BentoBox is a genomic data vizualization package for R. Using grid
graphics, BentoBox empowers users to programmatically and flexibly
generate multi-panel figures. BentoBox accomplishes these goals by
utilizing 1) a coordinate-based plotting system, and 2) edge-to-edge
containerized data visualization. The coordinate-based plotting system
grants users precise control over the size, position, and arrangement of
plots. Its edge-to-edge plotting functions preserve the mapping between
user-specified containers and the represented data. This allows users to
stack plots with confidence that vertically aligned data will correspond
to the same regions. For more information about BenoBox’s philosophy and
design, check out the Our Philosophy page.
Specialized for genomic data, BentoBox also contains functions to read
and plot multi-omic data quickly and easily. BentoBox can address an
endless number of use cases, including: dynamic exploration of genomic
data, arrangment into multi-omic layouts, and survey plotting for
quickly viewing data across the genome. Check out our vignettes for
detailed examples and suggested use cases!
BentoBox can be installed from GitHub as follows:
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))
install.packages("BiocManager")
if (!requireNamespace("remotes", quietly = TRUE))
BiocManager::install("remotes")
remotes::install_github("PhanstielLab/BentoBox")
package.version("BentoBox")We can use any of the plotting functions to quickly plot a single data
type by simply ignoring the arguments that define the plotting location
(i.e. x, y, width, height, just, default.units).
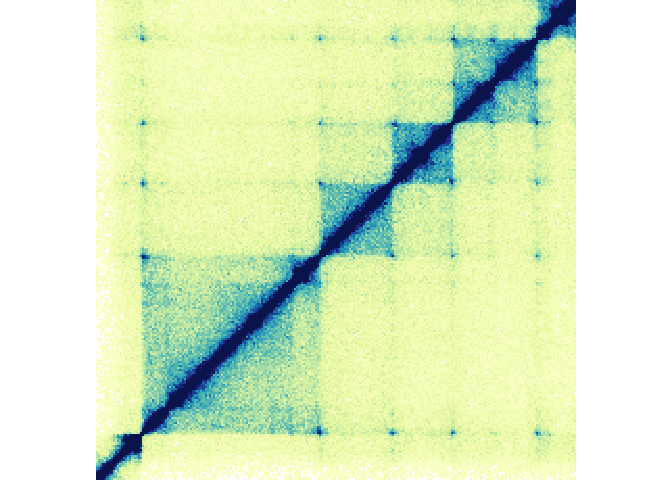
Lets demonstrate this by plotting the example Hi-C data included in bb_hicData (chr21:28000000-30300000):
## Load BentoBox
library(BentoBox)
## Load example Hi-C data
data("bb_hicData")
## Quick plot Hi-C data
hicPlot <- bb_plotHicSquare(data = bb_hicData,
chrom = "chr21", chromstart = 28000000, chromend = 30300000)In addition to plotting the Hi-C Data, this creates an S3 object of
class bb_hicSquare which stores all of the information about the
region being plotted, the genome assembly, and any plotting parameters.
class(hicPlot)
## [1] "bb_hicSquare"print(hicPlot)
## $chrom
## [1] "chr21"
##
## $chromstart
## [1] 2.8e+07
##
## $chromend
## [1] 30300000
##
## $altchrom
## [1] "chr21"
##
## $altchromstart
## [1] 2.8e+07
##
## $altchromend
## [1] 30300000
##
## $assembly
## $Genome
## [1] "hg19"
##
## $TxDb
## [1] "TxDb.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19.knownGene"
##
## $OrgDb
## [1] "org.Hs.eg.db"
##
## $gene.id.column
## [1] "ENTREZID"
##
## $display.column
## [1] "SYMBOL"
##
## $BSgenome
## [1] "BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19"
##
## attr(,"class")
## [1] "bb_assembly"
##
## $resolution
## [1] 10000
##
## $x
## NULL
##
## $y
## NULL
##
## $width
## NULL
##
## $height
## NULL
##
## $just
## [1] "left" "top"
##
## $color_palette
## function (n)
## {
## x <- ramp(seq.int(0, 1, length.out = n))
## if (ncol(x) == 4L)
## rgb(x[, 1L], x[, 2L], x[, 3L], x[, 4L], maxColorValue = 255)
## else rgb(x[, 1L], x[, 2L], x[, 3L], maxColorValue = 255)
## }
## <bytecode: 0x7fb5a5932f28>
## <environment: 0x7fb5a592fdb0>
##
## $zrange
## [1] 0 70
##
## $half
## [1] "both"
##
## $grobs
## gTree[GRID.gTree.1]
##
## attr(,"class")
## [1] "bb_hicSquare"
## attr(,"plotted")
## [1] TRUEbb_hicSquare objects, and all objects created by bb_plot functions,
can saved and used later in multi-plot arrangements (see
bb_pagePlotPlace() and related vignettes). For different types of
plots check out the rest of the plotting functions in the Reference
section.
We can use our own data by using bb_read functions. This can be useful
if there are additional processing steps required.
bb_readHic(hicFile = "path/to/file.hic", ...)Or if no processing is required, we can simply provide the file path
directly to the bb_plot function.
bb_plotHicSquare(hicData = "path/to/file.hic", ...)To add annotation features to a bb_plot object, or to view multiple
bb_plot objects simultaneously, we must:
- Create a BentoBox coordinate page with
bb_pageCreate(). - Provide values for the placement arguments (
x,y,width,height,just,default.units) inbb_plotfunctions.
As an annotation example, lets say we want to add a color scale legend for a Hi-C plot:
## Load BentoBox
library(BentoBox)
## Load example Hi-C data
data("bb_hicData")
## Create a BentoBox page
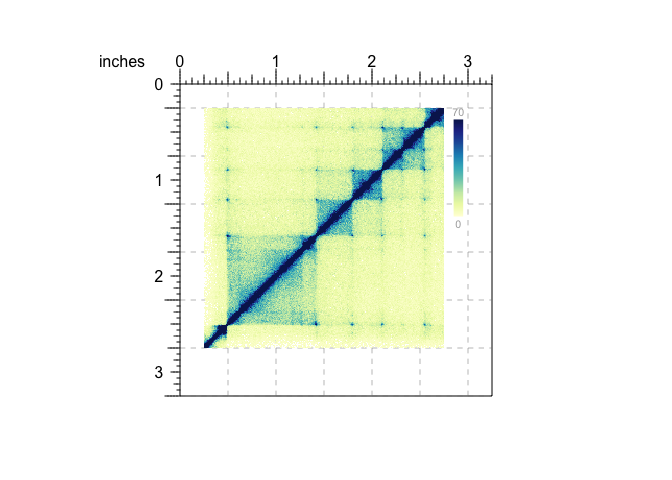
bb_pageCreate(width = 3.25, height = 3.25, default.units = "inches")
## Plot Hi-C data with placing information
hicPlot <- bb_plotHicSquare(data = bb_hicData,
chrom = "chr21", chromstart = 28000000, chromend = 30300000,
x = 0.25, y = 0.25, width = 2.5, height = 2.5, default.units = "inches")
## Add color scale annotation
bb_annoHeatmapLegend(plot = hicPlot,
x = 2.85, y = 0.25, width = 0.1, height = 1.25, default.units = "inches")By default, all placement coordinates are relative to the top right
corner of the page/plot. This can be adjusted for each function
individually with the just parameter. This allows us to use the most
convenient coordinates to place our plot and the ability to right, left,
center, top, bottom, or middle align every plotting element. For more
information on plot placement, check out the vignettes.
Now, let’s suppose we have both Hi-C data and signal track data such as
H3K27Ac bigWig files. We could enter the region information
(chr21:28000000-30300000) into both functions. But we can streamline
this process by taking advantage of the bb_params() function. Since
many functions share arguments, bb_params() lets us reduce repetition
by defining shared arguments in one place. Furthermore, we can
concatenate these bb_params objects, to create useful combinations of
parameter settings. For more information about bb_params() usage,
refer to the documentation or vignettes. The following code shows how we
can utilize these functions to plot Hi-C data H3K27Ac signal tracks, and
add a genomic label to a shared region:
## Load BentoBox
library(BentoBox)
## Load example Hi-C and signal track (H3K27Ac) data
data("bb_hicData")
data("bb_signalData")
## Define common region & plot-placement parameters
region <- bb_params(chrom = "chr21", chromstart = 28000000, chromend = 30300000)
params <- bb_params(x = 0.25, width = 2.5, default.units = "inches")
## Create a BentoBox page
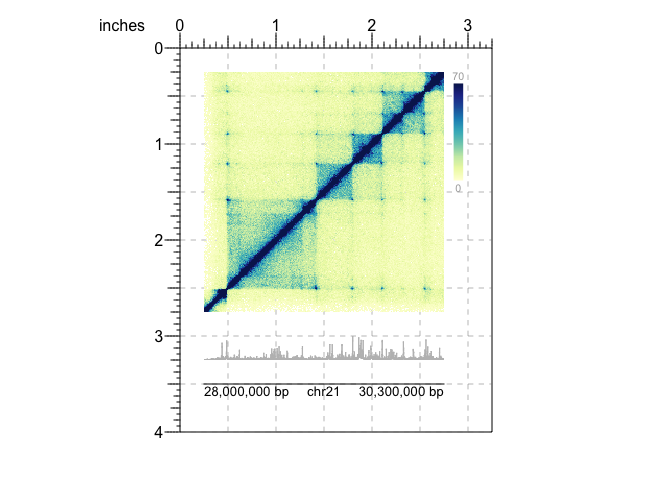
bb_pageCreate(width = 3.25, height = 4, default.units = "inches")
## Plot Hi-C data with combined bb_params objects
hicPlot <- bb_plotHicSquare(data = bb_hicData,
params = c(region, params),
y = 0.25, height = params$width)
## Add color scale annotation
bb_annoHeatmapLegend(plot = hicPlot,
x = 2.85, y = 0.25, width = 0.1, height = 1.25, default.units = "inches")
## Plot H3K27Ac signal track
bb_plotSignal(data = bb_signalData,
params = c(region, params),
y = 3, height = 0.25)
## Label genome coordinates
bb_plotGenomeLabel(params = c(region, params),
y = 3.5, length = params$width, scale = "bp")You might notice that using bb_params() we can remove quite a few of
the plotting arguments. The only things we need to specify are the data
to use and the y-coordinate to place each plot. Using c() we can also
combine distinct sets of bb_params() to create different combinations
of paramters for each function. We can also override arguments in
bb_params() objects by defining them in local functions if needed.
Another useful feature of bb_params() is the ability to build regions
and plots from gene names, given genomic annotation packages are loaded.
You can check which data packages belong to which assemblies by using
bb_defaultPackages(Genome) or make your own with bb_assembly():
bb_defaultPackages("hg19")
## List of 6
## $ Genome : chr "hg19"
## $ TxDb : chr "TxDb.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19.knownGene"
## $ OrgDb : chr "org.Hs.eg.db"
## $ gene.id.column: chr "ENTREZID"
## $ display.column: chr "SYMBOL"
## $ BSgenome : chr "BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19"
## - attr(*, "class")= chr "bb_assembly"Here is an example of using bb_params() to plot the IL1B gene using
the gene and geneBuffer arguments:
## Load assembly packages
library(TxDb.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19.knownGene)
library(org.Hs.eg.db)
library(BSgenome.Hsapiens.UCSC.hg19)
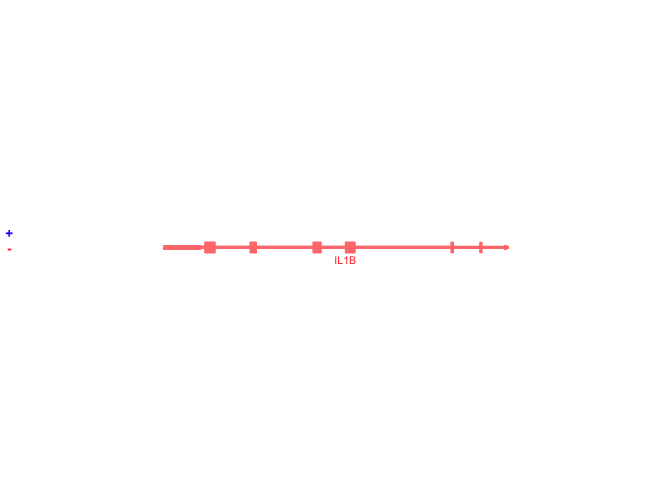
## Plot IL1B with no buffer
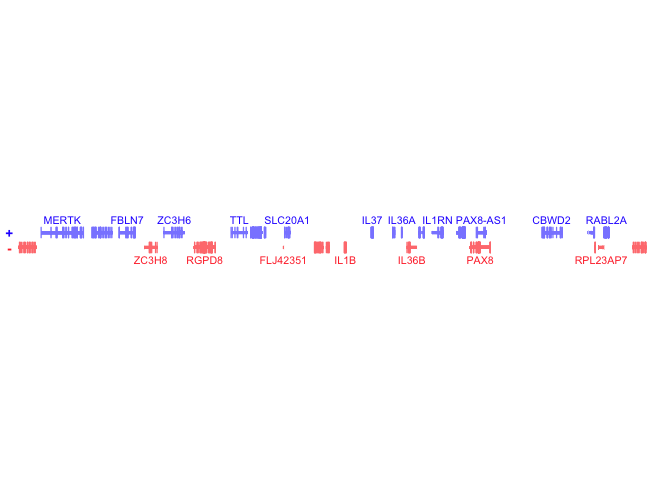
bb_plotGenes(params = bb_params(gene = 'IL1B'))## Plot genes with a 1000000bp (1Mb) buffer, centered on IL1B
bb_plotGenes(params = bb_params(gene = 'IL1B', geneBuffer = 1000000))BentoBox is incredibly flexible and functional. However, due to this
flexibility and like all programming packages, it may not always prevent
users from making unintentional mistakes. If plot sizes are entered
incorrectly or data is mishandled, it is possible to connect multi-omic
data incorrectly. Make sure you utilize package features that reduce
human error and increase re-usability of code to get the most milage out
of BentoBox.