Jenkins plugin to run dynamic slaves in a Kubernetes/Docker environment.
Based on the Scaling Docker with Kubernetes article, automates the scaling of Jenkins slaves running in Kubernetes.
The plugin creates a Kubernetes Pod for each slave started, defined by the Docker image to run, and stops it after each build.
Slaves are launched using JNLP, so it is expected that the image connects automatically to the Jenkins master. For that some environment variables are automatically injected:
JENKINS_URL: Jenkins web interface urlJENKINS_JNLP_URL: url for the jnlp definition of the specific slaveJENKINS_SECRET: the secret key for authentication
Tested with csanchez/jenkins-slave,
see the Docker image source code.
Create a cluster
gcloud beta container clusters create jenkins --num-nodes 1 --machine-type g1-small
and note the admin password and server certitifate.
Or use Google Developer Console to create a Container Engine cluster, then run
gcloud beta container get-credentials
kubectl config view --raw
the last command will output kubernetes cluster configuration including API server URL, admin password and root certificate
To inspect the json messages sent back and forth to the Kubernetes API server you can configure
a new Jenkins log recorder for org.apache.http
at DEBUG level.
Run mvn clean package and copy target/kubernetes.hpi to Jenkins plugins folder.
Docker image for Jenkins, with plugin installed. Based on the official image.
docker run --rm --name jenkins -p 8080:8080 -p 50000:50000 -v /var/jenkins_home csanchez/jenkins-kubernetes
A local testing cluster with one node can be created with Docker Compose
docker-compose up
When using boot2docker or Docker Engine with a remote host, the remote Kubernetes API can be exposed
with docker-machine ssh MACHINE_NAME -- -L 0.0.0.0:8080:localhost:8080 or boot2docker ssh -L 0.0.0.0:8080:localhost:8080
More info
Assuming you created a Kubernetes cluster named jenkins this is how to run both Jenkins and slaves there.
Create a GCE disk named kubernetes-jenkins to store the data, and format it as ext4.
Formatting is not needed in new versions of Kubernetes.
Creating the pods and services
gcloud preview container pods create --config-file ./src/main/kubernetes/pod.yml
gcloud preview container services create --config-file ./src/main/kubernetes/service-http.yml
gcloud preview container services create --config-file ./src/main/kubernetes/service-slave.yml
Open the firewall to the Jenkins master running in a pod
gcloud compute firewall-rules create jenkins-node-master --allow=tcp:8888 --target-tags k8s-jenkins-node
Connect to the ip of the network load balancer created by Kubernetes, port 8888. Get the ip with
gcloud compute forwarding-rules describe jenkins
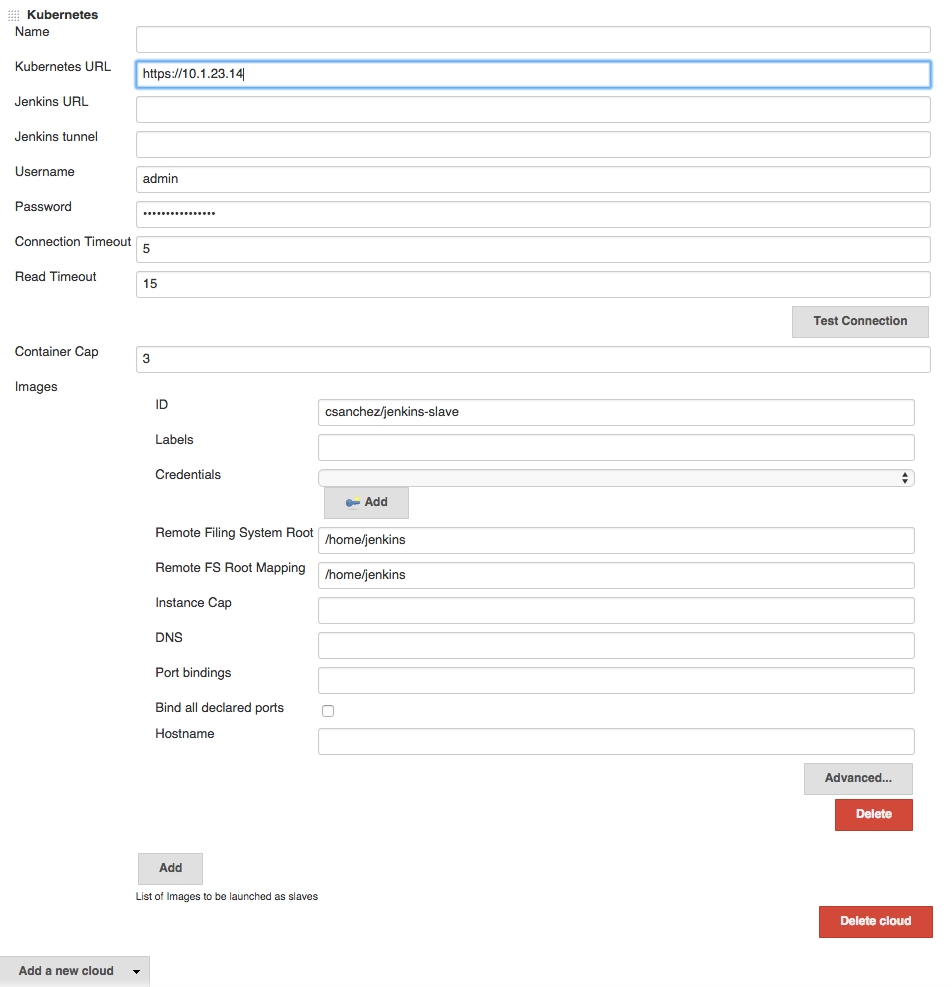
Configure Jenkins, adding the Kubernetes cloud under configuration, setting
Kubernetes URL to the container engine cluster endpoint, and the correct username and password.
Set Container Cap to a reasonable number for tests, i.e. 3.
Add an image with
- ID:
csanchez/jenkins-slave - Remote filesystem root:
/home/jenkins - Remote FS Root Mapping:
/home/jenkins
Now it is ready to be used.
Tearing it down
gcloud preview container pods delete jenkins
gcloud preview container services delete jenkins
gcloud preview container services delete jenkins-slave
docker build -t csanchez/jenkins-kubernetes .