git clone https://github.com/sunilale0/django-redis-key-value-store.git
cd django-redis-key-value-storeset up a virtual environment and then
pip install -r requirements.txt
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py runserverSet up Redis-Cli and test. Here, we are assuming that redis port is 6379, if it is different, set that value in django_redis/settings.py through variable REDIS_PORT .
Common use cases of Redis include
- Caching - It's faster than traditional databases. So, it is used for temporary data storage and retrieval.
- Message Queueing - Redis can also be used as a message broker for message queueing systems through its Publish/Subscribe messaging paradigm
- Data Storage - Redis can be used to store key-value data as NoSQL database
Example use: Twitter stores the most recent incoming tweets for a user on Redis to speed up the delivery of the tweets to client applications Pinterest uses Redis to store a list of users and boards a user follows, a list of a user's followers, and a list of people who follow your boards, among other lists to enchance the experience on the platform.
For windows go to here, download a .msi file with latest release tag.
For Mac/linux there is installation guide on their site.
Once it is verified that redis is installed. Enter Redis-cli by using the command. Remember the port number for later.
redis-cliTry out the commands below:
// SET sets a key hello with the value of "world" with an expiry of 10 seconds, "EX 10" is optional
SET hello "world" EX 10
// GET gets the value associated with the key hello
GET hello
// DEL deletes a key and the associated value
DEL hello
// GET gets the value associated with the key hello
GET hello
// if a key is set with expiry, we use TTL to view how much time is left
TTL hello
// use PERSIST to remove the expiry period
PERSIST hello
// use RENAME renames the key "hello" to "hello2"
RENAME hello hello2
// use FLUSHALL to delete all of the key-value entries in the current session of Redis
FLUSHALLHere, we will build an API using DJango and Django REST framework that can receive a key-value pair and store it in our Redis Server. Features:
- Retrieve values for given keys
- Retrieve all key-value pairs stored
- delete a key-value entry
Create a virtual environment and activate
py -m venv venv
venv\Scripts\activate
Install django djangorestframework and redis
pip install django djangorestframework redis
Start a project, create an app and migrate the models to the database
django-admin startproject django_redis .
django-admin startapp api
python manage.py migrate
python manage.py runserverAdd our app api and django REST framework to our project by adding the following inside INSTALLED_APPS list found in django_redis/settings.py
"rest_framework",
"api",Provide Host and Port number of Redis to Django by including the following in django_redis/settings.py
REDIS_HOST = "localhost"
REDIS_PORT = 6379Note: for now we will use a local Redis Instance, but a remote or Docker containerized instance of redis can also be used in the same way: defining the host and port.
Inside api/views.py start by importing some necessary libraries:
import json
from django.conf import settings
import redis
from rest_framework.decorators import api_view
from rest_framework import status
from rest_framework.response import Response
# Connect to our Redis instance
redis_instance = redis.StrictRedis(host=settings.REDIS_HOST, port = settings.REDIS_PORT, db = 0)Now add a view manage_items() which will be used to retrieve all the items currently set in our running Redis instance, and to create new entries in our Redis instance by passing a JSON object:
@api_view(["GET", "POST"])
def manage_items(request, *args, **kwargs):
if request.method == "GET":
items = {}
count = 0
for key in redis_instance.keys("*"):
items[key.decode("utf-8")] = redis_instance.get(key)
count += 1
response = {
"count": count,
"msg": f"Found {count} items.",
"items": items
}
return Response(response, status=200)
elif request.method == "POST":
item = json.loads(request.body)
key = list(item.keys())[0]
value = item[key]
redis_instance.set(key, value)
response = {
"msg": f"{key} successfully set to {value}"
}
return Response(response, 201)add another function manage_item() inside api/views.py that will be used to create, update and delete a single key-value in the Redis instance:
@api_view(["GET", "PUT", "DELETE"])
def manage_item(request, *args, **kwargs):
if request.method == "GET":
if kwargs["key"]:
value = redis_instance.get(kwargs["key"])
if value:
response = {
"key": kwargs["key"],
"value": value,
"msg": "success"
}
return Response(response, status=200)
else:
response = {
"key": kwargs["key"],
"value": None,
"msg": "Not Found"
}
return Response(response, status=404)
elif request.method == "PUT":
if kwargs["key"]:
request_data = json.loads(request.body)
new_value = request_data["new_value"]
value = redis_instance.get(kwargs["key"])
if value:
redis_instance.set(kwargs["key"], new_value)
value = redis_instance.get(kwargs["key"])
response = {
"key": kwargs["key"],
"value": value,
"msg": f"Successfully updated {kwargs['key']}"
}
return Response(response, status=200)
else:
response = {
"key": kwargs["key"],
"value": None,
"msg": "Not found"
}
return Response(response, status=404)
elif request.method == "DELETE":
if kwargs["key"]:
result = redis_instance.delete(kwargs["key"])
if result == 1:
response ={
"msg": f"{kwargs['key']} successfully deleted"
}
return Response(response, status=200)
else:
response = {
"key": kwargs["key"],
"value": None,
"msg": "Not found"
}
return Response(response, status=404)manage_item() wil use a key of the item passed in the URL, to identify and perform the indicate operation: GET, PUT or DELETE.
Now, create a new file in api/ caled urls.py and add the following:
from django.urls import path
from rest_framework.urlpatterns import format_suffix_patterns
from .views import manage_items, manage_item
urlpatterns={
path("", manage_items, name="items"),
path("<slug:key>", manage_item, name="single_item")
}
urlpatterns = format_suffix_patterns(urlpatterns)Finally include api/urls.py in the main project by adding the following in django_redis/urls.py:
from django.urls import path, include # include added
urlpatterns = [
# ...,
path("api/", include("api.urls")),
]We can directly visit http://localhost:8000/api/ to view, we can only view what is stored in our Redis instance from here, which is nothing.
So, go to redis-cli and add some values like:
SET hi "hello"
SET oh "no"reload http://localhost:8000/api/.
We can also see a value in a key by doing http://localhost:8000/api/hi.
But to update a value and to post a value we need to use Postman. Download and install.
After installing, open it. You will see a signup option, but there will also a link to skip signing up and go directly into the application.
there, test the addresses used above in GET mode.
POST test:
select address http://localhost:8000/api/name
select POST, got to Body tab and select raw and select JSON(application/json) and add the following:
{
"name": "unknown"
}hit send. You should see a message below that says
{
"msg": "name successfully set to unknown"
}PUT test:
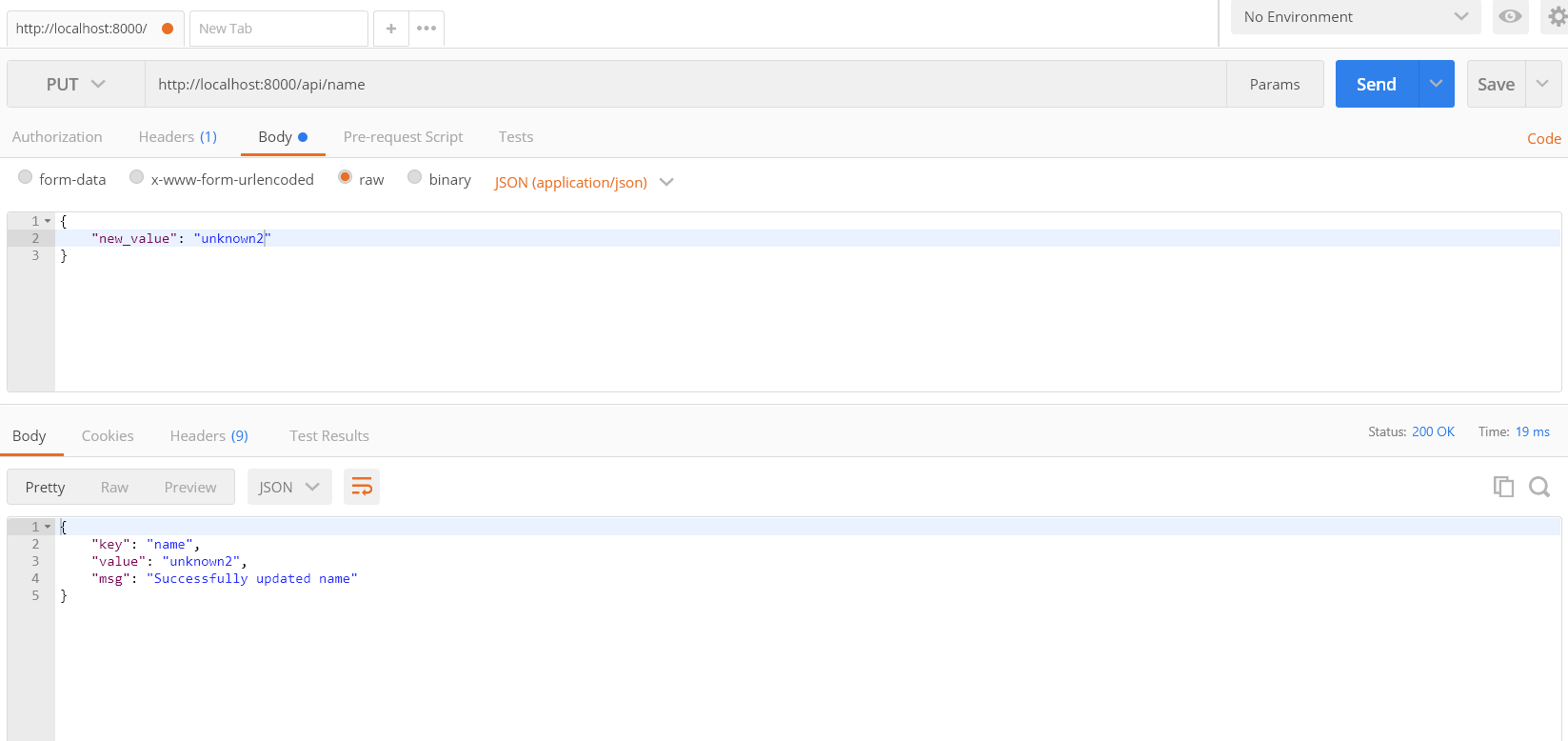
select address http://localhost:8000/api/name
select PUT, got to Body tab and select raw and select JSON(application/json) and add the following:
{
"new_value": "unknown2"
}hit send. You should see a message below that says
{
"key": "name",
"value": "unknown2",
"msg": "Successfully updated name"
}PUT in postman looks like the following
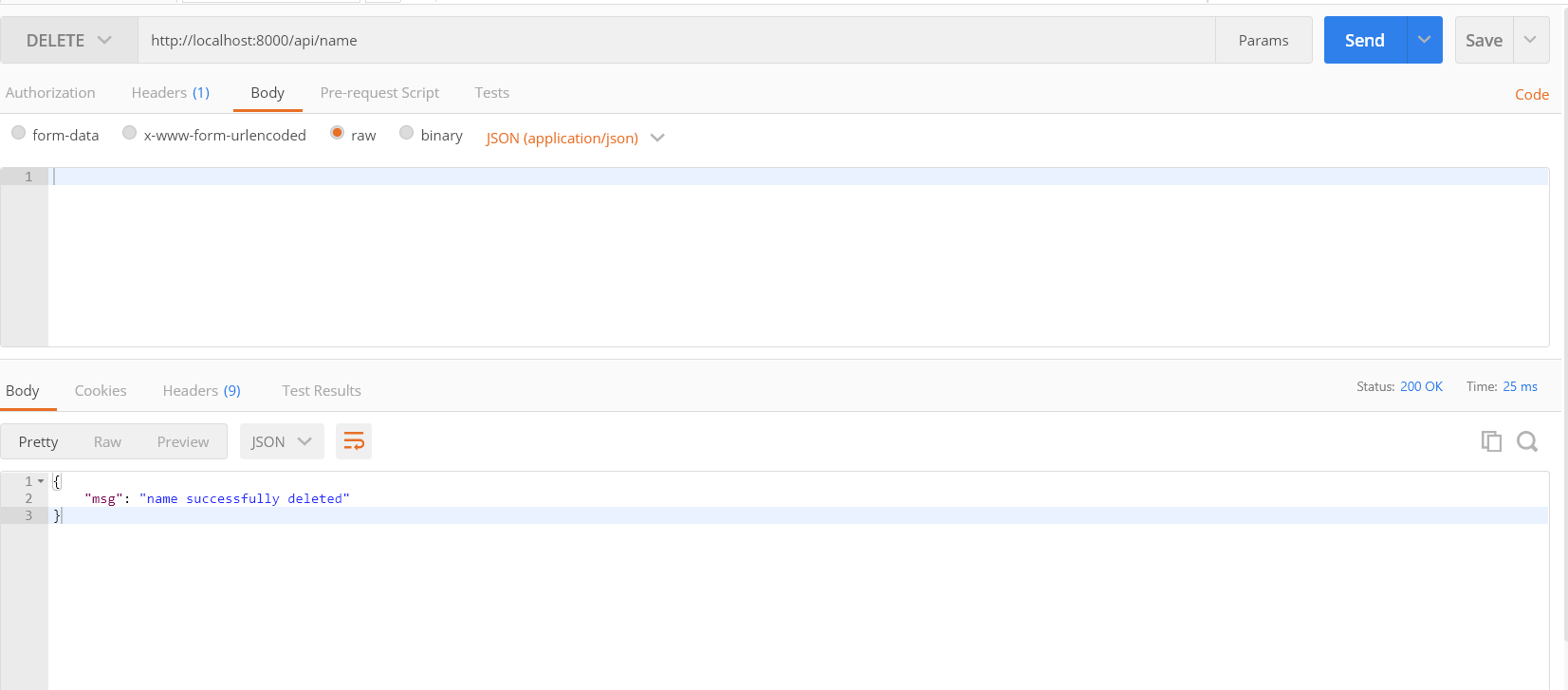
DELETE in postman will look like the following:
A simple django application with djano REST framework and storage operations on redis is now complete.
Thanks StackAbuse for the tutorial. Report issues here. Ideas go here.