Tablesaw is easiest way to do data science in Java. It includes a data-frame, an embedded column-store, and hundreds of methods to transform, summarize, or filter data. If you work with data in Java, it will probably save you time and effort.
It also includes support for descriptive statistics, data visualization, and machine learning. There are other, more elaborate platforms for data science in Java. They were designed to work with vast amounts of data, and that requires a big stack: Spark, Hadoop, HDFS, Pig, Yarn, maybe.
With Tablesaw, you can manipulate half a billion rows on a laptop and over 2 billion records on a server. All it takes to get started is one maven dependency:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.lwhite1</groupId>
<artifactId>tablesaw</artifactId>
<version>0.7.6</version>
</dependency>
- You can find an introductory tutorial here: https://jtablesaw.wordpress.com/an-introduction/ The early drafts of a User Guide are also available on that site
- The JavaDoc can be found here: http://lwhite1.github.io/tablesaw/apidocs/
- If you have questions of any kind: Ask them in the Issues section of this Repo.
A 1.0 release is planned for early September.
- Import data from RDBMS and CSV files, local or remote (http, S3, etc.)
- Combine files
- Add and remove columns
- Sort, Group, Filter
- Map/Reduce operations
- Store tables in a fast, compressed columnar storage format
- Descriptive stats: mean, min, max, median, sum, product, standard deviation, variance, percentiles, geometric mean, skewness, kurtosis, etc.
- Regression: Least Squares
- Classification: Logistic Regression, Linear Discriminant Analysis, Decision Trees, k-Nearest Neighbors, Random Forests
- Clustering: k-Means, x-Means, g-Means
- Association: Frequent Item Sets, Association Rule Mining
- Feature engineering: Principal Components Analysis
- Scatter plots
- Line plots
- Vertical and Horizontal Bar charts
- Histograms
- Box plots
- Quantile Plots
- Pareto Charts
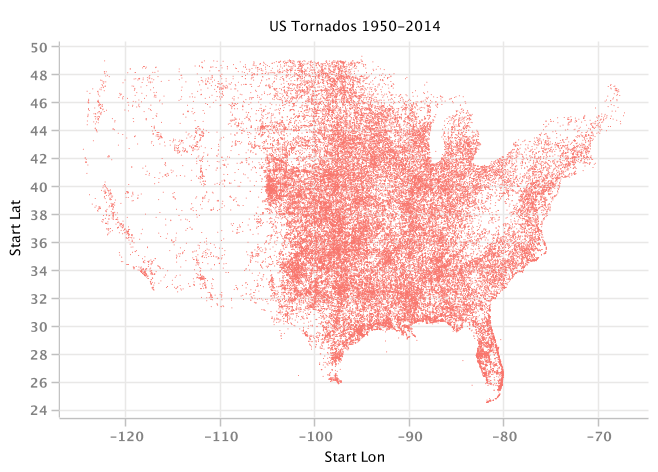
Here's an example where we use XChart to map the locations of tornadoes:
You can see examples and read more about plotting in Tablesaw here: https://jtablesaw.wordpress.com/2016/07/30/new-plot-types-in-tablesaw/.
You can load a 500,000,000 row, 4 column csv file (35GB on disk) entirely into about 10 GB of memory. If it's in Tablesaw's .saw format, you can load it in 22 seconds. You can query that table in 1-2 ms: fast enough to use as a cache for a Web app.
BTW, those numbers were achieved on a laptop.
The goal in this example is to identify the production shifts with the worst performance. These few lines demonstrate data import, column-wise operations (differenceInSeconds()), filters (isInQ2()) grouping and aggegating (median() and .by()), and (top(n)) calculations.
Table ops = Table.createFromCsv("data/operations.csv"); // load data
DateTimeColumn start = ops.dateColumn("Date").atTime(ops.timeColumn("Start"));
DateTimeColumn end = ops.dateColumn("Date").atTime(ops.timeColumn("End");
LongColumn duration = start.differenceInSeconds(end); // calc duration
duration.setName("Duration");
ops.addColumn(duration);
Table filtered = ops.selectWhere( // filter
allOf
(column("date").isInQ2(),
(column("SKU").startsWith("429")),
(column("Operation").isEqualTo("Assembly"))));
Table summary = filtered.median("Duration").by("Facility", "Shift"); // group medians
FloatArrayList tops = summary.floatColumn("Median").top(5); // get "slowest"If you see something that can be improved, please let me know.