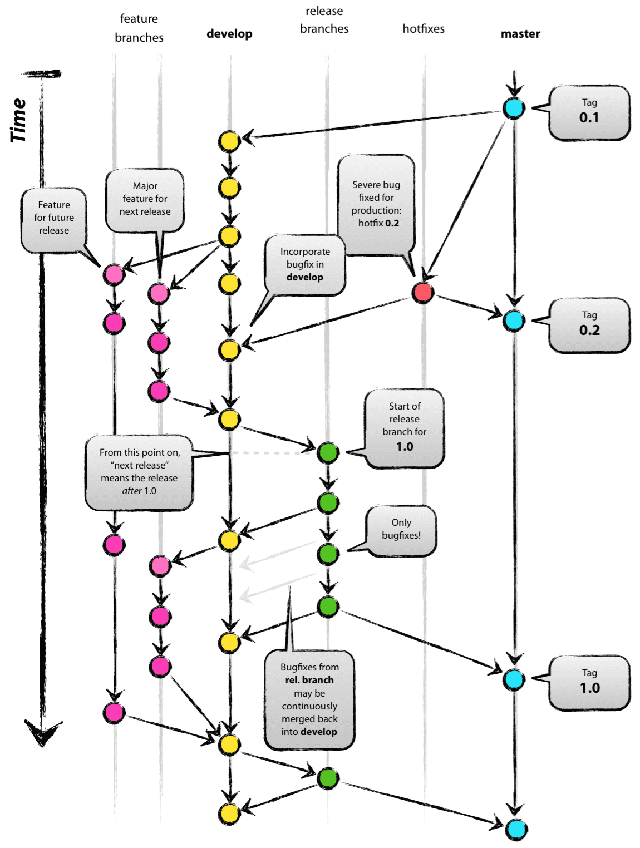
gitflow is a git branching methodology that Vincent Driessen created and has been adopted by many companies with great success. Atlassian even covers gitflow in their git tutorials.
master
masteris master. ;) It will have anything that is in production.
developThis branch for the most part parallels
masterand is kept up-to-date.
feature/{feature_name}This branch contains a new feature to be introduced within the codebase.
release/{version_number}This branch is prepared after feature, bugfix, et cetera branches are merged into the
developbranch. Essentially, a release is prepared after a developer finishes work in dev and is ready to have it sent to QA.
hotfix/{hotfix_name}This branch is used for any bugfixes that are usually found after a release that are necessary to be rolled out as top priority.
bugfix/{bugfix_name}Bugfix branches are coupled with release/* branches. During QA if there are bugs that need to be addressed, a bugfix branch will be used to merge into the release branch and the develop branch.
These are the typical environments that are used within any sofware development cycle.
Dev
developQA
Production
New feature during a sprint/dev-cycle
Development on a new feature will start by branching off of the
developbranch. After development is complete, thefeaturebranch is merged back into the develop branch.** Note:
featurebranches do not get deleted until the release it will be in gets merged intomasterCreating a release
After all of the development on any feature branches are complete and they are merged back into the develop branch, you can branch off of the
developbranch to create areleasebranch.At this stage is where you will decide on the version number and also begin QA.
Bugfix found during QA
A
bugfixbranch is used to address any bugs found during QA. This branch is created by branching off of the respectivereleasebranch from which the bug was found.After development is complete, the
bugfixbranch gets merged back into its respectivereleasebranch and thedevelopbranch.Creating a hotfix
A
hotfixbranch is created by branching off ofmasteror the latesttag. So essentially, whatever is live in production already. A version bump can be done in thehotfixbranch in lieu of creating areleasebranch.Tagging
A tag is created after the
releasebranch is QA'd and merged intomaster.
Two developers, same codebase
During a sprint/dev-cycle, two developers need to work on features that are in the same codebase. Both developers clone the repository and both create their respective branches off of the latest
developbranch.After the
featurebranches are done, they are merged back intodevelop.A
releasebranch is created by one person who will branch off ofdevelopsince it has all of the completed features.The
releasebranch can now be sent over for QA.After QA passes, a production rollout can take place; the
releasebranch can be merged intomasteranddevelop.Bug found in QA
During QA, if a bug is found, a
bugfixbranch can be created by branching off of thereleasebranch in which the bug came from. Thebugfixbranch is then merged into thereleasebranch again.Critical bug found after production rollout
If a bug has been found after a release has been rolled out in production and development has already started for another dev-cycle, a
hotfixbranch can be used.The
hotfixbranch branches off ofmaster(or the latest tag). After development is done, thehotfixbranch gets merged intomasteranddevelop.Other development in the dev-cycle can continue as normal since the
hotfixbranch is branched off ofmaster.Cherry picking features
As mentioned earlier,
featurebranches do not get deleted until thereleasebranch they are in are merged intomaster. Keeping these branches around until then allow features to be cherry picked.There will be some instances where some features need to be delivered faster than others. In this case, it would be suitable to create a release with only the features wanted; the remaining features can be released in another
releasebranch.