Hyperledger Fabric sample Using Event Handling with the next generation IBM Blockchain Platform
This code pattern demonstrates leveraging the event handling feature within an application that is based on using an IKS cluster with IBM Blockchain Platform V2.0 service on IBM Cloud. We apply this use case to an auction use case. It shows how events can be emitted by using the Hyperledger Fabric SDK and subscribed to by external applications. The application is implemented in Node.js and is using the Hyperledger Fabric SDK for node.js to connect with the network, set up an event listener and catch tranactional events.
A client application may use the Fabric Node.js client to register a "listener" to receive blocks as they are added to the channel ledger. This is known as "channel-based events", and it allows a client to start to receive blocks from a specific block number, allowing event processing to run normally on blocks that may have been missed. The Fabric Node.js client can also assist client applications by processing the incoming blocks and looking for specific transactions or chaincode events. This allows a client application to be notified of transaction completion or arbitrary chaincode events without having to perform multiple queries or search through the blocks as they are received. After the transaction proposal has been successfully endorsed, and before the transaction message has been successfully broadcasted to the orderer, the application should register a listener to be notified of the event when the transaction achieves finality, which is when the block containing the transaction gets added to the peer's ledger/blockchain.
Fabric committing peers provides an event stream to publish blocks to registered listeners. A Block gets published whenever the committing peer adds a validated block to the ledger. There are three ways to register a listener to get notified:
-
register a
block listenerto get called for every block event. The listener will be passed a fully decoded Block object. -
register a
transaction listenerto get called when the specific transaction by id is committed (discovered inside a published block). The listener will be passed the transaction id, transaction status and block number. -
register a
chaincode event listenerto get called when a specific chaincode event has arrived. The listener is be passed the ChaincodeEvent, block number, transaction id, and transaction status.
In this pattern we are registering a transaction event. So when a transaction is completed/committed - an event will get triggered and the application will catch it and report it.
Audience level : Intermediate Developers
If you have an IBM Cloud Lite account, you can also use the IBM Blockchain Platform Service free for 30 days to do this pattern. Additionally, IKS is free too.
When you have completed this code pattern, you will understand how to:
- Package the smart contract using IBM Blockchain Platform Extension for VS Code
- Setup a Hyperledger Fabric network on IBM Blockchain Platform 2.0
- Install and instantiate smart contract package onto the IBM Blockchain Platform 2.0
- Develop a Node.js server with the Hyperledger Fabric SDK to interact with the deployed network and setup your applications to trigger and catch events
UPDATE
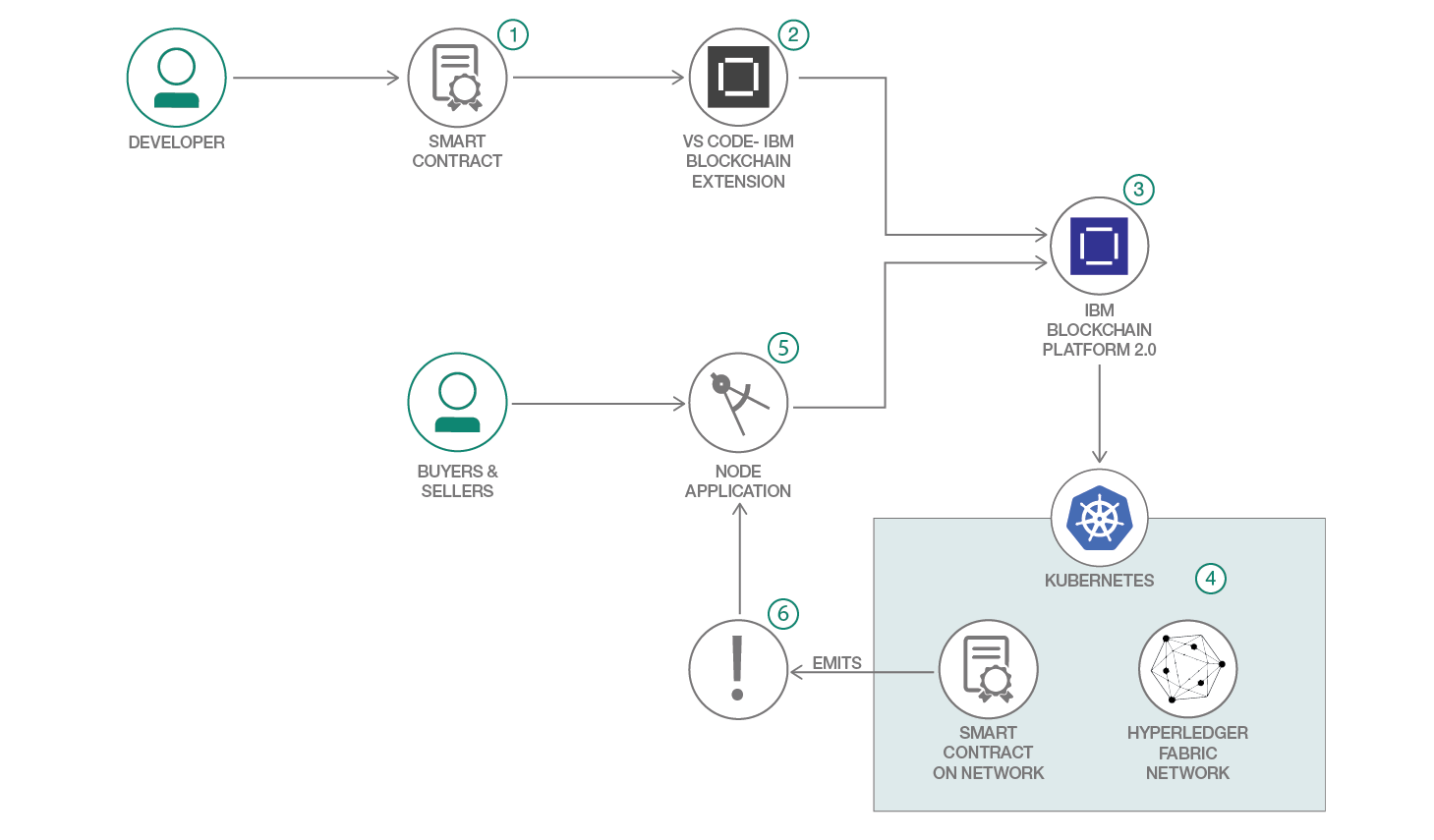
- The developer develops a smart contract using Node.js
- Use the IBM Blockchain Platform Extension for VS Code to package the Decentralized Energy smart contract.
- Setup and launch the IBM Blockchain Platform 2.0 service
- The IBM Blockchain Platform 2.0 enables the creation of a network onto a IBM Kubernetes Service, enabling installation and instantiation of the Auction smart contract on the network
- The Node.js application uses the Fabric SDK to add a listener to specific transactions and subsequently interact with the deployed network on IBM Blockchain Platform 2.0 and issues transactions.
- Events are emitted as transactions are triggered and blocks are committed to the ledger. The events are sent back to the Node.js application.
- IBM Blockchain Platform 2.0 gives you total control of your blockchain network with a user interface that can simplify and accelerate your journey to deploy and manage blockchain components on the IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service.
- IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service creates a cluster of compute hosts and deploys highly available containers. A Kubernetes cluster lets you securely manage the resources that you need to quickly deploy, update, and scale applications.
- IBM Blockchain Platform Extension for VS Code is designed to assist users in developing, testing, and deploying smart contracts -- including connecting to Hyperledger Fabric environments.
- Hyperledger Fabric v1.4 is a platform for distributed ledger solutions, underpinned by a modular architecture that delivers high degrees of confidentiality, resiliency, flexibility, and scalability.
- Node.js is an open source, cross-platform JavaScript run-time environment that executes server-side JavaScript code.
- Hyperledger Fabric SDK for node.js provides a powerful API to interact with a Hyperledger Fabric blockchain.
- IBM Cloud account
- Node v8.x or greater and npm v5.x or greater
- VSCode version 1.26 or greater
- IBM Blockchain Platform Extension for VSCode
If you want to run this pattern locally, without any Cloud services, then all you need is VSCode and the IBM Blockchain Platform extension.
- Install VSCode
- Install IBM Blockchain Platform Extension for VSCode
- Node v8.x or greater and npm v5.x or greater
To run a local network, you can find steps here.
Follow these steps to set up and run this code pattern. The steps are described in detail below.
- Clone the repo
- Package the smart contract
- Create IBM Cloud services
- Build a network
- Deploy Auction Event Smart Contract on the network
- Connect application to the network
- Run the application
Clone this repository in a folder of your choice:
git clone https://github.com/IBM/auction-events.git
We will use the IBM Blockchain Platform extension to package the smart contract.
-
Open Visual Studio code and open the
contractfolder fromauction-eventsthat was cloned earlier. -
Press the
F1key to see the different VS code options. ChooseIBM Blockchain Platform: Package a Smart Contract Project.
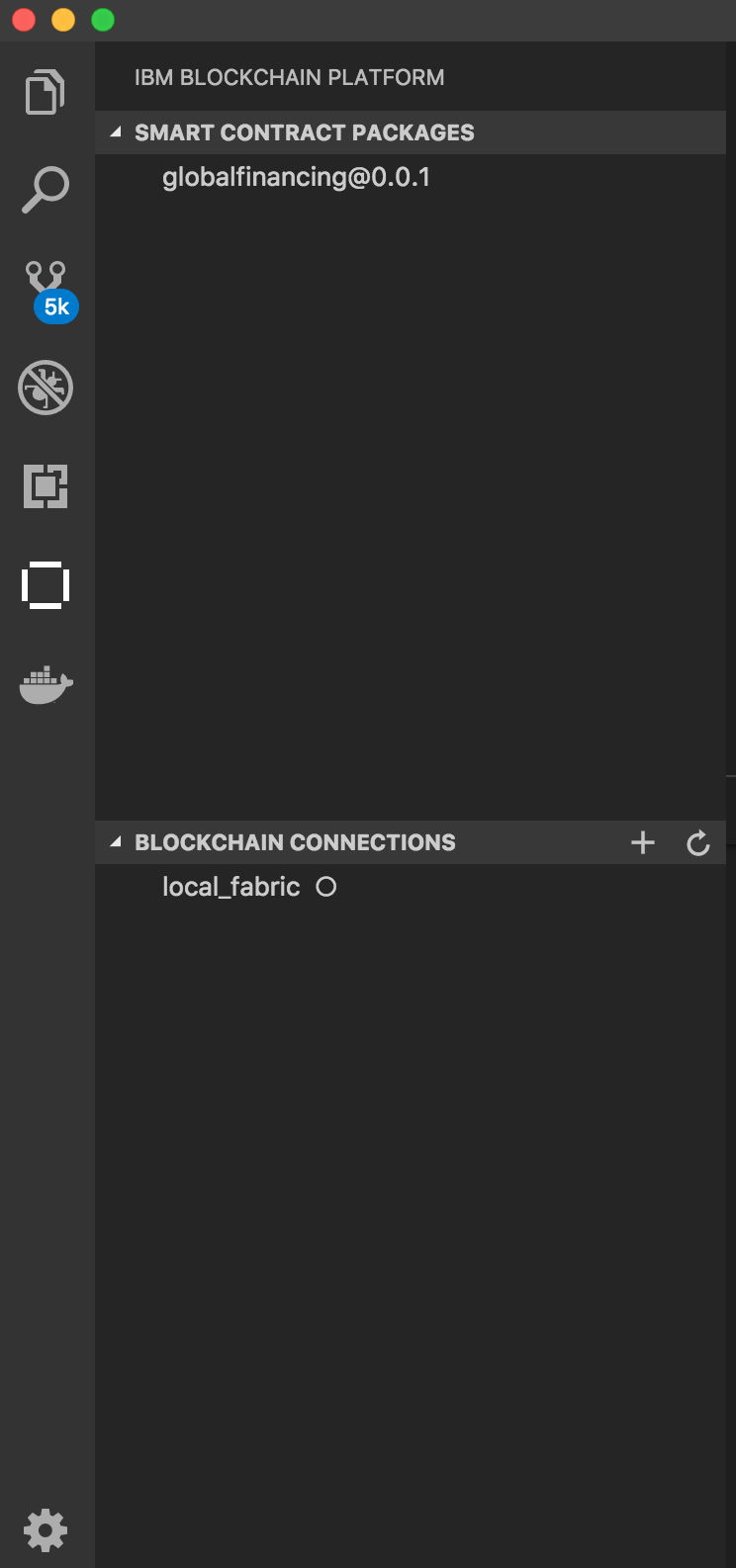
- Click the
IBM Blockchain Platformextension button on the left. This will show the packaged contracts on top and the blockchain connections on the bottom. Note You will seeauction@0.0.1instead of globalfinancing@1.0.0.
-
Next, right click on the packaged contract (in this case, select auction@0.0.1) to export it and choose
Export Package. -
Choose a location on your machine and save
.cdsfile. We will use this packages smart contract later to deploy on the IBM Blockchain Platform 2.0 service.
Now, we will start creating our Hyperledger Fabric network on the IBM Cloud.
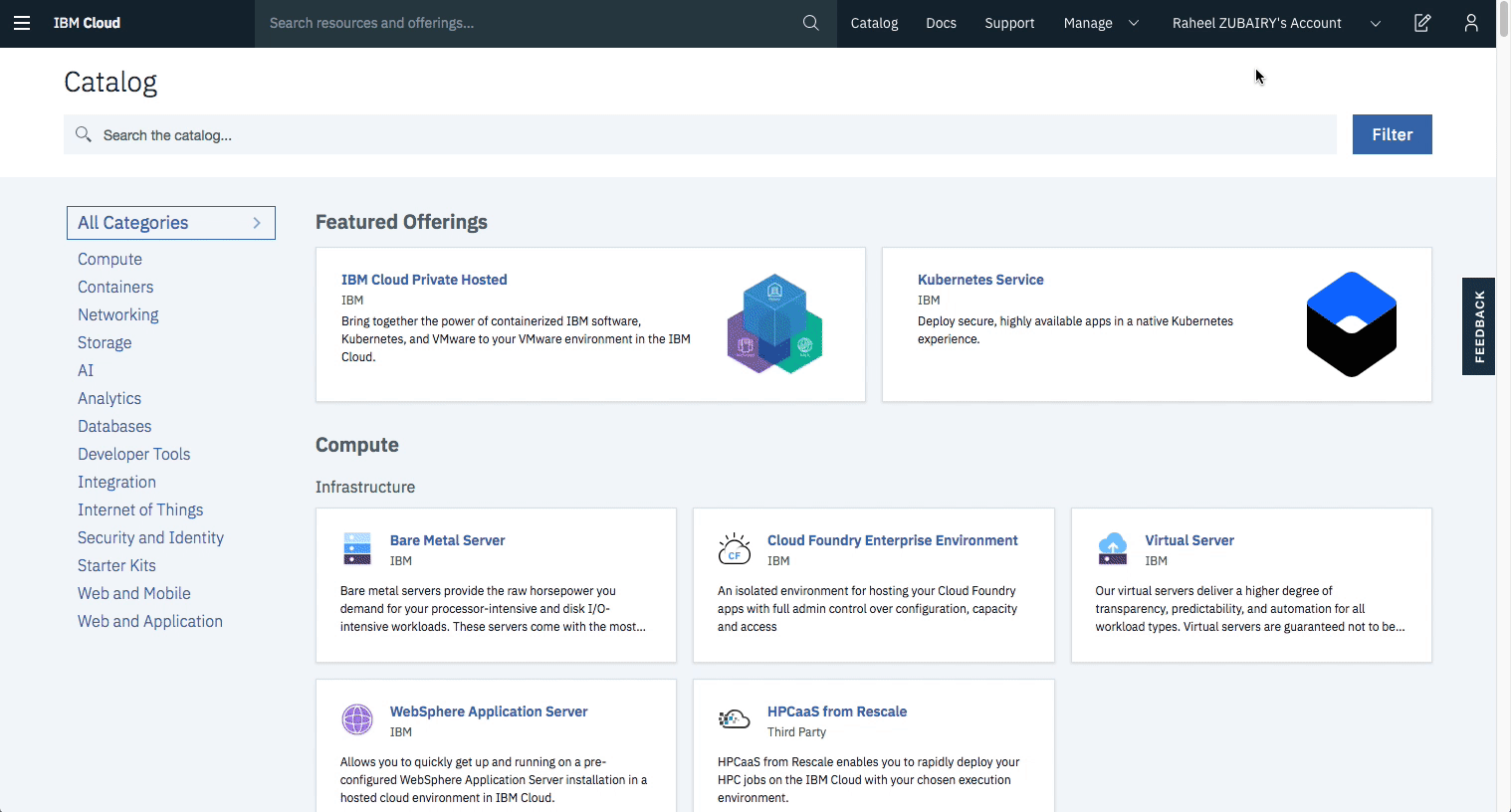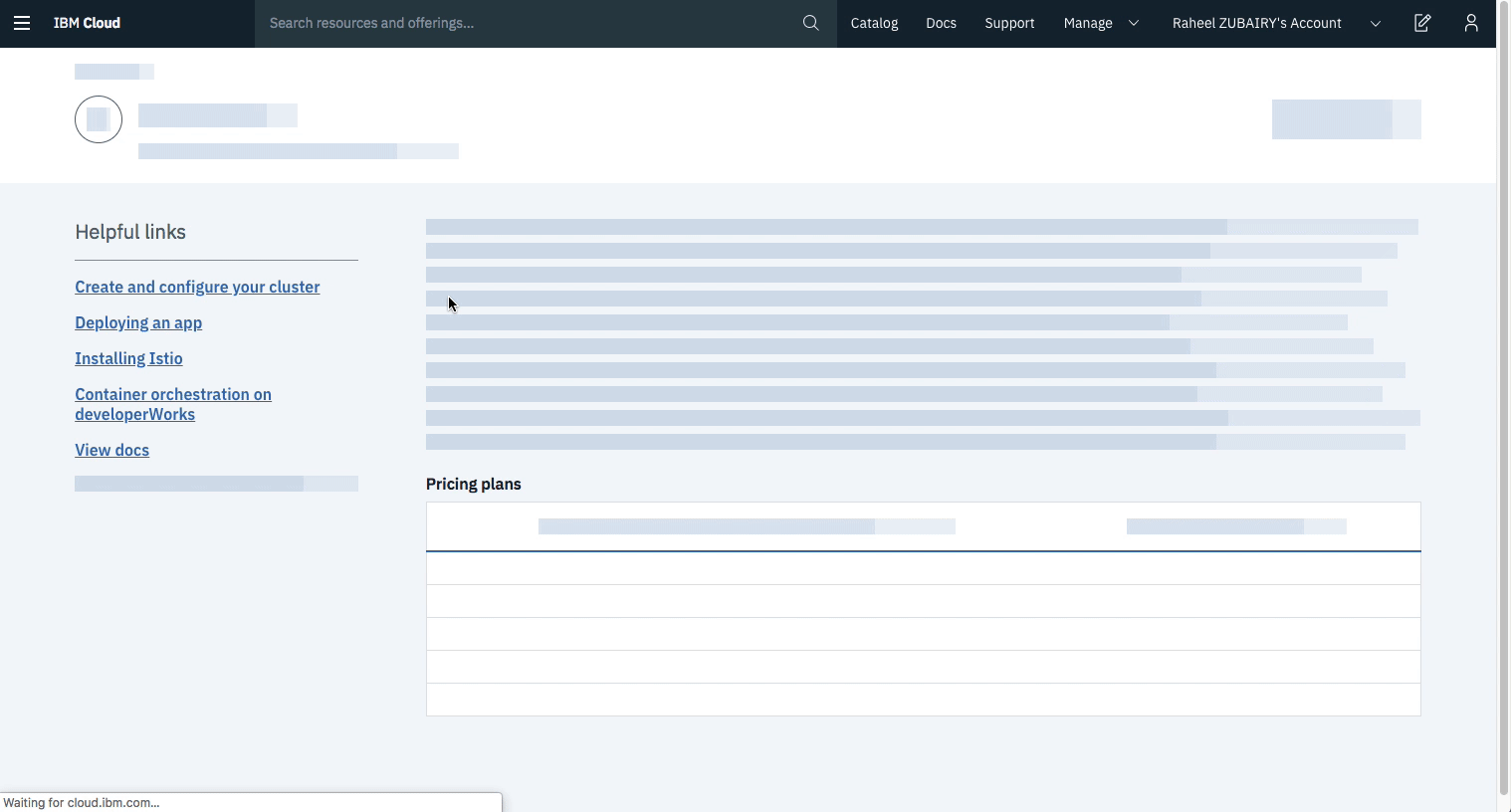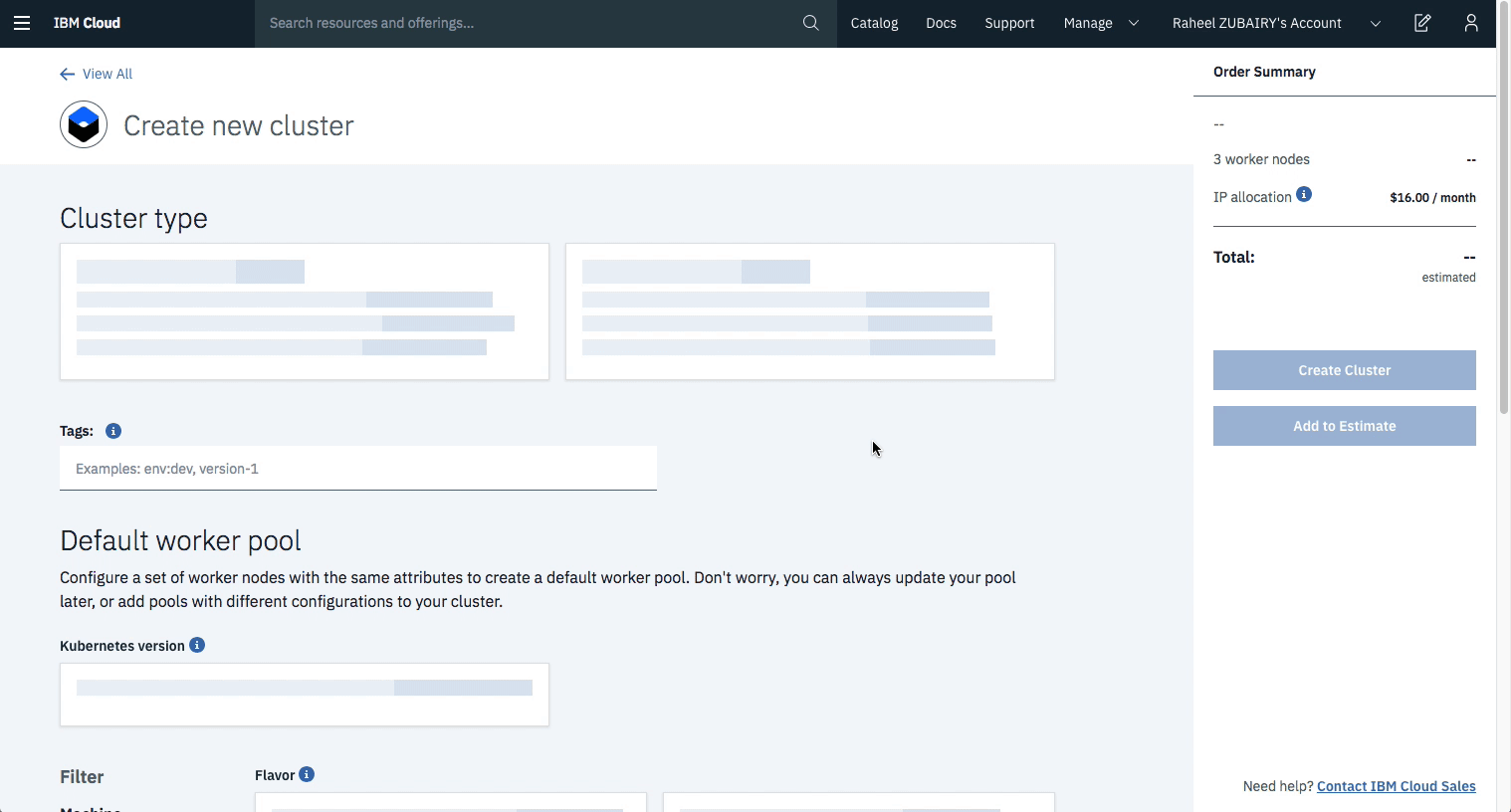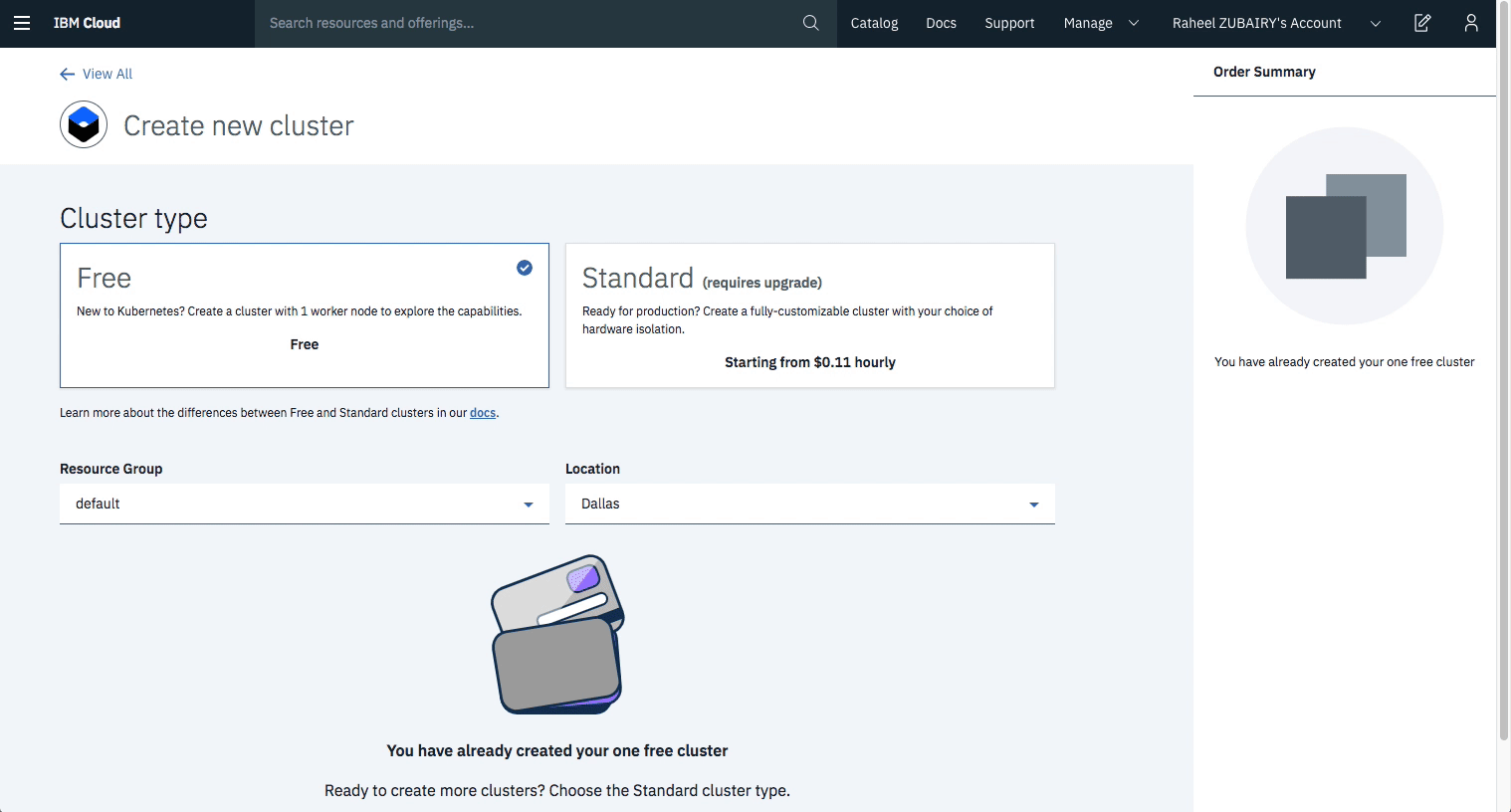
- Create the IBM Cloud Kubernetes Service. You can find the service in the
Catalog. For this code pattern, we can use theFreecluster, and give it a name. Note, that the IBM Cloud allows one instance of a free cluster and expires after 30 days.
- Create the IBM Blockchain Platform 2.0 service on the IBM Cloud. You can find the service in the
Catalog, and give a name.
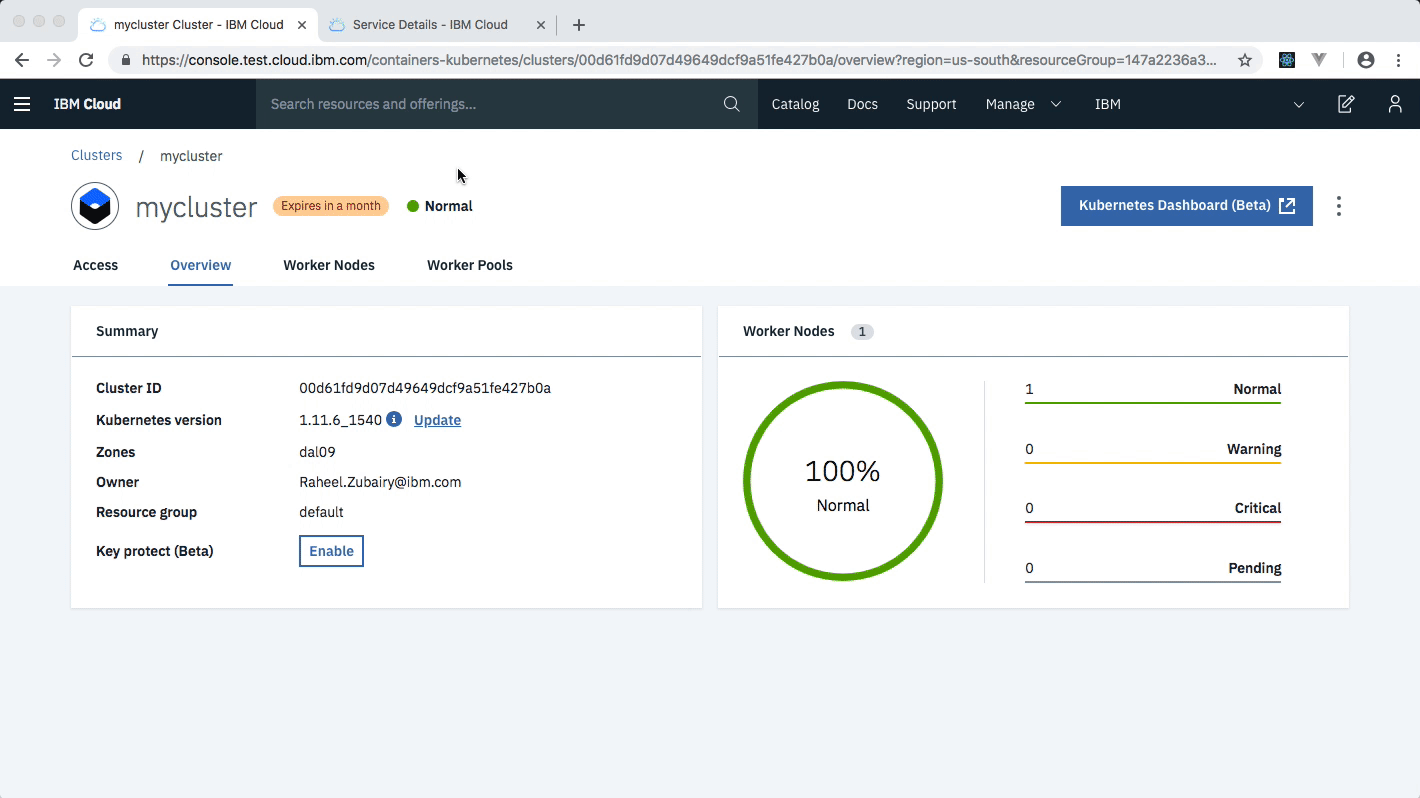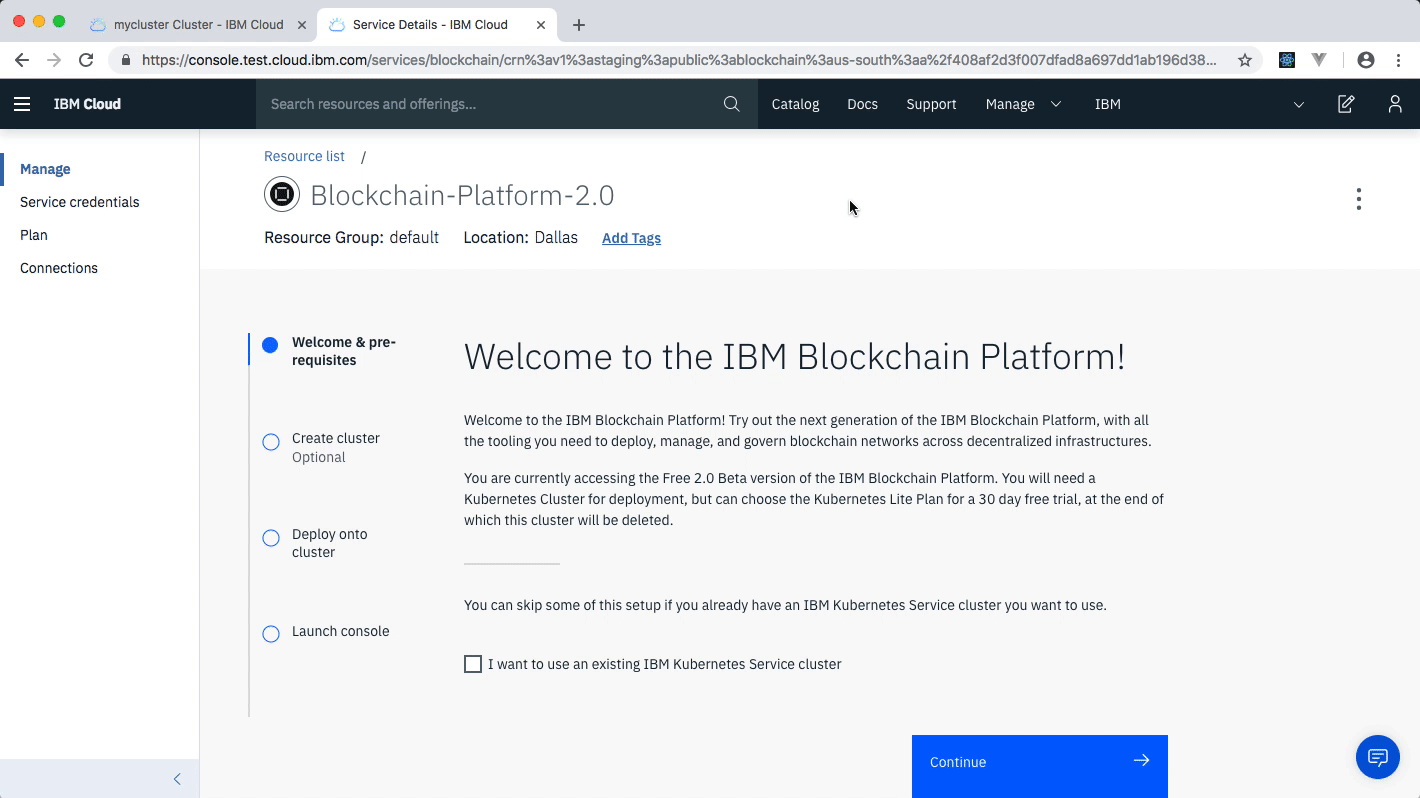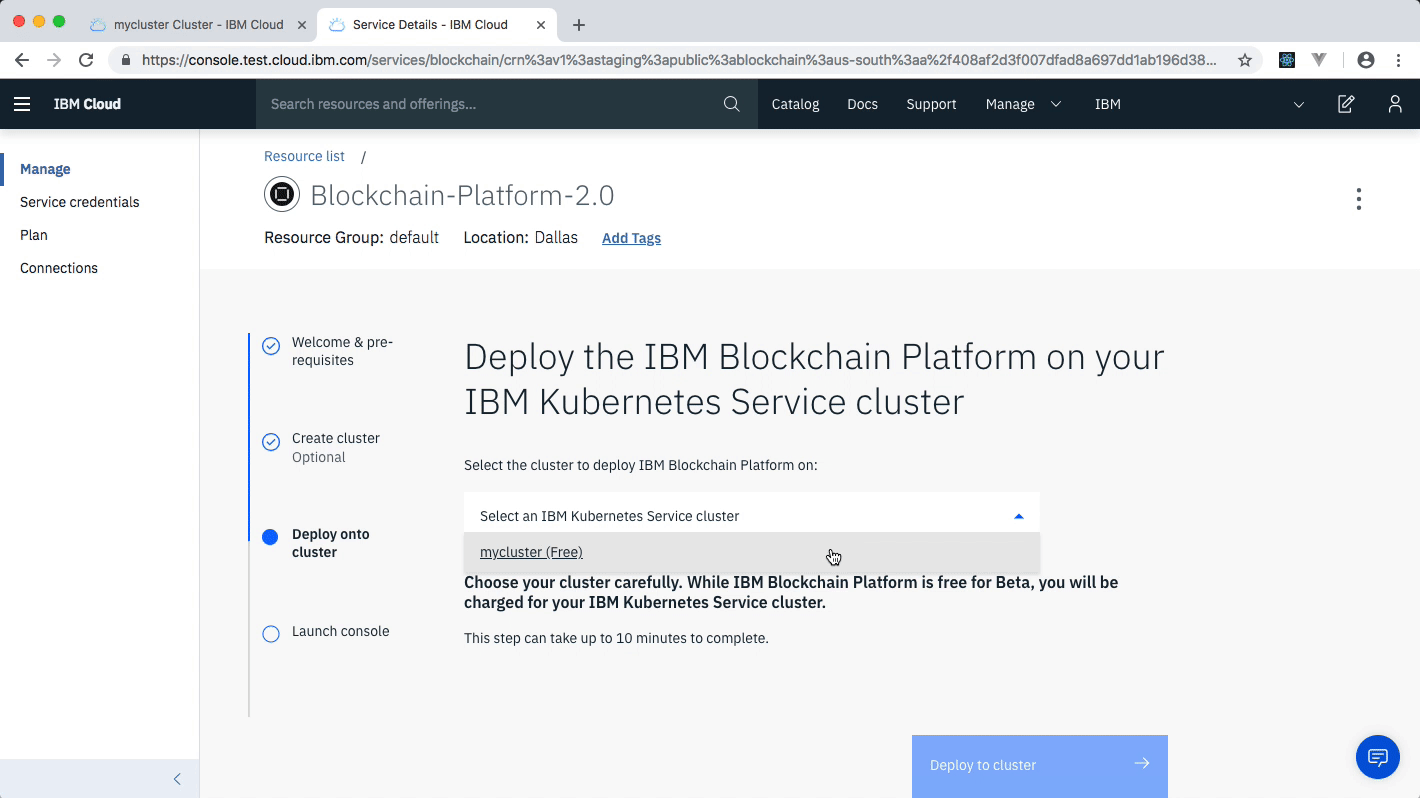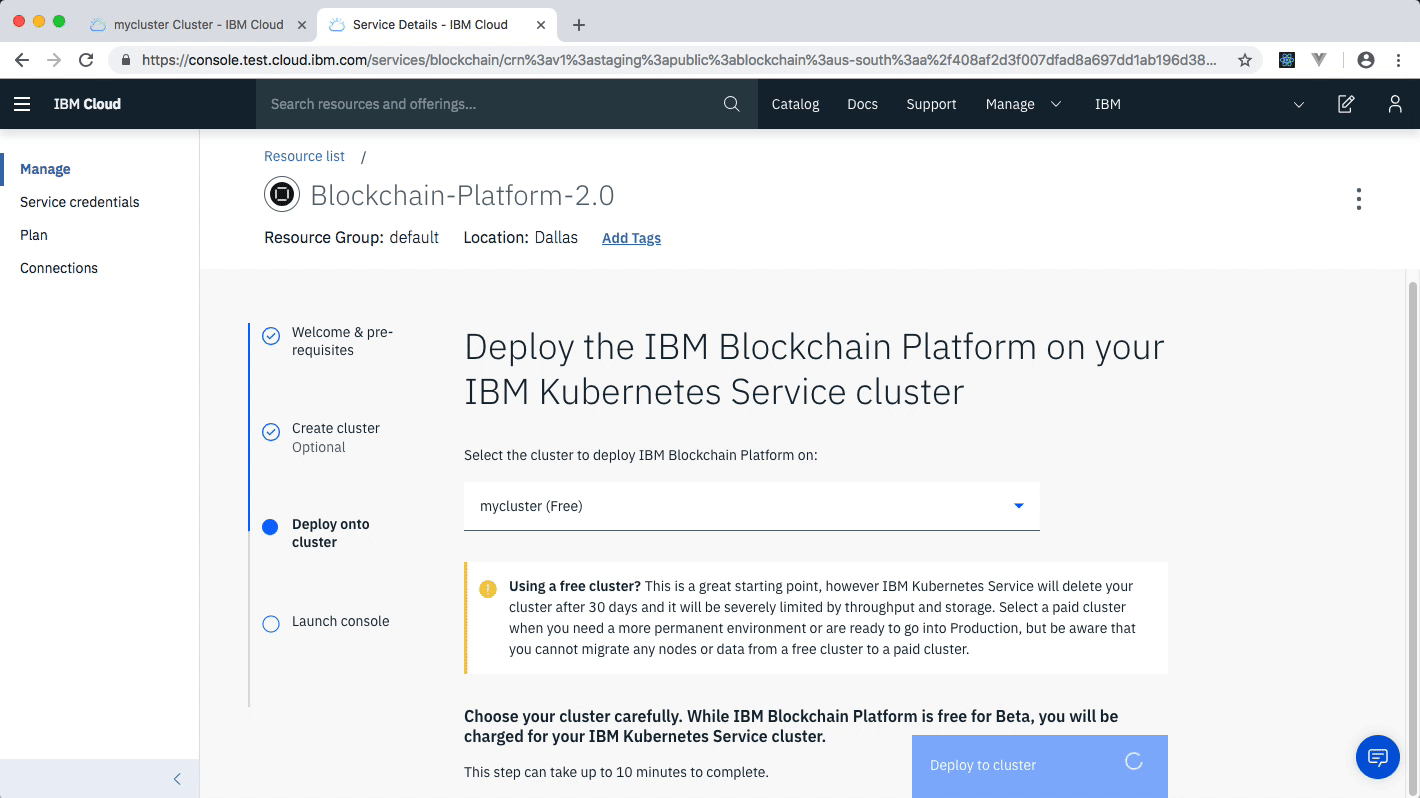
- After your kubernetes cluster is up and running, you can deploy your IBM Blockchain Platform on the cluster. The service walks through few steps and finds your cluster on the IBM Cloud to deploy the service on.
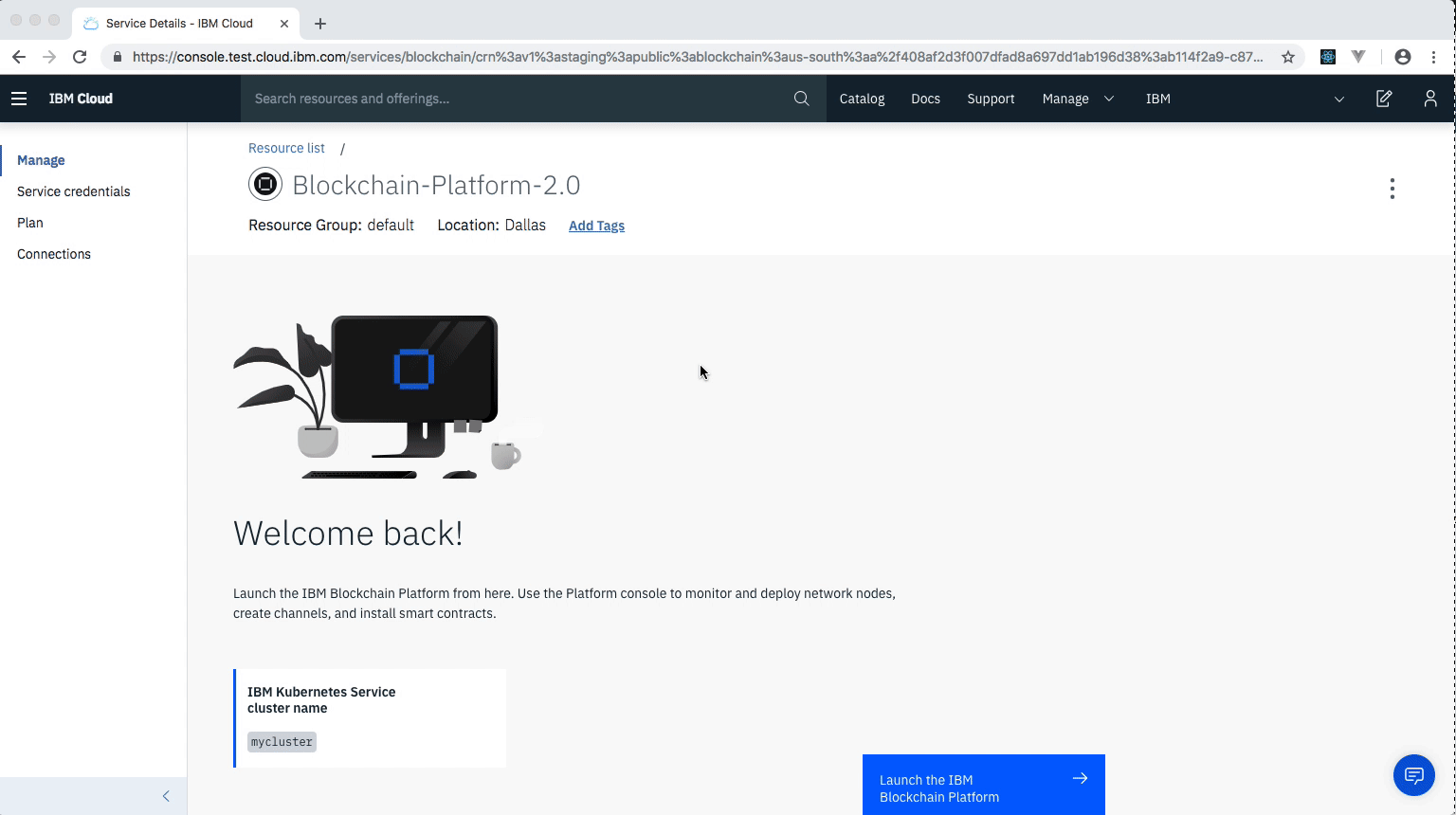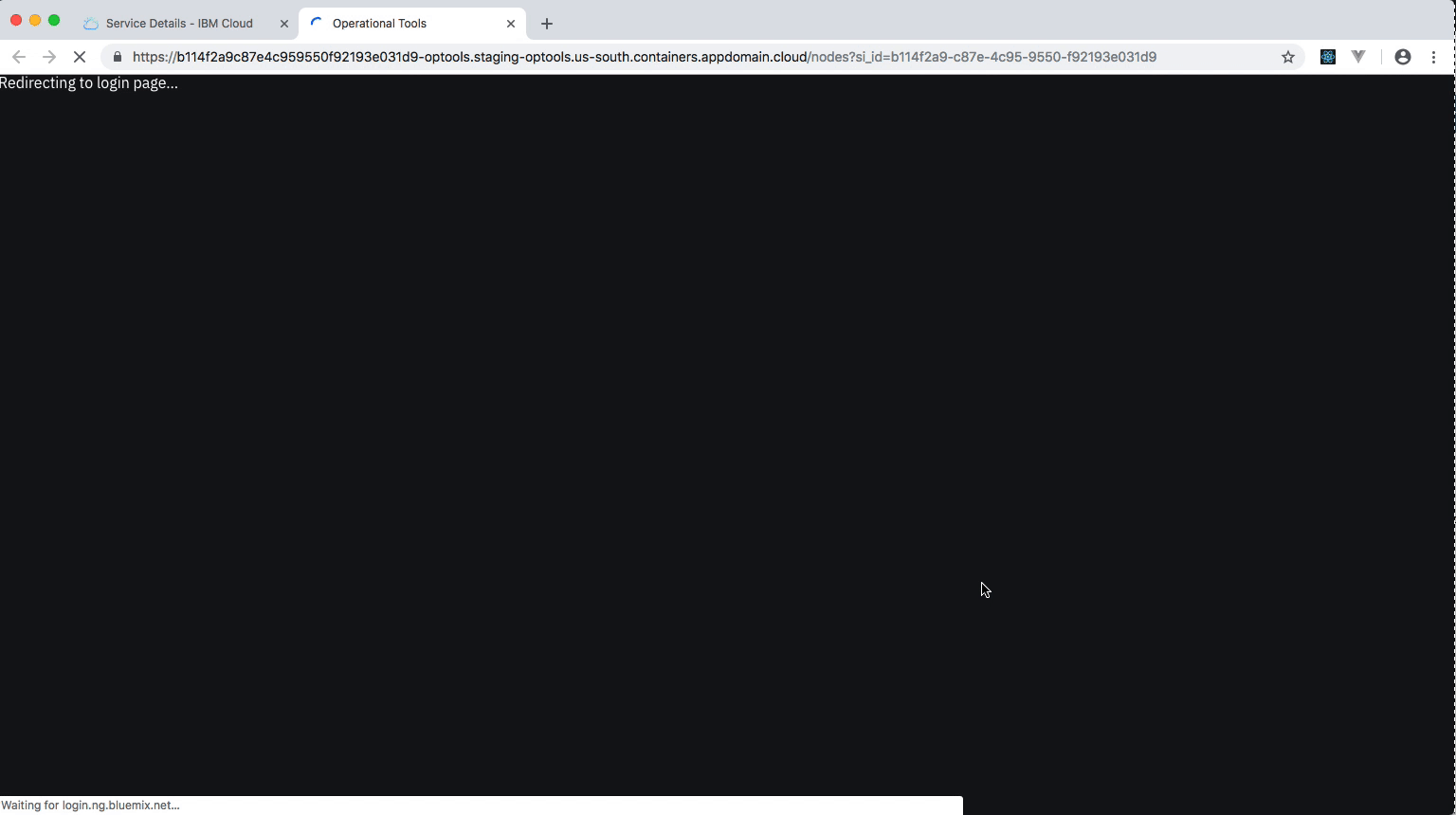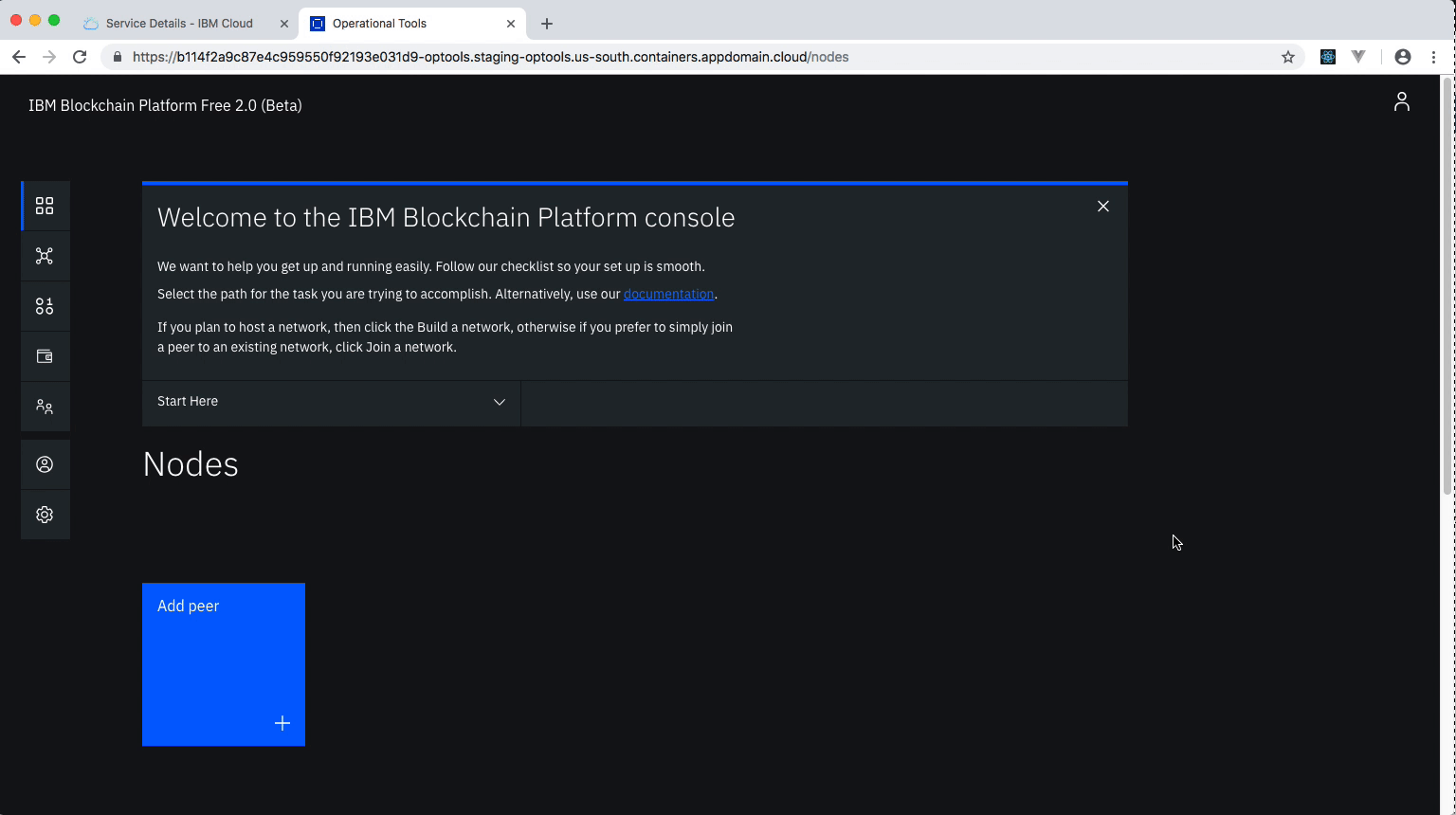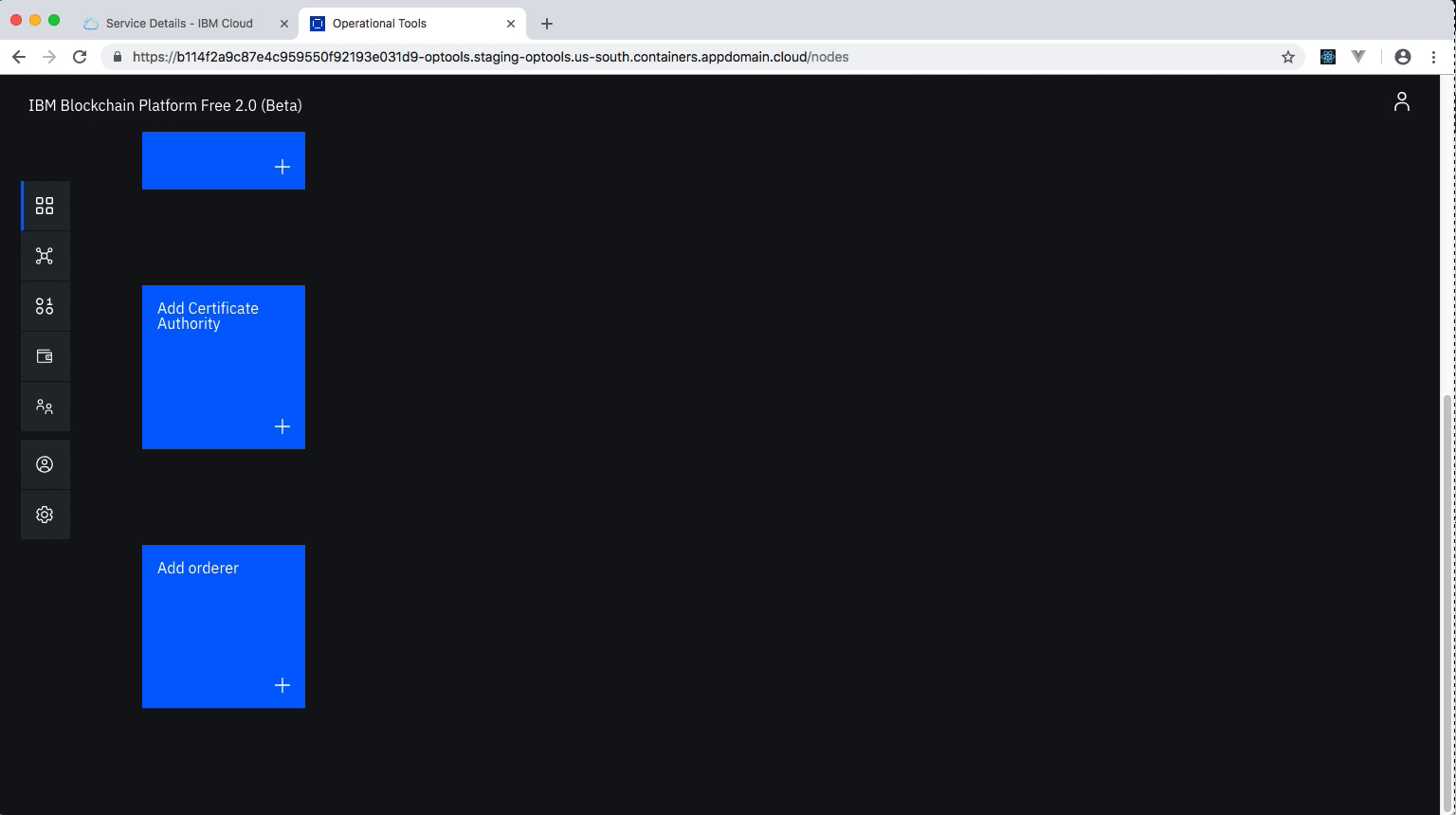
- Once the Blockchain Platform is deployed on the Kubernetes cluster, you can launch the console to start operating on your blockchain network.
We will build out the network as provided by the IBM Blockchain Platform documentation. This will include creating a channel with a single peer organization with its own MSP and CA (Certificate Authority), and an orderer organization with its own MSP and CA. We will create the respective identities to deploy peers and operate nodes.
-
- Click Add Certificate Authority.
- Click IBM Cloud under Create Certificate Authority and Next.
- Give it a Display name of
Org1 CA. - Specify an Admin ID of
adminand Admin Secret ofadminpw.
-
- Select the Org 1 CA Certificate Authority that we created.
- First, we will register an admin for our organization "org1". Click on the Register User button. Give an Enroll ID of
org1admin, and Enroll Secret oforg1adminpw. Click Next. Set the Type for this identity asclientand select from any of the affiliated organizations from the drop-down list. We will leave the Maximum enrollments and Add Attributes fields blank. - We will repeat the process to create an identity of the peer. Click on the Register User button. Give an Enroll ID of
peer1, and Enroll Secret ofpeer1pw. Click Next. Set the Type for this identity aspeerand select from any of the affiliated organizations from the drop-down list. We will leave the Maximum enrollments and Add Attributes fields blank.
-
- Navigate to the Organizations tab in the left navigation and click Create MSP definition.
- Enter the MSP Display name as
Org1 MSPand an MSP ID oforg1msp. - Under Root Certificate Authority details, specify the peer CA that we created
Org1 CAas the root CA for the organization. - Give the Enroll ID and Enroll secret for your organization admin,
org1adminandorg1adminpw. Then, give the Identity name,Org1 Admin. - Click the Generate button to enroll this identity as the admin of your organization and export the identity to the wallet. Click Export to export the admin certificates to your file system. Finally click Create MSP definition.
- Create a peer
- On the Nodes page, click Add peer.
- Click IBM Cloud under Create a new peer and Next.
- Give your peer a Display name of
Peer Org1. - On the next screen, select
Org1 CAas your Certificate Authority. Then, give the Enroll ID and Enroll secret for the peer identity that you created for your peer,peer1, andpeer1pw. Then, select the Administrator Certificate (from MSP),Org1 MSP, from the drop-down list and click Next. - Give the TLS Enroll ID,
admin, and TLS Enroll secret,adminpw, the same values are the Enroll ID and Enroll secret that you gave when creating the CA. Leave the TLS CSR hostname blank. - The last side panel will ask you to Associate an identity and make it the admin of your peer. Select your peer admin identity
Org1 Admin. - Review the summary and click Add Peer.
-
- Click Add Certificate Authority.
- Click IBM Cloud under Create Certificate Authority and Next.
- Give it a unique Display name of
Orderer CA. - Specify an Admin ID of
adminand Admin Secret ofadminpw.
-
- In the Nodes tab, select the Orderer CA Certificate Authority that we created.
- First, we will register an admin for our organization. Click on the Register User button. Give an Enroll ID of
ordereradmin, and Enroll Secret ofordereradminpw. Click Next. Set the Type for this identity asclientand select from any of the affiliated organizations from the drop-down list. We will leave the Maximum enrollments and Add Attributes fields blank. - We will repeat the process to create an identity of the orderer. Click on the Register User button. Give an Enroll ID of
orderer1, and Enroll Secret oforderer1pw. Click Next. Set the Type for this identity aspeerand select from any of the affiliated organizations from the drop-down list. We will leave the Maximum enrollments and Add Attributes fields blank.
-
- Navigate to the Organizations tab in the left navigation and click Create MSP definition.
- Enter the MSP Display name as
Orderer MSPand an MSP ID oforderermsp. - Under Root Certificate Authority details, specify the peer CA that we created
Orderer CAas the root CA for the organization. - Give the Enroll ID and Enroll secret for your organization admin,
ordereradminandordereradminpw. Then, give the Identity name,Orderer Admin. - Click the Generate button to enroll this identity as the admin of your organization and export the identity to the wallet. Click Export to export the admin certificates to your file system. Finally click Create MSP definition.
-
- On the Nodes page, click Add orderer.
- Click IBM Cloud and proceed with Next.
- Give your peer a Display name of
Orderer. - On the next screen, select
Orderer CAas your Certificate Authority. Then, give the Enroll ID and Enroll secret for the peer identity that you created for your orderer,orderer1, andorderer1pw. Then, select the Administrator Certificate (from MSP),Orderer MSP, from the drop-down list and click Next. - Give the TLS Enroll ID,
admin, and TLS Enroll secret,adminpw, the same values are the Enroll ID and Enroll secret that you gave when creating the CA. Leave the TLS CSR hostname blank. - The last side panel will ask to Associate an identity and make it the admin of your peer. Select your peer admin identity
Orderer Admin. - Review the summary and click Add Orderer.
-
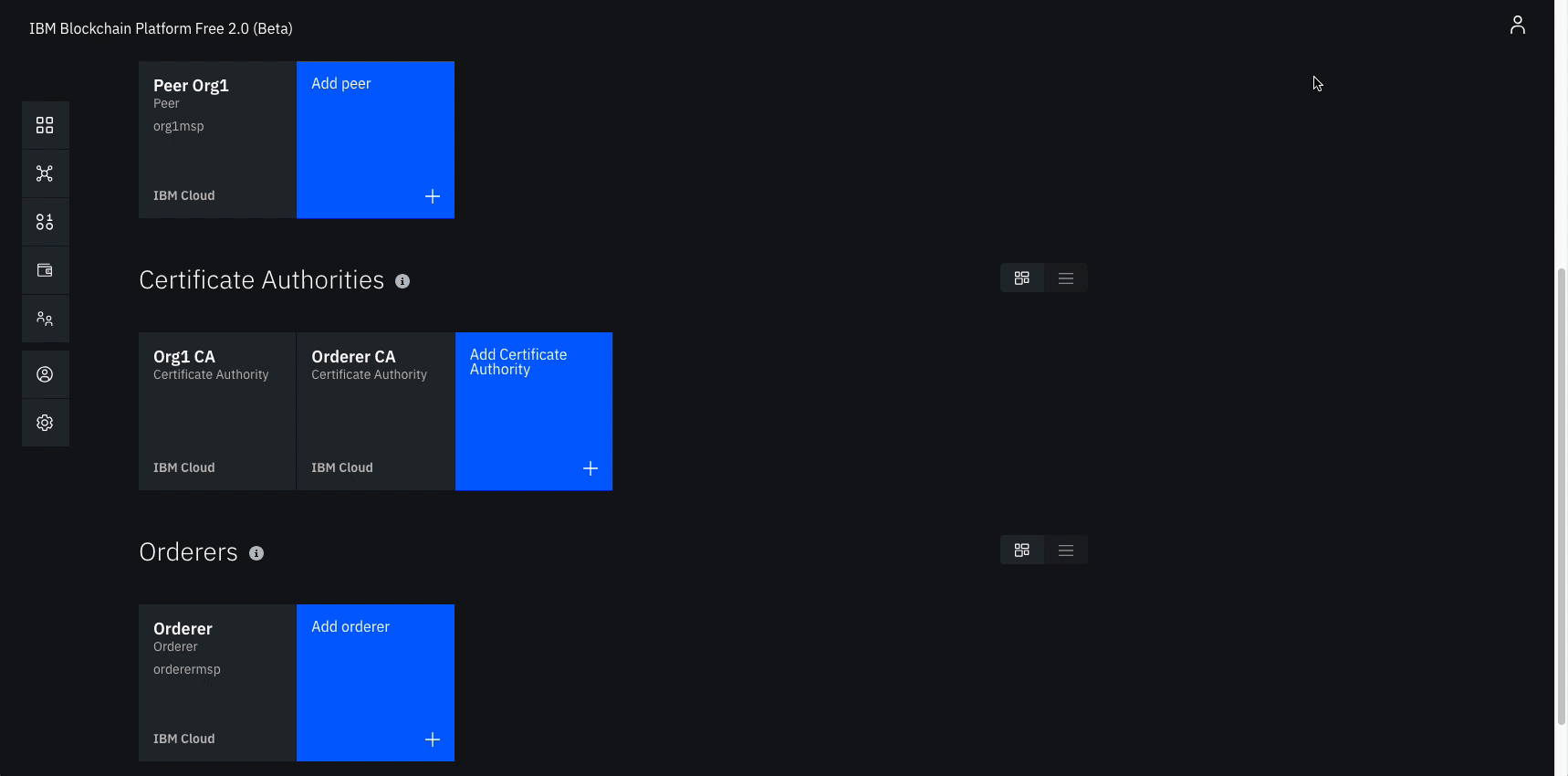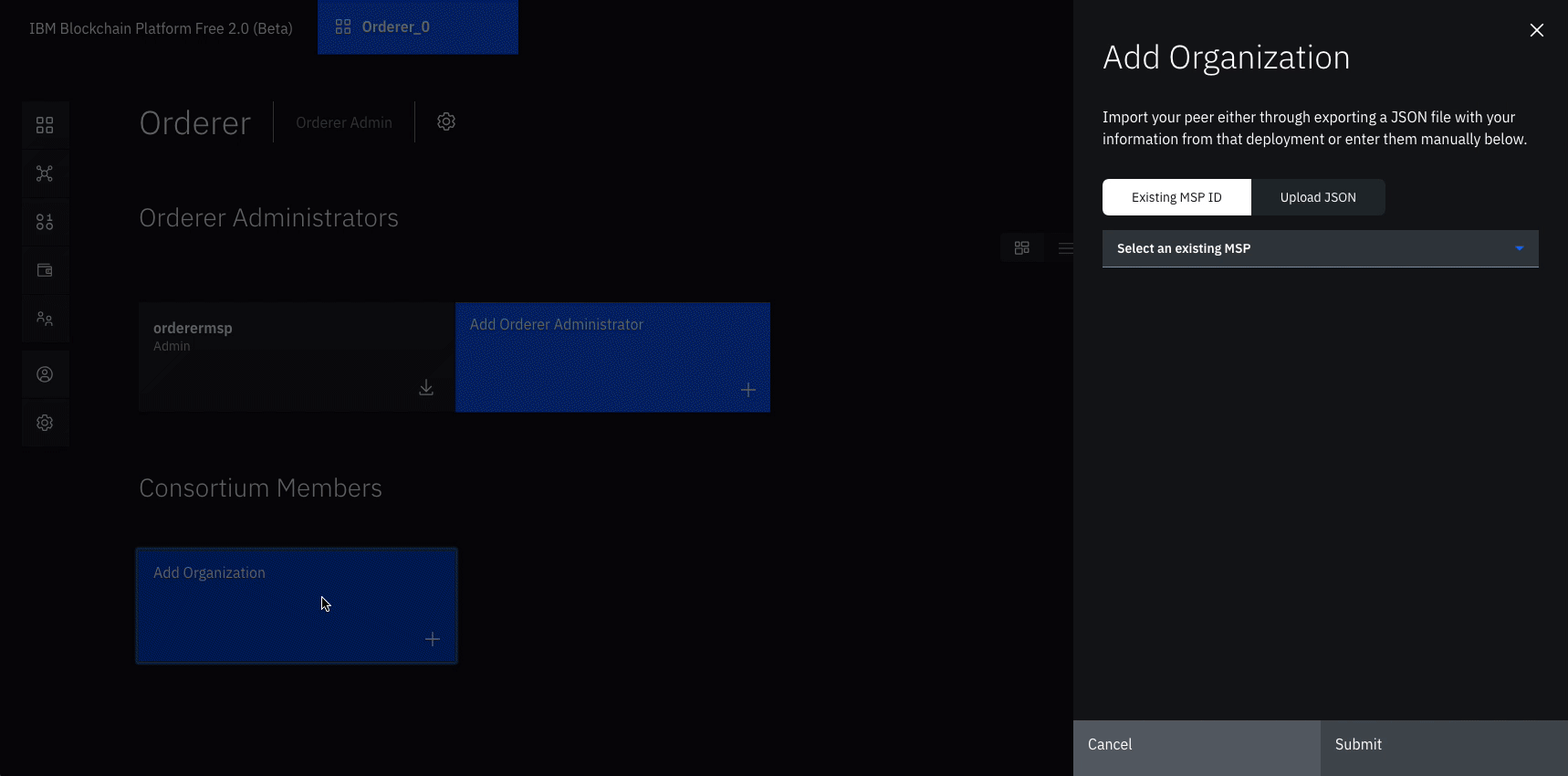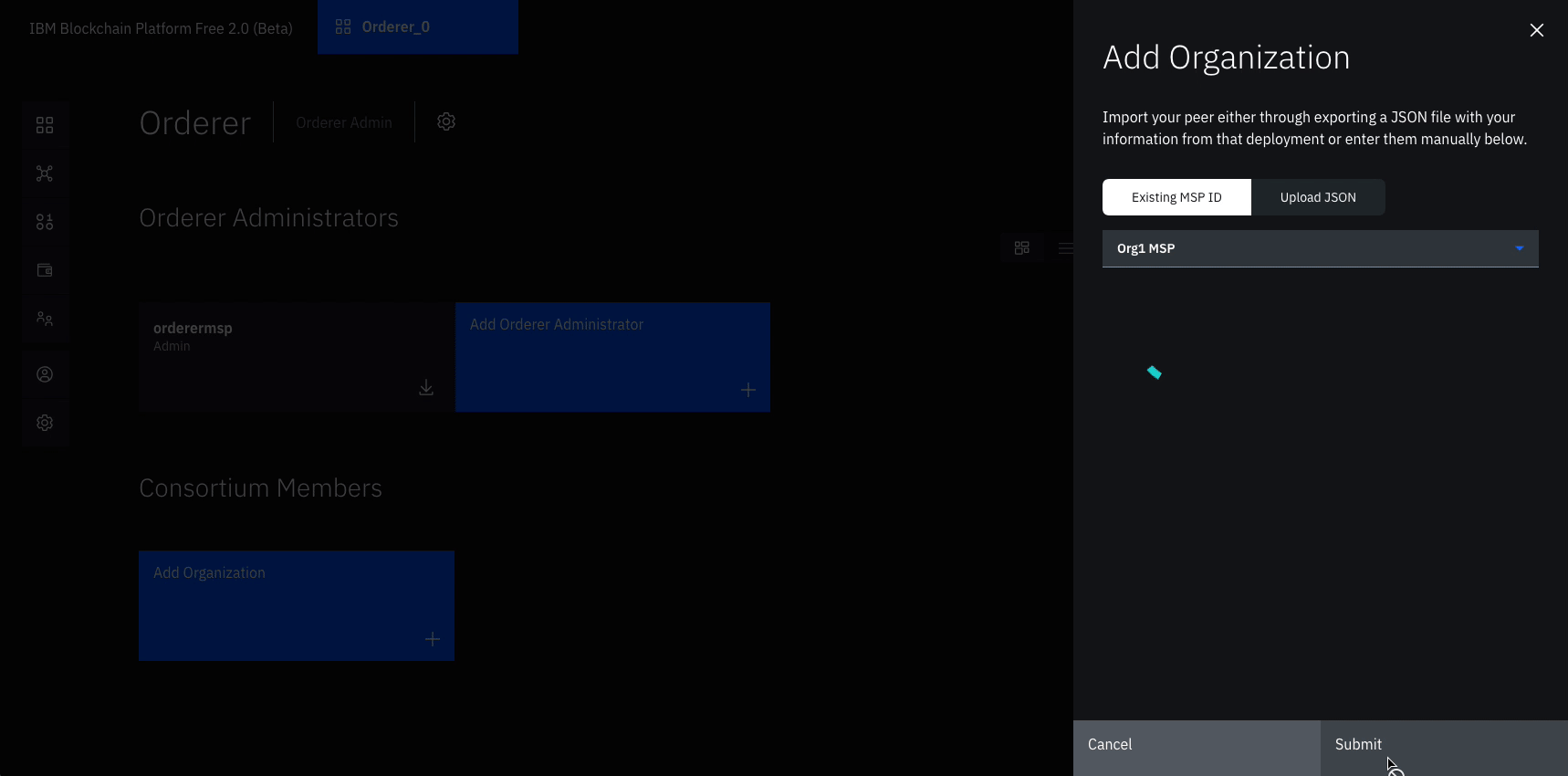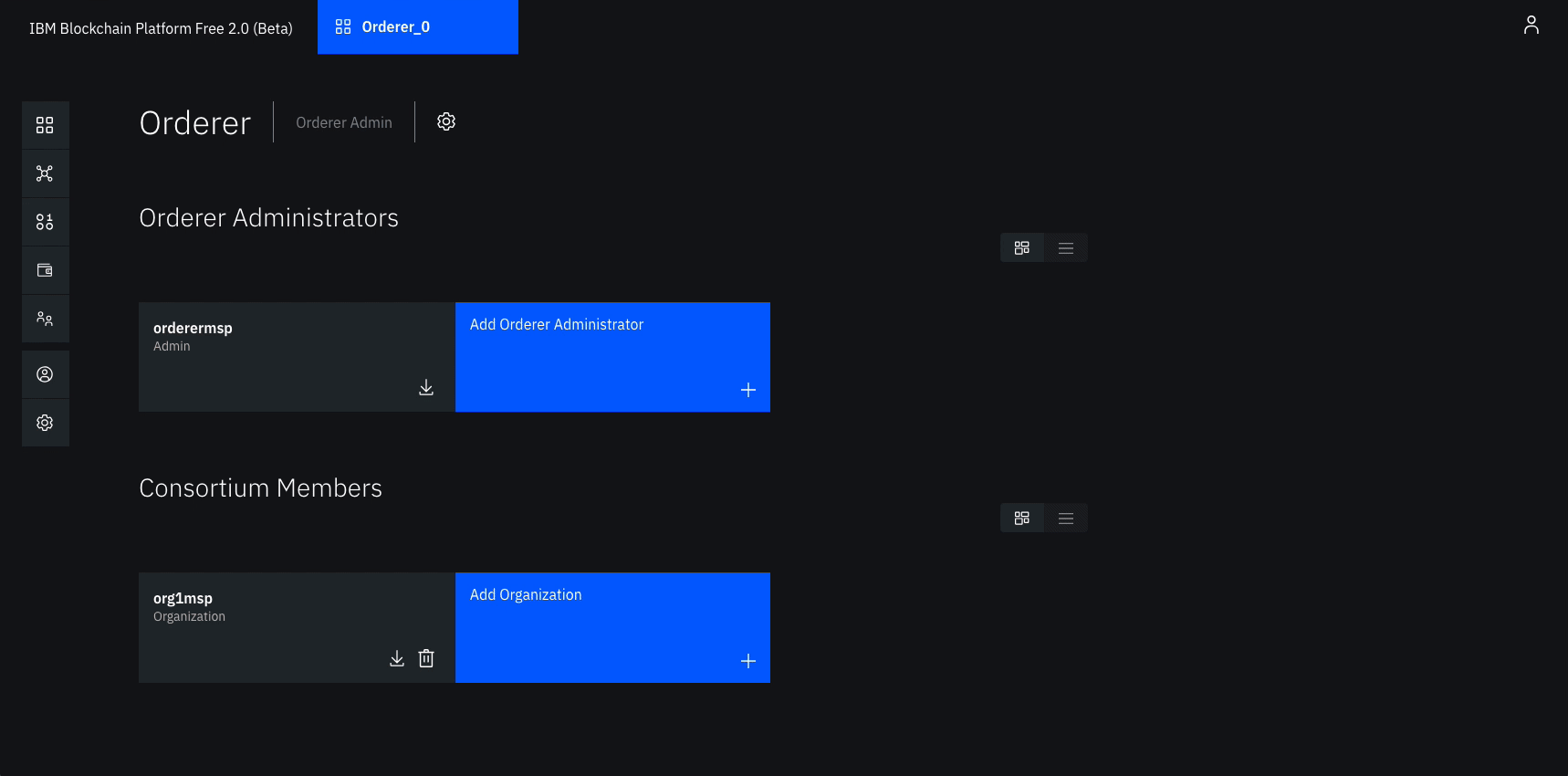
- Navigate to the Nodes tab, and click on the Orderer that we created.
- Under Consortium Members, click Add organization.
- From the drop-down list, select
Org1 MSP, as this is the MSP that represents the peer's organization org1. - Click Submit.
-
- Navigate to the Channels tab in the left navigation.
- Click Create channel.
- Give the channel a name,
mychannel. - Select the orderer you created,
Ordererfrom the orderers drop-down list. - Select the MSP identifying the organization of the channel creator from the drop-down list. This should be
Org1 MSP (org1msp). - Associate available identity as
Org1 Admin. - Click Add next to your organization. Make your organization an Operator.
- Click Create.
-
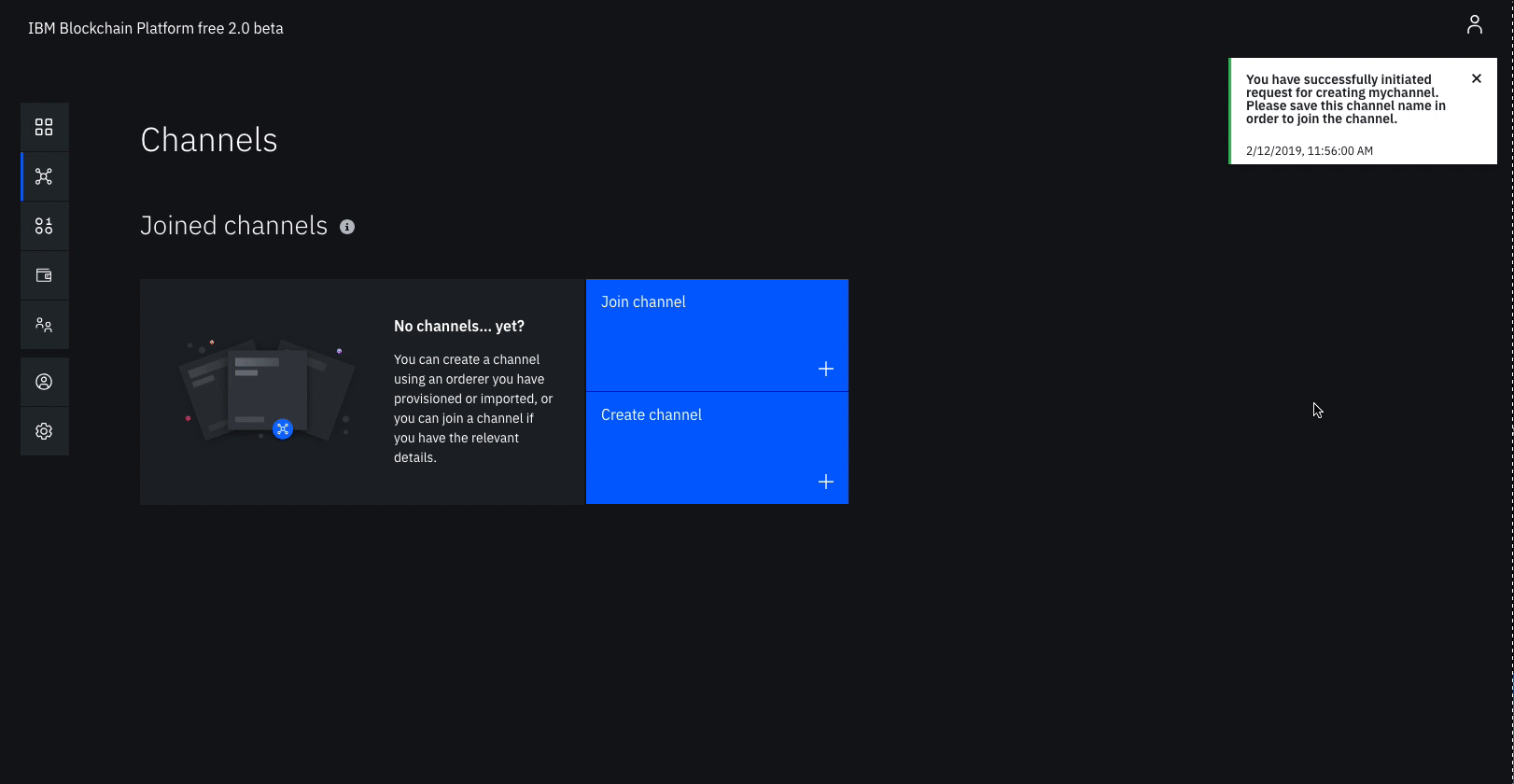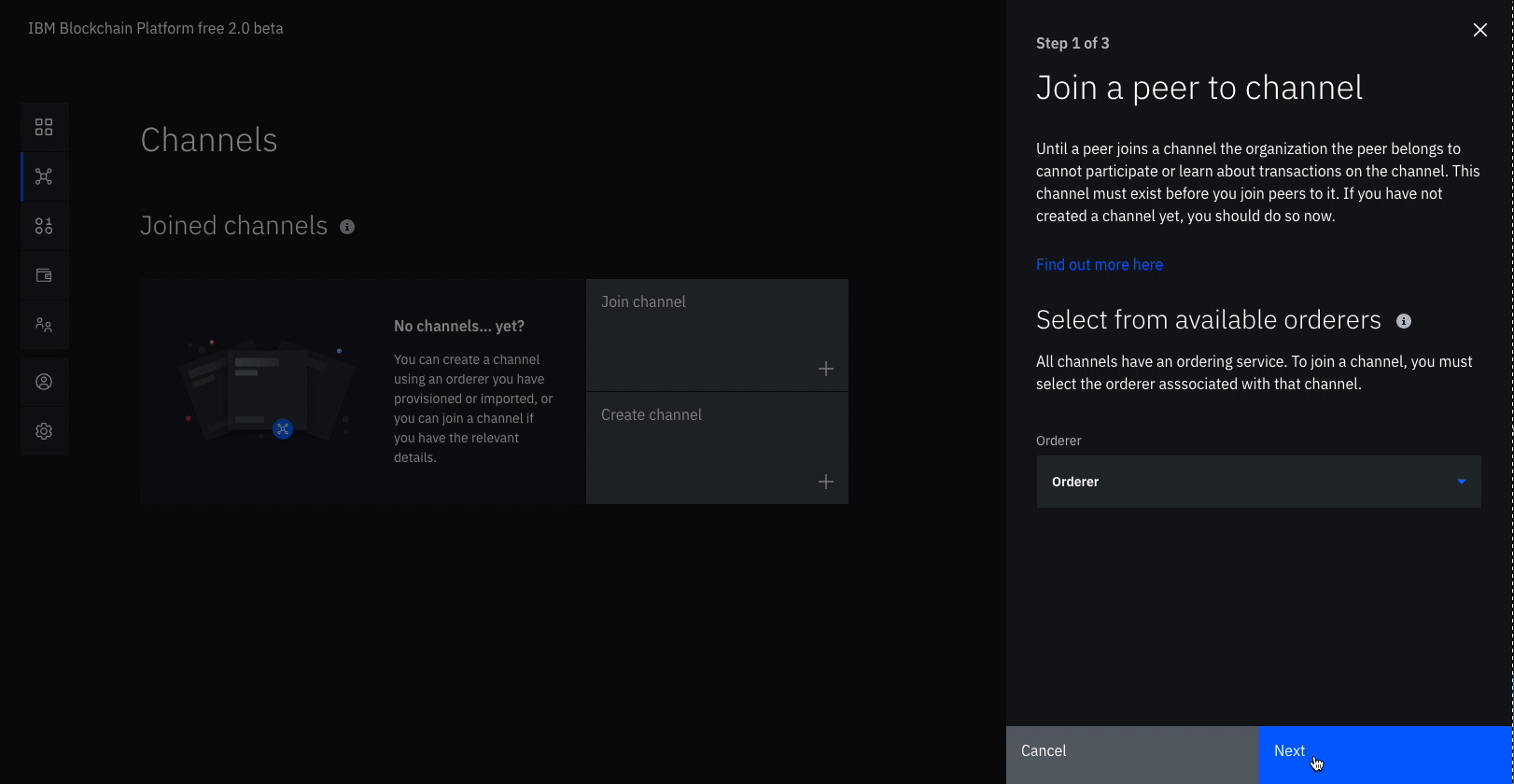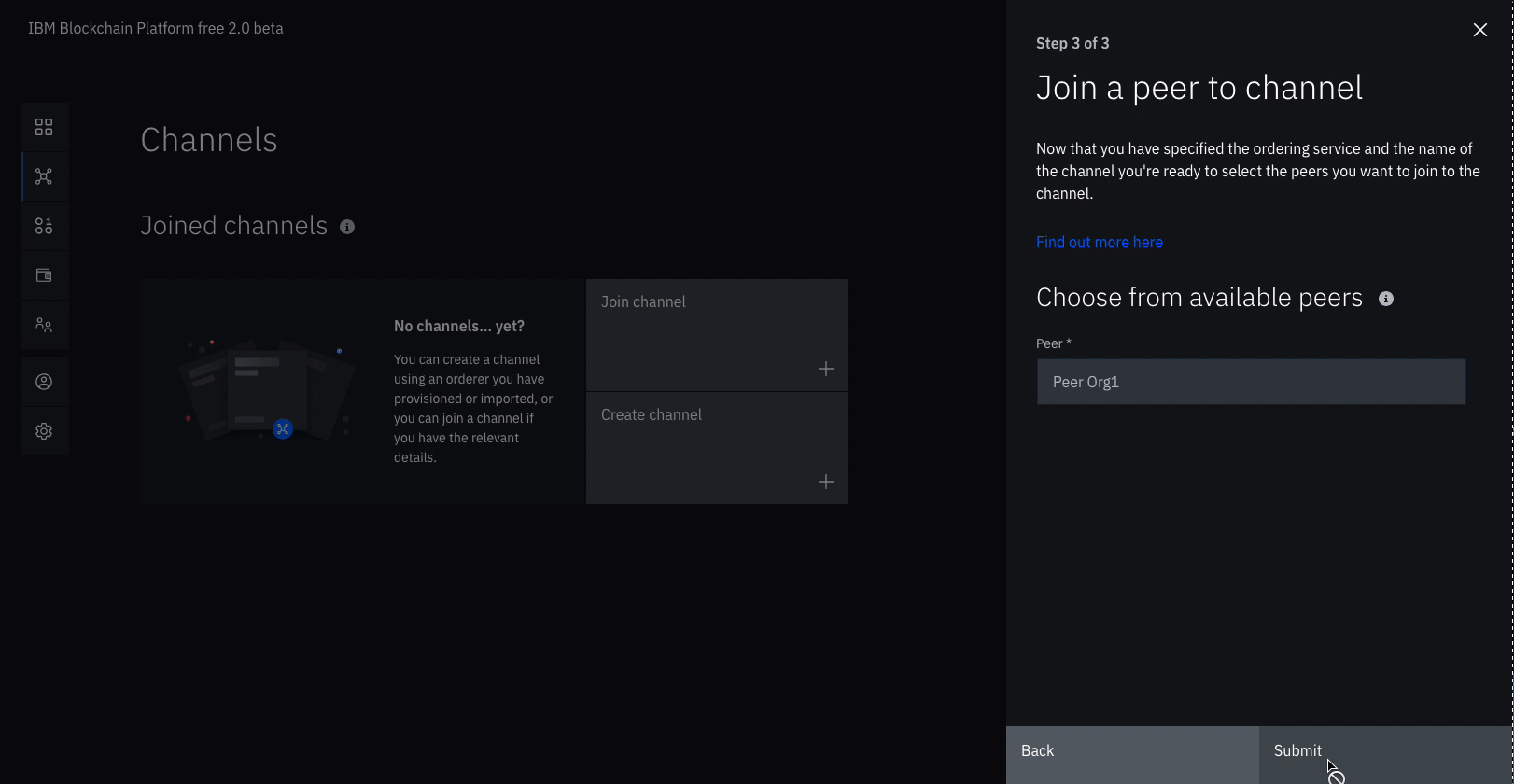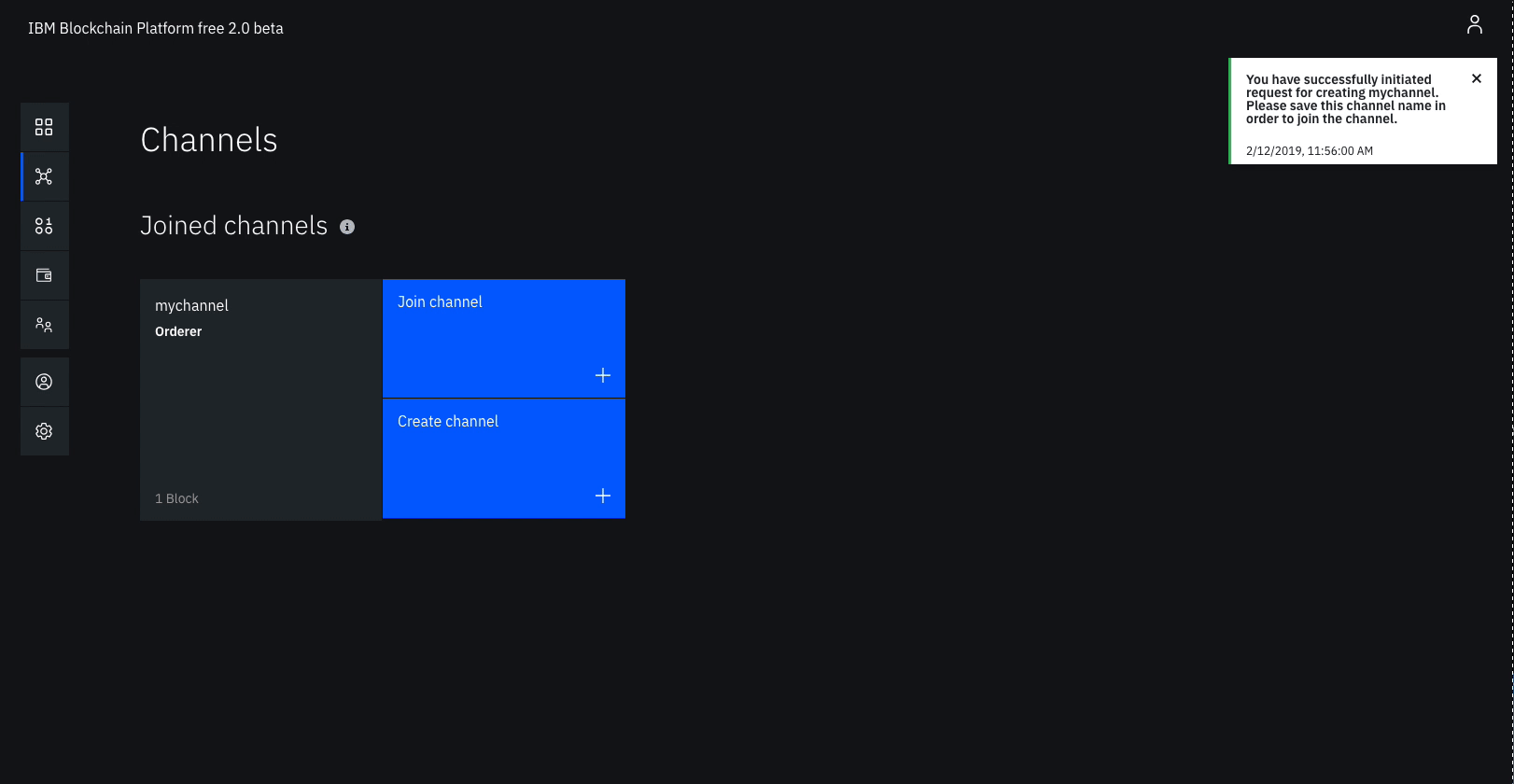
- Click Join channel to launch the side panels.
- Select your
Ordererand click Next. - Enter the name of the channel you just created.
mychanneland click Next. - Select which peers you want to join the channel, click
Peer Org1. - Click Submit.
-
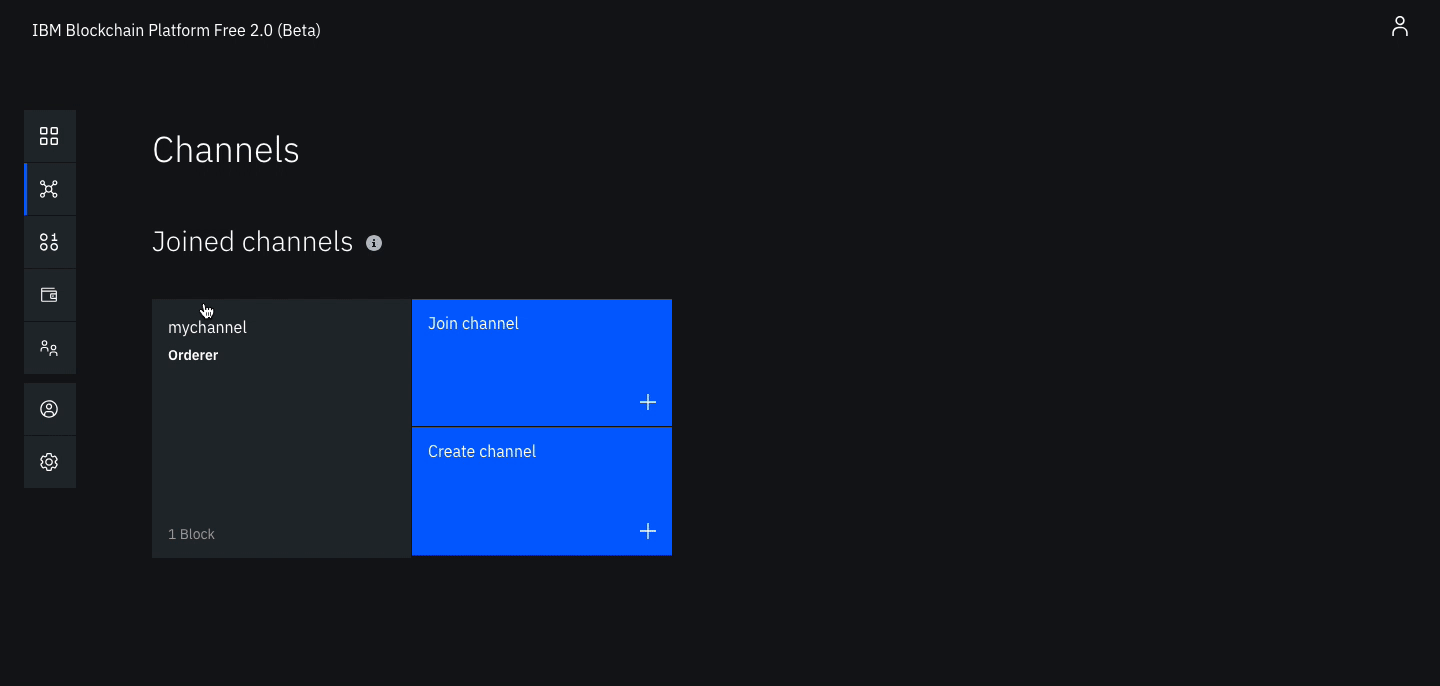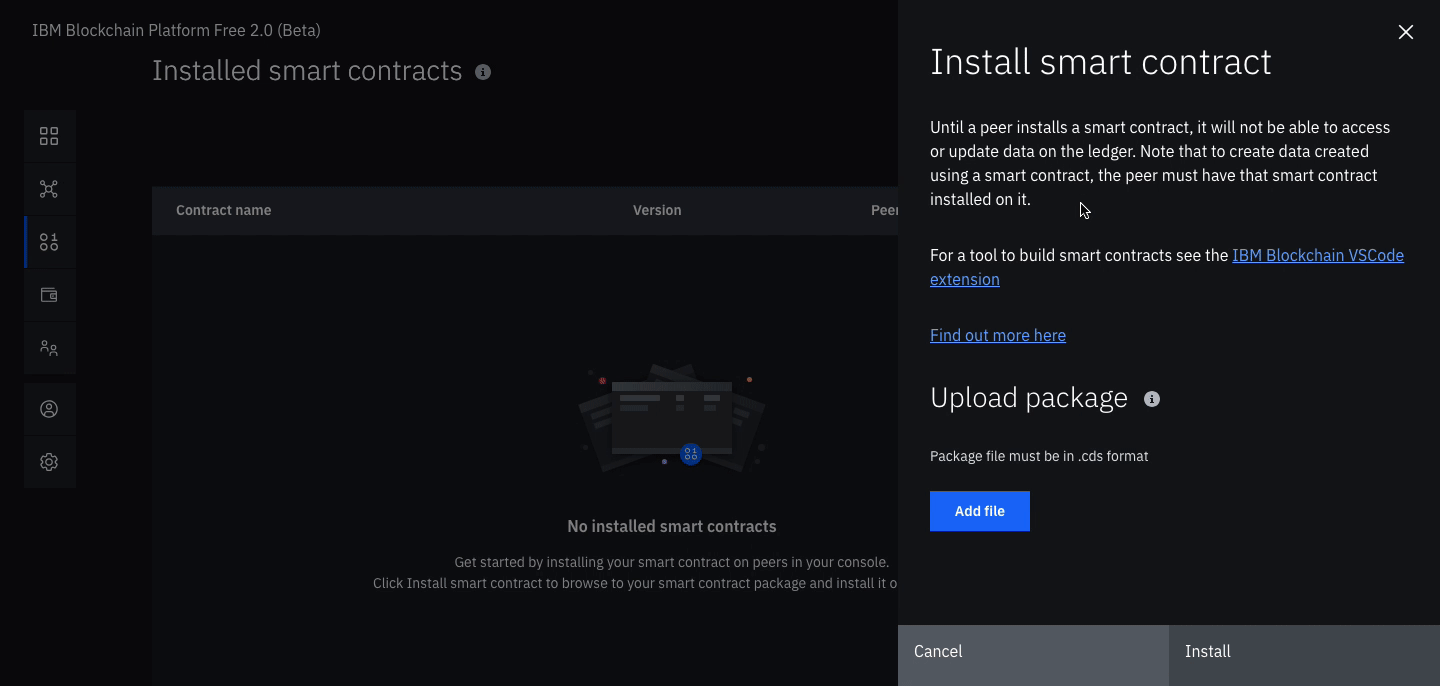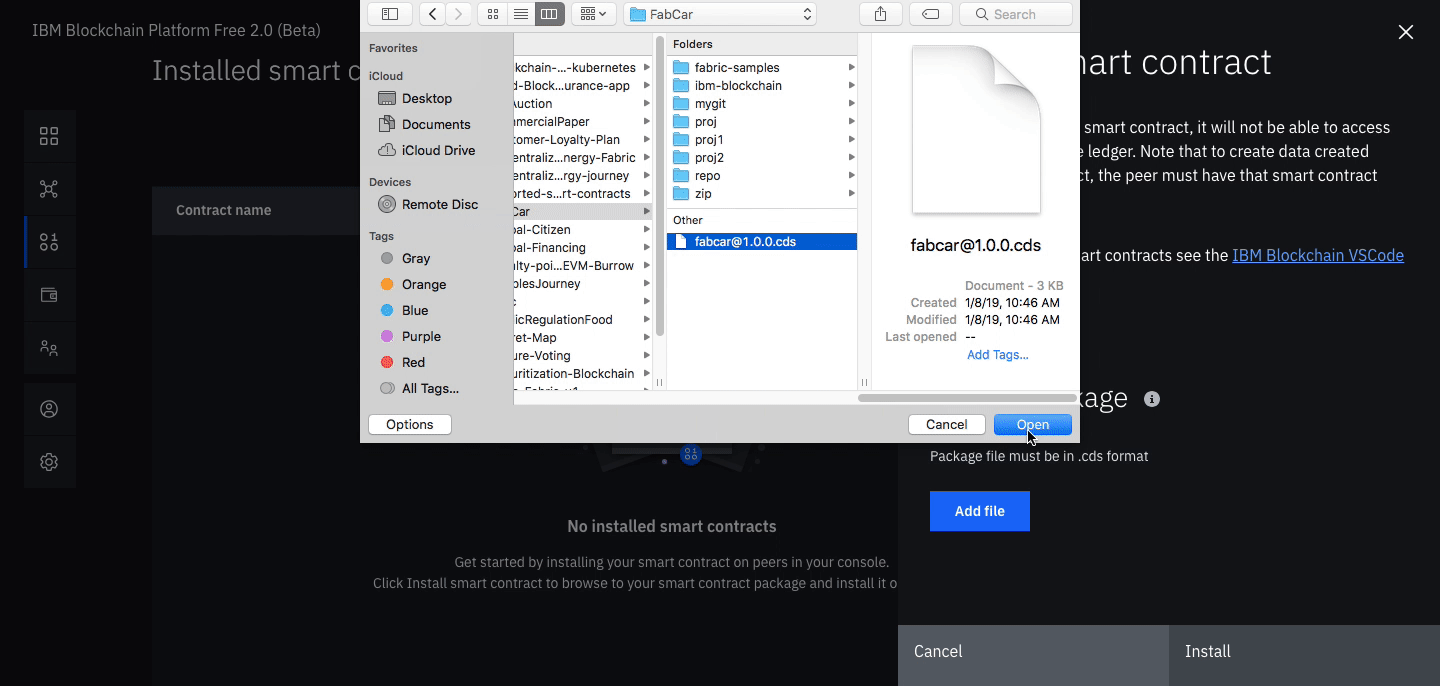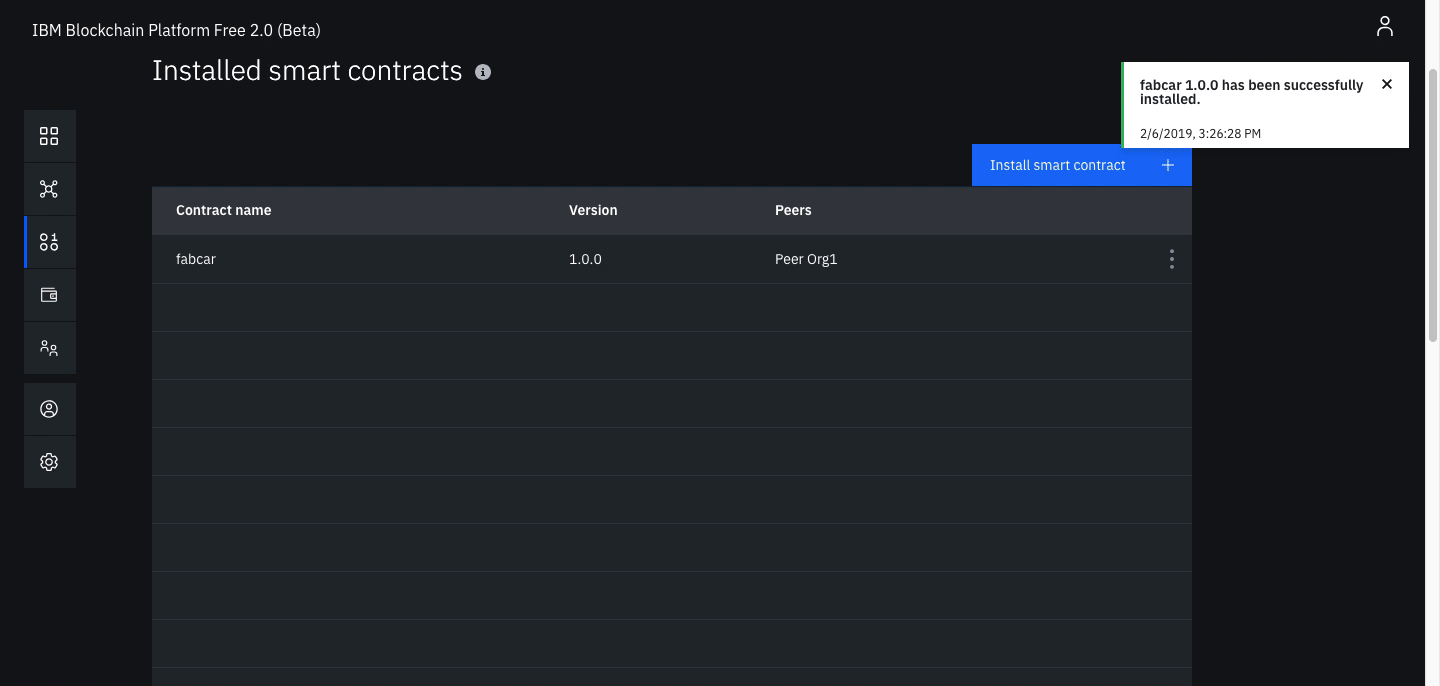
Install a smart contract (note: substitute the word
auctionwhere ever you see the wordfabcarin the graphics)- Click the Smart contracts tab to install the smart contract.
- Click Install smart contract to upload the Auction smart contract package file, which you packaged earlier using the Visual Studio code extension.
- Click on Add file and find your packaged smart contract.
- Once the contract is uploaded, click Install.
-
Instantiate smart contract (note: substitute the word
auctionwhere ever you see the wordfabcarin the graphics)- On the smart contracts tab, find the smart contract from the list installed on your peers and click Instantiate from the overflow menu on the right side of the row.
- On the side panel that opens, select the channel,
mychannelto instantiate the smart contract on. Click Next. - Select the organization members to be included in the policy,
org1msp. Click Next. - Give Function name of
instantiateand leave Arguments blank. Note:instantiateis the method in themy-contract.jsfile that initiates the smart contracts on the peer. Some may name thisinitLedger. - Click Instantiate.
-
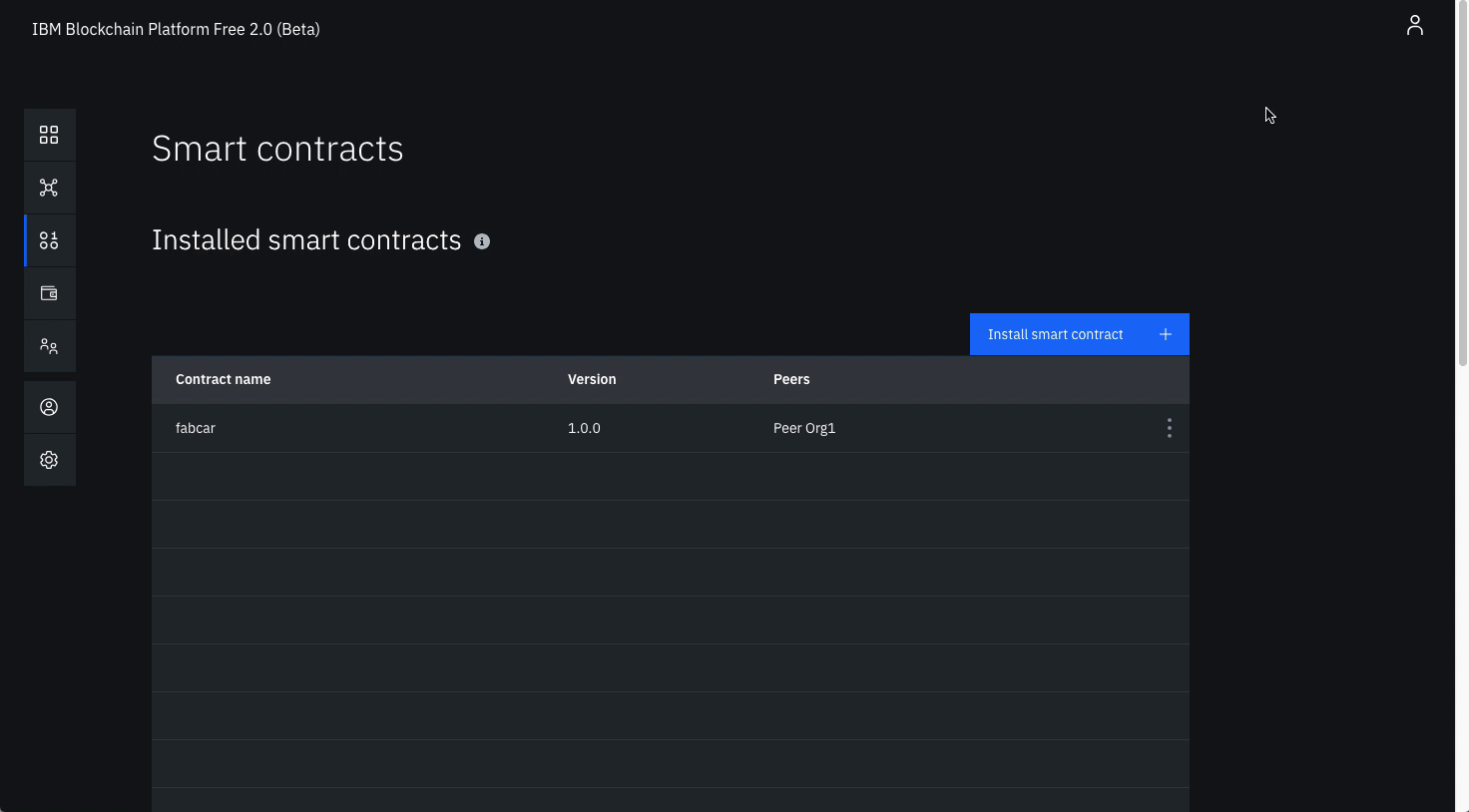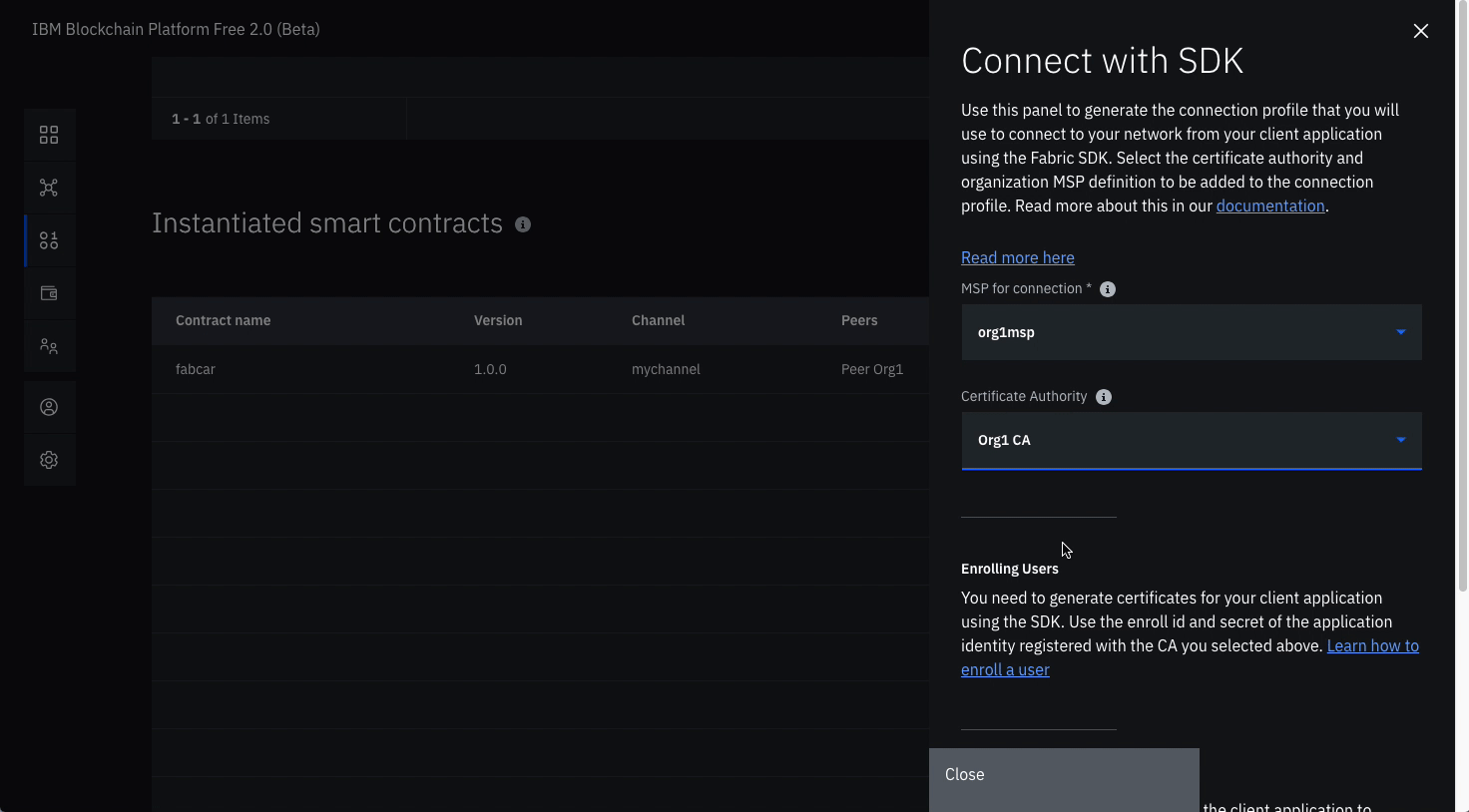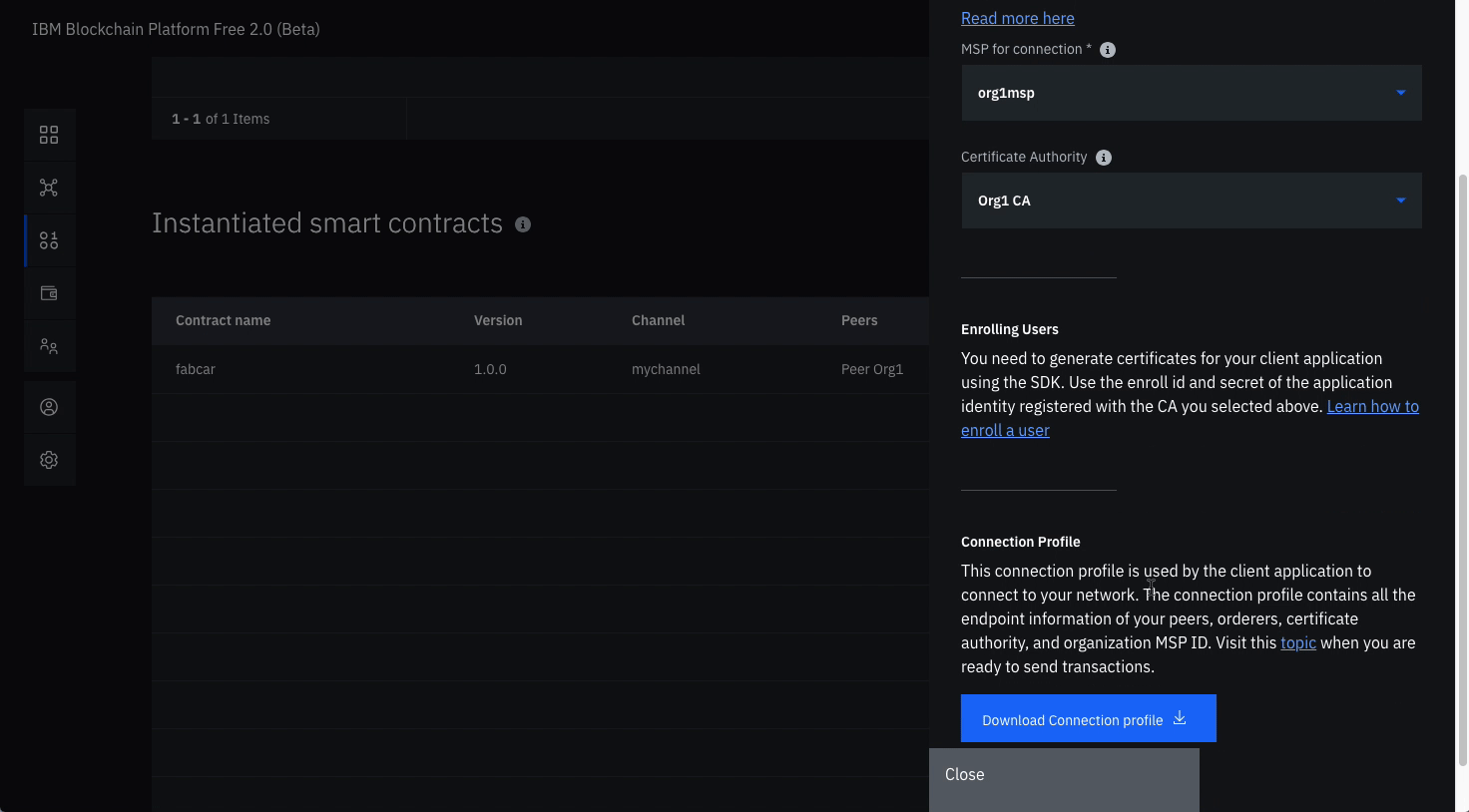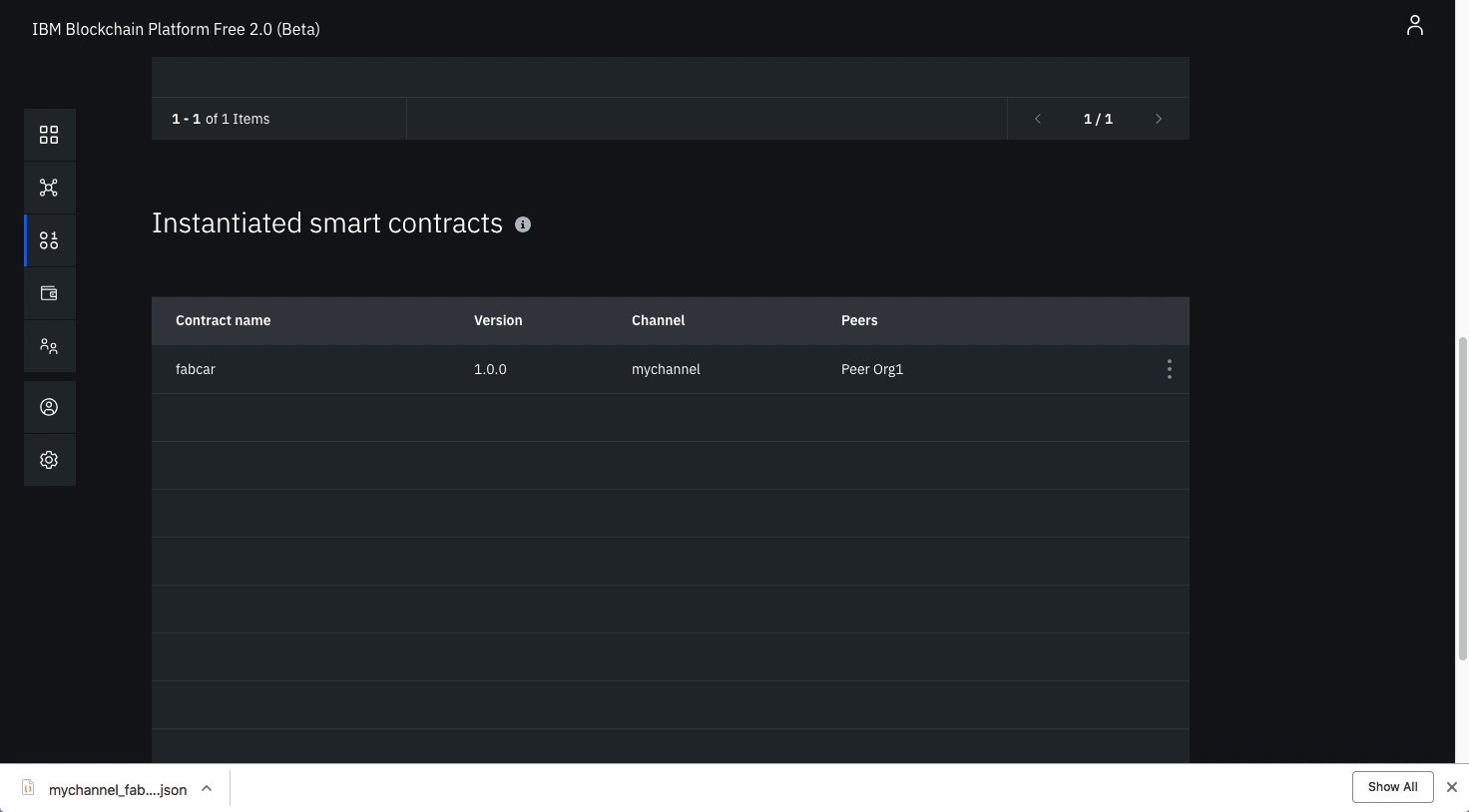
Connect with sdk through connection profile (note: substitute the word
auctionwhere ever you see the wordfabcarin the graphics)- Under the Instantiated Smart Contract, click on
Connect with SDKfrom the overflow menu on the right side of the row. - Choose from the dropdown for MSP for connection,
org1msp. - Choose from Certificate Authority dropdown,
Org1 CA. - Download the connection profile by scrolling down and clicking Download Connection Profile. This will download the connection json which we will use soon to establish connection.
- You can click Close once the download completes.
- Under the Instantiated Smart Contract, click on
-
- Go to the Nodes tab on the left bar, and under Certificate Authorities, choose your organization CA, Org1 CA.
- Click on Register user.
- Give an Enroll ID and Enroll Secret to administer your application users,
app-adminandapp-adminpw. - Choose
clientas Type and any organization for affiliation. We can pickorg1to be consistent. - You can leave the Maximum enrollments blank.
- Under Attributes, click on Add attribute. Give attribute as
hf.Registrar.Roles=*. This will allow this identity to act as registrar and issues identities for our app. Click Add-attribute. - Click Register.
-
- Copy the connection profile you downloaded into application folder
- Update the config.json file with:
- The connection json file name you downloaded.
- The enroll id and enroll secret for your app admin, which we earlier provided as
app-adminandapp-adminpw. - The orgMSP ID, which we provided as
org1msp. - The caName, which can be found in your connection json file under "organization" -> "org1msp" -> certificateAuthorities". This would be like an IP address and a port.
- The peer, , which can be found in your connection json file under "organization" -> "org1msp" -> peers". This would be like an IP address and a port.
- The username you would like to register.
- Update gateway discovery to
{ enabled: true, asLocalhost: false }to connect to IBP.
{
"channel_name": "mychannel",
"smart_contract_name": "auction",
"connection_file": "mychannel_auction_profile.json",
"appAdmin": "app-admin",
"appAdminSecret": "app-adminpw",
"orgMSPID": "org1msp",
"caName": "173.193.79.114:32615",
"peer": "grpcs://173.193.79.114:30324",
"orderer": "grpcs://173.193.79.114:32018",
"userName": "user1",
"gatewayDiscovery": { "enabled": true, "asLocalhost": false }
}-
-
First, navigate to the
applicationdirectory, and install the node dependencies.cd application npm install -
Run the
enrollAdmin.jsscriptnode enrollAdmin.js
-
This will create a directory called wallet and insert the user Admin along with its certificate authority.
-
You should see the following in the terminal:
msg: Successfully enrolled admin user app-admin and imported it into the wallet
-
In the newest version of the Hyperledger Fabric Node SDK (1.4 release) there are three main event types that can be subscribed to
- Contract events - these have to be emitted from the chaincode by calling the stub.setEvent(name,payload) method. An example can be seen in the auction chaincode on line 141 of contract/lib/auction.js. These types of events are great, since you can customize exactly what data you want to send to the client application. Note that these events will only be triggered once a certain function within your chaincode is called.
- Transaction (Commit) events - these are automatically emitted after a transaction is committed to the ledger.
- Block events - these are emitted automatically when a block is committed. Note that there can be mutliple transactions in a block, so you may get multiple transaction events for one block event.
- To illustrate each of these three main event types, we will have a separate script
for each, that will show each of the events in action. First, let's check out the
contractEvents.jsfile. This file uses theaddContractListenerfunction to look for anyTradeEventevents that may be published from our chaincode. You can see in ourcontractdirectory, that ourStartBidding,Offer, andCloseBiddingfunctions all emit an event my callingawait ctx.stub.setEvent('TradeEvent', Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(tradeEvent)));Then, our callback function in ourcontractEvents.jsfile will fire once it has detected that theTradeEventis sent. Go ahead and runcontractEvents.jsby typing in the following command in terminal
application$ node contractEvents.js
Wallet path: /Users/Horea.Porutiu@ibm.com/Workdir/testDir/auction-events/application/wallet
gateway connect
************************ Start Trade Event *******************************************************
type: Start Auction
ownerId: auction@acme.org
id: l1
description: Sample Product
status: {"code":1,"text":"FOR_SALE"}
amount: 50
buyerId: auction@acme.org
Block Number: 124 Transaction ID:
6be255d6c2ab968ab9f0bd4bbc3477f51f1e02512d11e86fc509f2f6f0e51a7e Status: VALID
************************ End Trade Event ************************************
closebiddingResponse:
{"listingId":"l1","offers":[{"bidPrice":100,"memberId":"memberB@acme.org"},{"bidPrice":50,"memberId":"memberA@acme.org"}],"productId":"p1","reservePrice":50,"state":"{\"code\":3,\"text\":\"SOLD\"}"}
Transaction to close the bidding has been submittedThis above output parses the trade event - it shows us the type of the event, the owner, the id, the description of the product the status, etc. This is all things we have built and emitted within our chaincode. Great. Now that we understand how contract events work, let's move onto the block event listener.
-
Block events are different than contract events since you have less control of what exactly is being output. Go ahead and check out
blockEvents.js. Note that there may be multiple transactions within one block, and you can edit how many transactions are in your block by editing the block batch size for a channel. You can read more details about this here. The main components of the block are the block header, the block data, and the block metadata.- The block header contains the block number, (starting at 0 from the genesis block) and increased by 1 for every new block appended to the blockchain. It also has the current block hash (the hash of all transactions in the current block), and the previous block hash.
- The block data contains a list of the transactions in order.
- The block metadata contains the time when the block was written, the certificate, public key and signature of the block writer.
-
Go ahead and run the
blockEvents.jsscript by typing in the following commands in the terminal. For eachcontract.submitTransactionwe submit, we will have a new block added to the ledger. Notice the output will be divided by header, data, and metadata. You can then parse those respective parts of the output to learn more about each specific part of the block.
application$ node blockEvents.js
Wallet path: /Users/Horea.Porutiu@ibm.com/Workdir/testDir/auction-events/application/wallet
gateway connect
*************** start block header **********************
{ number: '396',
previous_hash: 'af979a1632e1ba69a75256dce4bafad40e93ebec6ee17de5b2923bbeb5abfec8',
data_hash: '4db396d91151c432e1f17f32254565bc2445975d6d8c9000ff74a5c2a845dd26' }
*************** end block header **********************
*************** start block data **********************
{ signature: <Buffer 30 44 02 20 14 31 37 8d be 63 99 69 cc b7 35 30 b7 71 d8 0f 38 98 70 c6 7a cb fa a6 ed c3 a8 eb 28 c1 90 9f 02 20 05 4a 5d 66 61 4a 4f e9 42 37 11 b1 ... >,
payload:
{ header:
{ channel_header:
{ type: 3,
version: 1,
timestamp: '2019-08-30T00:10:45.075Z',
channel_id: 'mychannel',
tx_id: 'cb12f4a9209c0c35d20213c4d2c517c2b199761cb29902a11bc955eba291acc6',
epoch: '0',
extension: <Buffer 12 09 12 07 61 75 63 74 69 6f 6e>,
typeString: 'ENDORSER_TRANSACTION' },
signature_header:
{ creator:
{ Mspid: 'org1msp',
IdBytes: '-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----\nMIICaTCCAhCgAwIBAgIUC2iFJ+dVTbE8QSVoqjjno3mT9sowCgYIKoZIzj0EAwIw\naDELMAkGA1UEBhMCVVMxFzAVBgNVBAgTDk5vcnRoIENhcm9saW5hMRQwEgYDVQQK\nEwtIeXBlcmxlZGdlcjEPMA0GA1UECxMGRmFicmljMRkwFwYDVQQDExBmYWJyaWMt\nY2Etc2VydmVyMB4XDTE5MDgyODE4MjQwMFoXDTIwMDgyNzE4MjkwMFowJjEPMA0G\nA1UECxMGY2xpZW50MRMwEQYDVQQDEwphcHAtYWRtaW4yMFkwEwYHKoZIzj0CAQYI\nKoZIzj0DAQcDQgAEMFDxKrg+VEO3mK5tfJKf7oULfagOMcAmX4T4NUmLI/ojsnTe\naTJUeJQQ3Vyp1L7pV3hZGvY9HlZUt6uVoLjju6OB2TCB1jAOBgNVHQ8BAf8EBAMC\nB4AwDAYDVR0TAQH/BAIwADAdBgNVHQ4EFgQU/GYKt2Q4Bk7aKon90K66rlgwWlAw\nHwYDVR0jBBgwFoAUUii9qu9Xs+cjOsm1MaM+xK1UCL4wdgYIKgMEBQYHCAEEansi\nYXR0cnMiOnsiaGYuQWZmaWxpYXRpb24iOiIiLCJoZi5FbnJvbGxtZW50SUQiOiJh\ncHAtYWRtaW4yIiwiaGYuUmVnaXN0cmFyLlJvbGVzIjoiKiIsImhmLlR5cGUiOiJj\nbGllbnQifX0wCgYIKoZIzj0EAwIDRwAwRAIgQEaWB8YVEfO67OAWLypnQX//0nrg\nOGtLqVv/HRkg2TsCIC4cn04cmTjLWg/GVGuXSLlaZV1SZFlGvd9lNDN2ytea\n-----END CERTIFICATE-----\n' },
nonce: <Buffer fa 18 68 a7 a9 8b 74 10 8e 41 75 22 0d 74 8a 60 86 15 1f e3 13 59 d3 06> } },
data:
{ actions:
[ { header:
{ creator: [Object],
nonce: <Buffer fa 18 68 a7 a9 8b 74 10 8e 41 75 22 0d 74 8a 60 86 15 1f e3 13 59 d3 06> },
payload: { chaincode_proposal_payload: [Object], action: [Object] } } ] } } }
*************** end block data **********************
*************** start block metadata ****************
{ metadata:
[ { value: '\n\u0000\u0012\n\n\b\n\u0001\u0001\u0010\u0002\u0018�\u0003',
signatures:
[ { signature_header:
{ creator: [Object],
nonce: <Buffer 0b f0 46 f5 17 1e 74 f3 c4 34 75 aa b0 85 80 f6 4e 4c d0 f5 ba a0 26 b4> },
signature: <Buffer 30 45 02 21 00 b7 12 42 a3 43 21 8b a3 ea e1 56 af e4 63 2c 7e cc c6 c3 bf b7 e5 01 73 69 27 ce 4b 13 63 d3 5b 02 20 1d a1 e8 38 f6 fb 48 bb 3c 9a 01 ... > } ] },
{ value: { index: '0' }, signatures: [] },
[ 0 ] ] }
*************** end block metadata ****************To learn more about the specifics of what is included inside of a block, read this page.
- Lastly, let's go ahead and listen for transaction events. This is even more
granular than block events, since multiple transactions can comprise a block.
We will use the
transaction.addCommitListenerto listen to transactions. Go ahead and look at thetransactionEvents.jsfile. What we are doing, is that we are adding a committ listener, such that when we submit a transaction, and it is committed, we will get the transactionId, status, and blockheight back. Go ahead and runtransactionEvents.jsfile, and you should see the following output in your terminal:
application$ node transactionEvents.js
Wallet path: /Users/Horea.Porutiu@ibm.com/Workdir/testDir/auction-events/application/wallet
gateway connect
transaction committed
'ef7f833d6039e41c5054d0bba0d327cfc14bfd7be836a6c5e65547320880d1af'
'VALID'
405
transaction committed end
Transaction to add seller has been submitted
application$ - Nice job! You've now learned how to
-
If you receive the following error on submitting transaction:
error: [Client.js]: Channel not found for name mychannelIt is safe to ignore this error because the ibp2.0 beta has service discovery enabled. (In order to use service discovery to find other peers please define anchor peers for your channel in the ui). If you really want the message to go away you can add the channels section to the connection profile, but it is a warning rather than a true error telling the user the channel is found but not in the connection profile
As an example you can manually add the following json and updated the IP address and ports manually:
"channels": { "mychannel": { "orderers": [ "169.46.208.151:32078" ], "peers": { "169.46.208.151:31017": {} } } }, -
In the invoke-emit.js application, you will see the following code: It is important to note that in order for the
getClientmethod to actually get the connection.profile content, you need to have line #4 occur before line #6. If you don't, then theclientconstant will benull. It is important you have the order correct to run the code successfully.
1. // A gateway defines the peers used to access Fabric networks
2. await gateway.connect(ccp, { wallet, identity: appAdmin , discovery: {enabled: true, asLocalhost:false }});
3. console.log('Connected to Fabric gateway.');
4. const network = await gateway.getNetwork(channelName);
5. // Get addressability to network
6. const client = gateway.getClient();
7. const channel = client.getChannel('mychannel');
8. console.log('Got addressability to channel');
9. const channel_event_hub = channel.getChannelEventHub('173.193.79.114:30324');This application can be expanded in a couple of ways:
- Create a wallet for every member and use the member's wallet to interact with the application.
- Add a UI application in place of the
invoke.jsnode application to execute the transactions.
This code pattern is licensed under the Apache Software License, Version 2. Separate third-party code objects invoked within this code pattern are licensed by their respective providers pursuant to their own separate licenses. Contributions are subject to the Developer Certificate of Origin, Version 1.1 (DCO) and the Apache Software License, Version 2.