This tutorial is based on this learning group https://learn.0xparc.org/materials/halo2/learning-group-1
You can find the part 2 of this tutorial here => https://github.com/enricobottazzi/halo2-more-examples
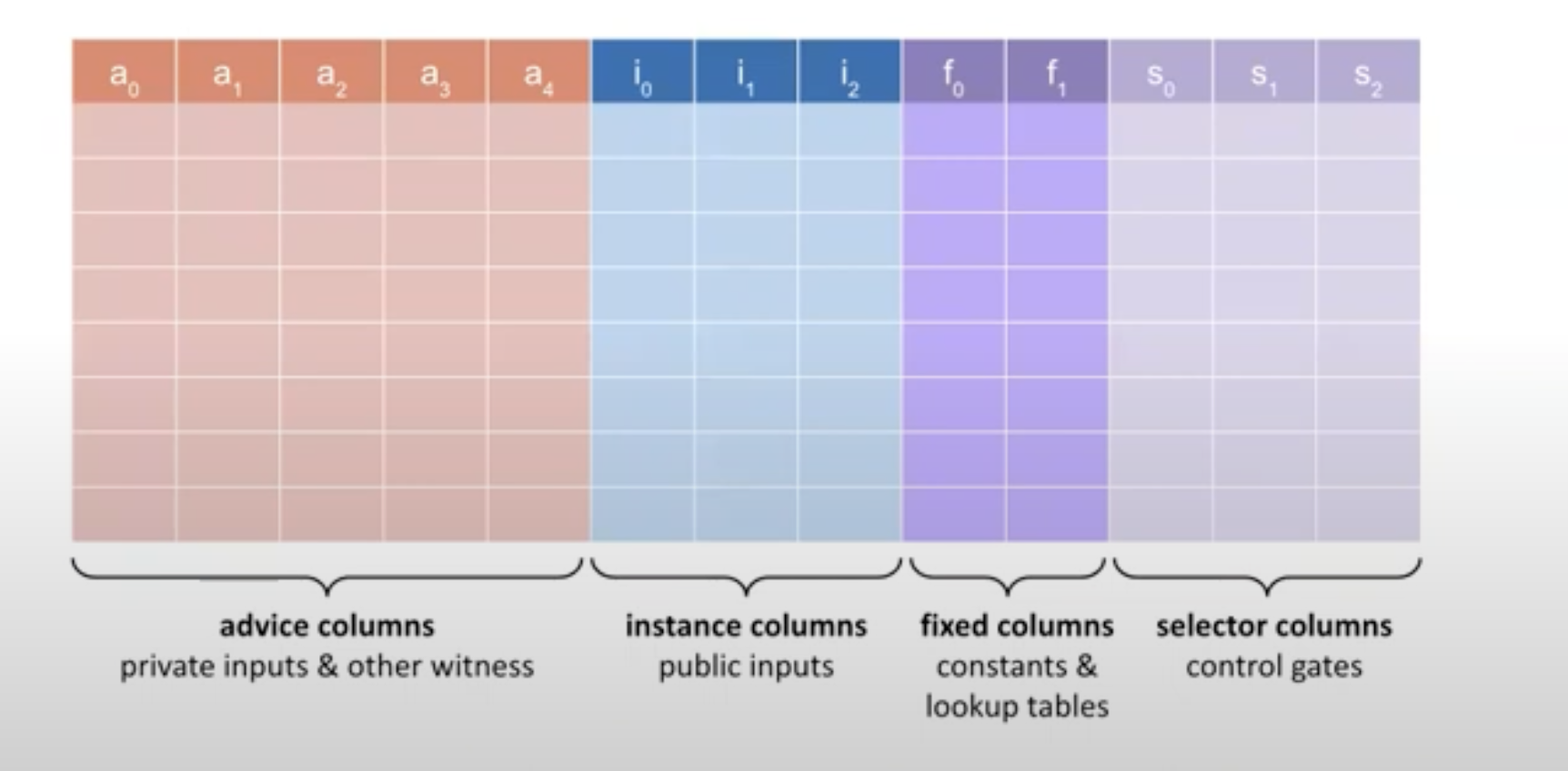
Type of columns
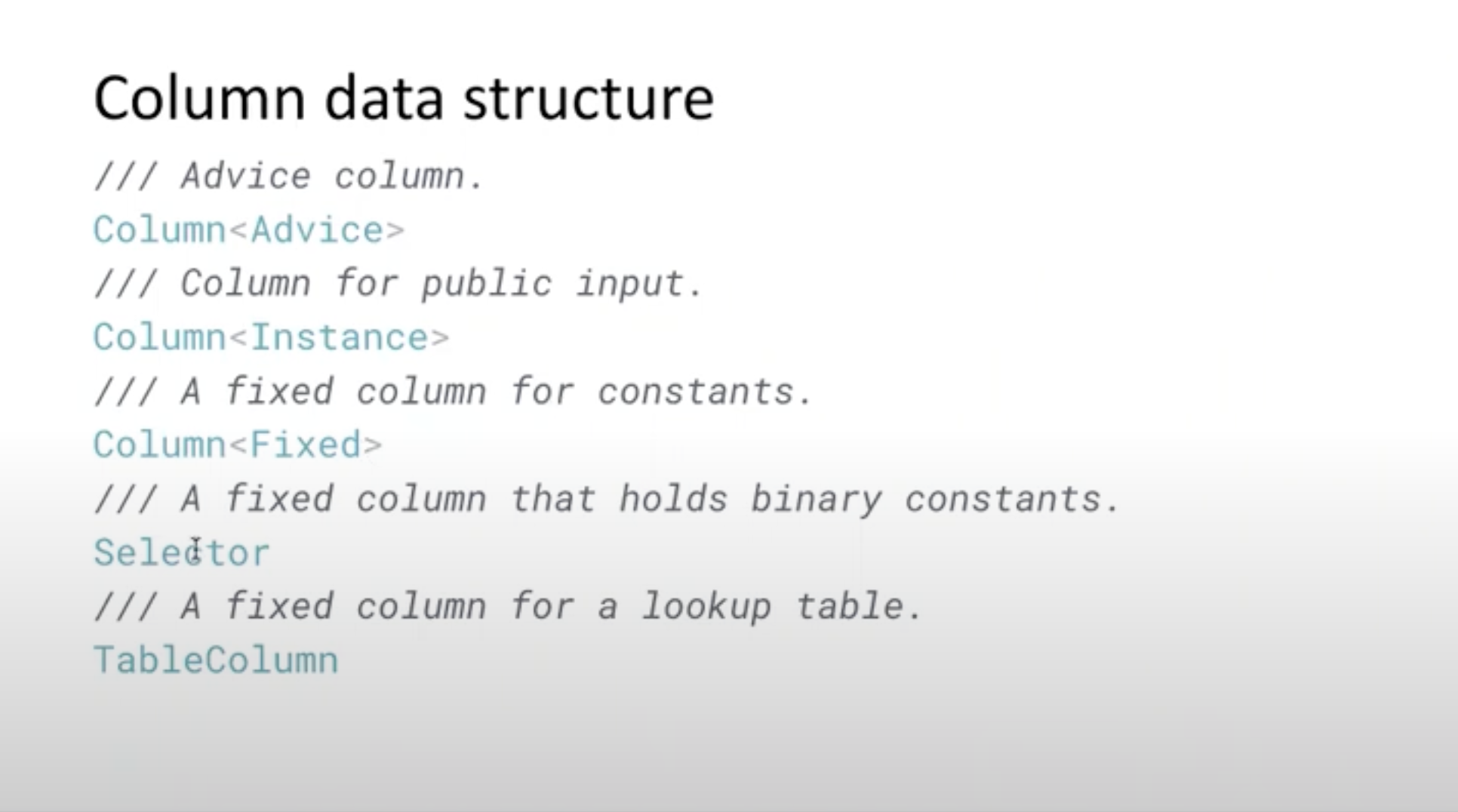
Core apis for data structures
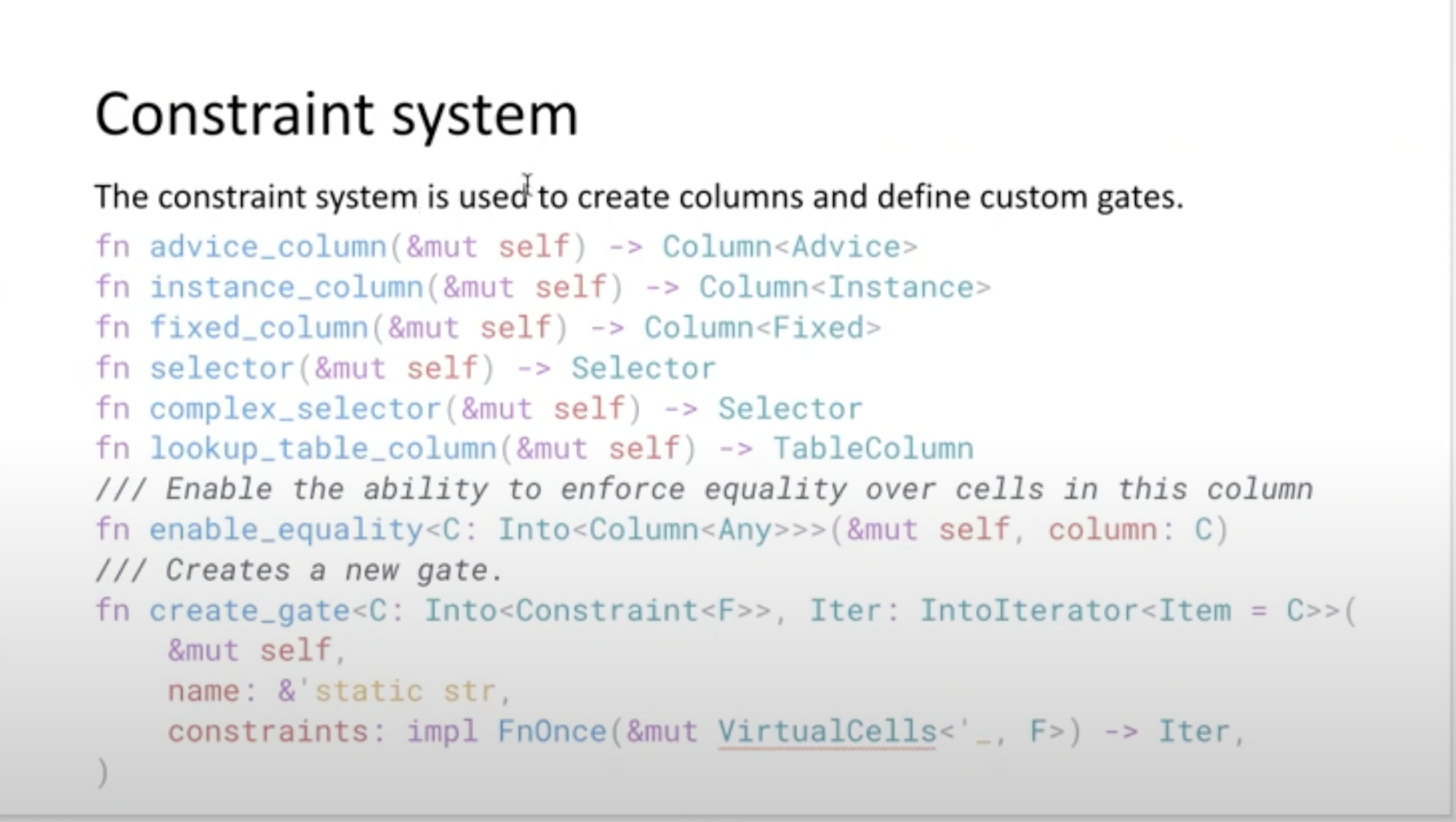
Core apis for constraint system
The first 6 apis are used to create columns. selector is used for custom gates. complex_selector can be used in look up arguments.
The last 2 apis are used to set up actual constraints such as copy constraints and custom gates. In particular, for copy constraint/permutation check, the enable_equality API must be used together with the copy_advice API (see example1.rs for more details).
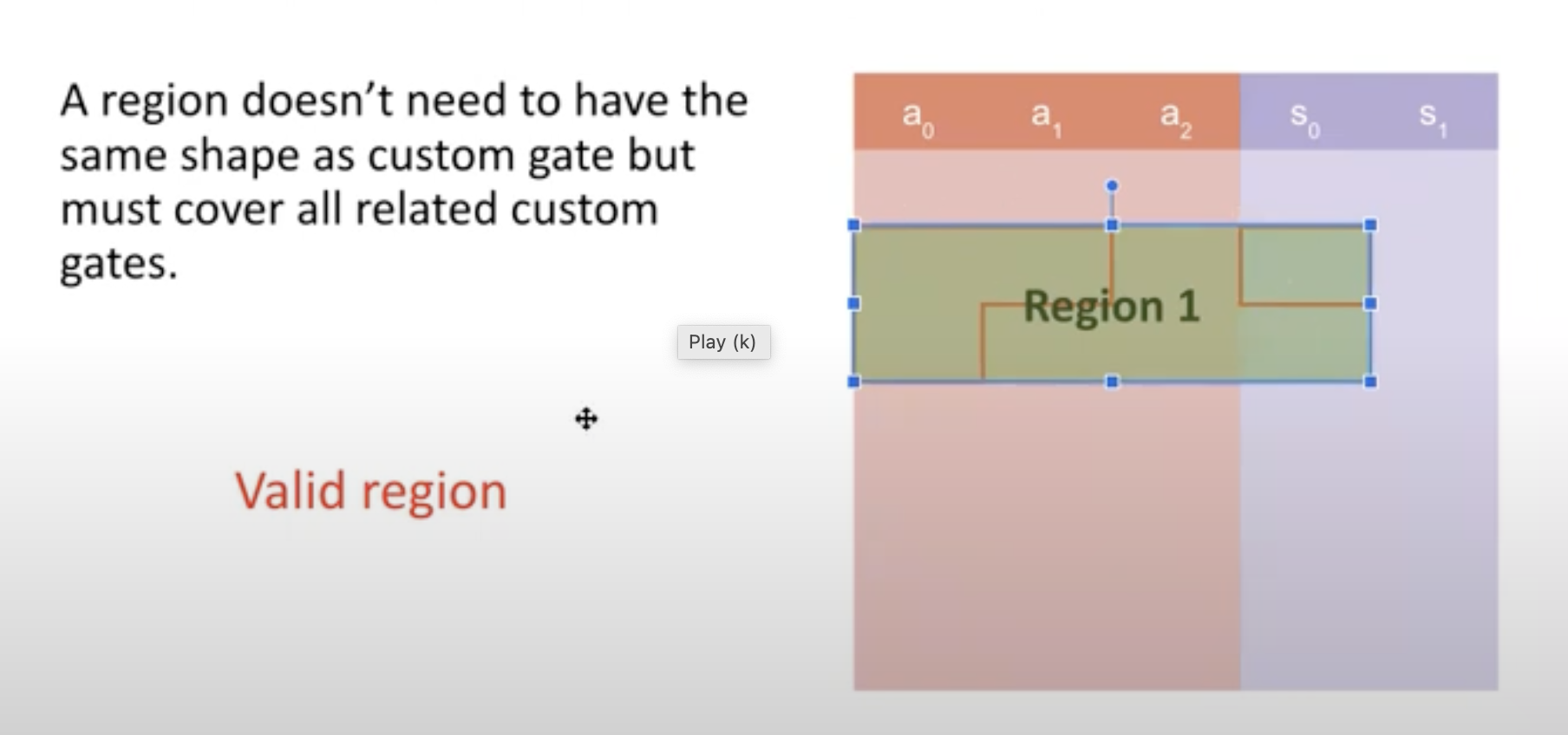
Concept of layouter
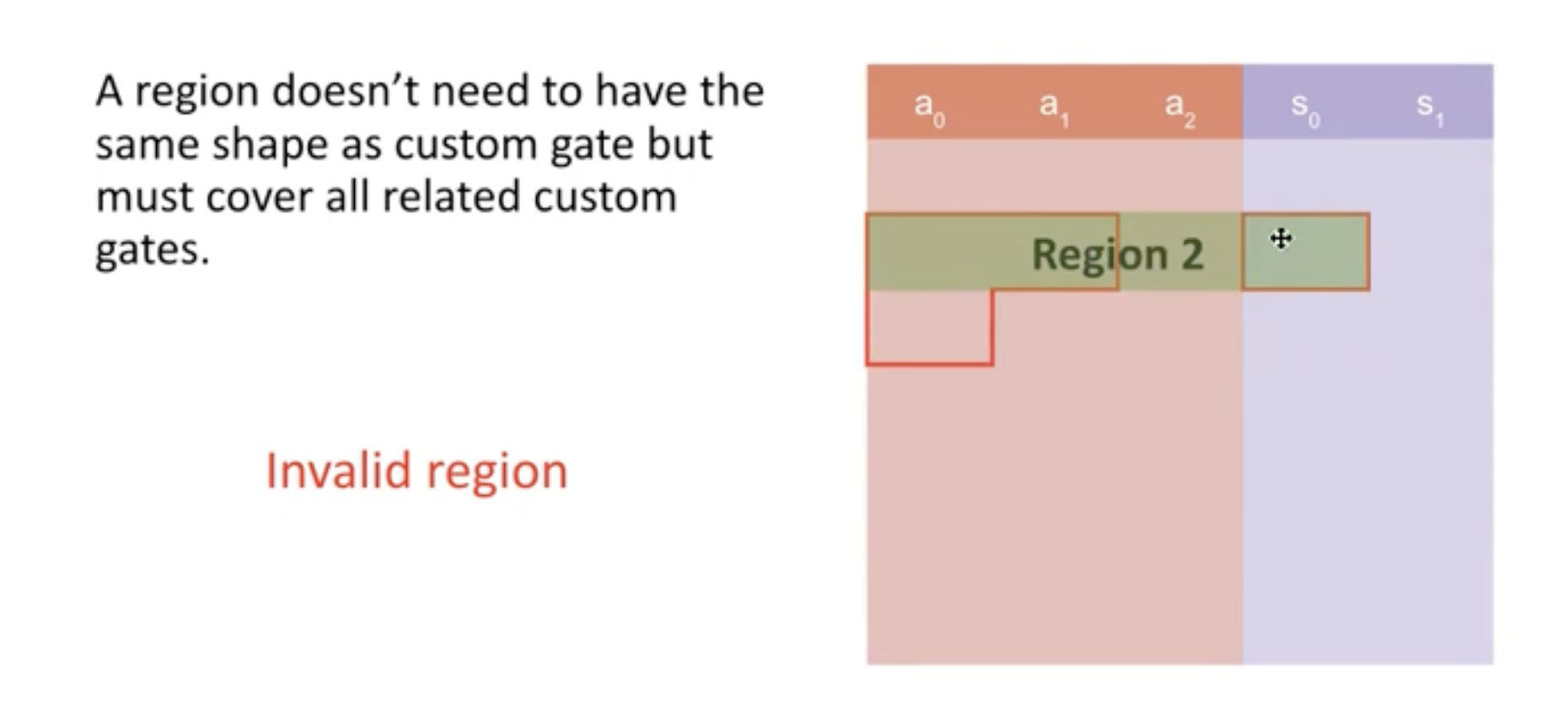
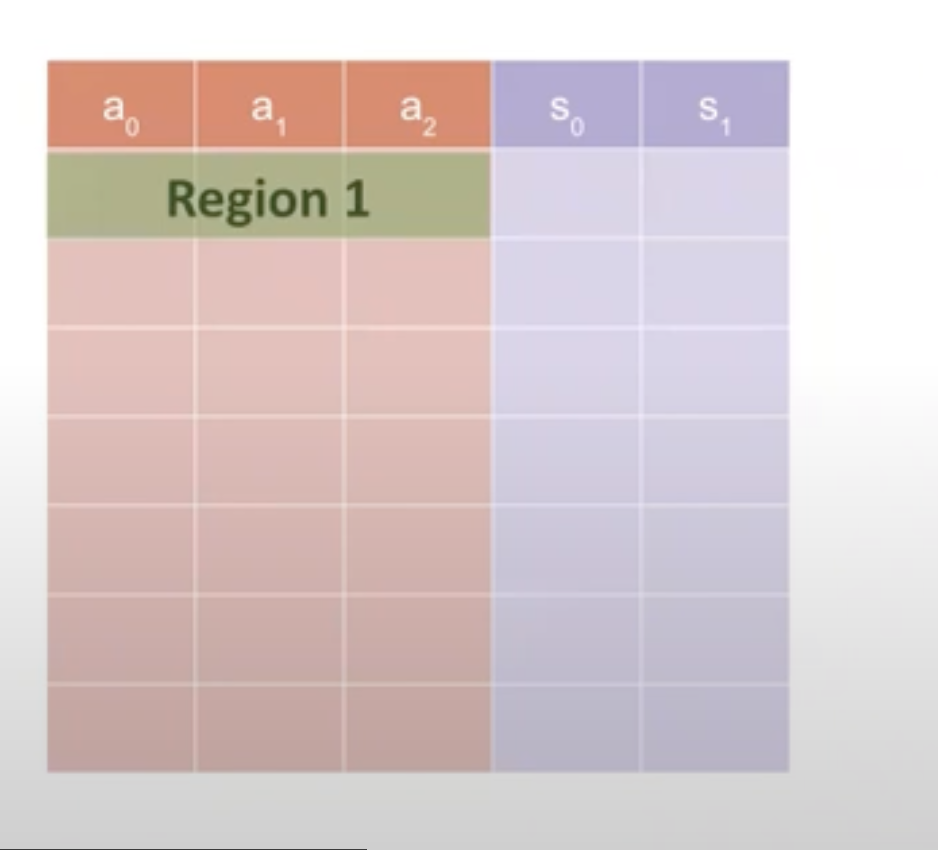
The layouter will be used during the assignment, namely when you fill up a table with the witness. Each time you will fill up a region. You won't fill the entire table at once. It takes a region as input and assign values to that region.
A region must be designed in a way that fully covers a custom gate.
How to implement a circuit
The chip is not strictly necessary, but it is good to create gadgets. For more complex circuits you will have multiple chips and use them as lego blocks. A Circuit can use different chips.
Q: Is there a solidity snark verifier for halo2?
A: Yes, you can use halo2-wrong by pse for that
Q: Do you need to supply the entire witness or can you let the circuit generate it by itself?
A: You need to supply the entire witness, but, of course, you can create scripts that are able to do that. For example you can check the assign_row method inside the example1.rs file.
Q: What is the rotation doing?
A: In the example we used the rotation feature when querying values that will be used to set up custom gates. In the case of the example we are creating a custom gate that covers only one row. So we query value from the current row using cur(). If we wanted to create more complex gates we could use the next() or prev() method to query values from the next row or also access value from a specifc row by specifying the offset!
Q: Is the name of the constraint something arbitrary or is this encoded in the package?
A: Yes we can set any name we want
Q: What does meta represent?
A: Meta is an instance of a default constraint system. You can see it's been used inside the mock prover when calling the configure function
let mut cs = ConstraintSystem::default();
let config = ConcreteCircuit::configure(&mut cs);The process look like:
key gen time
- create a circuit instance
- define the constraint system by calling
configure synthesizeruns ignoring witness assignment
proving time
- the prover receives a circuit instance
- The prover assign the values inside the circuit by calling
synthesize
Q: What does pub a and pub b mean inside our MyCircuit struct?
A: There are just two fields assigned to the circuit struct. The pub is a rust keyword that allows you to access the field from outside the struct. These 2 fields are the used inside the assign_first_row method to set the first row of the circuit. The other rows of the circuit are computed starting from the first row using the assign_row method.
Q: Where does region come from in assign_region method (file example1.rs)?
A: This may sound confusing because it seems like the region is an input parameter coming out of nowhere. In order to understand it we should go back to the assign_region method defined on the Layouter trait. The assign region function takes an assignment as input which is a closure that takes a mutable reference to a Region instance as its argument, and returns a result of type AR. The closure is responsible for assigning variables and constraints to the Region. So, to answer the initial question, the region parameter used inside layouter.assign_region is not derived from any external source; rather, it is created by the assign_region method itself and passed to the closure as an argument.
Q: When would you even set the selector to 0?
A: You can set the selector to 0 when you want to skip a constraint. Also the number of rows is always 2^k, so if you are not using the entire rows you can set the selector to 0.
Q: Would it be possible to create a region that doesn't involve any selector?
A: Yes, for example when you want to initalize some input values. You can create a region that doesn't involve any selector and just assign values to the table.
Run example 1
You can find all the reference inside the repository itself!
cargo run --bin example1
The example 1 refers to this video => https://learn.0xparc.org/materials/halo2/learning-group-1/halo2-api
Run example 2
The example 2 refers to this video => https://learn.0xparc.org/materials/halo2/learning-group-1/halo2-api-continued
The example adds the instance columns on top of the first example
cargo run --all-features --bin example2 to print out the graph of the circuit
Run example 3
The example 3 refers to this video starting from minute 21 => https://learn.0xparc.org/materials/halo2/learning-group-1/halo2-api-continued
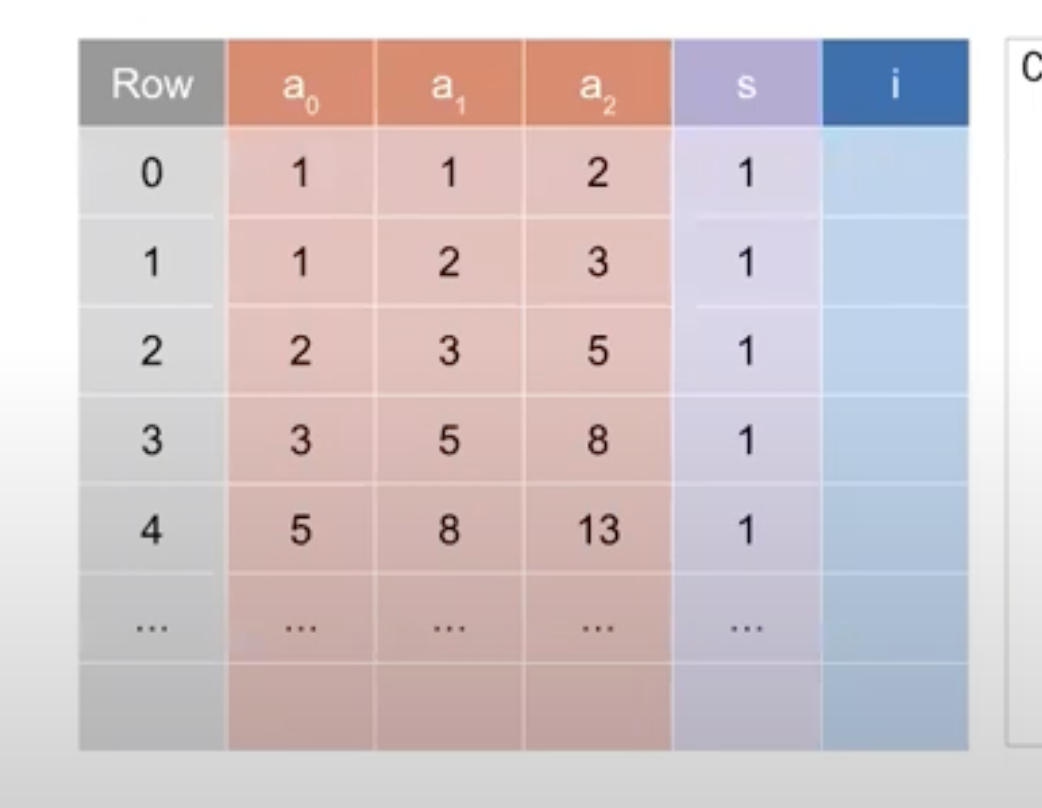
The example adds some optimization on top of the second example. In particular we can see that in the example 1 and 2 the structure of the table contained three column and each row was responsible for a fibonacci operation. This can be described by this table
| a | b | c |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 1 | 2 | 3 |
| 2 | 3 | 5 |
| 3 | 5 | 8 |
| 5 | 8 | 13 |
| 8 | 13 | 21 |
| 13 | 21 | 34 |
| 21 | 34 | 55 |
We can see that we are performing a lot of redundant computation. Especially the 2 permutation checks between two rows (prev_b=a and prev_c = b`) are not really necessary. We create an advice table that has this structure. This will eliminate the need for these permutation checks.
1 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
5 |
8 |
13 |
21 |
34 |
55 |
The new custom gate structure can be visualed like this
In the example 3 we consider only a single advice column
cargo run --all-features --bin example3 to print out the graph of the circuit
- What are the layouters/regions and why would you use that? and what is the offset here?
A: A region is like a block that can span on multiple lines and selectors and within this block you are concerned about relative offsets. Inside a region you basically need cells to be placed in specific position on relative to the other. If you do not care about how two blocks interact with each other, then you should define them in separate regions. By setting separate regions, you let the layouter perform some optimization on the layout of your region!
- Do I need to create a region for every value that I assign into the circuit? What does region1 in the example mean? It seems there's no custom gates there...
- What is FloorPlanner?
- Where am I enforcing the permutation check? Is
copy_advicethe way to set copy constraints? Or is itenable_equality? - What is a fiboChip, how do you define it?
- What should we pass inside instance? Why do we pass an empty vector?
- K is the size of the circuit. What does that mean? This is performed in the main function.
- What if I have empty rows? Do I need to fill up each row?
- What is the type of optmization that we are performing in example3?
A: In the example3 we are fewer advice columns (we move from 3 to 1) and we perform lesser permutation checks
- Why we change the type to AssignedCell <F,F>? Now we no longer access a value from a cell using
0 - Are values included in the fixed column to be considered as public values? Or are these part of the witness?