In this project I use pretrained BERT from Hugging Face to classify scientific papers into different categories based on their title and abstract. This is a multi label classification problem. Each paper can have multiple topics/tags associated with it.
Processing steps:
- Data preprocessing
- Preprocess text data for BERT
- Build PyTorch Dataset (tokenization with BERT tokenizer, attention mask and padding)
- Use transfer learning to build Multi-label Text Classifier (MLTC) using the Transformers library by Hugging Face
- Fine tune the model
- Evaluate the model on test data
- Predict topic of an article based on the title and/or abstract
In this project I use arXiv dataset and metadata of more than 1.7 million scholarly articles in the fields of physics, mathematics, computer science, quantitative biology, quantitative finance, statistics, electrical engineering and systems science, and economics.
The data is freely available and, for instance, can be obtained here. I use arxiv-metadata-oai-snapshot-2020-08-14.json metadata json file (2.8GB) which contains all the meta information about the article, including "title", "abstract", and "categories".
Here is an example
{"id":"0704.0001",
"submitter":"Pavel Nadolsky",
"authors":"C. Bal\\'azs, E. L. Berger, P. M. Nadolsky, C.-P. Yuan",
"title":"Calculation of prompt diphoton production cross sections at Tevatron and\n LHC energies",
"comments":"37 pages, 15 figures; published version",
"journal-ref":"Phys.Rev.D76:013009,2007","doi":"10.1103/PhysRevD.76.013009",
"report-no":"ANL-HEP-PR-07-12",
"categories":"hep-ph",
"license":null,
"abstract":" A fully differential calculation in perturbative quantum chromodynamics is\npresented for the production of massive photon pairs at hadron colliders. All\nnext-to-leading order perturbative contributions from quark-antiquark,\ngluon-(anti)quark, and gluon-gluon subprocesses are included, as well as\nall-orders resummation of initial-state gluon radiation valid at\nnext-to-next-to-leading logarithmic accuracy. The region of phase space is\nspecified in which the calculation is most reliable. Good agreement is\ndemonstrated with data from the Fermilab Tevatron, and predictions are made for\nmore detailed tests with CDF and DO data. Predictions are shown for\ndistributions of diphoton pairs produced at the energy of the Large Hadron\nCollider (LHC). Distributions of the diphoton pairs from the decay of a Higgs\nboson are contrasted with those produced from QCD processes at the LHC, showing\nthat enhanced sensitivity to the signal can be obtained with judicious\nselection of events.\n",
"versions":[
{"version":"v1",
"created":"Mon, 2 Apr 2007 19:18:42 GMT"},
{"version":"v2",
"created":"Tue, 24 Jul 2007 20:10:27 GMT"}],
"update_date":"2008-11-26",
"authors_parsed":[
["Bal\u00e1zs","C.",""],
["Berger","E. L.",""],
["Nadolsky","P. M.",""],
["Yuan","C. -P.",""]]}
The data is parsed, preprocessed and filtered in this notebook notebooks/data-preparation.ipynb. Some of the categories such as acc-phys, econ are underrepresented in the arXiv, I will exclude the categories with very low frequencies to simplify the task (this is a proof of concept project).
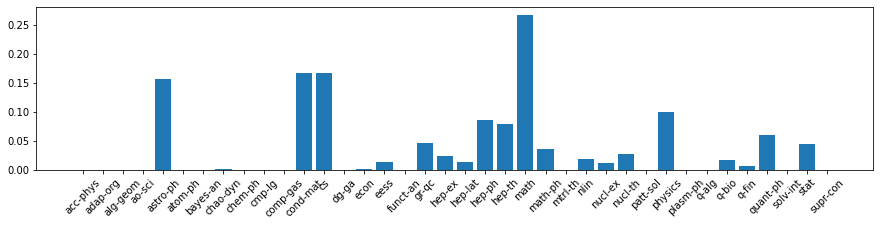
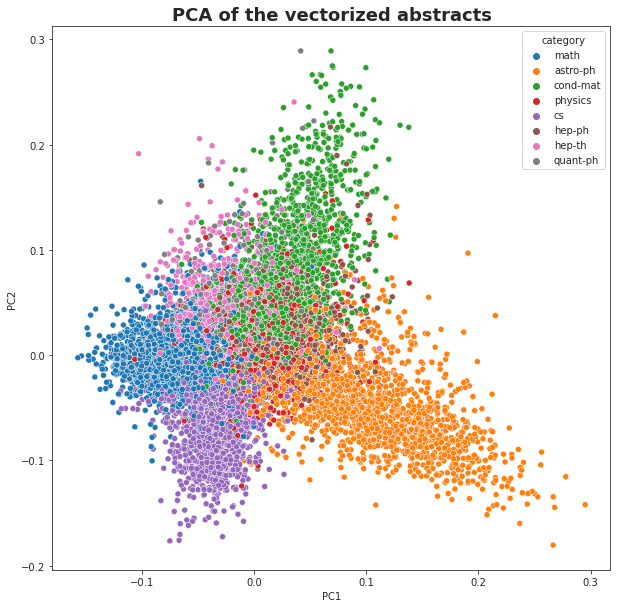
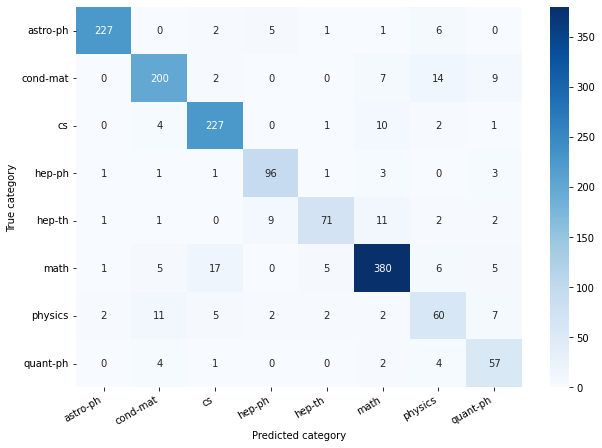
After the filtering end encoding only 8 most popular categories are present in the final dataset that we will use. The PCA analysis of the most popular categories confirms the presence of the signal of the dataset (see the notebook).
Note that the PCA is performed using articles with a single label across the topics to get a clear signal.
See notebooks/multi-label-text-classification-BERT.ipynb.
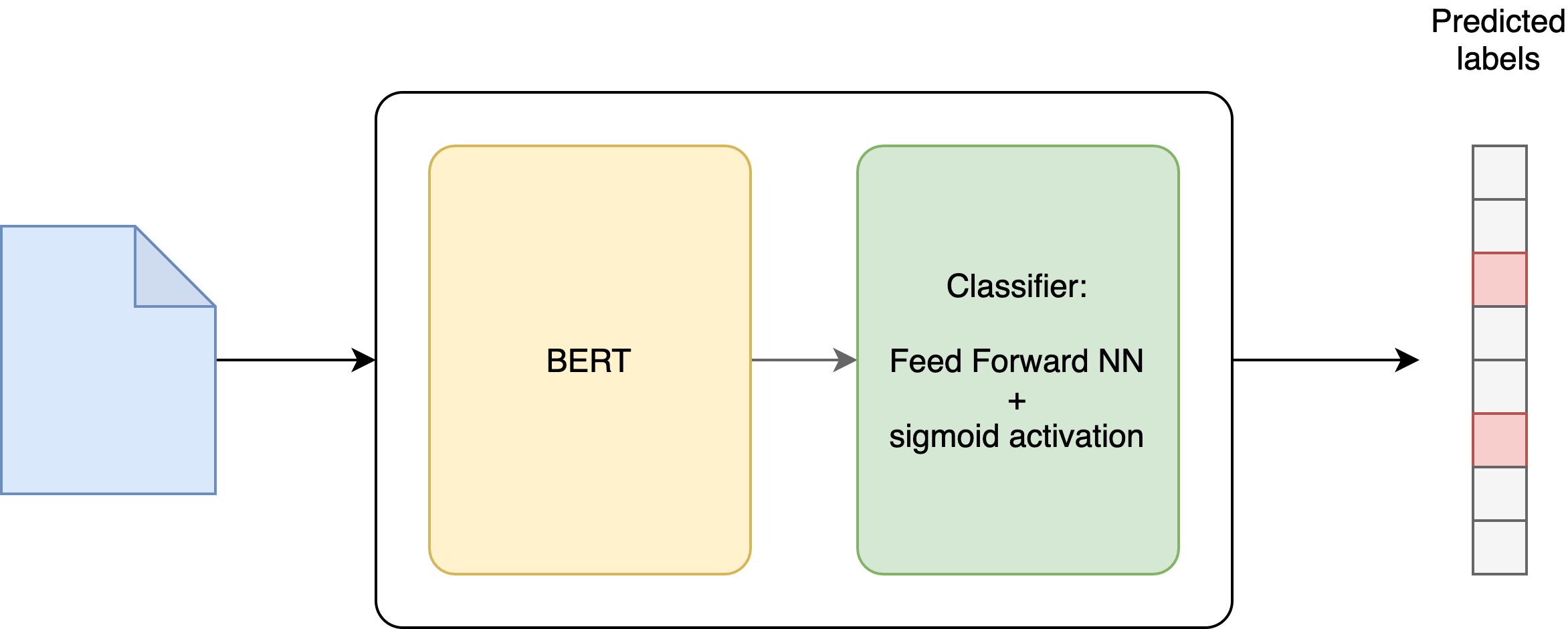
The model that we use for the multi-label text classification is relying on the pretrained BERT model from Hugging Face. We fine-tune the pretrained BERT model with one additional output layer that handles the labeling task. The additional layer includes a feed forward neural network with sigmoid activation. This allows to obtain a score (0/1) for each label independently.
Notes:
- For training use
BCEWithLogitsLoss(). This loss combines a Sigmoid layer and the BCELoss in one single class. This version is more numerically stable than using a plain Sigmoid followed by a BCELoss as, by combining the operations into one layer, we take advantage of the log-sum-exp trick for numerical stability. - Therefore the model should not include the Sigmoid activation, the sigmoid activation should be added during the evaluation stage.
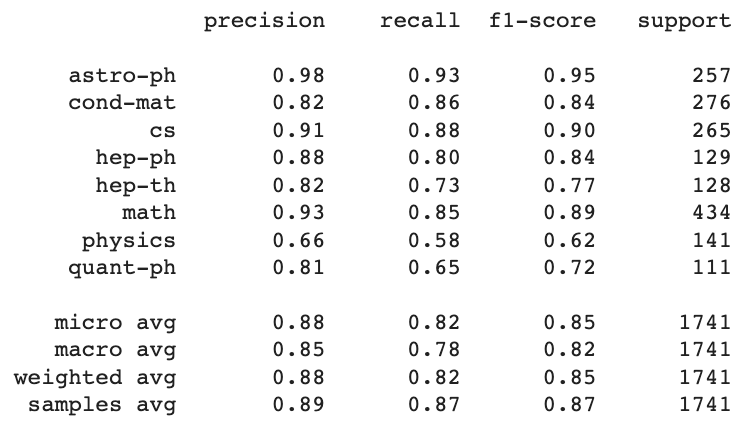
- Accuracy measures the fraction of correctly predicted labels, for example,
target=[0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1],output=[1,0,0,0,0,0,0,1], thereforeacc=6/8=0.75. You may see that we've missed the label, however due to the large number of zeros the accuracy is high. - A more informative metrics: precision, recall, F1 score
- Some metrics are defined for binary classification tasks (e.g. F1 score, ROC-AUC).
- We can extend a binary metric to multiclass or multilabel problems by treating the problem as a collection of binary problems, one for each class.
- The binary metric should be properly averaged across the set of classes
- "macro averaging" mean of the binary metrics, all the classes have equal weights. The metric (for example, precision) for each class is computed independently.
- "weighted averaging" accounts for class imbalance, each class' score weighted by its presence in the true data sample (support column)
- "micro averaging" aggegate the contribution of all classes to compute the average metric. Precision=(TP_a+TP_b+TP_c)/Total. Micro-averaging may be preferred in multilabel settings, including multiclass classification where a majority class is to be ignored; micro averaging properly captures class imbalances, it is less misleading than macro averaging.
- "samples" apply only to multilabel problems. Calculates metrics for each sample and returns their average.
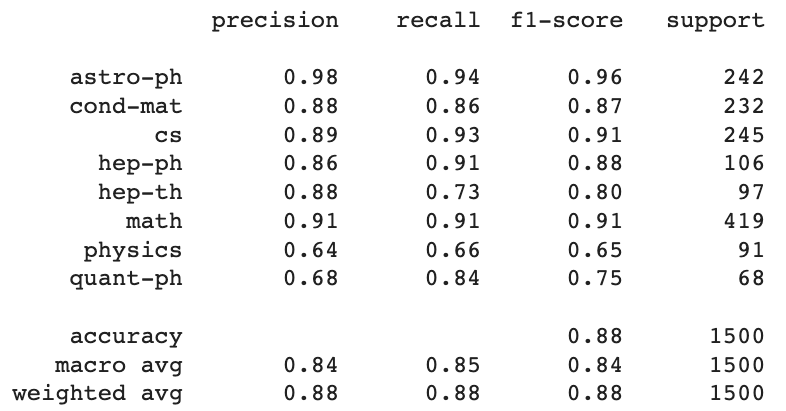
For the multi-class classification we can use soft-max instead of sigmoid activation. For simplicity, I use the same network and the loss function as previously, however the predicted class is found using the maximum score. For the training data, to increase the performance we filter out the samples with multiple lablels. See notebooks/multi-class-text-classification-BERT.ipynb for details.