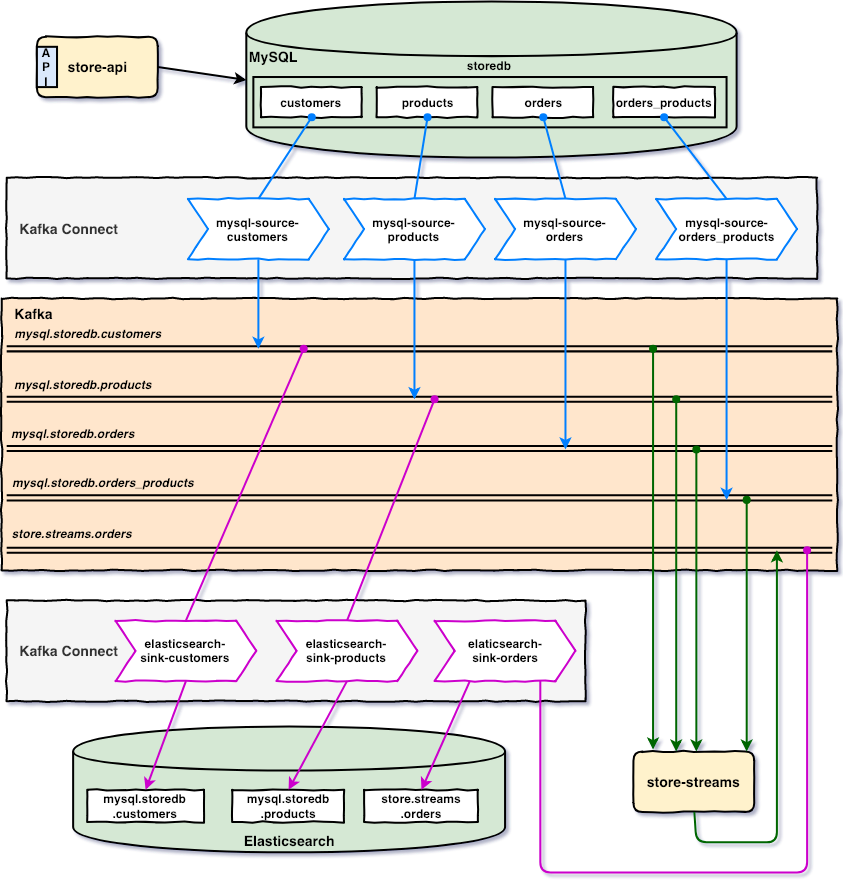
The main goal of this project is to play with Kafka, Kafka Connect and Kafka Streams. For this, we have: store-api that inserts/updates records in MySQL; Source Connectors that monitor inserted/updated records in MySQL and push messages related to those changes to Kafka; Sink Connectors that listen messages from Kafka and insert/update documents in Elasticsearch; finally, store-streams that listens messages from Kafka, treats them using Kafka Streams and push new messages back to Kafka.
-
Monolithic
Spring Bootapplication that exposes a REST API to manageCustomers,ProductsandOrders. The data is stored inMySQL. -
Spring Bootapplication that connects toKafkaand usesKafka Streams APIto transform some "input" topics into a new "output" topic inKafka.
In order to run this project, you can use JSON or Avro format to serialize/deserialize data to/from the binary format used by Kafka. The default format is JSON. Throughout this document, I will point out what to do if you want to use Avro.
-
Open a terminal and inside
springboot-kafka-connect-jdbc-streamsroot folder rundocker-compose up -dNote: During the first run, an image for
kafka-connectwill be built, whose name isspringboot-kafka-connect-jdbc-streams_kafka-connect. Run the command below to rebuild it.docker-compose build -
Wait for all Docker containers to be up and running. To check it, run
docker-compose ps
In order to have topics in Kafka with more than 1 partition, we have to create them manually and not let the connectors to create them for us. So, for it:
-
Open a new terminal and make sure you are in
springboot-kafka-connect-jdbc-streamsroot folder -
Run the script below
./create-kafka-topics.shIt will create the topics
mysql.storedb.customers,mysql.storedb.products,mysql.storedb.orders,mysql.storedb.orders_productswith5partitions.
Connectors use Converters for data serialization and deserialization. If you are configuring For JSON (de)serialization, the converter used is JsonConverter. On the other hand, the converter used is AvroConverter.
Important: if the Source Connector Converter serializes data, for instance, from JSON to bytes (using JsonConverter), then the Sink Connector Converter must also use JsonConverter to deserialize the bytes, otherwise an error will be thrown. The document Kafka Connect Deep Dive – Converters and Serialization Explained explains it very well.
Steps to create the connectors:
-
In a terminal, navigate to
springboot-kafka-connect-jdbc-streamsroot folder -
Run the following script to create the connectors on
kafka-connect- For JSON (de)serialization
./create-connectors-jsonconverter.sh - For Avro (de)serialization
./create-connectors-avroconverter.sh
- For JSON (de)serialization
-
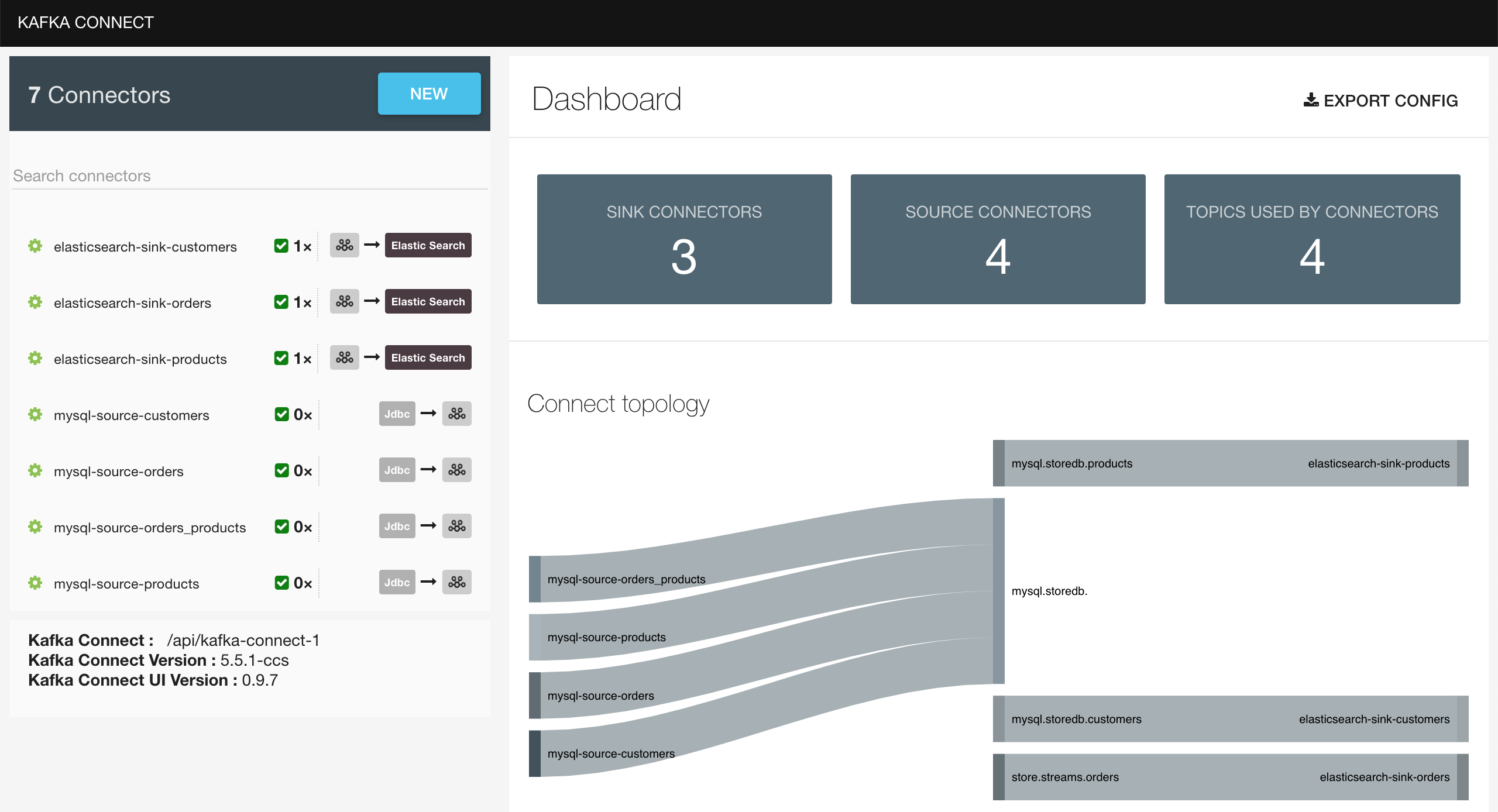
You can check the state of the connectors and their tasks on
Kafka Connect UIor running the following script./check-connectors-state.sh -
Once the connectors and their tasks are ready (
RUNNINGstate), you should see something like{"name":"mysql-source-customers","connector":{"state":"RUNNING","worker_id":"kafka-connect:8083"},"tasks":[],"type":"source"} {"name":"mysql-source-products","connector":{"state":"RUNNING","worker_id":"kafka-connect:8083"},"tasks":[],"type":"source"} {"name":"mysql-source-orders","connector":{"state":"RUNNING","worker_id":"kafka-connect:8083"},"tasks":[],"type":"source"} {"name":"mysql-source-orders_products","connector":{"state":"RUNNING","worker_id":"kafka-connect:8083"},"tasks":[],"type":"source"} {"name":"elasticsearch-sink-customers","connector":{"state":"RUNNING","worker_id":"kafka-connect:8083"},"tasks":[{"id":0,"state":"RUNNING","worker_id":"kafka-connect:8083"}],"type":"sink"} {"name":"elasticsearch-sink-products","connector":{"state":"RUNNING","worker_id":"kafka-connect:8083"},"tasks":[{"id":0,"state":"RUNNING","worker_id":"kafka-connect:8083"}],"type":"sink"} {"name":"elasticsearch-sink-orders","connector":{"state":"RUNNING","worker_id":"kafka-connect:8083"},"tasks":[{"id":0,"state":"RUNNING","worker_id":"kafka-connect:8083"}],"type":"sink"} -
On
Kafka Connect UI(http://localhost:8086), you should see -
If there is any problem, you can check
kafka-connectcontainer logsdocker logs kafka-connect
-
store-api
-
Open a new terminal and make sure you are in
springboot-kafka-connect-jdbc-streamsroot folder. -
Run the command below to start the application
./mvnw clean spring-boot:run --projects store-api -Dspring-boot.run.jvmArguments="-Dserver.port=9080"Note
It will create all tables, such as:
customers,products,ordersandorders_products. We are usingspring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=updateconfiguration.It will also insert some customers and products. If you don't want it, just set to
falsethe propertiesload-samples.customers.enabledandload-samples.products.enabledinapplication.yml.
-
-
store-streams
-
Open a new terminal and inside
springboot-kafka-connect-jdbc-streamsroot folder. -
To start application, run
- For JSON (de)serialization
./mvnw clean spring-boot:run --projects store-streams -Dspring-boot.run.jvmArguments="-Dserver.port=9081" - For Avro (de)serialization
./mvnw clean spring-boot:run --projects store-streams -Dspring-boot.run.jvmArguments="-Dserver.port=9081" -Dspring-boot.run.profiles=avroThe command below generates Java classes from Avro files present in
src/main/resources/avro./mvnw generate-sources --projects store-streams
- For JSON (de)serialization
-
If you get an exception saying
Unexpected state transition from ERROR to REBALANCING, rerunstore-streams
-
-
In a terminal, make sure you are inside
springboot-kafka-connect-jdbc-streamsroot folder -
Run the following script to build the application's docker image
./docker-build.sh
-
store-api
Environment Variable Description MYSQL_HOSTSpecify host of the MySQLdatabase to use (defaultlocalhost)MYSQL_PORTSpecify port of the MySQLdatabase to use (default3306) -
store-streams
Environment Variable Description KAFKA_HOSTSpecify host of the Kafkamessage broker to use (defaultlocalhost)KAFKA_PORTSpecify port of the Kafkamessage broker to use (default29092)SCHEMA_REGISTRY_HOSTSpecify host of the Schema Registryto use (defaultlocalhost)SCHEMA_REGISTRY_PORTSpecify port of the Schema Registryto use (default8081)
-
In a terminal, make sure you are inside
springboot-kafka-connect-jdbc-streamsroot folder -
In order to run the application's docker containers, you can pick between
JSONorAvro- For JSON (de)serialization
./start-apps.sh - For Avro (de)serialization
./start-apps.sh avro
- For JSON (de)serialization
-
Wait for application's Docker containers
STATUSto beUp (healthy). You can check by runningdocker ps -f name=store-api -f name=store-streams
| Application | URL |
|---|---|
| store-api | http://localhost:9080/swagger-ui.html |
| store-streams | http://localhost:9081/actuator/health |
-
Let's simulate an order creation. In this example, customer with id
1{"id":1, "name":"John Gates", "email":"john.gates@test.com", "address":"street 1", "phone":"112233"}will order one unit of the product with id
15{"id":15, "name":"iPhone Xr", "price":900.00}In a terminal, run the following
curlcommandcurl -i -X POST localhost:9080/api/orders \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{"customerId": 1, "paymentType": "BITCOIN", "status": "OPEN", "products": [{"id": 15, "unit": 1}]}'The response should be
HTTP/1.1 201 { "id": "47675629-4f0d-440d-b6df-c829874ee2a6", "customerId": 1, "paymentType": "BITCOIN", "status": "OPEN", "products": [{"id": 15, "unit": 1}] } -
Now, if we check
Elasticsearchagaincurl "localhost:9200/store.streams.orders/_search?pretty"We should have one order with a customer and products names.
{ "took" : 844, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 1, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 1.0, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "store.streams.orders", "_type" : "order", "_id" : "47675629-4f0d-440d-b6df-c829874ee2a6", "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : { "payment_type" : "BITCOIN", "created_at" : 1606821792360, "id" : "47675629-4f0d-440d-b6df-c829874ee2a6", "customer_name" : "John Gates", "customer_id" : 1, "status" : "OPEN", "products" : [ { "unit" : 1, "price" : 900, "name" : "iPhone Xr", "id" : 15 } ] } } ] } } -
In order to create random orders, we can use also the
simulationendpoint ofstore-apicurl -i -X POST localhost:9080/api/simulation/orders \ -H 'Content-Type: application/json' \ -d '{"total": 10, "sleep": 100}'
-
Kafka Topics UI
Kafka Topics UIcan be accessed at http://localhost:8085 -
Kafka Connect UI
Kafka Connect UIcan be accessed at http://localhost:8086 -
Schema Registry UI
Schema Registry UIcan be accessed at http://localhost:8001 -
Schema Registry
You can use
curlto check the subjects inSchema Registry- Get the list of subjects
curl localhost:8081/subjects - Get the latest version of the subject
mysql.storedb.customers-valuecurl localhost:8081/subjects/mysql.storedb.customers-value/versions/latest
- Get the list of subjects
-
Kafka Manager
Kafka Managercan be accessed at http://localhost:9000Configuration
- First, you must create a new cluster. Click on
Cluster(dropdown on the header) and then onAdd Cluster - Type the name of your cluster in
Cluster Namefield, for example:MyCluster - Type
zookeeper:2181inCluster Zookeeper Hostsfield - Enable checkbox
Poll consumer information (Not recommended for large # of consumers if ZK is used for offsets tracking on older Kafka versions) - Click on
Savebutton at the bottom of the page.
- First, you must create a new cluster. Click on
-
Elasticsearch
Elasticsearchcan be accessed at http://localhost:9200- Get all indices
curl "localhost:9200/_cat/indices?v" - Search for documents
curl "localhost:9200/mysql.storedb.customers/_search?pretty" curl "localhost:9200/mysql.storedb.products/_search?pretty" curl "localhost:9200/store.streams.orders/_search?pretty"
- Get all indices
-
MySQL
docker exec -it mysql mysql -uroot -psecret --database storedb select * from orders; -
Kafkacat
docker run --tty --interactive --rm --network=springboot-kafka-connect-jdbc-streams_default \ confluentinc/cp-kafkacat:6.1.1 kafkacat -b kafka:9092 \ -f '\nKey (%K bytes): %k\t\nValue (%S bytes): %s\n\Partition: %p\tOffset: %o\n--\n' \ -t store.streams.orders -C -c1
- To stop applications
- If they were started with
Maven, go to the terminals where they are running and pressCtrl+C - If they were started as Docker containers, go to a terminal and, inside
springboot-kafka-connect-jdbc-streamsroot folder, run the script below./stop-apps.sh
- If they were started with
- To stop and remove docker-compose containers, network and volumes, go to a terminal and, inside
springboot-kafka-connect-jdbc-streamsroot folder, run the following commanddocker-compose down -v
To remove the Docker images created by this project, go to a terminal and, inside springboot-kafka-connect-jdbc-streams root folder, run the script below
./remove-docker-images.sh
- Product
pricefield, numeric.mapping doesn't work for DECIMAL fields #563. For now, the workaround is usingStringinstead ofBigDecimalas type for this field.
- https://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/spring-cloud-stream-binder-kafka/current/reference/html/spring-cloud-stream-binder-kafka.html#_kafka_streams_binder
- https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-stream-samples/tree/master/schema-registry-samples
- https://www.confluent.io/blog/simplest-useful-kafka-connect-data-pipeline-world-thereabouts-part-1 (2 and 3)
- https://www.confluent.io/blog/kafka-connect-deep-dive-converters-serialization-explained