- 1 Lesson Structure
- 2 (5 min) Warm Up
- 3 Demonstrating SQLite & Python
- 3.1 Connecting to our sqlite db using sqlite3
- 3.2 Listing the tables in our db
- 3.3 Now select everything from the employees table just to get a feel for it
- 3.4 Now let's load this into a dataframe using the
.read_sqlmethod, we'll use some of the same components from above. - 3.5 (3 min) What are the pros and cons of loading a sql query into a dataframe?
- 3.6 A throwback favorite
- 3.7 WHY SHOULD YOU ALWAYS SPECIFY YOUR PRIMARY KEYS!?
- 4 Exercises
YWBAT
- perform a query that is ordered by a value
- load query results as a dataframe
- build functions to perform queries
- execute a query using multiple joins
- write an order by query on a given table
- convert the customers table to a dataframe using pandas and sqlite3
- compare and contrast using a dataframe vs using the results as a list, from a query
- write a single join query
- write a multiple join query
- Take Questions
- Warm Up
- Connect to our sqlite db
- Compare and contrast reading a query as a list vs reading a query as a dataframe
- Practice various queries
- Complete a Join Query
- Complete a query using multiple Joins
- wrap up
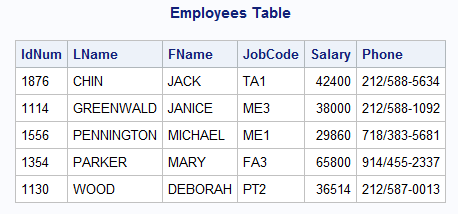
Given the following 'Employees' table, write a query that completes the following task. Send your query to me in a private chat here in zoom.
Expected Result:
- IdNum, LName, FName and Salary
- Order it by salary, starting with the highest salary
Solution
SELECT IdNum, LName, FName, Salary
FROM Employees
ORDER BY Salary DESCimport pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import sqlite3
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltconn = sqlite3.connect('data.sqlite')
cursor = conn.cursor()# table_names to be a list of my table_names
query = "SELECT name FROM sqlite_master WHERE type='table';"
res = cursor.execute(query).fetchall()
print(res) # Notice these are tuples, let's extract only the names in the next celltable_names = [r[0] for r in res]
table_namesquery = 'select * from employees;'
res = cursor.execute(query).fetchall()
res[:2]Now let's load this into a dataframe using the .read_sql method, we'll use some of the same components from above.
query = 'select * from employees;'
df = pd.read_sql(query, conn)
df.head() # Much better and more readable! def load_df(table_name=None, conn=None):
query = 'select * from {}'.format(table_name)
df = pd.read_sql(query, conn)
return dfd = {} # table_name: dataframe of table
for table_name in table_names:
d[table_name] = load_df(table_name, conn)[Discussion here]
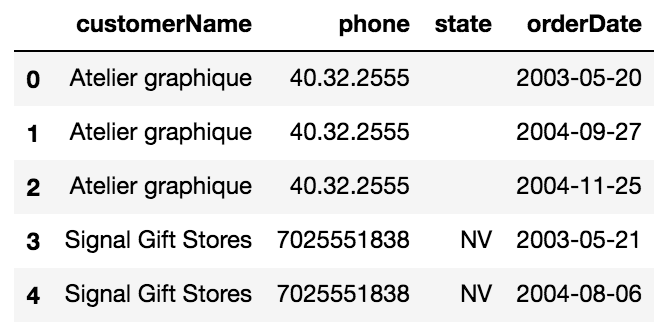
Create the following table using the customers table and the orders table
# First look at the customers dataframe
# Then look at the orders dataframeQuery 1 - Solution
query = """
SELECT c.customerName, c.phone, c.state, o.orderDate FROM
customers as c
JOIN orders as o using (customerNumber);
"""query = """SELECT
"""join_1 = pd.read_sql(query, conn)
join_1.head()Create a query that results in a table with the every customer number for an employee along with the employee name and number.
Ex:
# Work herequery = """
SELECT
"""
pd.read_sql(query, conn).head()Query 2 - Solution
query = """
select e.firstname, e.lastname, e.employeenumber, c.customerNumber
from employees as e
join customers as c
on e.employeenumber = c.salesrepemployeenumber;"""# Now let's take this and incorporate the next table orders
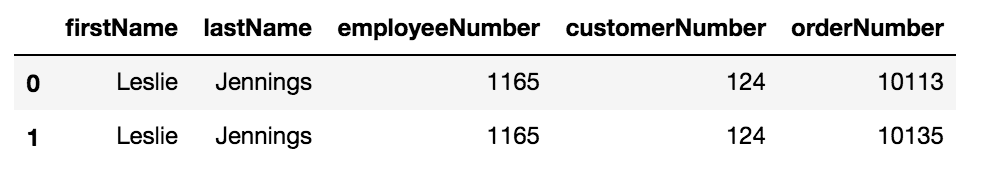
orders_df.head(1)Create a query that results in a table with every order number for every customer number for an employee along with the employee name and number.
Ex:
# Work herequery = """
SELECT
"""
pd.read_sql(query, conn).head()Query 3 - Solution
query = """
select e.firstname, e.lastname, e.employeenumber, c.customerNumber, o.orderNumber
from employees as e
join customers as c
on e.employeenumber = c.salesrepemployeenumber
join orders as o
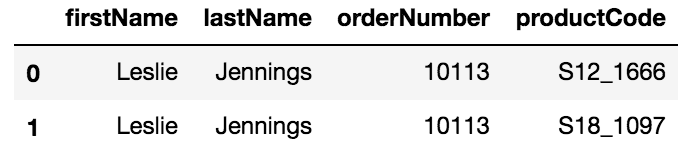
on o.customerNumber = c.customerNumber;"""Write a query that results in the following:
Employee First and Last Name, order number and each product code for that order.
There should be a row for each product code
Screenshot:
# work here
query = """
select
"""
pd.read_sql(query, conn).head(2)Query 4 Solution
query = """
select e.firstname, e.lastname, o.orderNumber, od.productCode
from employees as e
join customers as c
on e.employeenumber = c.salesrepemployeenumber
join orders as o
on o.customerNumber = c.customerNumber
join orderdetails as od
on od.orderNumber = o.orderNumber;"""
```
</details>
## Query Exercise 5
Write a query that results in the following:
Employee First and Last Name and each product name they sold, add an alias to match the image below
*There should be a row for each product name*
Screenshot:
<img src="images/query5.png" width="500"/>
```python
# work here
query = """
select
"""
pd.read_sql(query, conn).head(2)Query 5 Solution
query = """
select e.firstname, e.lastname, p.productName
from employees as e
join customers as c
on e.employeenumber = c.salesrepemployeenumber
join orders as o
on o.customerNumber = c.customerNumber
join orderdetails as od
on od.orderNumber = o.orderNumber
join products as p
on p.productCode = od.productCode;"""
```
</details>
## Great! It's working. Let's add some group by to remove duplicates!
**Add aliases to result in the following**
<img src="images/query5.png" width="500"/>
```python
# remember the alias' from above
query = '''SELECT ...'''
final_df = pd.read_sql(query, conn)
final_df.head(2)Final Query Solution
query = """
select e.firstname as fn, e.lastname as ln, p.productName as pn
from employees as e
join customers as c
on e.employeenumber = c.salesrepemployeenumber
join orders as o
on o.customerNumber = c.customerNumber
join orderdetails as od
on od.orderNumber = o.orderNumber
join products as p
on p.productCode = od.productCode
group by fn, ln, pn;"""