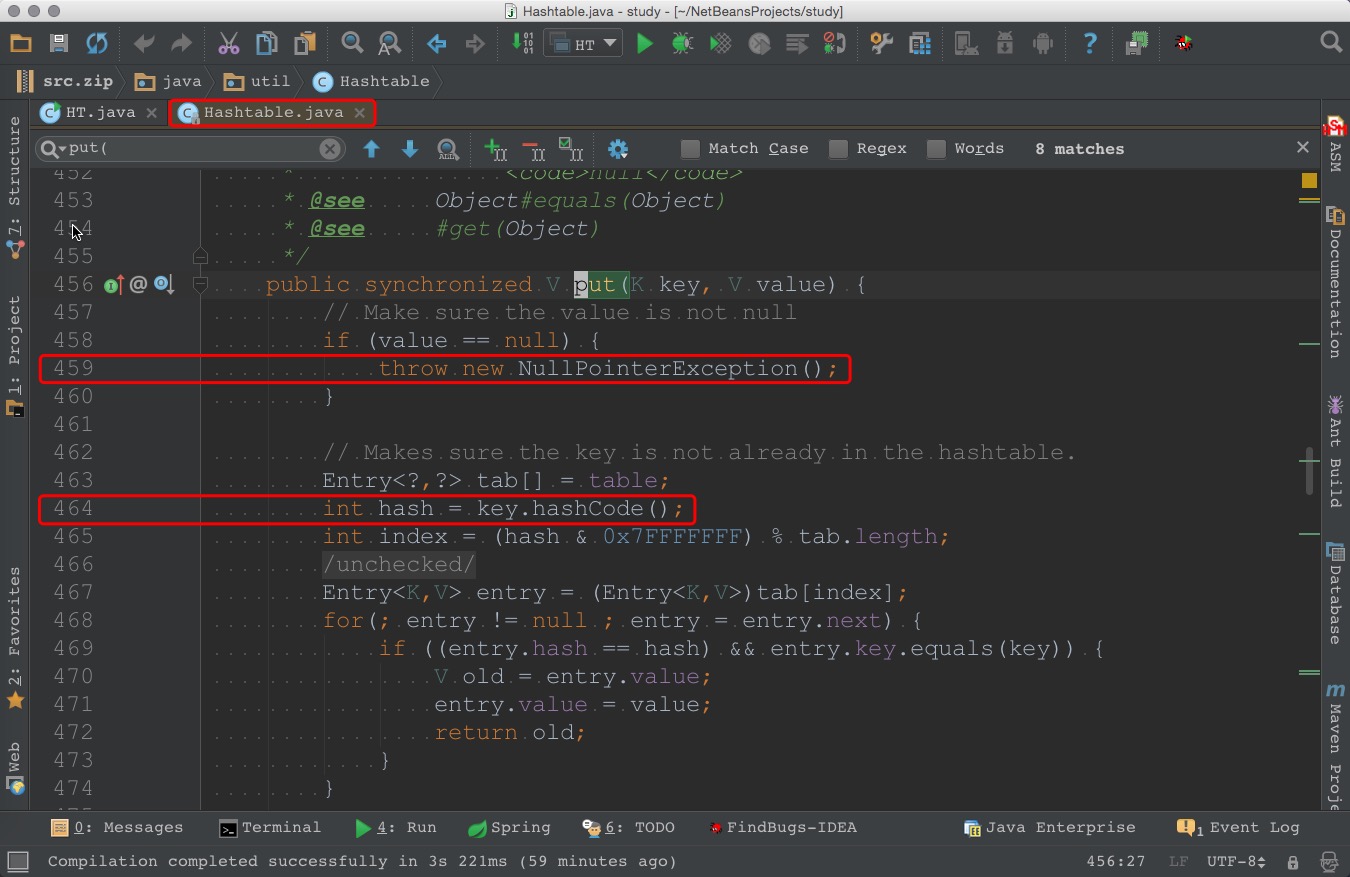
Hashtable中key和value都不允许为null(如果key为空,会在上图所示的 464 行抛空指针异常,如果value为空,会在 上图所示的 459 行抛空指针异常)。
HashMap中key和value都可以为null。HashMap中的put(...)方法的代码如下
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with <tt>key</tt>, or
* <tt>null</tt> if there was no mapping for <tt>key</tt>.
* (A <tt>null</tt> return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated <tt>null</tt> with <tt>key</tt>.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}HashMap 的 put(...) 方法中会调用 hash(...) 方法。hash(...) 方法的代码如下
/**
* Computes key.hashCode() and spreads (XORs) higher bits of hash
* to lower. Because the table uses power-of-two masking, sets of
* hashes that vary only in bits above the current mask will
* always collide. (Among known examples are sets of Float keys
* holding consecutive whole numbers in small tables.) So we
* apply a transform that spreads the impact of higher bits
* downward. There is a tradeoff between speed, utility, and
* quality of bit-spreading. Because many common sets of hashes
* are already reasonably distributed (so don't benefit from
* spreading), and because we use trees to handle large sets of
* collisions in bins, we just XOR some shifted bits in the
* cheapest possible way to reduce systematic lossage, as well as
* to incorporate impact of the highest bits that would otherwise
* never be used in index calculations because of table bounds.
*/
static final int hash(Object key) {
int h;
return (key == null) ? 0 : (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}可见
- 如果 key 为
null,则hash(...)方法的返回值为 0 - 如果 key 不是
null,则hash(...)方法的返回值为key.hashCode() ^ key.hashCode()
-
扩容
HashMap中桶的数量始终是 2 的幂次,Hashtable中桶的数量不需要是 2 的幂次。 因为HashMap中桶的数量始终是 2 的幂次,所以HashMap在计算 kv 对所对应的桶下标时,就可以利用位运算来做到,而Hashtable中则是通过%来进行取余。HashMap扩容时,新的桶数=旧的桶数*2,而Hashtable扩容时,新的桶数=旧的桶数*2+1(计算逻辑可以参考下图所示的 394 行)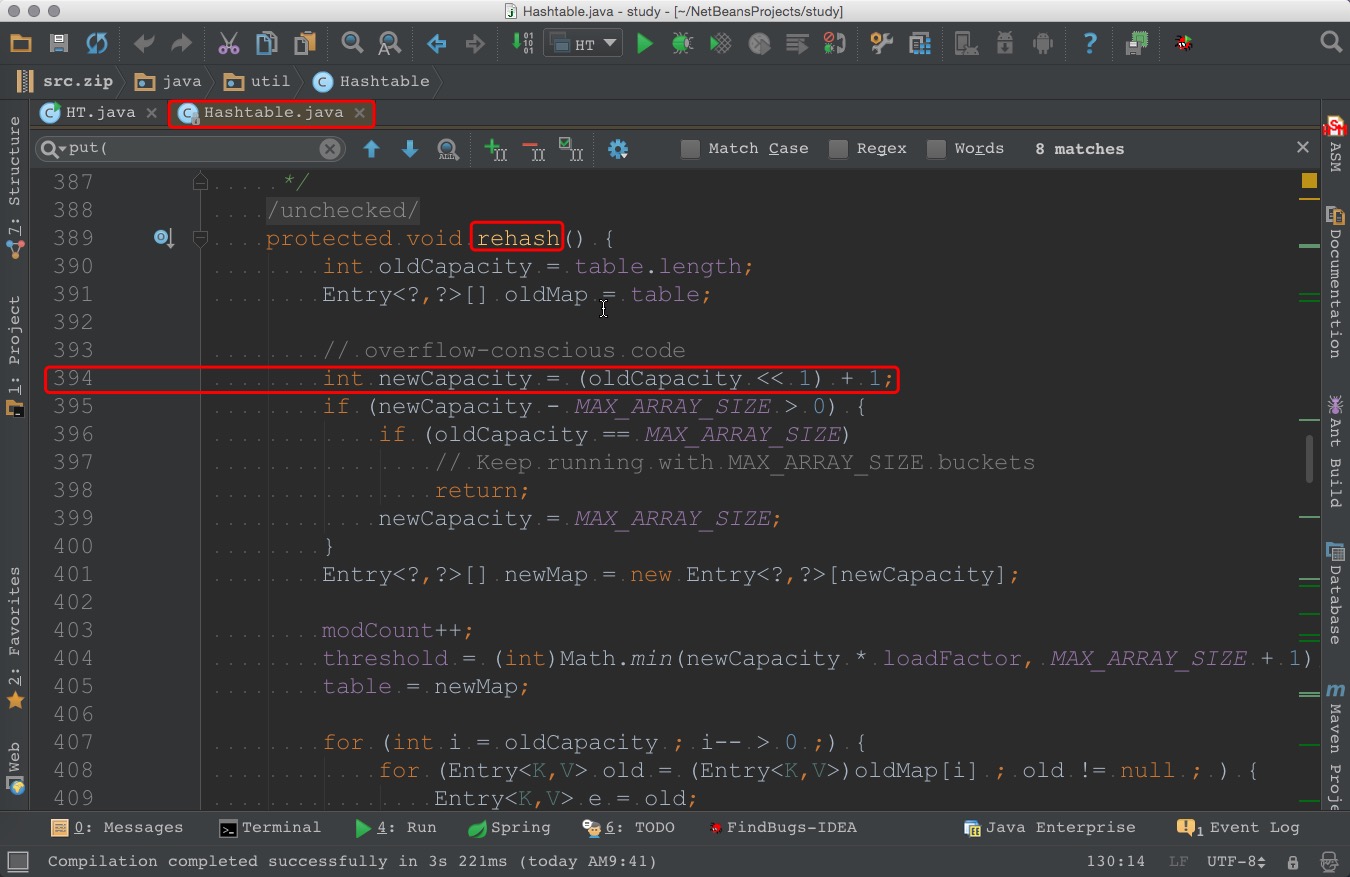 如果使用
如果使用 Hashtable的无参构造函数,则Hashtable的初始桶数会是11,第一次扩容后变为11*2+1=23,第二次扩容后变为23*2+1=47。令a[0]=11,a[i]表示第i次扩容后的桶数,则a[n+1] = 2*a[n] + 1,所以a[n+1] + 1 = 2 * (a[n] + 1), 所以a[n] = (3*2^(n+2))-1。
我写了一个简单的程序,可以用于观察Hashtable的结构以及它扩容前后的变化。其运行效果如下图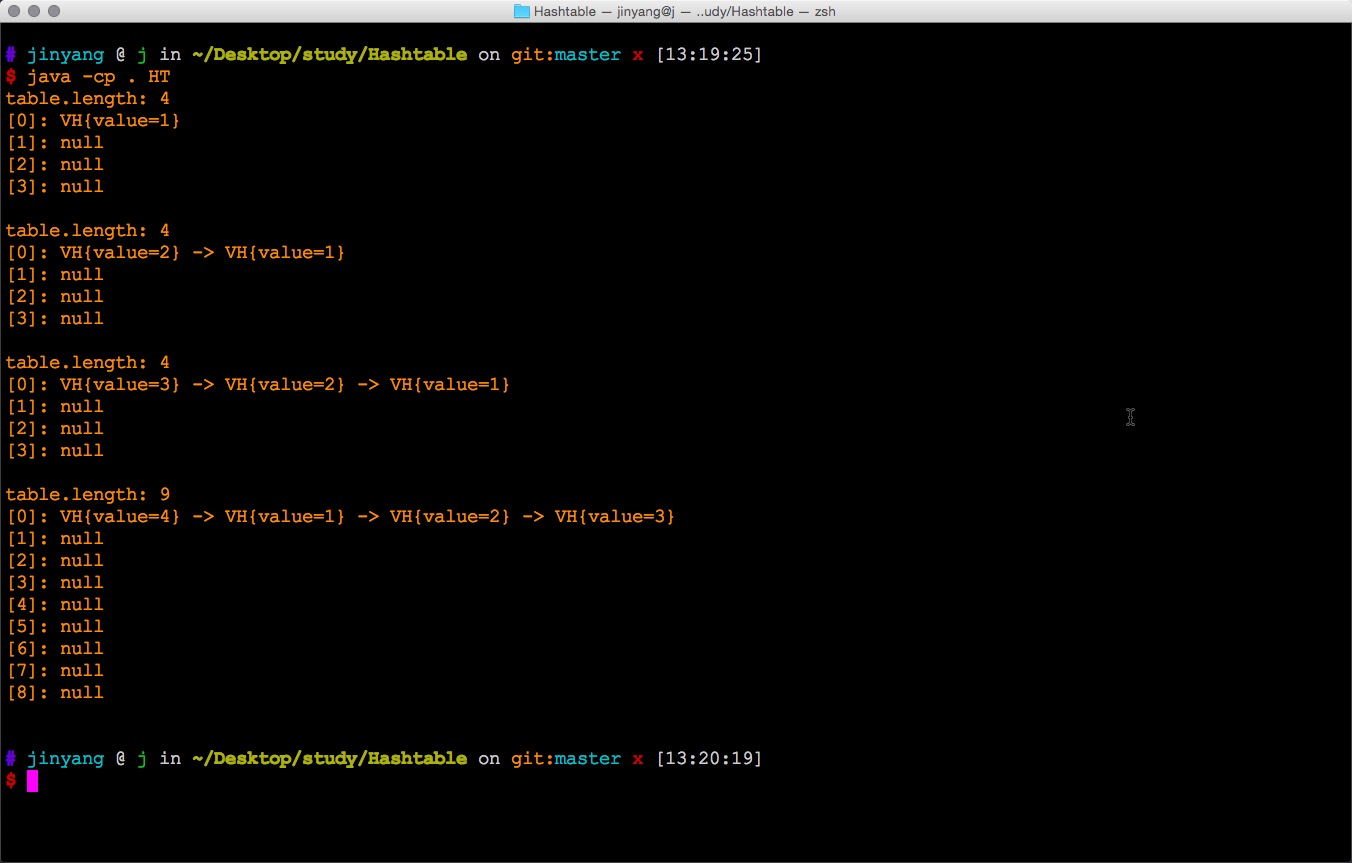
-
对 hash 碰撞的处理
Hashtable中仅使用拉链法来处理碰撞(归属于同一个桶的所有Entry会形成一个单链表),而HashMap则会在一定情况下将链表转化为红黑树。所以当 hash 冲突很多时,Hashtable的性能就会明显下降。