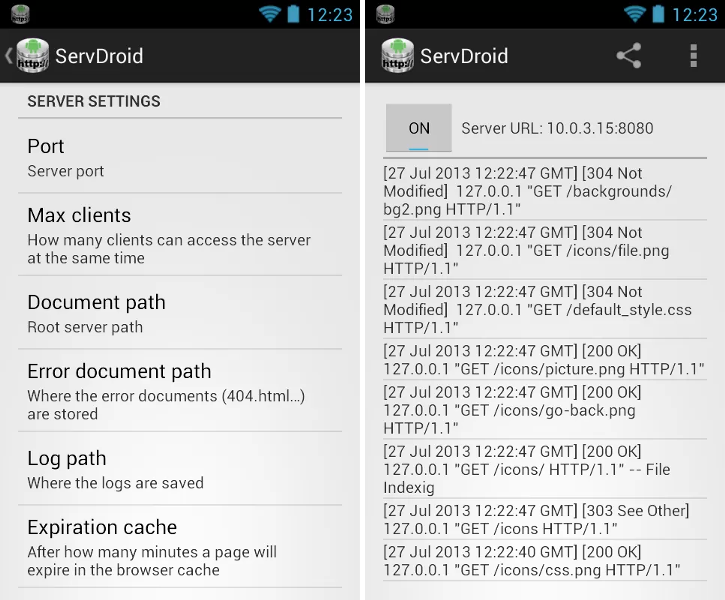
ServDroid is an small web server for the Android platform.
- Auto start options
- Can run under port 1024 (iptables and super user rights are required). Check the wiki for more information
- Only serves HTML pages (Servlets implementations will be considered for in future versions).
- Log of all requests are saved in the Android database. This information can be dumped to a text file.
- ServDroid can be configured to vibrate when a request is received.
- The 404 error page can be personalised. Available on Google Play store
This project uses ActionBarSherlock. In order to be able to use it run the following commands on the root project path:
git submodule init
git submodule update
The version 0.2.4 and above allows the developer to manage the ServDroid service from an other application.
If you have an application which needs to manage a web server you can use the ServDroid for this purpose. In this page you will learn how to connect to the ServDroid service in order to manage through using a simple helper.
You can find a simple example in the ServDroid repository
First you need to copy the following files to your project:
- org.servDroid.db.LogMessage.java
- org.servDroid.db.LogMessage.aidl
- org.servDroid.helper
- org.servDroid.helper.IServiceHelper.java
- org.servDroid.helper.ServiceHelper.java
- org.servDroid.server.service
- org.servDroid.server.service.params
- org.servDroid.server.service.ServerValues.java
- org.servDroid.server.service.ServiceController.aidl
You also can take them from the example code in the repo. (just copy the whole org.servDroid package from the example project)
Then prepare your manifest adding this lines:
<service android:name="org.servDroid.server.service.ServerService">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="org.servDroid.server.service.ServiceController" />
</intent-filter>
</service>We need to create the ServiceHelper instance in onCreate
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
mServiceHelper = new ServiceHelper(this);
// We can change the periodicity of getting status change notifications
//mServiceHelper.setStatusTimeRefresh(2500);
}Connect the instance to the service and disconnect it when it is not needed any more
@Override
protected void onResume() {
...
mServiceHelper.connect();
// We also can run code when the service is binded:
// mServiceHelper.connect(myRunnable);
super.onResume();
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
...
mServiceHelper.disconnect();
super.onPause();
}Now we have our helper binded with the service, so we can work with the server.
status = mServiceHelper.getServiceController().getStatus();
if (status == ServerValues.STATUS_RUNNING) {
mServiceHelper.getServiceController().stopService();
} else if (status == ServerValues.STATUS_STOPPED) {
ServerParams params = new ServerParams("/sdcard/", "/sdcard/error", 30, true, 8080, 10);
mServiceHelper.startServer(params);
}If you want to get notifications when the status of the server changes you can register your own listener. Just remember to unregister it when you will not need it anymore
@Override
protected void onResume() {
// Register a listener to get notified when the status changes
mServiceHelper.addServerStatusListener(this);
mServiceHelper.connect();
...
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
// Before disconnect, remove the status listener
mServiceHelper.removeServerStatusListener(this);
mServiceHelper.disconnect();
...
}And finally, just get the status events and manage them as you need
@Override
public void onServerStatusChanged(ServiceController serviceController, int status) {
switch (status) {
case IServiceHelper.STATUS_CONNECTED:
// Create a log line to append to the ServDroid logs
LogMessage logLine = new LogMessage();
logLine.setInfoEnd("Service linked succesfull from an external application");
logLine.setTimeStamp(System.currentTimeMillis());
try {
// Send the line
mServiceHelper.getServiceController().addLog(logLine);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
updateStatusText("Status: Connected");
break;
case IServiceHelper.STATUS_DISCONNECTED:
updateStatusText("Status: Disconnected");
break;
case IServiceHelper.STATUS_STOPPED:
updateStatusText("Status: Connected / Server stopped");
break;
case IServiceHelper.STATUS_RUNNING:
updateStatusText("Status: Connected / Server running");
break;
default:
break;
}
}If you want to access directly the instance that is connected to the service it is possible to get it using the helper:
ServiceController serviceController = mServiceHelper.getServiceController();The available functions are documented in the file org.servDroid.server.service.ServiceController.aidl:
- startService()
- restartService()
- stopService()
- getStatus()
- getCurrentParams()
- getDefaultPortOnRoot()
- getVersion()
- addLog()
- getLogList()
/**
* Start the server with the defined parameters
*
* @param params
* The parameter with the configuration of the server
*
* @return True if the server has been initialized, false otherwise
*/
boolean startService(in ServerParams params);
/**
* Restart the server with the defined parameters
*
* @param params
* The parameter with the configuration of the server
*
* @return True if the server has been initialized, false otherwise
*/
boolean restartService(in ServerParams params);
/**
* Stop the server.
*
* @return True if the server has been stopped, false otherwise
*/
boolean stopService();
/**
* Get the status of the server:<br>
* {@link ServerValues.STATUS_RUNNING} The server is running <br>
* {@link ServerValues.STATUS_STOPED} The server is stopped <br>
*
* @return True if the server has been initialized, false otherwise
*/
int getStatus();
/**
* Get the parameters in use by the server.
* @return The {@link ServerParams} in use for the server
*/
ServerParams getCurrentParams();
/**
* This is the default port opened when the user ask for opening a port
* under 1024. <br>
* The system will try to use iptables like this:<br>
* iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-port
* DEFAULT_PORT_ON_ROOT
* @return The default port when the root permissions are required.
*/
int getDefaultPortOnRoot();
/**
* Use this function to enable and disable the vibrations
* when a request is received.
* @param params
* True to vibrate if a petition is accepted, false otherwise.
*/
void setVibrate(in boolean vibrate);
/**
* Get the servDroid software version
* @return The ServDroid.web version
*/
String getVersion();
/**
* Create a new log entry using the the IP, request path, some extra
* information. If the log is added successfully return the new rowId for
* that log entry, otherwise return a -1 to indicate failure.
*
* @param msg
* The message to be stored in the log
* @return rowId or -1 if failed
*/
long addLog(in LogMessage msg);
/**
* Return the ArrayList which contains the log list
*
* @param numRows
* The number of rows to get
*
* @return List with the log entries
*/
List<LogMessage> getLogList(in int numRows);