Addressing the issue of student dropout stands as a pivotal challenge within educational institutions, underscoring the significance of proactively identifying students who are susceptible to discontinuing their studies. Such timely identification not only holds the potential to bolster retention rates but also to foster a climate of enhanced student accomplishment.
This undertaking sets forth a comprehensive objective: the construction of a predictive machine learning model adept at discerning students in jeopardy of dropping out. By achieving this, the project endeavors to usher in a regime of prompt intervention and tailored assistance, ensuring that struggling students receive the support they need to persist and thrive.
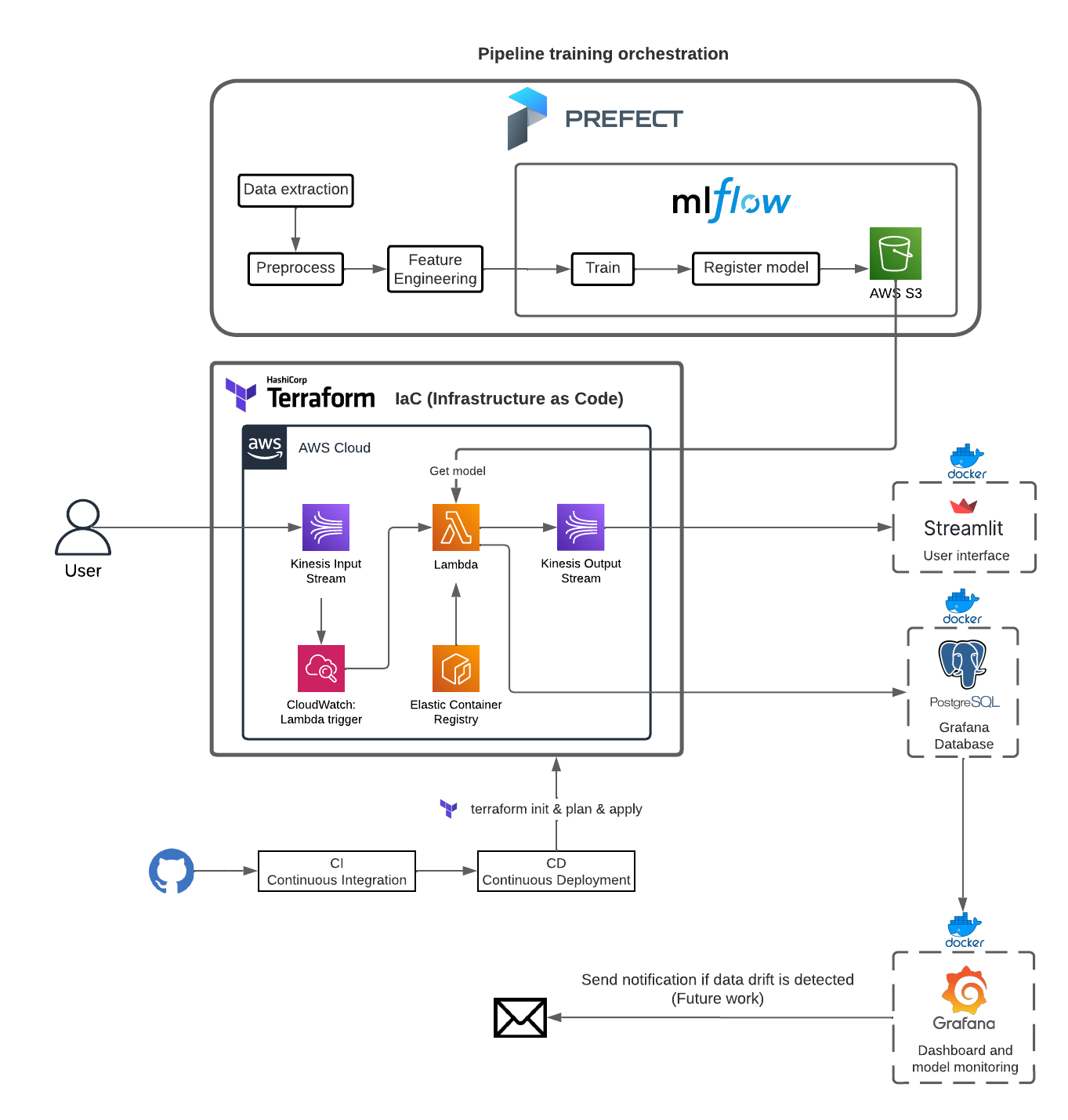
The primary aim of this endeavor is the formulation of a resilient machine learning model, one that excels in accurately prognosticating instances of student attrition within educational establishments. This aspiration is fortified through the strategic application of MLOps methodologies. By harnessing the capabilities of AWS's technological stack and employing Terraform for the facilitation of Infrastructure as Code (IaC), a comprehensive end-to-end data pipeline is poised to materialize.
This intricate pipeline encompasses a spectrum of functionalities including streamlined orchestration, real-time streaming predictions, meticulous experiment monitoring, and the seamless integration of continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) protocols via GitHub workflows. It is imperative to underscore that this holistic approach extends to encompassing both unit and integration tests, thereby fortifying the reliability and efficacy of the model. Furthermore, the incorporation of meticulously crafted shell scripts serves as a cornerstone, driving automated processes that underpin efficient model deployment mechanisms.
A dataset created from a higher education institution (acquired from several disjoint databases) related to students enrolled in different undergraduate degrees, such as agronomy, design, education, nursing, journalism, management, social service, and technologies.
URL: https://archive-beta.ics.uci.edu/dataset/697/predict+students+dropout+and+academic+success
-
AWS Kinesis: Facilitates the seamless management of event inputs and outputs, ensuring a smooth flow of data within the ecosystem.
-
AWS Lambda: Acts as the orchestrator, efficiently handling the execution of functions and managing the intricacies of the underlying processes.
-
S3: Assumes the role of a robust storage repository, housing and preserving MLflow buckets that encapsulate valuable artifacts and data.
-
MLFlow: Emerges as an indispensable tool for experiment tracking and model registry, offering a structured approach to managing the entire machine learning lifecycle.
-
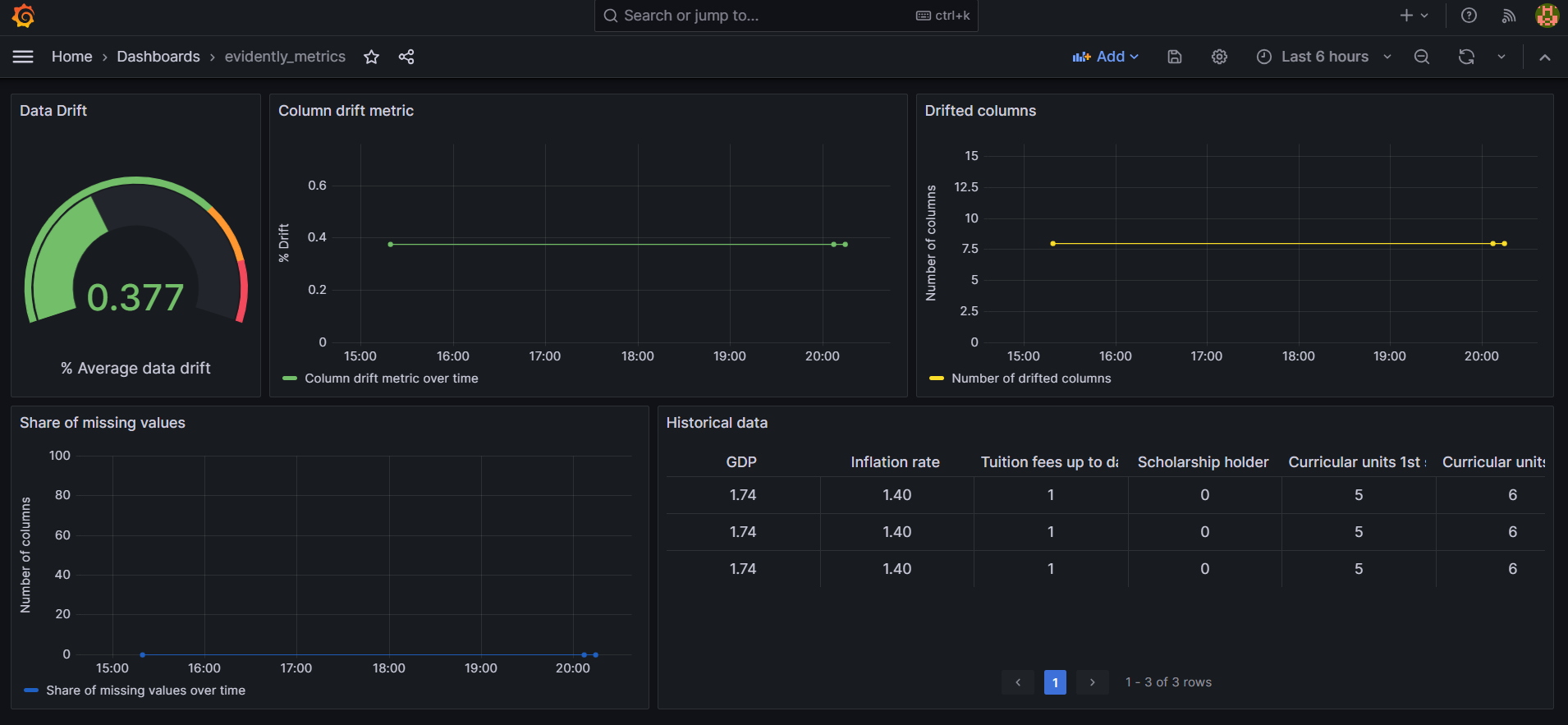
Grafana: Empowers the monitoring of models and the timely detection of any deviations or drifts that might arise, bolstering the model's reliability.
-
Streamlit: Presents an intuitive and user-friendly interface, leveraging its capabilities to create an uncluttered yet effective platform for interacting with deployed models.
-
Pre-commit: Functions as a gatekeeper, ensuring stringent quality checks are in place before any code is committed, maintaining the integrity of the codebase.
-
Unit and Integration Tests: Take on the responsibility of validating the functionality of the code components, ensuring that each piece works as intended individually and when integrated.
-
CI/CD Workflow: Embodies a comprehensive approach to Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment, underlining the importance of maintaining a fluid and automated development cycle.
-
Terraform: Steps forward as a pivotal resource, aiding in the construction of an AWS-based infrastructure with precision and reproducibility, an essential element of the project's foundation.
.
├── .github # CI/CD workflows
├── config/ # Config files
├── images/ # Assets
├── infrastructure/ # Terraform files for IaC
| ├── modules/ # Modules to create AWS resources
| | ├── ecr/ # ECR resource for the docker registry
| | ├── kinesis/ # Kinesis resource for input/output events
| | ├── lambda/ # Lambda resource for executing the function
| | ├── s3/ # S3 resource to store mlflow models
| ├── vars/ # Variables
├── model_monitoring/ # Directory for monitoring the model
├── notebooks/ # Notebooks used to analysis prior to development
├── orchestration/ # Directory for workflow orchestration-related files
├── scripts/ # Bash scripts
├── streaming/ # Directory for handling streaming dataastAPI directoryF
| ├── integration-tests/ # Integration tests for the streaming module
| | ├── artifacts/ # Files to manage global configuration variables and settings
| | | ├── encoders/ # Pickle files of LabelEncoder
| | | ├── model/ # Files related to the model
| ├── tests/ # Unit tests for the streaming module
| ├── lambda_function.py # Entrypoint for the application
| ├── model.py # Functions and classes related to the model
├── streamlit/ # User Interface built on Streamlit to interact with the model
├── .env.example # Template to set environment variables
├── .pre-commit-config.yaml # Configuration file for pre-commit hooks
├── docker-compose.yaml # Docker configuration for building the application
├── Dockerfile # Docker configuration for building the application
├── Makefile # Configuration of commands to automate the applications
├── Pipfile # Requirements for development and production
├── Pipfile.lock # Lock file for Pipfile dependencies
└── pyproject.toml # Project metadata and dependencies (PEP 518)
└── README.md
Run notebooks in notebooks/ directory to conduct Exploratory Data Analysis and experiment with features selection and feature creation using Feature-engine module ideally created for these purposes (See References for further information). Diverse experiments were carry out using RandomForest, SVM, XGBoost, with the latter showing the best performance. The resultant features were persistent into a yaml file containing other global properties. In this project, just 7 features were extracted out of the 37 original through Recursive Feature Addition technique.
This project is only reproducible across cloud technologies.
The following picture illustrate the complete architecture created for this project
The following requirements need to be installed in your system:
- Python 3.10
- Docker Desktop
- Terraform: https://developer.hashicorp.com/terraform/downloads
- make: To run make commands in Makefile
Rename .env.example to .env and set the variables accordingly. Make sure your AWS user has the right policies to reproduce this project, to be honest I only added these ones:
- AdministratorAccess
- IAMAccessAdvisorReadOnly
- IAMUserChangePassword
It is important you keep all variables into this file due to many files will read it to guarantee reproducibility.
-
Create a S3 Bucket with the name
tf-state-student-dropout, it is used by Terraform to store the states -
Run
make create_infrastructure. It will take arund 5 minutes
- Setup in EC2: Into the EC2 CLI type this
sudo yum update
yum install pip
pip install mlflow psycopg2-binary
mlflow server \
--host 0.0.0.0 \
--port 5000 \
--default-artifact-root ${BUCKET} \
--backend-store-uri postgresql://${MLFLOW_DB_USER}:${MLFLOW_DB_PASSWORD}@${HOST}:5432/${MLFLOW_DB_NAME}- Activate local environment
- pip install pipenv
- Windows:
source "$(pipenv --venv)/Scripts/activate"UNIX:pipenv shell
- Setup pre-commit
Jump this steps if you do not wish commit changes to this repo
Run make setup
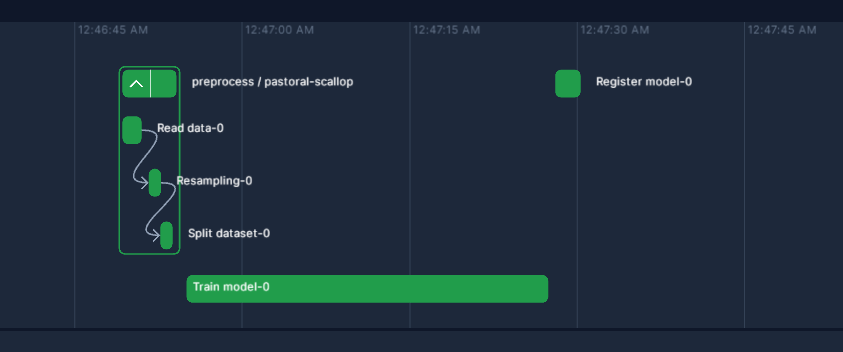
- Training workflow: Get data, preprocess, train and register model
prefect cloud login
python orchestration/train.pyExpected output in Prefect:
- Or execute them separately if you wish to experiment with other models or hyperparams:
python orchestration/preprocess.py
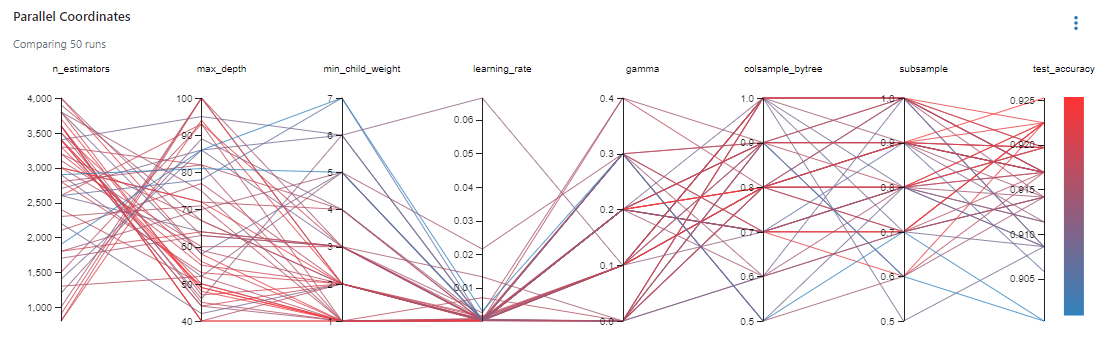
python orchestration/create_experiment.py (Optional) Used to test with different models
python orchestration/optimize.pyThe experiment's chart view should look like this after running optimize.py script:
- Finally, deployment:
python orchestration/deployment.py
prefect agent start -p default-agent-poolStart services:
Run make start_services in order to start the following services
-
http://localhost:3000: Grafana monitor -
http://localhost:8282: Adminer -
http://localhost:8501: Streamlit UI -
http://localhost:8080: Backend service -
http://localhost:5432: Postgres
Go http://localhost:8501 on your browser to visualize a basic but useful user interface to interact with model by sending data to kinesis stream which will trigger an event onto lambda function, as a result you will see the prediction itself along with model metadata.
Go to http://localhost:3000 to explore model performance
Go to http://localhost:8282 to open the database manager in order to explore the database content. So, you need to pick Postgres as database, and fill in the other fields according the configuration you set in the .env file
Run make destroy to destroy the AWS resources created by Terraform and avoiding charges
- Testing the code: unit tests with pytest
- Integration tests with docker-compose
- Testing cloud services with LocalStack
- Code quality: linting and formatting
- Git pre-commit hooks
- Makefile
- Infrastructure as Code
- CI/CD and GitHub Actions
This project continues improving to prevent you from going through some steps which could be easily automatable.
- Send notification when data drift is detected using Prefect
- Migrate from pipenv to Poetry
- Create AWS Load Balancer
- Create more unit tests
- Incorporate multi-staging in docker images
-
M.V.Martins, D. Tolledo, J. Machado, L. M.T. Baptista, V.Realinho. (2021) "Early prediction of student’s performance in higher education: a case study" Trends and Applications in Information Systems and Technologies, vol.1, in Advances in Intelligent Systems and Computing series. Springer. DOI: 10.1007/978-3-030-72657-7_16
-
Feature-engine: https://feature-engine.trainindata.com/en/latest/