This repository holds a small example of a Python stack that enables visualization of geospatial raster data. It consists of three main elements,
- A few scripts that convert wgrib2 files / numpy arrays into cloud optimized geotiff (COG)
- A script that launches a Terracotta tile server to serve the geotiff files
- A demo application written in Dash that visualizes the data using the dash-leaflet library
Special care has been taken to ensure WYSIWYG pixel drilling, i.e. a 1:1 correspondence between the values shown on the map and the sampled valued.
Clone the repo, and enter the folder,
git clone git@github.com:thedirtyfew/terracotta-dash-example.git && cd terracotta-dash-example
Create a virtual environment and install Python requirements,
python3 -m venv venv && source venv/bin/activate && pip install -r requirements.txt
Next, we need some data. In this example, we'll use weather data from GFS (downloaded and parsed using the gfs_to_npz.py script) , but any geospatial raster data would do. Before the data can be loaded by the tile server, it must be converted into COG,
python3 npz_to_tiff.py
The tiles are served to the map component via a tile server. In this example, Terracotta is used. To start it, run
python3 tc_server.py
With the tile server running, start the demo application in a different terminal,
python3 app.py
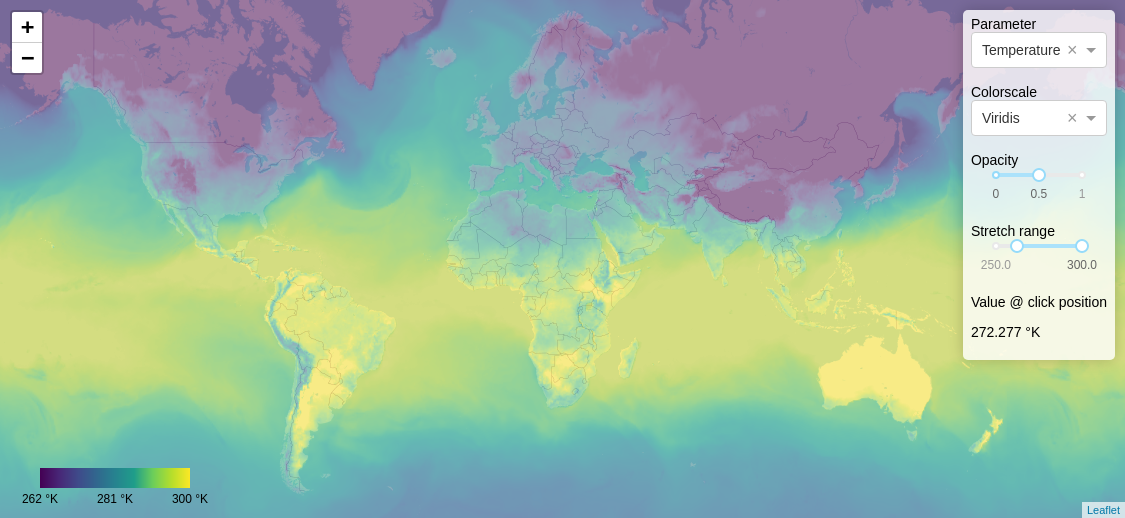
If you open a browser and go to http://localhost:8050, you should see a map like this
It is straight forward to visualize other geospatial raster data, you just need to setup a pipeline to convert them into COG. The npz_to_tiff.py script, which takes simple numpy arrays as input, should be a good starting point.
Both Terracotta and Dash are based on Flask. In production, a proper web server (such a gunicorn) should be used.
To ensure a 1:1 correspondence between the values shown on the map, and the sampled valued,
-
The data must be interpolated onto a grid that is regular in the projection in which the data is viewed. Most web maps, including this example, use
epsg:3857. This task is performed by theinterpolate_onto_gridfunction -
The pixels of the data grid must be aligned with map tiles. This is ensured by passing
web_optimized=Trueto thecog_translatefunction -
The tile server cannot perform any post processing (e.g. interpolation) of the data. With Terracotta, this is achieved via the settings
REPROJECTION_METHOD="nearest"