24 Days of JavaScriptmas
Attempting 24 days of increasingly difficult JavaScript challenges December 1, 2020 - December 24,2020 as per Scrimba 's rules.
Table of contents
- Day 1
- Day 2
- Day 3
- Day 4
- Day 5
- Day 6
- Day 7
- Day 8
- Day 9
- Day 10
- Day 11
- Day 12
- Day 13
- Day 14
- Day 15
- Day 16
- Day 17
- Day 18
- Day 19
- Day 20
- Day 21
- Day 22
- Day 23
- Day 24
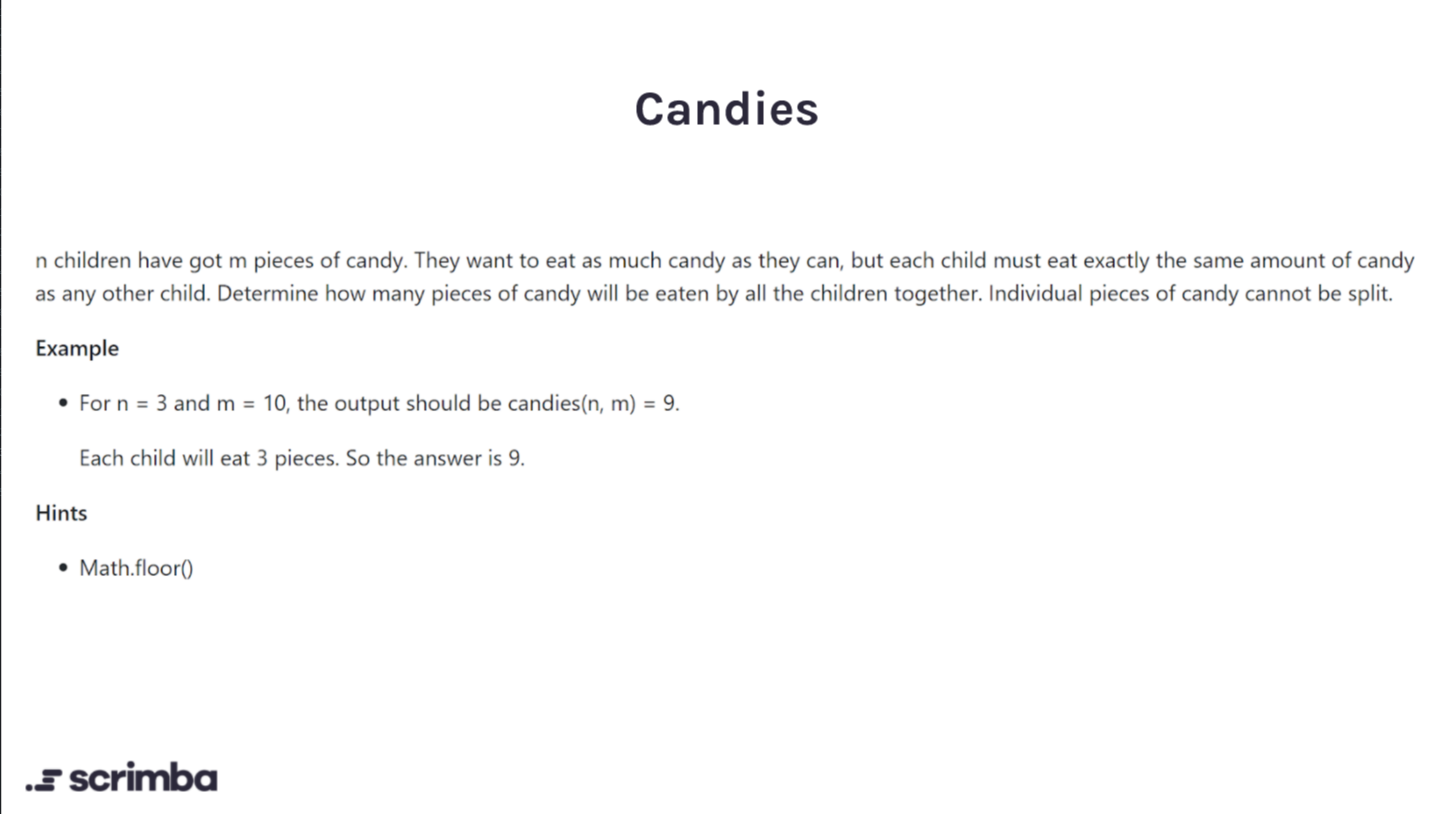
Day 1
Answer:
const candies = (children, candy) => {
const amountEatenEach = Math.floor(candy / children);
return amountEatenEach * children;
}
Logic:
Divide number of candies by number of children and round down. (Math.floor). This is how many pieces each child will get individually, but the question asks the total pieces eaten so you multiply by the # of children.
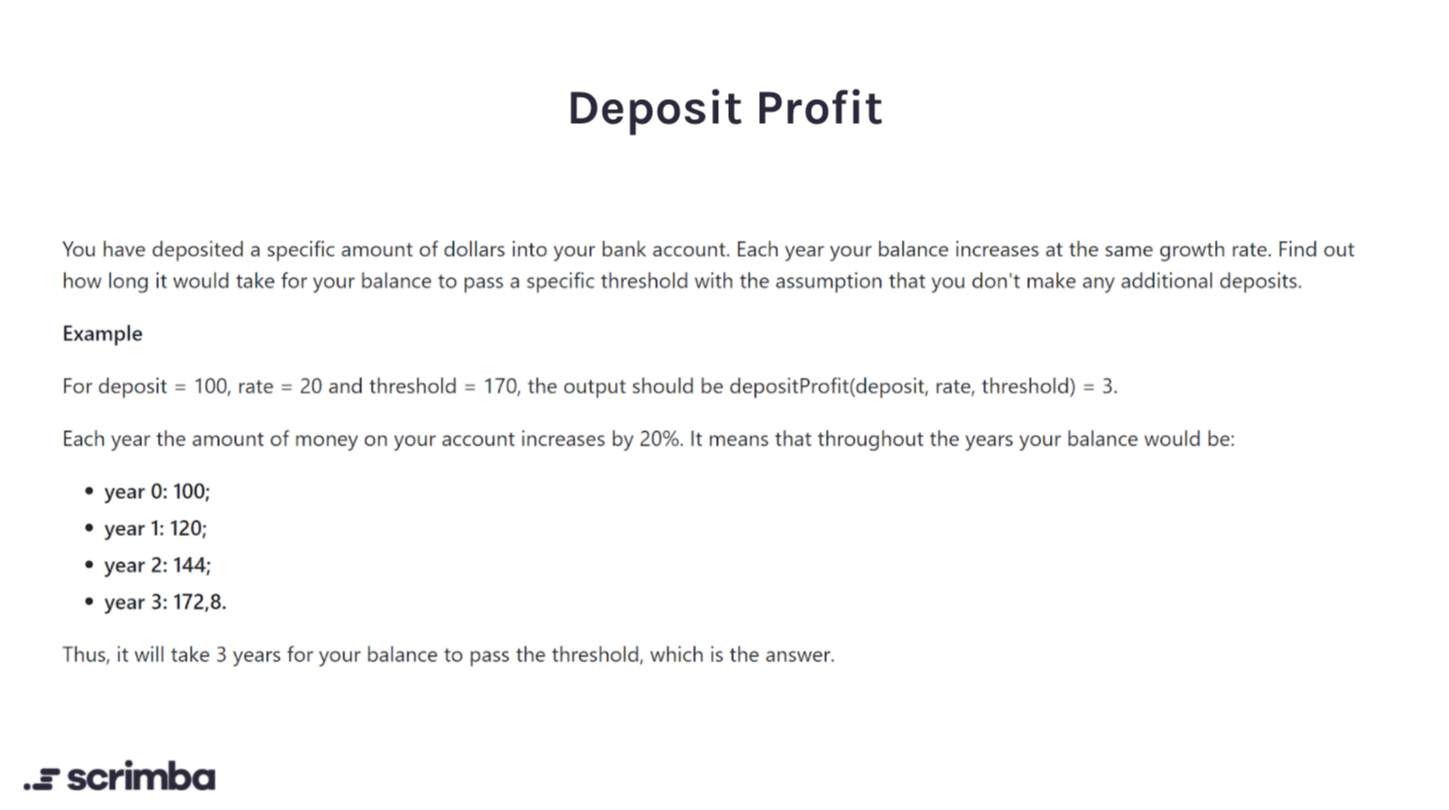
Day 2
Answer:
const depositProfit = (deposit, rate, threshold) => {
let years = 0;
while(deposit < threshold){
deposit += deposit * (rate/100);
years++;
}
return years;
}
Logic:
Keep accruing money each year; the balance increase by the % that is specified by the rate parameter. Once the money in the account exceeds the threshold parameter stop and return how many years it will take. Since rate is a percentage divide by 100.
Day 3
Answer:
const chunkyMonkey = (values, size) => {
let pos = 0;
const retArr = [];
let lengthCut = size;
let segment;
do {
segment = values.slice(pos, lengthCut);
retArr.push(segment);
pos += size;
lengthCut += size;
}
while ( values.slice(pos, lengthCut).length > 0); //If done this is empty
return retArr;
}
Logic:
Need some mechanism to continually slice the values array till it cannot no longer be sliced. To continue running something until our desired value is reached we usually need some type of loop (while or for) or some kind of recursive solution. I stuck with the former and created a do-while loop; the only difference a do-while and while is the do-while loop runs the body of the loop at least once.
- In the "do" block I initially slice the array using the starting position (pos) and the variable lengthCut which is intially equal to size.
- That sliced segment gets pushed into the array we wish to return
- Afterwards increment the pos variable by the size to account for segments you already sliced off.
- Similarly, length cut is incremented by the size as well; note the second argument of slice() is not the amount to cut off but rather the endIndex. To correctly get both the new start position and endIndex they must be incremented by size to
- After all these calculations in the do block of the loop the while portion checks if the next calculated (using the newly incremeneted pos and lengthCut) segment is returned as [] meaning we are at the end of the array and cannot possibly slice anymore.
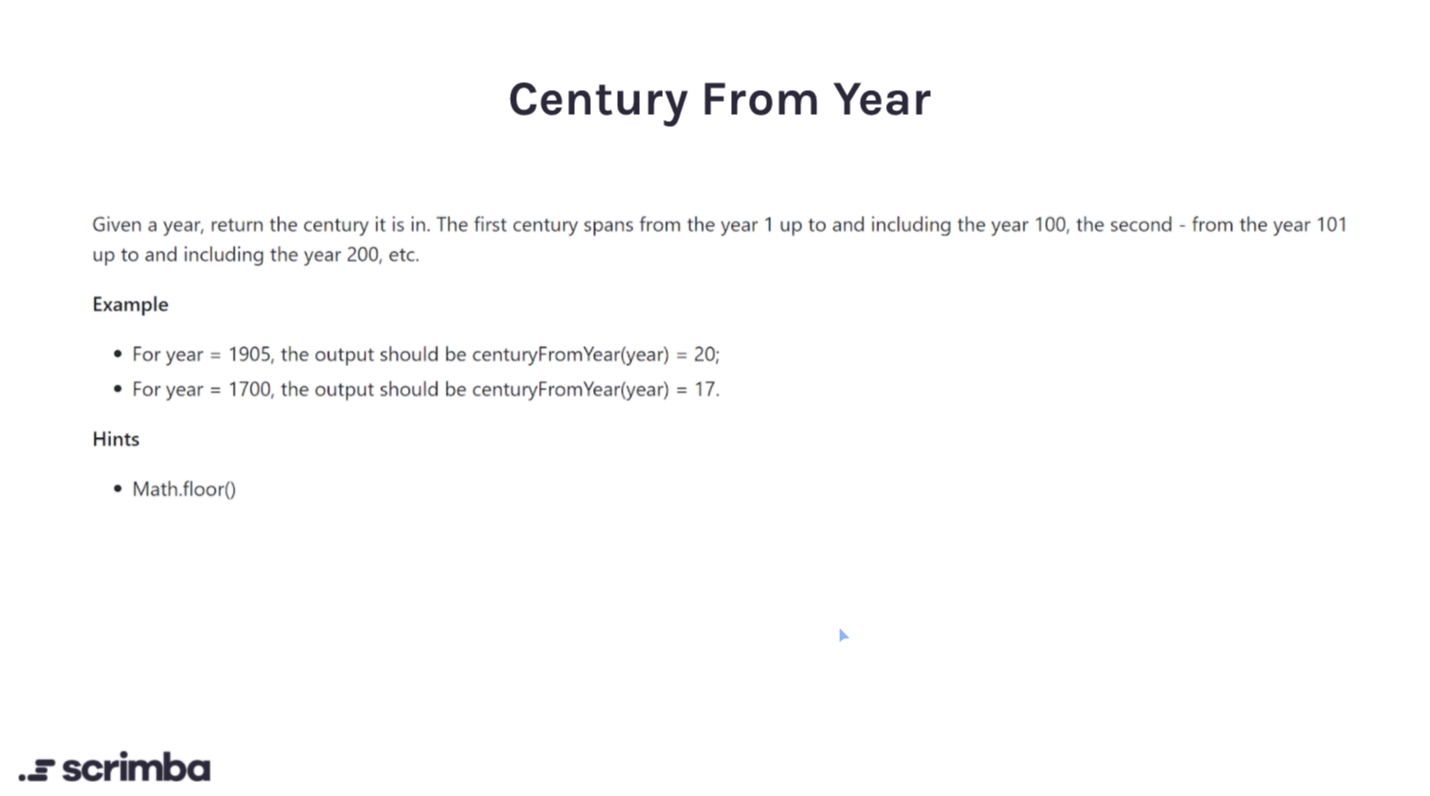
Day 4
Answer:
const centuryFromYear = (year) => year % 100 === 0 ? Math.floor(year/100) + 0 : Math.floor(year/100) + 1;
Logic:
A century is loosely defined as a period of 100 years (with some edge cases on the end years ). Generally to calculate a century you just need (year / 100) + 1. For the edge cases like 1800, 1700 etc.. we don't need to add + 1. All the afforementioned dates indicate a new century is about to begin; we can determine this because all the edge case years are divisible by 100.
Day 5
Answer:
const reverseAString = (str) => str.split('').reduce((acc, nextChar) => nextChar + acc, '');
Logic:
There are many different ways to reverse a string including a reverse for-loop, converting the string to an array then using the Array.reverse() method and then converting back. I used reduce as a challenge; here's the explaination 1) The function takes in a string a returns the result of the inputted string split into an array of characters and then reduced. 2) reduce() accumlates a value and iterates over an array doing something (adding subtracting etc...) by invoking the callback you provided to reduce(). The value returned from your callback is the new value feed in as the first argument of your callback in the next iteration of the loop 3) In shorter terms we start the reduce with an empty string '' loop over all the chars of the string where for each we append the next character ahead of the previous characters resulting in a reversed string
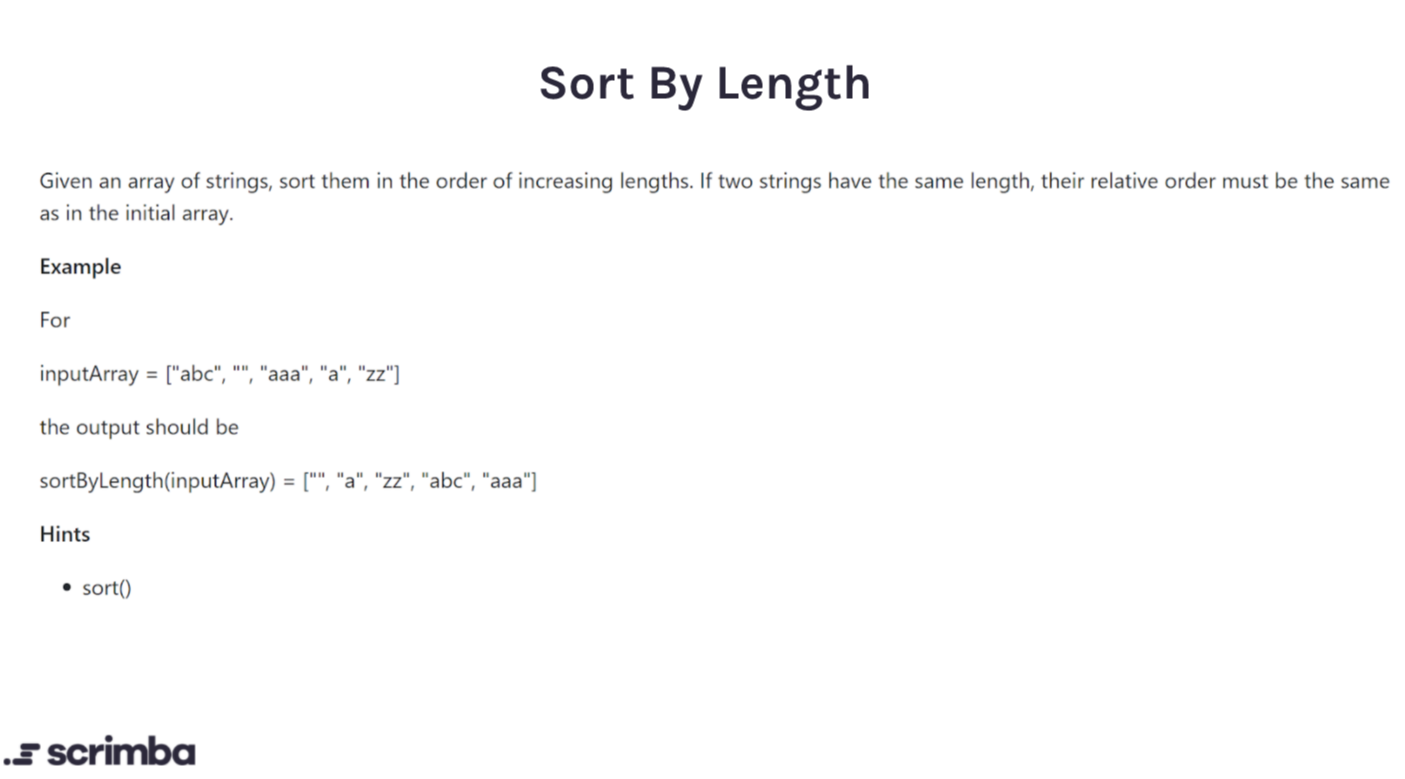
Day 6
Answer:
const sortByLength = (strs) => strs.sort((a, b) => a.length === b.length ? 0 : a.length > b.length ? 1 : -1);
Logic:
Looking into Array.sort() we see that just using that on array of strings sorts successfully but the default implementation will swap positions of strings alphabetically meaning that it will break this questions condition of 'If twos strings have the same length, their relative order must be the same in the intial array.' Meaning that we can still use Array.sort() but pass in a callback compare function that takes the next two elements out of the array and compares them sorting the two elements in a particular order depending on if your callback returns 0, a # greater than 1 or a # less than 1. (See docs)
My sort function uses a double ternary expression but is the same as an if/ else if. Here are the cases 1) a === b return 0 meaning the length is the same don't change original positions 2) a > b returns 1 meaning a is bigger and b is placed first 3) a < b returns -1 meaning b is bigger than a and is placed first
Day 7
Answer:
const countVowelConsonant = (str) => {
const newStr = str.toLowerCase();
const vowels = ['a', 'e', 'i', 'o', 'u'];
const isVowel = (char) => vowels.find((input) => input === char);
let sum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
const char = str[i];
sum += isVowel(char) ? 1 : 2;
}
return sum;
}
Logic:
We simply need to loop through the string (string[n] can access individual chars) and for check if the current char is a vowel or a consonant. If a vowel add 1 to the sum if not add 2. I created an array of vowels and a helper function to check if a char is in the value array (also could have used Array.includes()).
Day 8
Answer:
//See CSS file for grid layout...
const dice = document.querySelector('.dice');
dice.addEventListener('click', function(e){
dice.innerHTML = '';
const randomNum = Math.floor( Math.random() * 6) + 1;
dice.innerHTML = `${new Array(randomNum).fill('<div class="dot"></div>').join(' ')}`
});
Logic:
This is primarily testing 3 things; can you get a random number, can you alter the DOM/ use eventListeners and can you design a 2 column 3 row layout. 1. Random number in JS : Math.floor(Math.random() * max) + 1. Math.floor() rounds the result down to the nearest whole number. Math.random() returns a num between 0 and 1 exclusive (never quite reaches 0 or 1). Multiplying the result of random with your max will give you a decimal between 0 (not including 0) and max -1. We add the one at the end to account for the fact that it may be rounded down to 0 and to bring the max value able to be returned from this statement is now 1 - [CHOOSEN MAX NUM] 2. We use the document object to retrieve one of our HTML nodes as an object and attach a click event listener to it. 3. Inside the event listener we generate a random num, and populate the dice with the correct number of .dot divs. For this I opted to fill an empty array with length of generated random number full of .dot div's as strings. Then I join the array converting it back into a string and splitting each index by a space and finally the ${} evaluates that large returned string of all the necessary dots.
Day 9
Answer:
const sumOddFibonacciNumbers = (num) => {
let sumOfOdds = 1; //Start at 1 to account for the first fib num always being odd and 1.
let currentFibNum = 1;
let previous = 1;
let temp;
while(num >= currentFibNum){
if(currentFibNum % 2 !== 0){
sumOfOdds+= currentFibNum;
}
temp = currentFibNum;
currentFibNum += previous;
previous = temp;
}
return sumOfOdds;
}
Logic:
At first seeing the words Fibonacci I assumed the easiest solution would be to use some form of recursion since that is the preferred way to get the nth Fibonocci number. Without changing the signature of the function (aka the parameters and what type of value is returned) I couldn't find a way to make a recursive solution work. The alternative route was to use a while loop and count the fibonacci numbers up from the starting pair (1, 1) and on each new calculation of currentFibNum we check if it is odd, if so add it to the running sum.
The rest of the body of the while loop just continues the fibonacci sequence by adding (currentFibNum + previous) to get the new fib num and then using the previous value of currentFibNum to set previous.
Day 10
Answer:
const adjacentElementsProduct = (inputArray) => {
/* Never told how to handle [], and [x] edge cases... */
if (inputArray.length <= 0) return 0;
if (inputArray.length === 1) return inputArray[0];
/*
Setting this initially to -1 will not work for edge cases like
the array [2,-3] where the largest product is -6.
*/
let largestProd = inputArray[0] * inputArray[1];
let leftIdx = 1;
let rightIdx = 2;
for (let i = 0; i < inputArray.length; i++) {
const leftNum = inputArray[leftIdx];
const rightNum = inputArray[rightIdx];
if (leftNum && rightNum && rightNum * leftNum > largestProd) {
largestProd = rightNum * leftNum;
}
leftIdx++;
rightIdx++;
}
return largestProd;
};
Logic:
We need to loop through the given input array comparing adjacent elements while regularly checking if inputArray[n] is undefined to see if the loop is done. The question doesn't say what to do for edge cases where the input array is [], or [x]. For these cases I return 0 and x respectively. We have a variable largestProd to keep track of which product is currently the largest. I wanted to initialize this variable to -1 or some large negative number but then realized I couldn't guarantee the inputArray would not look like this [100, -1] meaning there certainly a possiblity that the largest product is a negative number. So I instead opted to set the largestProduct to the product of the first 2 indicies because by that line in the function we already know inputArray's length is at least 2.
Day 11
Answer:
const avoidObstacles = (nums) => {
const sorted = nums.sort();
let lowestNonDivisibleNum = 2;
let position = 0;
while(position < sorted.length){
// Were stopped by obstacle
if(sorted[position] % lowestNonDivisibleNum === 0){
lowestNonDivisibleNum++;
position = -1 ;
}
position++;
}
return lowestNonDivisibleNum;
}
Logic:
The hardest part of this problem is understanding what they are actually asking which is to find the lowest integer not divisible by any element in the array. Since you are required to go through the entire array again even if you encounter one element that is divisible by your current lowest number sorting the array is not actually necessary. When an obstacle is encountered (the if is entered) we increment our lowestNonDivisibleNum and set position = -1 so it can be incremented back to 0 and we can start re-checking the loop.
Day 12
Answer:
const validTime = (time) => {
if (time.length !== 5) return false;
if (typeof time !== 'string') return false;
if (time[0] === '2' && Number(time[1]) > 3) return false;
const hourTens = Number(time.slice(0, 1)); // 0 - 2
const hourOnes = Number(time.slice(1, 2)); // 0 - 9
const minuteTens = Number(time.slice(3, 4)); // 0 - 5
const minuteOnes = Number(time.slice(4, 5)); // 0 - 9
if (hourTens < 0 || hourTens > 2) return false;
if (hourOnes < 0 || hourOnes > 9) return false;
if (minuteTens < 0 || minuteTens > 5) return false;
if (minuteOnes < 0 || minuteOnes > 9) return false;
return true;
};
Logic:
There is most likely a better solution to this using regex but I took the brute force approach. Slice the time string to get the tens and ones place of both the hours and the minutes. Check the valid values in each position (e.g. first number can only be between 0 - 2 etc...). If any of the four digits has an invalid value it will return false, otherwise it will return true. The 3 if statements at the top ensure the function returns false under the following 3 conditions
- The input string is not 5 characters long meaning it is in the incorrect format
- The type of the input is for some reason not a string
- An edge case where if the first number is a 2 then the number right next to it can only be 0-3 because the 24 hour clock goes from 00 - 23.
Day 13
Answer:
const extractEachKth = (nums, index) => {
if (index <= 1) return nums;
return nums.filter((_, idx) => (idx + 1) % index !== 0);
};
Logic:
Loop through the given array and for each kth index (denoted by parameter called index) remove that element from the array and start the counting from 0 again to find the next kth element. Finally return the new array with all kth elements removed. For my base case I just made sure any k < -1 would just return the unchanged array because there is no good way to implement these cases. For the actual code I filtered the input array using (_, idx) as my callback to indicate that even though you must ask for the callback params in order (ELEMENT, INDEX, ARRAY) (see the callback for Array.filter()...) we don't need access to the actual element in the array just its index position. To account for the kth element being counted starting from 1 and because arrays are 0 based I account for this discrepancy by first adding 1 to the current elements index. If the current index position of the element we are on is divisible by k (meaning it is a kth element) return false and remove it.
Day 14
Answer:
const arrayMaximalAdjacentDifference = (nums) => {
if (nums.length === 0) return nums;
if (nums.length === 1) return Math.abs(nums[0]);
let largestDiff = -1;
nums.forEach((_, idx) => {
let left = nums[idx];
let right = nums[idx + 1];
let curDiff = Math.abs(left - right);
if (left && right && curDiff > largestDiff) {
largestDiff = curDiff;
}
});
return largestDiff;
};
Logic:
We need to iterate through the array and compare every adjacent element and calculate the absolute value of their differences. If the currently calculated difference is greater than the intial value (-1 is choosen to start as |x| > -1 always) we place the new highest difference in the largestDiff variable. Using forEach but just for the index position. The if statement in the forEach checks if any of the indicies are out of bounds/undefined, if not just compare the numbers.
Day 15
Answer:
const prevButton = document.querySelector('.previous');
const nextButton = document.querySelector('.next');
let photoIndex = Number(
getComputedStyle(document.documentElement).getPropertyValue('--photoIndex')
); // 0 at start
const numPhotos = getComputedStyle(document.documentElement).getPropertyValue(
'--numPhotos'
); //5
prevButton.addEventListener('click', function (e) {
if (photoIndex > 0) {
photoIndex--;
document.documentElement.style.setProperty('--photoIndex', photoIndex);
fadeButtonOnEnd();
}
});
nextButton.addEventListener('click', function (e) {
if (photoIndex < numPhotos - 1) {
photoIndex++;
document.documentElement.style.setProperty('--photoIndex', photoIndex);
fadeButtonOnEnd();
}
});
/* Both buttons should check their state (what index) then determine if they need their opacity lowered */
function fadeButtonOnEnd() {
photoIndex === 0
? prevButton.classList.add('end')
: prevButton.classList.remove('end');
photoIndex === numPhotos - 1
? nextButton.classList.add('end')
: nextButton.classList.remove('end');
}
Logic:
We need a way to switch the photos in the .gallery container (all images are in the HTML markup the ones that are not showing are overflowing to the right of the container, we don't see them because of overflow:hidden property). My initial thought would be to just have a container with a single image that I would replace the src attribute on click through JavaScript. Fortunately the way the CSS is set up for this encourages you to go for a mostly CSS solution with a bit of JavaScript. For me I created some CSS variables to keep track of some numbers so I don't have to hard code or calculate the the offest needed to show the new photo. Each photo width is 200px with a right margin of 20px. Transforming the X position of gallery by -220px or 220px moves to the previous photo and next photo respectively. My CSS variables use other variables and the calc() functionality to calculate the offset (not hard coded) and the current index I am on.
:root{
--numPhotos: 5;
--photoWidth: 200px;
--photoIndex: 0;
--photoOffset: calc(calc(var(--photoWidth) * -1) - 20px);
}
.gallery{
...
transform: translateX(calc( var(--photoIndex) * var(--photoOffset)));
transition: transform 0.5s ease;
...
}
All I simply need to do when a button is clicked (next or prev) is increment the photoIndex variable, then through the magic of CSS variables the new offset is calculated! I added in a transition to make it flow nicely and did a little extra adding a smooth scrolling background image property.
Day 16
Answer:
const insertDashes = (str) => {
const strArr = str.split('');
let dashArr = [];
for (let i = 0; i < strArr.length; i++) {
const [curChar] = strArr[i];
//if space just keep it
if (curChar !== ' ') {
const nextChar = strArr[i + 1];
nextChar && nextChar !== ' '
? dashArr.push(curChar, '-')
: dashArr.push(curChar);
} else {
dashArr.push(curChar);
}
}
console.log(dashArr.join(''));
return dashArr.join('');
};
Logic:
Convert to an array iterate through array and for each...
- Get char in current index
- Check if current char is a space, if so push it into dash array as is
- if the curChar is not a space check the next Char in the i + 1 th index
- If nextChar exists (not out of bounds) and is not a space we add the curChar with a dash in front of it (note Array.push() takes multiple args)
- If nextChar either does not exist (end of string) or if it is a space just push the current Char into the dash array it doesn't need dashes because the next char in front is a space or the end of the string.
Day 17
Answer:
exports.differentSymbolsNaive = (str) =>{
let uniqueArr = [];
str.split('').forEach(char => {
if(!uniqueArr.includes(char)) uniqueArr.push(char);
});
return uniqueArr.length;
}
Logic:
Loop through a string (could have used a for-loop but converted to an array via split('') in order to use forEach()). Have a separate array to keep unique chars and only push if the uniqueArray doesn't already have that char within it. We check this via Array.includes().
Day 18
Answer:
const arrayPreviousLess = (nums) => {
const answer = [];
nums.forEach((_, index) => {
//Look backwards from current position
let newLowest = nums[index];
for (let i = index; i >= 0; i--) {
if (newLowest > nums[i]) {
newLowest = nums[i];
break;
}
}
newLowest === nums[index] ? answer.push(-1) : answer.push(newLowest);
});
return answer;
};
Logic:
For each position in the array you need to start another loop and iterate to the left; the first value found to the left of the current index i that is lower than the element inside the array at position arr[i] replaces the element in position i. If there is no lower element or you are at index 0 (starting) replace the value with -1 instead.
Day 19
Answer:
const alphabetSubsequence = (str) {
// any char always > ''
let prevChar = '';
for (const curChar of str.split('')) {
if (curChar > prevChar) {
prevChar = curChar;
} else {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
Logic:
Iterate through each character in the given string by splitting it into an array of characters then looping over that arrray (I choose a for... of loop). Start the local var prevChar = '' as this ensures the first character in any string will always be > "" in terms of alphabetal/ charCode values. This ensures that 2 things
- That the if statement will always enter and set prevChar = curChar to for the first (0th) index
- The function will not return false, as far as we know just examining the first char the string should always be consider sorted. After that we compare the current character of the string to the previous one, if the currentChar is not bigger than the previousChar (even if they are equal) the string is not sorted and we return false, otherwise true.
Day 20
Answer:
const domainType = (domains) => {
return domains.map(domain => {
switch(domain.slice(domain.lastIndexOf('.')+1)){
case 'org':
return 'organization';
case 'com':
return 'commercial';
case 'info':
return 'information';
case 'net':
return 'network';
}
});
}
Logic:
Map over the array and for find the position of the last '.' char in the string using String.lastIndexOf(''). This method returns the index of the string where the '.' char was found, because the TLD is found after the '.' we add one to this result and then slice the string there. Then a switch was used to check and return the appropriate types.
Day 21
Answer:
const sumOfTwo = (nums1, nums2, value) => {
let retVal = false;
for(let i = 0; i < nums1.length ; i++){
let firstElem = nums1[i];
for(let j = 0; j < nums2.length ; j++){
let secondElem = nums2[j];
if(firstElem + secondElem === value) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
Logic:
You need to pick one element from one array, loop through the entirety of the second array checking if the first element picked added to any element from the second array adds up to the specified value. This is easily done with a nested for loop as opposed to Array.forEach() so I could return from within the loop as soon as a pair that matches is found.
Day 22
Answer:
const extractMatrixColumn = (matrix, column) => {
/* Return largest possible index in row (if column num doesn't exist) */
return matrix.map((row) => {
let colNum = column;
let insertElem = row[colNum];
while (insertElem === undefined) {
colNum--;
insertElem = row[colNum];
}
return insertElem;
});
};
Logic:
Loop through the array of arrays (called a matrix); each inner array is considered the row portion of a 2D array. Within each of those inner arrays (rows) we pull out the specified column num (in our case 2) and try to get the 2nd element (actually 3rd b/c arrays are 0 based). I used map and returned the result when I found the appropriate column in a row. Of course, if a row is too small to access the specified column I made a small while loop instead send the next highest defined column if the specified number does not exist.
Day 23
Answer:
const tweetArea = document.querySelector('#string');
const counter = document.querySelector('#counterFooter');
const tweetBtn = document.querySelector('#btn');
//REMAINING CHARS
let remaining = 140;
const MAX_CHARS = 140;
tweetArea.addEventListener('keydown', (e) => {
const selectedText = handleSelect();
const { key } = e;
if (selectedText) {
remaining = MAX_CHARS - tweetArea.textContent.length;
counter.textContent = `${remaining}/140`;
} else {
if (remaining <= 0) {
key === 'Backspace' ? remaining++ : remaining--;
} else if (remaining >= 140 && key !== 'Backspace') {
remaining--;
} else if (remaining < 140 && remaining > 0) {
key === 'Backspace' ? remaining++ : remaining--;
} else {
e.preventDefault();
e.stopPropagation();
}
}
remaining <= 20
? (counter.style.color = 'red')
: (counter.style.color = 'white');
//Disable if no more chars
if (remaining < 0) {
tweetBtn.setAttribute('disabled', true);
tweetBtn.classList.add('buttonDisabled');
} else {
tweetBtn.setAttribute('disabled', true);
tweetBtn.classList.remove('buttonDisabled');
}
counter.textContent = `${remaining}/140`;
});
/* Current the above code doesn't work if you select chunks of text to cut out or in*/
function handleSelect() {
if (typeof window.getSelection != 'undefined') {
return window.getSelection().toString();
}
}
Logic:
My solution to this is a bit contrived; the conditional logic is very messy and nested and I don't look at the length of the text in the textArea to reconcile it with the number counter but instead try to keep track of that state through the local variable called remaining. Doing it in this manner meant in a chunk of text was selected and pasted in or deleted the number would not be accurate in order to account for this I created a helper function that returns the string of the selected text each time the keydown event fires. If there is selected text I adjust the remaining characters if not calculate as normal.
Day 24
//HINT: ONLY EDIT THE SPIN() AND STOP() FUNCTIONS
//globals
var pushed = false //Has the stop button been pushed - false is default
var targetInt; //The target number to stop the wheel on
var spinningElem = document.getElementById('spinning'); //The spinning number
let num = 0;
//event listener
document.getElementById("buttonPressed").addEventListener("click", buttonPressed);
//When the stop button is pushed
function buttonPressed(){
pushed = true;
}
//set the target Int
function setTargetInt(){
var targetElem = document.getElementById('targetNum');
targetInt=Math.floor(Math.random() * 101)
targetElem.innerHTML = targetInt;
}
//sleep const
const sleep = (milliseconds) => {
return new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, milliseconds))
}
//EDIT THIS FUNCTION
const spin = async () => {
//WRITE YOUR CODE HERE
await sleep(75) //Paste this wherever you need to sleep the incrimentor
if(pushed){
stop(num); //Trigger this function when the STOP button has been pushed
}else{
spinningElem.textContent = ++num;
spin();
}
}
//EDIT THIS FUNCTION
function stop(i){
//WRITE YOUR CODE HERE
var result = document.getElementById('result'); //display your result message here
result.textContent = i === targetInt ? 'You win!' : `Oh no, you lose! Off by ${Math.abs(i- targetInt)}`
}
//main
setTargetInt();
spin()
Logic:
This could have easily been implemented using setInterval() (you can also specify the delay) but the value in this exercise is to check if you can use recursion and give it a way to stop based on the global variable for pushed. The sleep function given just returns a promise the resolves after the specified time which we await in our async function. On eahc iteration of spin we upate the number and check if the button was pushed.