Complete MongoDB Administration Guide Tutorial
cmder - A Portable console emulator for Windows
A document database:
- stores data in separate documents that are independent of each other. Each document has a set of fields that can differ one from another.
- stores data using
json format.
JSON stands for JavaScript Object Notation where:
- the basic syntax is: {“key”: value}. The key must be enclosed in quotes.
- the supported data types are: String, Number, Boolean, Array, Object, Null
Example:
{
"String": "That’s a sample string",
"Number": 3,
"Boolean": true,
"Array": [1, 2, 3],
"Object":
{
"Key1": 1,
"Key2": "Tow",
"Key3": false,
"Key4": ["first", "second"],
"Key5":
{
"nestedobjectkey1": "nested",
"nestedobjectkey2": false,
}
}
"Null": null # meaning that the value is absent.
}BSON stands for Binary JSON. It extends JSON with additional data types:
- (1.1) String
- (1.2) Number:
- Double
- 32-bit Integer
- 64-bit Integer
- (1.3) Boolean
- (1.4) Array
- (1.5) Object
- (1.6) Null
- (2) Regular Expression
- (3) Timestamp
- (4) Binary data
- (5) Date
- (7) ObjectId
- (8) and others.
📝 MongoDB stores documents in BSON format.
The extended JSON is used to convert JSON to BSON and vice versa. It has a shell mode and a strict mode of operation:
📝 The Shell Mode:
- uses inline
BSONtypes - is the internal MongoDB mode
- is compatible with MongoDB shell
- can be represented as follows:
{ "_id": ObjectId("ifjdfdslfkdf"), "age": NumberInt(39), "registered": ISODate("2024-01-02T01:24:10 -02:00") }
📝 The Strict Mode:
- represents BSON types using special key names prepended with $
- is compatible with the
JSONstandard - is used in all JSON parsers
- can be represented as follows:
{ "_id": {"$oid": "ifjdfdslfkdf"}, "age": 39, "registered": {"$date": "2024-01-02T01:24:10 -02:00"} }
Both modes are supported by:
- external MongoDB drivers and REST API
- mongoimport utility
MongoDB has the following structure:
Databases(
Collections(
Documents{
"key": value pairs
} // Documents stored in BSON format
) // Collections
) // Databases independent from each other
MongoDB has the following architecture:
:one: mongod: is the service used to launch the MongoDB server.
2️⃣ mongosh: is the MongoDB command line bundled to MongoDB server. It is launched by using the mongo command.
3️⃣ mongoimport: is used to import a subset of data to a MongoDB database.
Further reading here
4️⃣ mongoexport: is used to export a subset of the database.
5️⃣ mongodump: is used to backup the data of a MongoDB server in a dump file.
6️⃣ mongorestore: is used to restore the data from a dump file into a MongoDB server.
7️⃣ mongostat: is used to monitor in real time the MongoDB performance.
Different tools to interact with MongoDB Server are:
mongo shell: is a command line client that allows you to connect and interact manually with a local MongoDB server.Robot 3T (Robomongo)andMongoDB Compassare client applications that also let you connect and interact manually with a MongoDB server.MongoDriveris an interface that enables you to connect and interact via a programming language (PowerShell, Python, etc.) with MongoDB Server.
NB: MongoDB server and MongoDB shell support SSL encryption. It is highly recommended to connect and interact remotely with them using SSL encryption.
You can install MongoDB
Locally on your PC (not scalable, not reliable):
- 🟢 It is a single server
- 🟢 It is suitable for educational or development purpose
- 🔴 It is not suitable for production applications
By using Dedicated or Virtual managed servers:
- 🟢 You have a full control
- 🔴 It come with management overhead (manual scalability)
By using Cloud Databases as a service:
- 🟢 It is suitable for production applications
- 🟢 It offers a replica-set out of the box
- 🟢 It is easy to manage and to scale
- 🔴 It offers free size-limited options available
winget search --name mongodb
<# Output example
Name Id Version Source
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
MongoDB MongoDB.Server 6.0.6 winget
NoSQLBooster for MongoDB NoSQLBooster.NoSQLBooster 6.2.17 winget
MongoDB Shell MongoDB.Shell 1.10.1 winget
MongoDB CLI MongoDB.MongoDBCLI 1.30.0 winget
MongoDB Atlas CLI MongoDB.MongoDBAtlasCLI 1.5.1 winget
MongoDB Tools MongoDB.DatabaseTools 100.7.3 winget
MongoDB Compass Readonly MongoDB.Compass.Readonly 1.41.0.0 winget
MongoDB Compass Isolated Edition MongoDB.Compass.Isolated 1.41.0.0 winget
MongoDB Compass MongoDB.Compass.Full 1.41.0.0 winget
MongoDB Compass Community MongoDB.Compass.Community 1.41.0 winget
#><#
Installs the selected package, either found by searching a configured source or directly from a manifest. By default, the query must case-insensitively match the id, name, or moniker of the package.
--id Filter results by id.
-e,--exact Find package using exact match
-s,--source Find package using the specified source.
-h, --silent Runs the installer in silent mode. This suppresses all UI. The default experience shows installer progress.
#>
winget install --id MongoDB.Server --exact --source winget --silent
<# Output example
Found MongoDB [MongoDB.Server] Version 6.0.6
This application is licensed to you by its owner.
Microsoft is not responsible for, nor does it grant any licenses to, third-party packages.
Downloading https://fastdl.mongodb.org/windows/mongodb-windows-x86_64-6.0.6-signed.msi
██████████████████████████████ 481 MB / 481 MB
Successfully verified installer hash
Starting package install...
Successfully installed
#>➕ Append the path of MongoDB executable to the user environment variable
C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Server\6.0\bin
winget install --id MongoDB.Shell --exact --source winget --silent
<# Output example
Found MongoDB Shell [MongoDB.Shell] Version 1.10.1
This application is licensed to you by its owner.
Microsoft is not responsible for, nor does it grant any licenses to, third-party packages.
Downloading https://downloads.mongodb.com/compass/mongosh-1.10.1-x64.msi
██████████████████████████████ 35.4 MB / 35.4 MB
Successfully verified installer hash
Starting package install...
Successfully installed
#>Restart PowerShell and launch the mongosh console:
mongosh
<# Output example
Current Mongosh Log ID: 65a6593fc593e766a03346f8
Connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/?directConnection=true&serverSelectionTimeoutMS=2000&appName=mongosh+1.10.1
Using MongoDB: 6.0.6
Using Mongosh: 1.10.1
For mongosh info see: https://docs.mongodb.com/mongodb-shell/
To help improve our products, anonymous usage data is collected and sent to MongoDB periodically (https://www.mongodb.com/legal/privacy-policy).
You can opt-out by running the disableTelemetry() command.
test>
#>
winget install --id MongoDB.Compass.Community --exact --source winget --silent
<# Output example
Found MongoDB Compass Community [MongoDB.Compass.Community] Version 1.41.0
This application is licensed to you by its owner.
Microsoft is not responsible for, nor does it grant any licenses to, third-party packages.
Downloading https://github.com/mongodb-js/compass/releases/download/v1.41.0/mongodb-compass-1.41.0-win32-x64.msi
██████████████████████████████ 127 MB / 127 MB
Successfully verified installer hash
Starting package install...
Successfully installed
#>➕ Append the path of MongoDB executable to the user environment variable
C:\Program Files\MongoDB Compass
Show Compass Version
MongoDBCompass.exe --version
Retrieve MongodDB Compass options
MongoDBCompass.exe --help
<# Available options
--version Show Compass Version
--trackUsageStatistics (*) Enable Usage Statistics
--autoUpdates (*) Enable Automatic Updates
--enableShell (*) Enable MongoDB Shell
--enableImportExport (*) Enable import / export feature
--enableExplainPlan (*) Enable explain plan feature in CRUD and aggregation view
--enableSavedAggregationsQueries (*) Enable saving and opening saved aggregations and queries
--maxTimeMS (*) Upper Limit for maxTimeMS for Compass Database Operations
--protectConnectionStringsForNewConnections (*)If true, "Edit connection string" is disabled for new connections by default
#>Launch MongoDB Compass in PowerShell
# Open a connexion on mongodb://127.0.01:27017 without blocking the terminal
# if the root user is not yet set
MongoDBCompass.exe mongodb://localhost:27017 &
<# Output example
Id Name PSJobTypeName State HasMoreData Location Command
-- ---- ------------- ----- ----------- -------- -------
1 Job1 BackgroundJob Running True localhost MongoDBCompass.exe mongo…
#># Open a connexion on mongodb://127.0.01:27017 without blocking the terminal
# if the root user is not set
MongoDBCompass.exe mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017 &# Create the MongoDB source directory in the C drive C:\data\db
New-Item -ItemType Directory "\data\db"
# In my case I have rather created the MongoDB source directory in the git directory
New-Item -ItemType Directory "$env:USERPROFILE\ProjectsDM\MongoDBAdministrationDM\DataPersistence\db"Connect to a MongoDB server located on a local computer
mongosh 127.0.0.1
<# Output example
Current Mongosh Log ID: 65a664a5a78f6c13fe515109
Connecting to: mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017/?directConnection=true&serverSelectionTimeoutMS=2000&appName=mongosh+1.10.1
Using MongoDB: 6.0.6
Using Mongosh: 1.10.1
For mongosh info see: https://docs.mongodb.com/mongodb-shell/
test>
#>Retrieve all establishe MongoDB connections
Get-NetTCPConnection -State Established | Where-Object {$_.LocalPort -eq 27017}
<# Output example
LocalAddress LocalPort RemoteAddress RemotePort State AppliedSetting OwningPr
ocess
------------ --------- ------------- ---------- ----- -------------- --------
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 60217 Established Internet 14056
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 60129 Established Internet 14056
#>Get all TCP connections that use a TCP applied setting of Internet.
Get-NetTCPConnection -AppliedSetting InternetMake a MongoDB server accepts connections from any IP address
# Run PowerShell with highest priviledges
# Open the configuration file
notepad.exe $env:ProgramFiles\MongoDB\Server\6.0\bin\mongod.cfg
# code $env:ProgramFiles\MongoDB\Server\6.0\bin\mongod.cfg # In VS code terminal onlyAdd this lines in the network interfaces section:
# network interfaces
net:
port: 27017
#bindIp: 127.0.0.1
bindIp: 0.0.0.0Restart the MongoDB service
# Run PowerShell with highest priviledges
Get-Service -Name "MongoDB" | Restart-ServiceConnect to a MongoDB server located on a remote computer in the same network
<#
Username: unser name in the remote database
Username: unser pasword in the remote database
IPAddressRemoteComputer: IP address of the remote computer
DatabaseName: MongoDB authentiction database on the remote computer
#>
mongosh mongodb://Username:Password@IPAddressRemoteComputer:27017/DatabaseNameDatabase Architecture
.\DataPersitence\DatabaseArchitecture.md
Manage Users
.\DataPersitence\db\ManageMockUsers.md
# Connection example to the admin database
mongo "mongodb://root:root@ec2-34-216-244-19.us-west-2.compute.amazonaws.com/admin"3️⃣ Hetzner Dedicated Servers and Virtual Private Servers (VPS)
4️⃣ GoDaddy Dedicated Servers and VPS
1️⃣ Introduction to MongoDB Cloud
2️⃣ Create MongoD Atlas Cluster
3️⃣ Verify connection to the Cloud MongoDB Replica Set
# Connection example to the admin database
mongo "mongodb://cluster0-shard-00-00-fdpbt.mongodb.net:27017,cluster0-shard-00-01-fdpbt.mongodb.net:27017,cluster-00-02-fdpbt.net:27017/?replicatSet=Cluster0-shard-0" --ssl --authenticationDatabase admin -username root --password rootMongoDB Server:
- 1️⃣ Windows Service is named
MongoDB - 2️⃣ daemon is named
Mongod
MongoDB Server Version
mongod --version
<# Output example
db version v6.0.6
Build Info: {
"version": "6.0.6",
"gitVersion": "26b4851a412cc8b9b4a18cdb6cd0f9f642e06aa7",
"modules": [],
"allocator": "tcmalloc",
"environment": {
"distmod": "windows",
"distarch": "x86_64",
"target_arch": "x86_64"
}
}
#>Or
mongosh
db.version()
// 6.0.6Verify which JavaScript engine is used in you MongoDB Server
mongosh
db.serverBuildInfo()
/*
{
version: '6.0.6',
gitVersion: '26b4851a412cc8b9b4a18cdb6cd0f9f642e06aa7',
targetMinOS: 'Windows 7/Windows Server 2008 R2',
modules: [],
allocator: 'tcmalloc',
javascriptEngine: 'mozjs', //modernized JavaScript
sysInfo: 'deprecated',
versionArray: [ 6, 0, 6, 0 ],
openssl: { running: 'Windows SChannel' },
buildEnvironment: {
distmod: 'windows',
distarch: 'x86_64',
cc: 'cl: Microsoft (R) C/C++ Optimizing Compiler Version 19.31.31107 for x64',
ccflags: '/nologo /WX /FImongo/platform/basic.h /fp:strict /EHsc /W3 /wd4068 /wd4244 /wd4267 /wd4290 /wd4351 /wd4355 /wd4373
/wd4800 /wd4251 /wd4291 /we4013 /we4099 /we4930 /errorReport:none /MD /O2 /Oy- /bigobj /utf-8 /permissive- /Zc:__cplusplus /Zc:sizedDealloc /volatile:iso /diagnostics:caret /std:c++17 /Gw /Gy /Zc:inline',
cxx: 'cl: Microsoft (R) C/C++ Optimizing Compiler Version 19.31.31107 for x64',
cxxflags: '/TP',
linkflags: '/nologo /DEBUG /INCREMENTAL:NO /LARGEADDRESSAWARE /OPT:REF',
target_arch: 'x86_64',
target_os: 'windows',
cppdefines: 'SAFEINT_USE_INTRINSICS 0 PCRE_STATIC NDEBUG BOOST_ALL_NO_LIB _UNICODE UNICODE _SILENCE_CXX17_ALLOCATOR_VOID_DEPRECATION_WARNING _SILENCE_CXX17_OLD_ALLOCATOR_MEMBERS_DEPRECATION_WARNING _SILENCE_CXX17_CODECVT_HEADER_DEPRECATION_WARNING _SILENCE_ALL_CXX20_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS _CONSOLE _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS _ENABLE_EXTENDED_ALIGNED_STORAGE _SCL_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS _WIN32_WINNT 0x0A00 BOOST_USE_WINAPI_VERSION 0x0A00 NTDDI_VERSION 0x0A000000 BOOST_THREAD_VERSION 5 BOOST_THREAD_USES_DATETIME BOOST_SYSTEM_NO_DEPRECATED BOOST_MATH_NO_LONG_DOUBLE_MATH_FUNCTIONS BOOST_ENABLE_ASSERT_DEBUG_HANDLER BOOST_LOG_NO_SHORTHAND_NAMES BOOST_LOG_USE_NATIVE_SYSLOG BOOST_LOG_WITHOUT_THREAD_ATTR ABSL_FORCE_ALIGNED_ACCESS'
},
bits: 64,
debug: false,
maxBsonObjectSize: 16777216,
storageEngines: [ 'devnull', 'ephemeralForTest', 'wiredTiger' ],
ok: 1
}
*/MongoDB Shell:
- 1️⃣ is based on JavaScript
- 2️⃣ uses SpiderMonkey JavaScript engine starting from v3.2
- 3️⃣ supports ECMAScript 6 (ES6) starting from v3.2
- 4️⃣ supports mongo shell and server-side JavaScript
- 5️⃣ uses
mongoshin Windows OS andmongoin Linux and Mac OS to start his console
MongoDB Shell Version
mongosh --version
// 1.10.1Or
mongosh
version()
// 1.10.1Show available commands
help
/*
`use` : Set current database
`show` :
- 'show databases'/'show dbs': Print a list of all available databases.
- 'show collections'/'show tables': Print a list of all collections for current database.
- 'show profile': Prints system.profile information.
- 'show users': Print a list of all users for current database.
- 'show roles': Print a list of all roles for current database.
- 'show log <type>': log for current connection, if type is not set uses 'global' 'show logs': Print all logs.
`exit` Quit the MongoDB shell with exit/exit()/.exit
`quit` Quit the MongoDB shell with quit/quit()
`Mongo` Create a new connection and return the Mongo object. Usage: new Mongo(URI, options [optional])
`connect` Create a new connection and return the Database object. Usage: connect(URI, username [optional], password [optional])
it result of the last line evaluated; use to further iterate
`version` Shell version
`load` Loads and runs a JavaScript file into the current shell environment
`enableTelemetry` Enables collection of anonymous usage data to improve the mongosh CLI
`disableTelemetry` Disables collection of anonymous usage data to improve the mongosh CLI
`passwordPrompt` Prompts the user for a password
`sleep` Sleep for the specified number of milliseconds
`print` Prints the contents of an object to the output
`printjson` Alias for print()
`convertShardKeyToHashed` Returns the hashed value for the input using the same hashing function as a hashed index.
`cls` Clears the screen like console.clear()
`isInteractive` Returns whether the shell will enter or has entered interactive mode
*/mongosh
typeof db
// objectShow all methods of the db object
mongosh
db. // press tab twice to show all methods of the db object
db.c // press tab twice to show all commands having the prefix cShow a function declaration
mongosh
db.version
/*
[Function: version] AsyncFunction {
apiVersions: [ 0, 0 ],
returnsPromise: true,
serverVersions: [ '0.0.0', '999.999.999' ],
topologies: [ 'ReplSet', 'Sharded', 'LoadBalanced', 'Standalone' ],
returnType: { type: 'unknown', attributes: {} },
deprecated: false,
platforms: [ 'Compass', 'Browser', 'CLI' ],
isDirectShellCommand: false,
acceptsRawInput: false,
shellCommandCompleter: undefined,
help: [Function (anonymous)] Help
}
*/Call a function
mongosh
db.version()
// 6.0.6| Number ID | Type | Syntax | String ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Double | 0.0 | "dbouble" |
| 2 | String | "" | "string" |
| 3 | Object | {} | "object" |
| 4 | Array | [] | "" |
| 7 | ObjectId | ObjectId() | "objectId" |
| 8 | Boolean | true/false | "boolean" |
| 9 | Date | ISODate() | "date" |
| 16 | 32-bit Integer | NumberInt() | "int" |
| 18 | 64-bit Integer | NumberLong() | "long" |
📝 Memo:
- 1️⃣If type of Number is not specified, it will be stored as Double BSON value, because MongoDB uses JavaScript engine which doesn't distinguish between integer and decimal numbers.
- 2️⃣
$typeis an operator in MongoDB to query documents by BSON type. - 3️⃣
_id:- makes each document unique across the database.
- is a mandatory document field
- can be assigned manually
- will be created automatically if not assigned manually (recommended)
- 4️⃣
ObjectId("65a6a8da4bd4f647147298dd"):- is a special BSON type used to assigne unique value to the
_id fieldof a document. - is 12 Bytes long divided in 4 parts:
- 1️⃣ 4 Bytes representing the document creation date in seconds since Unix epoch "65 a6 a8 da"
- 2️⃣ 3 Bytes representing the machine ID (MD5 hash of the hostname and MAC address) "4b d4 f6"
- 2️⃣ 2 Bytes representing the process ID "47 14"
- 2️⃣ 3 Bytes representing a counter (starts from random number) incremented for each new document inserted "72 98 dd"
- is a special BSON type used to assigne unique value to the
- 5️⃣ Dates in MongoDB server:
- are stored in ISO format
- new Date() and ISODate() generates the current timestamp in ISO format.
- Be carefull when converting date, because the month number start with 0 (January) for example. The output date could converted to the corresponding time zone date, or to UTC datetime.
Illustration
mongosh
var obj = {a: "", b: {}, c: [], d: true};
print(obj);
// { a: '', b: {}, c: [], d: true }
typeof obj.a;
typeof obj.b;
typeof obj.c;
obj.c instanceof Array;
typeof obj.d;
/*
string
object
object
true
boolean
test>
*/Generate an objecid
mongosh
ObjectId()
// ObjectId("65a6a8da4bd4f647147298dd")mongosh
new Date()
#Output: ISODate("2024-01-16T16:12:52.384Z")
ISODate()
// ISODate("2024-01-16T16:12:59.916Z")
Date()
// Tue Jan 16 2024 17:17:50 GMT+0100 (Central European Standard Time)In this section:
cnwill stand forCollectionNameowill stand forObjectaoowill stand forArrayOfObjectsqwill stand forquerysofwill stand forSetOfFields
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| db | Show the active Database |
| show dbs | Show all Databases |
| use DatabaseName | Change the active database |
| show collections | Show all Collections inside the active database |
📝 Memo:
- 1️⃣ There is no command to create new Database. Database will be created together with first collection.
- 2️⃣ The command
db.dropDatabase()drops the active database. - 3️⃣ As soon as you drop the last collection of an active database, the active database will be dropped as well automatically.
| Create | Read | Update | Delete |
|---|---|---|---|
| db.createUser() | db.getUsers(), db.getUser() | db.updateUser(), db.changeUserPassword() | db.dropAllUsers(), db.dropUser() |
| db.createRole() | db.getRoles(), db.getRole() | db.updateRole() | db.dropAllRoles(), db.dropAllRole() |
db.createCollection("cn"), db.createEncryptedCollection() |
db.getCollection("cn"), db.getCollectionInfos(), db.getCollectionNames(), db.printCollectionStats() |
db.getCollection("cn").drop() |
|
| db.createView() | |||
db.dropDatabase() |
| Grant | Revoke | Manage |
|---|---|---|
| db.grantRolesToRole() | db.revokeRolesFromRole() | db.version(), db.getMongo(), db.serverBuildInfo() |
| db.grantRolesToUser() | db.revokeRolesFromUser() | db.setLogLevel(), db.rotateCertificates(), db.listCommands() |
| db.grantPrivilegesToRole() | db.isMaster(), db.logout(), db.shutdownServer() |
Create a collection in the active database
mongosh mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017
use MockDatabase
MockDatabase> db.createCollection("MockUsers")
MockDatabase> show collections
// MockUsersPractice
//Connect to mongodb shell
mongosh mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017
// Create a db called demoDB
db
show dbs
use demoDB
db
show dbs
// Create 2 collections myCollection1 and myCollection2
db.createCollection("myCollection1")
db.createCollection("myCollection2")
show collections
show dbs
// Delete both collections. Delete also demoDB
db.getCollection("myCollection1").drop()
db.getCollection("myCollection2").drop()
show collections
db
show dbs
// Delete both collections. Delete also demoDB: This command drop all collections of the active database
db.dropDatabase()
show collections
db
show dbsCreate
db.createCollection("cn")Read
db.getCollection("cn").find(<o> or <aoo>)
db.getCollection("Collection1").findOne(<o>)Update
db.getCollection("cn").insertOne(<o>)
db.getCollection("cn").findOneAndUpdate(<o>)
b.getCollection("cn").findOneAndReplace(<o>)
db.getCollection("cn").insertMany(<aoo>)Delete
db.getCollection("cn").deleteOne(<o>)
db.getCollection("cn").findOneAndDelete(<o>)
db.getCollection("cn").deleteMany(<aoo>)
db.getCollection("cn").drop()Insert one or many documents
db.getCollection("cn").insert(<o> or <aoo>)
{
return WriteResult() or BulkWriteResult() Object # Information about how many documents were inserted
}
db.getCollection("cn").insertOne(<o>)
{
return _id # ID of the inserted Object
}
db.getCollection("cn").insertMany(<aoo>)
{
return [_ids] # Array IDs of inserted Objects
}Practice
mongosh mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017
use MyDB
db.createCollection("Collection1")
db.createCollection("Collection2")
show collections
db.getCollection("Collection1").insert({})
<# Output example
DeprecationWarning: Collection.insert() is deprecated. Use insertOne, insertMany, or bulkWrite.
{
acknowledged: true,
insertedIds: { '0': ObjectId("65b10cd806997e845fb8dded") }
}
#>
db.getCollection("Collection1").insertOne({})
# Retrieve all documents contained in Collection1
db.getCollection("Collection1").find({}) # or db.getCollection("Collection1").find()
<# Output example
[
{ _id: ObjectId("65b10cd806997e845fb8dded") },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b10d3206997e845fb8ddee") }
]
#>
db.getCollection("Collection1").insertMany([{}, {}, {}])
<#
{
acknowledged: true,
insertedIds: {
'0': ObjectId("65b1158c06997e845fb8ddf0"),
'1': ObjectId("65b1158c06997e845fb8ddf1"),
'2': ObjectId("65b1158c06997e845fb8ddf2")
}
}
#>
# Retrieve all documents contained in Collection1
db.getCollection("Collection1").remove({}) # db.getCollection("Collection1").remove()
<#
DeprecationWarning: Collection.remove() is deprecated. Use deleteOne, deleteMany, findOneAndDelete, or bulkWrite.
{ acknowledged: true, deletedCount: 6 }
#>
db.getCollection("Collection1").insertOne
(
{
"string": "Thats a sample string"
,"boolean": true
}
)
db.getCollection("Collection1").insertOne
(
{
"String": "That’s a sample string",
"Boolean": true,
"Number": 10,
"NumberInt": NumberInt(100),
"NumberLong": NumberLong(18347035035835),
"Date": new Date(),
"ISODate": ISODate(),
"Array": [1, 2, 3],
"Object":
{
"Key1": 1,
"Key3": false
}
}
)
db.getCollection("Collection1").findOne({})
db.getCollection("Collection1").findOne({"Boolean": true})📝 Memo
- A comma as record prefix works in MongoDB Compass mongosh BUT it fails in PowerShell mongosh (Shell Mode)
- A comma as record suffix works in MongoDB Compass mongosh AND in PowerShell mongosh (Stric Mode)
- A document id must be unique accross all documents in the same collection.
Warning: NumberLong: specifying a number as argument is deprecated and may lead to loss of precision, pass a string instead.
Challenge
mongosh mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017
use MyDB
db.getCollection("Collection2").insertOne
(
{
"name": "Mike",
"sports":
[
"Tennis",
"Football",
"Bowling"
],
"medalQuantity": NumberInt(35),
"info":
{
"champion": true,
"team":
{
"title": "Black Hawks",
"stats":
{
"winsToLooseRate": 0.65,
"wins": NumberInt(135)
}
}
},
"documentUpdatedAt": ISODate()
}
);
db.getCollection("Collection2").findOne({})Find one or many documents
db.getCollection("cn").find(<q> or <sof>)
{
return Cursor() Object # to iterate over to get documents in Extended JSON format
}
db.getCollection("cn").findOne(<q> or <sof>)
{
return Document() Object # in Extended JSON format
}📝 Memo
- A
cursorobject is a pointer to the start of an iterable object before its first child element. - It allows you to performe some actions on subsets of an iterable object by iterating over it. - It become exhausted when it reaches the end of the iterable object.
- The iteration can happen one by one or subset by subset until there is no more elements in the object.
- A
cursor in MongoDBworks as follows:- A MongoDB client (MongoDB Compass or Mongo Shell for example) call the find() function to retrieve documents stored in a MongoDB server.
- MongoDB server will filter the set documents corresponding to the search creteria. It will return a cursor pointing to the beginning of the set of documents instead of returning the set of documents directly.
- Subsets of documents (so called
batchs) according to thebatch sizedefined on the client, will be returned until the set is emptied.
Practice:
- Create a collection named Cursor and add 100 documents inside
- document key: index
- document value: 1 to 100
mongosh mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017
use MyDB
db.createCollection("Cursor");
var docsCount = 0;
docsCount = db.getCollection("Cursor").find({}).count();
print("# Documents: " + docsCount);
var docs = [];
for (let i = 101; i <= 300; i++)
{
obj =
{
index: NumberInt(i)
}
docs.push(obj);
}
db.getCollection("Cursor").insertMany(docs);
docsCount = db.getCollection("Cursor").find({}).count();
print("# Documents: " + docsCount);Experiment The Cursor iteration in mongosh
mongosh mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017
use MyDB
//Iterator size = 20
db.getCollection("Cursor").find({});
/*
[
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cc4"), index: 1 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cc5"), index: 2 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cc6"), index: 3 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cc7"), index: 4 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cc8"), index: 5 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cc9"), index: 6 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cca"), index: 7 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ccb"), index: 8 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ccc"), index: 9 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ccd"), index: 10 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cce"), index: 11 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ccf"), index: 12 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cd0"), index: 13 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cd1"), index: 14 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cd2"), index: 15 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cd3"), index: 16 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cd4"), index: 17 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cd5"), index: 18 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cd6"), index: 19 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cd7"), index: 20 }
]
Type "it" for more
MyDB> it
[
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cd8"), index: 21 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cd9"), index: 22 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cda"), index: 23 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cdb"), index: 24 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cdc"), index: 25 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cdd"), index: 26 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cde"), index: 27 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cdf"), index: 28 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ce0"), index: 29 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ce1"), index: 30 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ce2"), index: 31 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ce3"), index: 32 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ce4"), index: 33 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ce5"), index: 34 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ce6"), index: 35 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ce7"), index: 36 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ce8"), index: 37 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ce9"), index: 38 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22cea"), index: 39 },
{ _id: ObjectId("65b264b5390fdbde5df22ceb"), index: 40 }
]
Type "it" for more
...
MyDB> it
no cursor
*/
//And so on, until the end of the result set is reached.📝 Memo
- The
batch sizeis the number of documents the mongodb server can send to the mongodb client in one shift. - The
iterator size, also called display batch size, is the number of documents from a batch on the client side we can get after each iteration. - The maximum batch size is
16 MB. - The default iterator size is
20 documents.
Assign the automatic cursor iteration by assigning it to a variable
mongosh mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017
use MyDB
//Store the cursor in myCursor
var myCursor = db.getCollection("Cursor").find({});
//Start cursor iteration manually to the number of documents corresponding to the iteration size defined
myCursor;
//Display the next element one at a time if it exist.
if(myCursor.hasNext())
{
myCursor.next(3);
}
//Iterate the cursor and access documents
myCursor.forEach(printjson);
//Store the cursor in myCursor
var myCursor = db.getCollection("Cursor").find({index: {$lte: 10}});
if (myCursor.hasNext()){
var documentArray = myCursor.toArray();
print("if");
} else {//If the cursor is exhausted let it point again at the beginning of the search result set
//Store the cursor in myCursor
var myCursor = db.getCollection("Cursor").find({index: {$lte: 10}});
// The toArray() method loads into RAM all documents returned by the cursor; the toArray() method exhausts the cursor.
var documentArray = myCursor.toArray();
print("else");
}
documentArray;Cursor Helper Methods
//Assign Cursor to a varaiable
var cursor = db.getCollection("cn").find();
//Iterate one document
cursor.next();
//Check if cursor has next document
cursor.hasNext();
//Quantity of documents left in current batch
cursor.objsLeftInBatch();
//Iterate all documents in ther cursor and push them to he array
cursor.toArray()
//Iterate all documents in the cursor and perform operation with each of them
cursor.forEach(\<function\>)
//Example
var cursor = db.getCollection("Cursor").find({index: {$lte: 15}});
cursor.forEach(printjson)
cursor.forEach(doc => print(`Index of the doc is ${doc.index}`));
//cursor.forEach(doc => print(`${doc}`)); print [objec object]
//cursor.forEach(doc => print("Index of the doc is ${doc.index}")); print static text
// Count number of documents in the cursor
cursor.count()
// Limit the number of documents in the cursor
cursor.limit(\<number\>)
// Skip certain number of documents in the cursor
cursor.skip(\<number\>)
// Sort documents in the cursor. 1 ascending order (default). -1 descending order.
cursor.sort({\<fieldName1\>: 1, \<fieldName2\>: -1, ...})
// The execution precedence is sort documents on the cursor, skip certain documents and limit the number of documents.
cursor.limit().skip().sort();
cursor.limit().skip().sort().count();
// Returns One Document in Extended JSON format
db.getCollection("Cursor").findOne(\<query\>, \<fields\>;)📝 Memo:
- Indepedently in which order they are chained, the precedence when called together is sort, skip and limit.
- limit, skip and sort don't impact the result of the count method. It allways returns the total number of documents in the cursor.
Challenge 1
var cursor = db.getCollection("Cursor").find({index: {$lte: 100}});
cursor.sort({index: -1}).skip(27).limit(4);Challenge 2
var cursor = db.getCollection("Cursor").find({index: {$lte: 100}});
var newCursor = cursor.sort({index: 1}).skip(65).limit(8);
newCursor.forEach(doc => print(`Document with _id ObjectId("${doc._id}") has index ${doc.index}`));How to display a method implementation
First install Robot3T
winget search --name robo3t
winget install --id 3TSoftwareLabs.Robo3T --exact --source winget --silentAppend the path to Robot3T executable to the user environment variable
$UserEnvVar = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path', 'User');
$NewPath = "C:\Program Files\Robo 3T 1.4.4";
$ExtendedUserEnvVar = $UserEnvVar+";"+$NewPath
# Apply the change
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('Path', $ExtendedUserEnvVar, 'User');
# Double check
[Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path', 'User');Launch Robo3T application
robo3t.exeThen experiment in Robt3T
var oneDocument = db.getCollection("Cursor").findOne();
oneDocument.Retrieve and modify the iterator size
mongosh mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017
DBQuery.shellBatchSize = 30
/*DeprecationWarning: DBQuery.shellBatchSize is deprecated, please use config.set("displayBatchSize") instead
30
*/
//display the current batch size
config.get("displayBatchSize");
//20
//modify the current batch size
config.set("displayBatchSize") = 10;
//set the batch size to his default value
config.get("displayBatchSize");Examine what happens behind the scene between mongodb server and client
Install the application wireshark by starting PowerShell with administrator priviledges
# Display which wireshark pakages are available
winget search --name wireshark
# Install the current version of wireshark
winget install --id WiresharkFoundation.Wireshark --exact --source winget --silent
# By successfull installation append the path to wireshark executable to the user envinronment variables Path attribute
#-----------------USER PROFILE ENVIRONMENT VARIABLE PATH---------------------
# Backup the current user and system environment variable PATH
$BackupUserEnvVarPath = "$env:USERPROFILE\BackupUserEnvVarPath.csv"
if(!(Test-Path $BackupUserEnvVarPath))
{
New-Item $BackupUserEnvVarPath
}
$UserEnvPath = [Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path', 'User')
Set-Content -Path $BackupUserEnvVarPath -Value $UserEnvPath
#Get-Content $BackupUserEnvVarPath
# Append the new path the user environment variable
$UserEnvPath = $UserEnvPath+";"+"C:\Program Files\Wireshark"
[Environment]::SetEnvironmentVariable('Path', $UserEnvPath, 'User')
# Verify
[Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path', 'User')
#-----------------SYSTEM ENVIRONMENT VARIABLE PATH---------------------
$BackupSystemEnvVarPath = "$env:USERPROFILE\BackupSystemEnvVarPath.csv"
if(!(Test-Path $BackupSystemEnvVarPath))
{
New-Item $BackupSystemEnvVarPath
}
Set-Content -Path $BackupSystemEnvVarPath -Value ([Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path', 'Machine'))
#Get-Content $BackupSystemEnvVarPath
[Environment]::GetEnvironmentVariable('Path', 'Machine')
# Start the wireshark application
wireshark.exe &If capture won't work with this error message
Local interfaces are unavailable because no packet capture driver is installed.
You can fix this by installing Npcap.
Install Npcap. It is the Nmap Project's packet capture (and sending) library for Microsoft Windows.
winget search --name npcap
winget install --id Insecure.Npcap --exact --source winget --silent
Retrieve the TCP connections of MongoDB server on port 27017
<#
The Get-NetTCPConnection cmdlet gets current TCP connections. Use this cmdlet to view TCP connection properties such as local or remote IP address, local or remote port, and connection state.
#>
Get-NetTCPConnection -LocalPort 27017
<#
LocalAddress LocalPort RemoteAddress RemotePo
rt
------------ --------- ------------- --------
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 58017
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 58014
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 58013
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 58027
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 58015
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 57390
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 58016
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 58018
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 58019
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 58028
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 56868
127.0.0.1 27017 127.0.0.1 56856
0.0.0.0 27017 0.0.0.0 0
#>Retrieve all connected IPv4 Network interfaces
<#
The Get-NetIPInterface cmdlet gets an IP interface, including IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, and the associated address configuration for the IP interfaces. Without parameters, this cmdlet gets all of the IP interface properties on the computer, including virtual interfaces and loopback interfaces.
#>
# Retrieve all connected IPv4 Network interfaces
Get-NetIPInterface -AddressFamily IPv4 -ConnectionState connected
<#
ifIndex InterfaceAlias AddressFamily NlMtu(Bytes) InterfaceMetric Dhcp ConnectionState PolicyStore
------- -------------- ------------- ------------ --------------- ---- --------------- -----------
46 Npcap Loopback Adapter IPv4 1500 25 Enabled Connected ActiveStore
17 Ethernet 2 IPv4 1500 25 Disabled Connected ActiveStore
1 Loopback Pseudo-Interface 1 IPv4 4294967295 75 Disabled Connected ActiveStore
15 WLAN IPv4 1500 35 Enabled Connected ActiveStore
#>Retrieve which network interface localhost is running on
<#
The Get-NetIPAddress cmdlet gets the IP address configuration, such as IPv4 addresses, IPv6 addresses and the IP interfaces with which addresses are associated. Without parameters, this cmdlet gets the entire IP address configuration for the computer
#>
# Retrieve which network interface localhost is running on
Get-NetIPAddress -AddressFamily IPv4 -IPAddress "127.0.0.1"
<#
IPAddress : 127.0.0.1
InterfaceIndex : 1
InterfaceAlias : Loopback Pseudo-Interface 1
AddressFamily : IPv4
Type : Unicast
PrefixLength : 8
PrefixOrigin : WellKnown
SuffixOrigin : WellKnown
AddressState : Preferred
ValidLifetime : Infinite ([TimeSpan]::MaxValue)
PreferredLifetime : Infinite ([TimeSpan]::MaxValue)
SkipAsSource : False
PolicyStore : ActiveStore
#>Run the wireshark application
wireshark.exe &In the search field write this (the ip address of the MongoDB server session)
ip.addr == 127.0.0.1
Open Capture / Options
Choose the Capture interface
Npcap Loopback Adapther
Capture filter for selected interfaces
src port 27017
Click start capture
Retrieve all documents by setting the server batch size to 30.
db.getCollection("Cursor").find().batchSize(30)📝 Memo
- The
batch sizeis the maximal number of documents that can be sent from the MongoDB server to the client in a one response. - Number of requests = Number of documents matching the find filter / batchSize
- So doesn't set the batch size too small.
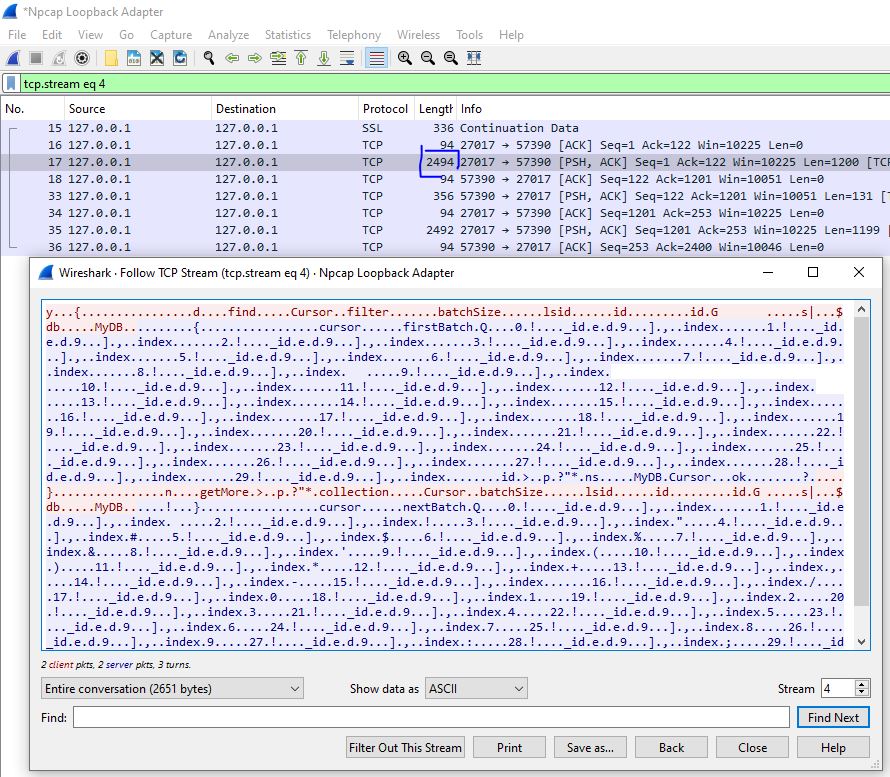
Right click on the stream with the biggest length, Follow / TCP Stream. You can observe on the following picture that the MongoDB send 30 documents to the MongoDB client at a time:
You can generate random json objects to query in this website: JSON GENERATOR.
Query data set:
- Path: ".\UdemyTutoDocs\persons.json"
- Number of objects: 1000
Obect property data types:
- _id: ObjectId
- index: Int32
- name: String
- isActive: Boolean
- registered: Date
- age: Int32
- gender: String
- eyeColor: String
- favouriteFruit: String
- comapany: Object
- title: String
- email: String
- phone: String
- location: Object
- country: String
- address: String
- tags: Array
// Match by field name and it's exact value
{
\<fieldName1\> : \<value1\> ,
\<fieldName2\> : \<value2\>,
...
}
// Match by field name and operators
{
\<fieldName1\>: {\<operator1\> : \<value1\>, \<operator2\> : \<value2\>, ...},
\<fieldName3\> : \<value3\>,
...
}
//Comparison Operators
$eq, $ne
$gt, $lt, $gte, $lte
// In operator
$in, $nin // require an array as a value
{
$in: [
{\<value1\>}
,{\<value2\>}
,...
]
}
// And operator used to combine multiple conditions that must match all.
{
$and: [
{\<condition1\>}
,{\<condition2\>}
,...
]
} // require an array as a value
// Or operator used to combine multiple conditions that can match.
{
$or: [
{\<condition1\>}
,{\<condition2\>}
,...
]
} // require an array as a value📝 Memo:
- The double quotes around field names are optional.
- You can use comparison operator with numbers, strings and date.
- The
,between key-value pairs in a query meansimplicit ANDoperator. - The
explicit ANDoperator$andmust be used if conditions contain same field or operator. Else upcoming conditions could override forme ones. - It is recommended to use
$ininstead of$orif conditions contain same fields. It is shorter and clearer. - Use the dot notation to query fields of nested documents, because the
.is used in JavaScript to access the properties of an object. - Fields accessed with dot notaion
.must be inside quotation marks. - Regex require more memory, because it doesn't use indexes. So use it only when necessary.
Connect to the database MyDB
mongosh mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017
use MyDBvar persons20YearsOld = db.getCollection("persons").find({age: 20});
// var persons20YearsOld = db.persons.find({age: {$eq: 20}}); //equivalent query
persons20YearsOld.count(); //46 persons
var personsFemaleWithGreenEyes = db.getCollection("persons")
.find({gender: "female", eyeColor: "green"});
personsFemaleWithGreenEyes.count(); //179 persons
var personsOlderThan20YearsOld = db.getCollection("persons").find({age: {$gt: 20}}).count(); //954 persons
var personsWithNotGreenEyeColor = db.getCollection("persons").find({eyeColor: {$ne: "green"}}).count(); //670 persons
var personsBetween25And30YearsOld = db.getCollection("persons").find({age: {$gte: 25, $lte: 30}}).count(); //269 persons
// Persons with name starting with at least n in alphabetical order = 284
db.getCollection("persons").find({name: {$gte: "N"}}).count();
// Persons with name starting with at least n in alphabetical order and sorted by name
db.getCollection("persons").find({name: {$gte: "N"}}).sort({"name": 1});
//Number of persons older than 27 and younger than 35. By assuming that person with age 27 are older than 27. = 353
db.getCollection("persons").find({age: {$gte: 27, $lt: 35}}).count();
//Persons older than 35 and having favorite fruit that is not banana = 191
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
age: {$gte: 35}
,favoriteFruit: {$ne: "banana"}
}
).count();
//Persons that are 21 or 22 years old = 116
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
age: {$in: [21, 22]}
}
).count();
//Persons that are not 21 and 22 years old = 884
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
age: {$nin: [21, 22]}
}
).count();
/*
Persons with green or brown eyeColor and with strawberry as favoriteFruit
*/
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
eyeColor: {$in: ["green", "brown"]}
,favoriteFruit: "strawberry"
}
).limit(11);
// Exclude all persons that 25 years old, then retrieve all persons older than 20 years old. = 950
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
$and: [
{age: {$ne: 25}}
,{age: {$gte: 20}}
]
}
).count();
// Exclude all persons that 25 years old, then override that result set with persons older than 20 years old. = 1000
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
age: {$ne: 25}
,age: {$gte: 20}
}
).count();
// Persons that 25 years old. = 50
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
age: {$eq: 25}
}
).count();
//Persons that are either active or have eyeColor blue = 677
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
$or: [
{isActive: true}
,{eyeColor: "blue"}
]
}
).count();
//Persons that have eyeColor either green or blue = 663
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
$or: [
{eyeColor: "green"}
,{eyeColor: "blue"}
]
}
).count();
//Persons that have eyeColor either green or blue = 663
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
eyeColor:
{
$in: [
"green"
,"blue"
]
}
}
).count();
/*
Persons younger than 24 or like bananas or color of eyes is either green or blue. = 738
*/
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
$or:
[
{age: {$lt: 24}}
,{favoriteFruit: "bananas"}
,{eyeColor: {$in: ["green", "blue"]}}
]
}
).count();
/*
Persons who are (older than 33 AND not 37 years old) OR live in Italy. Parentheses indicate precedence of the operations.
Expected = 460
Obtained = 460
*/
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
$or: [
{$and:
[
{age: {$gt: 33}}
,{age: {$ne: 37}}
]
}
,{"company.location.country": "Italy"}
]
}
).count();Query Syntaxes
//Array contains certain value
{\<fieldName\>: \<value\>}
//Specific element in array has certain value
{"\<fieldName\>.\<index\>": \<value\>}
//Array contains all specified values independent of order
{\<fieldName>: {"$all": [\<value1\> , \<value2\>, ...]}}
//Array is of certain size, have a certain number of elements
{\<fieldName\>: {"$size": \<number\>}}
//At least one nested document in the Array must match ALL conditions. Order of conditions doesn't matter.
{\<arrayField\> : {$elemMatch: {\<condition1\>, \<condition2\>, ...}}}Query Examples
/*
Find all persons with second tag "ad" and where tags array consists of exactly 3 tags
Expected: 2
Obtained: 2
*/
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
$and:
[
{"tags.1": "ad"}
,{tags: {"$size": 3}}
]
}
).count();
db.getCollection("first").find(
{
friends: {$elemMatch: {age: 23, name: "Lora"}}
}
)Query Syntax
// Check if a field exists inside a document
{fieldName: {$exists: true/false}}
// Check if a field inside a document has a given type. It helpful to update the type of certains fields existing in the document.
{fieldName: {$type: TypeName}}
{fieldName: {$type: TypeID}}
// Filter a document fields to retrieve just a subset of it. This technique is also called projection because you project a large document to obtain a small one.
{\<query>}
,{
fieldName1: 1 //Send to the client
,fieldName2: 0 //Filter out, or omit
}Practice
/*
Find all persons with blue eyes. Return only certain fields: name, age, gender, eyeColor and company
Expected: 333
Obtained: 333
*/
db.getCollection("persons").find(
{
eyeColor: "blue"
},
{
name: 1
,age: 1
,gender: 1
,eyeColor: 1
,company: 1
}
).count();Syntax
//Filter using Regular Expression
{\<fieldName\>: {$regex: /pattern/\<options\>}}
{\<fieldName\>: {$regex: "pattern"\<options\>}} //You can also use quotes instead of backslash
{\<fieldName\>: {$regex: /pattern/, $options: "\<options\>"}}
//Options
i: Case insensitive to match upper and lower case.
m: For patterns that include anchors (i.e. ^ for the start, $ for the end). If the pattern contains no anchors or if the string value has no newline characters (e.g. \\n), the m option has no effect.
x: "Extended" capability to ignore all white space characters in the $regex pattern unless escaped or included in a character class.
s: Methods
- update()
- updateOne()
- updateMany()
- replaceOne()
Operators
- $set
- $unset (alias $project)
- $rename
- $inc
- $mul
- $currentDate
- $pop
- $addToSet
Create the collection ShoppingCard and fill it with documents
use MyDB
db.ShoppingCart.insertMany(
[
{index: NumberInt(1)}
,{index: NumberInt(2)}
,{index: NumberInt(3)}
,{index: NumberInt(4)}
,{index: NumberInt(5)}
]
);Syntax
//the parameters query and update are mandatory.
db.\<collection\>.method(
\<query\>
,\<update\>
,\<options\>
);
/* Update the first matching document by default
upsert: true (update + insert) --> equivalent to updateOne()
- Creates a new document if no documents match the query.
- Updates a single document that matches the query.
multi: true --> equivalent to updateMulti()
- updates multiple documents that meet the query criteria
*/
db.\<collection\>.update(
\<query\>
,\<update\>
,\<options\>
);
/*
Possible outputs
//One document found and successfully updated
WriteResult(
{
"nMatched": 1,
"nUpserted": 0,
"nModified": 1
}
)
//One document found and but not updated because existing and new value match. No update required.
WriteResult(
{
"nMatched": 1,
"nUpserted": 0,
"nModified": 0
}
)
//No matching document.
WriteResult(
{
"nMatched": 0,
"nUpserted": 0,
"nModified": 0
}
)
*/
//Replace or set value of document fields
{
$set:
{
\<fieldName1\>: \<value1\>
,\<fieldName2\>: \<value2\>
,...
}
}
// Remove certain fields from documents. When you have added them by mistake for example
{
$unset:
{
\<fieldName1\>: \<anyValue\>
,...
}
}
// Replace the content one document by the content of another. Memo: `_id` remains unchanged
db.\<collection\>.replaceOne(
\<query\>
,\<replacement\>
,\<options\>
)Examples
//Update the shopping cart number 2 by adding a cartId and a customer object having a name, email and age
db.getCollection("ShoppingCart").updateOne(
// query object
{index: 2}
// update object
,{$set:
{
cartId: NumberInt(325)
,customer:
{
name: "Mike Foster"
,email: "mforster@test.com"
,age: NumberInt(27)
}
,cart: []
}
}
// options objects
);
//Update the shopping cart number 1 by adding a cartId and a customer object having a name, email and age
db.getCollection("ShoppingCart").updateOne(
// query object
{index: 1}
// update object
,{$set:
{
cartId: NumberInt(325)
,customer:
{
name: "Mike Foster"
,email: "mforster@test.com"
,age: NumberInt(27)
}
,cart: []
}
}
// options objects
);
// Remove and modify some fields of the document 1
db.getCollection("ShoppingCart").updateOne(
// query object
{index: 1}
// update object
,{$set:
{
cartId: NumberInt(1)
,cart: ""
}
}
// options objects
);
// Replace the content one document by the content of another. Memo: `_id` remains unchanged
db.ShoppingCart.replaceOne(
// query object
{index: 3}
//replacement object
,{
index: 3
,processed: true
,cart: ["item1", "item2"]
}
);
/*
{
acknowledged: true,
insertedId: null,
matchedCount: 1,
modifiedCount: 1,
upsertedCount: 0
}
*/
db.ShoppingCart.updateOne(
// query object
{index: 4}
//update object
,{
$set:
{
index: 4
,processed: true
,cart: ["item1", "item2"]
}
}
);
/*
{
acknowledged: true,
insertedId: null,
matchedCount: 1,
modifiedCount: 1,
upsertedCount: 0
}
*/
// Combine multiple update operators
db.ShoppingCart.updateOne(
// query object
{index: 5}
//update object
,{
$set:
{
cartId: NumberInt(435)
,"customer.name": "Samanta Larsen"
,"customer.email": "slarsen@test.com"
}
,$unset:
{
newOrder: 1
}
}
);
/*
{
acknowledged: true,
insertedId: null,
matchedCount: 1,
modifiedCount: 1,
upsertedCount: 0
}
*/📝 Memo:
- During the update operation, if a field doesn't exist, nothing happens.
- Renamed fields will be append at the of document fields.
Syntax
// Rename a field
{
$rename:
{
\<fieldName1\>: \<newfieldName1\>,
...
}
}
// Get the current system tiemstamp
//1. Method: Set the value of the field to the current date
{
$currentDate:
{
\<fieldName1\>: true
,...
}
}
//2. Method: Set the value of the field to the current date
{
$set:
{
\<fieldName1\>: ISODate()
// \<fieldName1\>: new Date()
}
}Examples
db.ShoppingCart.find(
{cartId: {$exists: true}}
).count(); //3
// Rename cartId with orderId in all matching documents
db.ShoppingCart.updateMany(
{
// cartId: {$exists: true}
orderId: {$exists: true}
}
,{
$rename:
{
// cartId: "orderId"
orderId: "cartId"
}
}
);
db.ShoppingCart.find(
{orderId: {$exists: true}}
).count(); //3
//Set the createAt field of the document with the cartId 325 to the current field
db.ShoppingCart.find(
{
createAt: {$exists: false}
,cartId: 325
}
).count();
db.ShoppingCart.updateMany(
{
createAt: {$exists: false}
,cartId: 325
}
,{
$set:
{
createAt: ISODate()
// createAt: new Date()
}
}
);
db.ShoppingCart.updateMany(
{
createAt: {$exists: false}
,cartId: 325
}
,{
$currentDate:
{
createAt: true
}
}
);
// add the updateAt to all documents if it doesn't exist and set it to the current timestamp
db.ShoppingCart.updateMany(
{
updateAt: {$exists: false}
}
,{
$set:
{
updateAt: ISODate()
}
}
);📝 Memo:
-
Modifier operatorssuch as $each, $sort perform pre-processing operations. -
$eachis a modifier used inside$pushand$addToSetoperators. -
$
-
$push
-
$pull
-
$pullAll
-
$pop
-
$addToSet
Syntaxes
// Appends element to the array without checking if it exists or not. Create an array if it doesn't exist
{
$push:
{
\<arrayFieldName\>: \<element\>
}
}
// Appends element to the array if it doesn't exist. Create an array if it doesn't exist.
// Saver variant ot $push
{
$addToSet:
{
\<arrayFieldName\>: \<element\>
}
}
// Delete element the first (-1) or last (1) element of an array. As if it was a queue.
// It remains an empty array after deleting the last element.
{
$pop:
{
\<arrayFieldName\>: \<-1 | 1\>
}
}
// Removes all elements in the Array matching specific element or condition
{
$pull:
{
\<arrayFieldName\>: \element | condition\>
}
}
// Removes all elements in the Array matching values mentioned int the list: No use condition possible
{
$pullAll:
{
\<arrayFieldName\>:
[
<\value1\>
,<\value2\>
,...
]
}
}
// Equivalent to
{
$pull:
{
\<arrayFieldName\>:
{
$in:
[
<\value1\>
,<\value2\>
,...
]
}
}
}Examples
//Add one element named item1 to cart array having the cardId 325
db.ShoppingCart.updateOne(
{cartId: 325},
{
$push:
{
cart: "item1"
}
}
);
//Add many elements named item2 and item3 to cart array having the cardId 325
db.ShoppingCart.updateMany(
{cartId: 325},
{
$push:
{
cart:
{
$each:
[
"item2"
,"item3"
]
}
}
}
);
// Experiment the $pull operator
db.ShoppingCart.updateMany(
{cartId: 325},
{
$addToSet:
{
spentAmount:
{
$each:
[
NumberInt(400)
,NumberInt(700)
,NumberInt(200)
,NumberInt(800)
,NumberInt(500)
]
}
}
}
);
// Delete spent amount 200
db.ShoppingCart.updateMany(
{cartId: 325},
{
$pull:
{
spentAmount: 200
}
}
);
// Delete spent amount greater than 400
db.ShoppingCart.updateMany(
{cartId: 325},
{
$pull:
{
spentAmount:
{
$gt: 400
}
}
}
);The dollar sign operator points to certains elements in the array that matched the query. It is mustly used in conjonction with other operators. The dollar sign represents a dynamic index of elements in the array.
Syntax
{
$set: // or $unset
{
\<arrayField.$\>: \<value\>
}
}
{
$set: // or $unset
{
\<arrayField.$.field\>: \<value\>
}
}Examples
db.getCollection('ShoppingCart').updateOne(
// query
{
cartId: 435
},
//update
{
$push: {
cart: {$each: ["item1", "item2", "item3", "item4"]}
}
},
// update options (Optional)
{}
)
//Update the value of the item2 of the cart array
db.getCollection('ShoppingCart').updateOne(
// query
{
cartId: 435, cart: "item2"
},
//update
{
$set: {
"cart.$": "updatedItem2"
}
},
// update options (Optional)
{}
)
db.ShoppingCart.find({cartId: 435})
//Delete the value of the item3 of the cart array
db.getCollection('ShoppingCart').updateOne(
// query
{
cartId: 435, cart: "item3"
},
//update
{
$unset: {
"cart.$": 1
}
},
// update options (Optional)
{}
)
db.ShoppingCart.find({cartId: 435})
//Remove item3 from the cart array
db.getCollection('ShoppingCart').updateOne(
// query
{
cartId: 435
},
//update
{
$pull: {
cart: null
}
},
// update options (Optional)
{}
)
db.ShoppingCart.find({cartId: 435})
db.getCollection('ShoppingCart').updateOne(
// query
{
index: 5
},
//update
{
$set: {
cartId: NumberInt(456)
}
},
// update options (Optional)
{}
)
db.ShoppingCart.updateOne(
{
cartId: 456
},
{
$push:
{
cart:
{
$each:
[
{"title": "TV"},
{"title": "Phone"}
]
}
}
}
)
//Update specific nested document in the array
db.getCollection('ShoppingCart').updateOne(
// query
{
cartId: 456, "cart.title": "updatedTV"
},
//update
{
$set: {
"cart.$.title": "TV"
,"cart.$.price": NumberInt(340)
,"cart.$.quantity": NumberInt(2)
}
},
// update options (Optional)
{}
)
//Update specific nested document in the array
db.getCollection('ShoppingCart').updateOne(
// query
{
cartId: 456, "cart.title": "Phone"
},
//update
{
$set: {
"cart.$.price": NumberInt(150)
,"cart.$.quantity": NumberInt(1)
}
},
// update options (Optional)
{}
)
//Update specific nested document in the array by filtering whit more than one array fields
db.getCollection('ShoppingCart').updateOne(
// query
{
cart: {$elemMatch: {title: "Phone", price: 150}}
},
//update
{
$set: {
"cart.$.quantity": NumberInt(2)
}
},
// update options (Optional)
{}
)The $inc operator
Syntax
It increments value by specified amount
{
{
\<fieldName1\>: \<amount\>,
...
}
}Example
//Increment the quantity by 3
db.getCollection('ShoppingCart').updateOne(
// query
{
cart: {$elemMatch: {title: "Phone", price: 150}}
},
//update
{
$inc: {"cart.$.quantity": NumberInt(3)}
},
// update options (Optional)
{}
)
//Delete the field: quantity: 5
db.getCollection('ShoppingCart').updateOne(
// query
{
cartId: 456
},
//update
{
$unset: {"quantity": NumberInt(5)}
},
// update options (Optional)
{}
)
//Decrement the quantity by 2
db.getCollection('ShoppingCart').updateOne(
// query
{
cart: {$elemMatch: {title: "Phone", price: 150}}
},
//update
{
$inc: {"cart.$.quantity": NumberInt(-2)}
},
// update options (Optional)
{}
)Create a temp collection to experiment delete operations on.
db.TempCollection.insertMany(
[{},{},{},{},{}]
)// remove(): Removes all documents that matches the query
db.\<collection\>.remove(\<query\>)
db.\<collection\>.remove(\<query\>, true) //true tells MongoDB that just one document should be deleted
// deleteOne(): Removes one document that matches query
db.\<collection\>.deleteOne(\<query\>)
// deleteMany(): Remove all documents
db.\<collection\>.deleteMany(\<query\>)CAUTION:
- remove({}): will delete all documents in the collection
- deleteMany({}): will delete all documents in the collection
- remove({}, true): will delete the first document in the collection
- deleteOne({}): will delete the first document in the collection
Examples
db.TempCollection.remove
(
{
'_id': ObjectId('65ef53d63a7ff4e8f03a2ddf')
}
, true
)Syntax
// drop(): deletes collection with all documents and indexes
db.\<collection\>.drop()
//dropDatabase(): delete database with all collections and documents
use \<databaseName\>
db.dropDatabase()The aggregation process looks like a pipe which consists of subset of documents that match certain conditions.
📝 Memo:
- Aggregation request returns cursor from the server.
- db.<collection>.aggregate([]) is equivalent to db.<collection>.find({})
- Aggregation stages are independent.
- an aggregation expression refers to the name of the field in input documents
"$\<fieldName\>". Use the dot notation to reference a nested field. - Match uses standard MongoDB queries and supports all query operators.
- Find with a query is equivalent to aggregate with one stage operator.
- In the $group stage, keeps in mind that the number of field grouped by increase the number of possible combinations in the output set.
- Note that the match stage must be always added before the group stage, because grouping before matching requires more ressources. In this case, group field must look like: "_id.<fieldName>"
- db.<collection>.find().count() is a wrapper of db.<collection>.aggregate([{$count: "total"}]). These 2 methods are the most effective because they are performed on the server side.
- The sort stage is usually put after the match and group stages.
- The project stage is usually after the match stage. It can be used to restructure documents by renaming existing fields and adding new fields.
$limitis usually used in sampled aggregation requests with $limit as first stage; after $sort to produce topN results- In the $group stage, unary operators can be used only in conjunction with accumulators.
- $out writes resulting documents to the MongoDB collection. $out MUST be last stage in the pipeline. If output collection doesn't exist, it will be created automatically.
Load the persons.json collection
use MyDB
db.persons.insertMany(
//paste the content of Persons.json here
)Syntaxes
aggregate() Documents during the aggregation process pass through an array of different sequential stages separated by comma.
db.\<collection\>.aggregate(
[
\<stage1\>
,\<stage2\>
...
,\<stageN\>
]
)Each stage starts from the stage operator
{
$\<stageOperator\> :
{
// key-value quey pairs
}
}$match (01/08): filters document by certain queries. Match specific documents using query.
//Syntax
{
$match:
{
\<query\>
}
}
//Examples
//Match all cities in new york
{
$match:
{
city: "New York"
}
}
//Match all persons that are over 25 years old
{
$match:
{
age: {$gt: 25}
}
}
//Match all woman that are over 25 years old
{
$match:
{
$and:
[
{gender: "female"}
,{age: {$gt: 25}}
]
}
}
//Retrieve active persons
db.persons.aggregate(
[
{
$match:
{
isActive: true
}
}
]
)
//Retrieve all documents which size of the tags array is 3
db.persons.aggregate(
[
{
$match:
{
tags: {$size: 3}
}
}
]
)$group (02/08): groups documents by certain criteria. Groups input documents by certain expressions
//Memo: _id is a mandatory field while others are optionals
//Syntax
{
$group:
{
_id: \<expression\>
,\<field\>: {\<accumulator1\> : \<expression1\>}
, ...
}
}
//Examples
// Group the output set by distinct age
db.persons.aggregate([
{
$group: {
_id: "$age"
}
}
])
// Group the output set by age and gender
db.persons.aggregate([
{
$group: {
_id: {age: "$age", gender: "$gender"}
}
}
])
//Matches documents by gender female and groups them by eyeColor and age
db.persons.aggregate([
{//stage
$match: {
gender: "female"
}
}
,{//stage 2
$group: {
_id: {age: "$age", eyeColor: "$eyeColor"}
}
}
])$count (03/08): counts the number of objects or documents. Counts the number of the input documents.
//Syntax
{
$count: "<title>"
}
//Example
{
$count: "countries"
}Different count methods
//Server-side count. 0.21 sec for 1000 documents
db.persons.aggregate([{$count: "total"}])
//Server-side count. 0.21 sec for 1000 documents.
db.persons.find({}).count()
//Client-side count. count all documents in the cursor. 1.4 sec for 1000 documents
db.persons.aggregate([]).itcount()
//Client-side count. convert the cursor returned to an array and count the number of documents in the array. 1,7 sec for 1000 documents
db.persons.aggregate([]).toArray().length$sort (04/08): sorts objects. It is usually put after the match and group stages.
//Syntax
{
$sort:
{
\<field1\>: \<-1 | 1\> //descending or ascending order
,\<field2\>: \<-1 | 1\>
}
}
//Examples
{
$sort: {score: -1}
$sort: {age: 1, country: 1}
}$project (05/08): filters fields in the documents. It is similar to the field filtering in the find method. Includes, excludes or adds new field(s).
//Syntax
{
$project:
{
\<field1\>: \<0 | 1 | expression\> //exclude or include the field in the output set
,\<field2\>: \<0 | 1 | expression\>
,\<newField1\>: \<expression\>
}
}
//Examples
db.persons.aggregate
([
{
$project:
{
_id: 0
name: 1
,"company.title": 1
,age: 1
}
}
])
db.persons.aggregate
([
{
$project:
{
name: 1
,"company.title": 1
,age: 1
,newAge: "$age"
}
}
])
db.persons.aggregate
([
{
$project:
{
_id: 0
,name: 1
,info:
{
eyes: "$eyeColor"
,fruit: "$favoriteFruit"
,country: "$company.location.country"
}
}
}
])$limit (06/08): limits the number of documents. Similar to the limit operator of the find method. Outputs first N documents from the input.
//Syntax
{
$limit: \<number\>
}
//Example
{
$limit: 100
}
//Filter the first 100 persons of the input set older that 27 and group the by country
db.persons.aggregate([
{$limit: 100}
,{$match: {age: {$gt: 27}}}
,{$group: {_id: "$company.location.country"}}
])$unwind (07/08): Splits each document with specified array to several documents - one document per array element.
//Syntax
{
$unwind: \<arrayReferenceExpression\>
}
Illustration
- Input: Document1 { ... tags: ["first", "second", "third"] ...}
- $unwind: "$tags"
- Output: Document1 { ... tags: "first" ...}, Document2 { ... tags: "second" ...}, Document3 { ... tags: "third" ...}
//Examples
{$unwind: "$tags"}
{$unwind: "$hobbies"}
//$unwind combined with $project
db.persons.aggregate([
{$unwind: "$tags"}
,{$project: {name: 1, gender: 1, tags: 1}}
])
//$unwind combined with $group
db.persons.aggregate([
{$unwind: "$tags"}
,{$group: {_id: "$tags"}}
])$skip (07/08): skips a certain amount of documents.
Accumulators maintain state for each group of the documents
//Syntax
{
$\<accumulatorOperator\>: \<expression\>
}
Illustration
- Input: Document1 { ... quantity: 5, age: 25 ...}, Document2 { ... quantity: 30, age: 25 ...}, Document3 { ... quantity: 45, age: 25 ...}
- $group: {_id: "$age"}
- Output: $sum {$sum: "$quantity"}$sum (01/02): Sums numeric values for the documents in each group
//Syntax
{
$sum: \<expression | number\>
}
{
total: {$sum: "$quantity"}
}
//count the documents in the group. It is a simple way to count number of the documents in each group.
{count: {$sum: 1}}
//Group documents by age and count the number of documents in each group
db.persons.aggregate([
{
$group:{
_id: "$tags"
,count: {$sum: 1}
}
}
])
//Group documents by distinct tag and count the number of documents in each group
db.persons.aggregate([
{
$unwind: "$tags"
}
,{
$group:{
_id: "$tags"
,count: {$sum: 1}
}
}
])$avg (02/02): Calculates the average value of the certain values in the documents for each group
//Syntax
{
$avg: \<expression\>
}
db.persons.aggregate([
{
$group:
{
_id: "$eyeColor"
,avgAge: {$avg: "$age"}
}
}
])
db.persons.aggregate([
{
$group:
{
_id: "$eyeColor"
,avgAge:
{
$avg: { $round : ["$age", 2] }
}
}
}
])They are usually used in the $project stage because it operates on each independent document. In the $group stage, unary operators can be used only in conjunction with accumulators.
$type: returns the BSON type of teh field's value$or$and$lt$gt$multiply: multiplies two or mores values.
//Syntax
{
$type: \<expression\>
}
//Examples
{$type: "$age"}
{$type: "$name"}
db.persons.aggregate([
{
$project:
{
name: 1
,eyeColorType: {$type: "$eyeColor"}
,ageType: {$type: "$age"}
}
}
])$out (08/08): writes the result of the aggregation into another collection. writes resulting documents to the MongoDB collection. $out MUST be last stage in the pipeline. If output collection doesn't exist, it will be created automatically.
//Syntax
{
$out: "<outputCollectionName>"
}
//Examples
{
$out: "newCollection"
}
//Documents from the $group stage will be written to the collection "aggregationResults"
db.persons.aggregate([
{
$group:
{
_id:
{
age: "$age"
,eyeColor: "$eyeColor"
}
}
}
,{
$out: "aggregationResults"
}
])allowDiskTrue: true is an option that can be used to ask MongoDB to write stages data to the temporal files instead of RAM, because:
- all aggregation stages can use maximum 100 MB of RAM
- the server will return error if RAM limit is exceeded
- Usage: db.persons.aggregate([], {allowDiskUse: true})
📝 Memo:
- Indexes improve MongoDB query execution
- Without index whole collection must be scanned (COLLSCAN)
- Index stores sorted field values
- If appropriate index exists, MongoDB performs only index scan (IXSCAN)
- Indexes are created by key containing key-value pairs, where value is the sort order, 1 for ascending and -1 for descending order. They are stored along with the collection data in the MongoDB server.
- id index it unique although the unique key doesn't appear in the output
- The index on a collection's field must be unique
- Query using regex always scan all documents even if there is an index on the field queried.
Default _id index
- {_id: 1} is the default index in each MongoDB collection
- The name of this index is
_id_ - The default _id index is unique
- You cannot delete underscore id index.
Example of the default underscore id index
[
{
"v": 2, //verion 2
"key": {
"_id": 1 //ascending order
},
"name": "_id_",
"ns": "MyDB.persons" //namespace database MyDB and collection persons
}
, ...
]getIndexes(): returns current indexes for certain collection
//Syntax
use \<DatabaseName\>
db.\<CollectionName\>.getIndexes()
//Examples
use MyDB
db.persons.getIndexes()What field(s) should you use to create a collection index?
- Field(s) that has(have) distinct values
- and/or field(s) that you mostly use to query data in the collection.
- To sum up, it depends on the design of your front-end application.
Write resulting documents to the MongoDB collection
Syntax
//Syntax
db.\<collection\>.createIndex
(
{
\<KeyName\>: [-1 | 1]
}
,\<options\>
)
//Index creation options
//create index in the background. Other operations will not be blocked. This option is appropriate for large collections in production database
{background: true}
//create unique index. The fields' values must be unique across collections (or the collection???).
{unique: true}
//Specify custom name for the index.
{name: "<IndexName>"}Examples
//create new index by field age. Sort it in ascending order.
db.persons.createIndex({age: 1})
//create new index by field name. Sort it in ascending order.
db.persons.createIndex({name: 1})
//Clean the collection to remove duplicate indexes
db.persons.find({}).count()
db.persons.deleteMany({})
db.persons.find({}).count()
// Create an unique index on the index field of the persons collection
db.persons.createIndex(
{index: 1} //index field in ascending order
,{unique: true} //distinct index field values required
)
db.persons.getIndexes()
/*OUTPUT
[
{ v: 2, key: { _id: 1 }, name: '_id_' },
{ v: 2, key: { index: 1 }, name: 'index_1', unique: true }
]
*/
// Create an index on the name field of the persons collection. It wil happen in the background.
db.persons.createIndex(
{name: 1} //name field in ascending order
,{background: true} //background process
)
db.persons.getIndexes()
/*OUTPUT
[
{ v: 2, key: { _id: 1 }, name: '_id_' },
{ v: 2, key: { index: 1 }, name: 'index_1', unique: true },
{ v: 2, key: { name: 1 }, name: 'name_1', background: true }
]
*/
// Create an custom named index on the age field of the persons collection. It wil happen in the background.
db.persons.createIndex(
{age: 1} //age field in ascending order
,{name: "customAgeIndex"} //background process
)
db.persons.getIndexes()
/*OUTPUT
[
{ v: 2, key: { _id: 1 }, name: '_id_' },
{ v: 2, key: { index: 1 }, name: 'index_1', unique: true },
{ v: 2, key: { name: 1 }, name: 'name_1', background: true },
{ v: 2, key: { age: 1 }, name: 'customAgeIndex' }
]
*/Analyze query performance by using the explain() method. It returns information about the query
//Syntax
//Standard explain method
db.\<collection\>.explain().\<method\>
//Extended explain method
db.\<collection\>.explain("executionStats").\<method\>
//Examples
//Lookup the performance of this find query
db.persons.explain().find(
{
"age": {$gt: 25}
}
)
//Alternative syntax
db.persons.find(
{
"age": {$gt: 25}
}
).explain()
/*OUTPUT
{
explainVersion: '1',
queryPlanner: {
namespace: 'MyDB.persons',
indexFilterSet: false,
parsedQuery: {
age: {
'$gt': 25
}
},
queryHash: 'B18E568A',
planCacheKey: 'FDDFD434',
maxIndexedOrSolutionsReached: false,
maxIndexedAndSolutionsReached: false,
maxScansToExplodeReached: false,
winningPlan: {
stage: 'FETCH',
inputStage: {
stage: 'IXSCAN',
keyPattern: {
age: 1
},
indexName: 'customAgeIndex',
isMultiKey: false,
multiKeyPaths: {
age: []
},
isUnique: false,
isSparse: false,
isPartial: false,
indexVersion: 2,
direction: 'forward',
indexBounds: {
age: [
'(25, inf.0]'
]
}
}
},
rejectedPlans: []
},
command: {
find: 'persons',
filter: {
age: {
'$gt': 25
}
},
'$db': 'MyDB'
},
serverInfo: {
host: 'LAPTOP-JSB53U7K',
port: 27017,
version: '6.0.6',
gitVersion: '26b4851a412cc8b9b4a18cdb6cd0f9f642e06aa7'
},
serverParameters: {
internalQueryFacetBufferSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryFacetMaxOutputDocSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalLookupStageIntermediateDocumentMaxSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalDocumentSourceGroupMaxMemoryBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryMaxBlockingSortMemoryUsageBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryProhibitBlockingMergeOnMongoS: 0,
internalQueryMaxAddToSetBytes: 104857600,
internalDocumentSourceSetWindowFieldsMaxMemoryBytes: 104857600
},
ok: 1
}
*/
db.persons.explain().aggregate([
{
"$group": {_id: "$country"}
}
])
/*OUTPUT
{
explainVersion: '2',
queryPlanner: {
namespace: 'MyDB.persons',
indexFilterSet: false,
parsedQuery: {},
queryHash: '0E9762A5',
planCacheKey: '0E9762A5',
optimizedPipeline: true,
maxIndexedOrSolutionsReached: false,
maxIndexedAndSolutionsReached: false,
maxScansToExplodeReached: false,
winningPlan: {
queryPlan: {
stage: 'GROUP',
planNodeId: 2,
inputStage: {
stage: 'COLLSCAN',
planNodeId: 1,
filter: {},
direction: 'forward'
}
},
slotBasedPlan: {
slots: '$$RESULT=s8 env: { s2 = Nothing (SEARCH_META), s3 = 1710329563348 (NOW), s1 = TimeZoneDatabase(Etc/UCT...America/Coral_Harbour) (timeZoneDB) }',
stages: '[2] mkbson s8 [_id = s7] true false \n' +
'[2] group [s7] [] \n' +
'[2] project [s7 = fillEmpty (s6, null)] \n' +
'[2] project [s6 = getField (s4, "country")] \n' +
'[1] scan s4 s5 none none none none [] @"07c148e0-003c-465e-8e1a-ac2c2a6d1874" true false '
}
},
rejectedPlans: []
},
command: {
aggregate: 'persons',
pipeline: [
{
'$group': {
_id: '$country'
}
}
],
cursor: {},
'$db': 'MyDB'
},
serverInfo: {
host: 'LAPTOP-JSB53U7K',
port: 27017,
version: '6.0.6',
gitVersion: '26b4851a412cc8b9b4a18cdb6cd0f9f642e06aa7'
},
serverParameters: {
internalQueryFacetBufferSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryFacetMaxOutputDocSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalLookupStageIntermediateDocumentMaxSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalDocumentSourceGroupMaxMemoryBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryMaxBlockingSortMemoryUsageBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryProhibitBlockingMergeOnMongoS: 0,
internalQueryMaxAddToSetBytes: 104857600,
internalDocumentSourceSetWindowFieldsMaxMemoryBytes: 104857600
},
ok: 1
}
*/
db.persons.find(
{
"age": {$gt: 25}
}
).explain("executionStats")
/*OUTPUT
{
explainVersion: '1',
queryPlanner: {
namespace: 'MyDB.persons',
indexFilterSet: false,
parsedQuery: {
age: {
'$gt': 25
}
},
queryHash: 'B18E568A',
planCacheKey: 'FDDFD434',
maxIndexedOrSolutionsReached: false,
maxIndexedAndSolutionsReached: false,
maxScansToExplodeReached: false,
winningPlan: {
stage: 'FETCH',
inputStage: {
stage: 'IXSCAN',
keyPattern: {
age: 1
},
indexName: 'customAgeIndex',
isMultiKey: false,
multiKeyPaths: {
age: []
},
isUnique: false,
isSparse: false,
isPartial: false,
indexVersion: 2,
direction: 'forward',
indexBounds: {
age: [
'(25, inf.0]'
]
}
}
},
rejectedPlans: []
},
executionStats: {
executionSuccess: true,
nReturned: 692,
executionTimeMillis: 9,
totalKeysExamined: 692,
totalDocsExamined: 692,
executionStages: {
stage: 'FETCH',
nReturned: 692,
executionTimeMillisEstimate: 0,
works: 693,
advanced: 692,
needTime: 0,
needYield: 0,
saveState: 0,
restoreState: 0,
isEOF: 1,
docsExamined: 692,
alreadyHasObj: 0,
inputStage: {
stage: 'IXSCAN',
nReturned: 692,
executionTimeMillisEstimate: 0, //Estimated runtime
works: 693,
advanced: 692,
needTime: 0,
needYield: 0,
saveState: 0,
restoreState: 0,
isEOF: 1,
keyPattern: {
age: 1
},
indexName: 'customAgeIndex',
isMultiKey: false,
multiKeyPaths: {
age: []
},
isUnique: false,
isSparse: false,
isPartial: false,
indexVersion: 2,
direction: 'forward',
indexBounds: {
age: [
'(25, inf.0]'
]
},
keysExamined: 692,
seeks: 1,
dupsTested: 0,
dupsDropped: 0
}
}
},
command: {
find: 'persons',
filter: {
age: {
'$gt': 25
}
},
'$db': 'MyDB'
},
serverInfo: {
host: 'LAPTOP-JSB53U7K',
port: 27017,
version: '6.0.6',
gitVersion: '26b4851a412cc8b9b4a18cdb6cd0f9f642e06aa7'
},
serverParameters: {
internalQueryFacetBufferSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryFacetMaxOutputDocSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalLookupStageIntermediateDocumentMaxSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalDocumentSourceGroupMaxMemoryBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryMaxBlockingSortMemoryUsageBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryProhibitBlockingMergeOnMongoS: 0,
internalQueryMaxAddToSetBytes: 104857600,
internalDocumentSourceSetWindowFieldsMaxMemoryBytes: 104857600
},
ok: 1
}
*/
db.persons.aggregate([
{
"$group": {_id: "$country"}
}
]).explain("executionStats")
/*OUTPUT
{
explainVersion: '2',
queryPlanner: {
namespace: 'MyDB.persons',
indexFilterSet: false,
parsedQuery: {},
queryHash: '0E9762A5',
planCacheKey: '0E9762A5',
optimizedPipeline: true,
maxIndexedOrSolutionsReached: false,
maxIndexedAndSolutionsReached: false,
maxScansToExplodeReached: false,
winningPlan: {
queryPlan: {
stage: 'GROUP',
planNodeId: 2,
inputStage: {
stage: 'COLLSCAN',
planNodeId: 1,
filter: {},
direction: 'forward'
}
},
slotBasedPlan: {
slots: '$$RESULT=s8 env: { s2 = Nothing (SEARCH_META), s3 = 1710329923196 (NOW), s1 = TimeZoneDatabase(Etc/UCT...America/Coral_Harbour) (timeZoneDB) }',
stages: '[2] mkbson s8 [_id = s7] true false \n' +
'[2] group [s7] [] \n' +
'[2] project [s7 = fillEmpty (s6, null)] \n' +
'[2] project [s6 = getField (s4, "country")] \n' +
'[1] scan s4 s5 none none none none [] @"07c148e0-003c-465e-8e1a-ac2c2a6d1874" true false '
}
},
rejectedPlans: []
},
executionStats: {
executionSuccess: true,
nReturned: 1, // One document matches
executionTimeMillis: 3,
totalKeysExamined: 0, //No index on the field queried
totalDocsExamined: 1000, //All documents of the collection scanned
executionStages: {
stage: 'mkbson',
planNodeId: 2,
nReturned: 1,
executionTimeMillisEstimate: 3,
opens: 1,
closes: 1,
saveState: 1,
restoreState: 1,
isEOF: 1,
objSlot: 8,
fields: [],
projectFields: [
'_id'
],
projectSlots: [
7
],
forceNewObject: true,
returnOldObject: false,
inputStage: {
stage: 'group',
planNodeId: 2,
nReturned: 1,
executionTimeMillisEstimate: 3,
opens: 1,
closes: 1,
saveState: 1,
restoreState: 1,
isEOF: 1,
groupBySlots: [
7
],
usedDisk: false,
numSpills: 0,
spilledRecords: 0,
spilledDataStorageSize: 0,
inputStage: {
stage: 'project',
planNodeId: 2,
nReturned: 1000,
executionTimeMillisEstimate: 3,
opens: 1,
closes: 1,
saveState: 1,
restoreState: 1,
isEOF: 1,
projections: {
'7': 'fillEmpty (s6, null) '
},
inputStage: {
stage: 'project',
planNodeId: 2,
nReturned: 1000,
executionTimeMillisEstimate: 3,
opens: 1,
closes: 1,
saveState: 1,
restoreState: 1,
isEOF: 1,
projections: {
'6': 'getField (s4, "country") '
},
inputStage: {
stage: 'scan',
planNodeId: 1,
nReturned: 1000,
executionTimeMillisEstimate: 3, //Estimated runtime
opens: 1,
closes: 1,
saveState: 1,
restoreState: 1,
isEOF: 1,
numReads: 1000,
recordSlot: 4,
recordIdSlot: 5,
fields: [],
outputSlots: []
}
}
}
}
}
},
command: {
aggregate: 'persons',
pipeline: [
{
'$group': {
_id: '$country'
}
}
],
cursor: {},
'$db': 'MyDB'
},
serverInfo: {
host: 'LAPTOP-JSB53U7K',
port: 27017,
version: '6.0.6',
gitVersion: '26b4851a412cc8b9b4a18cdb6cd0f9f642e06aa7'
},
serverParameters: {
internalQueryFacetBufferSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryFacetMaxOutputDocSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalLookupStageIntermediateDocumentMaxSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalDocumentSourceGroupMaxMemoryBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryMaxBlockingSortMemoryUsageBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryProhibitBlockingMergeOnMongoS: 0,
internalQueryMaxAddToSetBytes: 104857600,
internalDocumentSourceSetWindowFieldsMaxMemoryBytes: 104857600
},
ok: 1
}
*/
db.persons.find({name: /al/i}).explain("executionStats")
/*
{
explainVersion: '1',
queryPlanner: {
namespace: 'MyDB.persons',
indexFilterSet: false,
parsedQuery: {
name: BSONRegExp('al', 'i')
},
queryHash: '501B9A8A',
planCacheKey: '862AB41F',
maxIndexedOrSolutionsReached: false,
maxIndexedAndSolutionsReached: false,
maxScansToExplodeReached: false,
winningPlan: {
stage: 'FETCH',
inputStage: {
stage: 'IXSCAN',
filter: {
name: BSONRegExp('al', 'i')
},
keyPattern: {
name: 1
},
indexName: 'name_1',
isMultiKey: false,
multiKeyPaths: {
name: []
},
isUnique: false,
isSparse: false,
isPartial: false,
indexVersion: 2,
direction: 'forward',
indexBounds: {
name: [
'["", {})',
'[/al/i, /al/i]'
]
}
}
},
rejectedPlans: []
},
executionStats: {
executionSuccess: true,
nReturned: 122,
executionTimeMillis: 33,
totalKeysExamined: 1000,
totalDocsExamined: 122,
executionStages: {
stage: 'FETCH',
nReturned: 122,
executionTimeMillisEstimate: 23,
works: 1001,
advanced: 122,
needTime: 878,
needYield: 0,
saveState: 1,
restoreState: 1,
isEOF: 1,
docsExamined: 122,
alreadyHasObj: 0,
inputStage: {
stage: 'IXSCAN',
filter: {
name: BSONRegExp('al', 'i')
},
nReturned: 122,
executionTimeMillisEstimate: 23,
works: 1001,
advanced: 122,
needTime: 878,
needYield: 0,
saveState: 1,
restoreState: 1,
isEOF: 1,
keyPattern: {
name: 1
},
indexName: 'name_1',
isMultiKey: false,
multiKeyPaths: {
name: []
},
isUnique: false,
isSparse: false,
isPartial: false,
indexVersion: 2,
direction: 'forward',
indexBounds: {
name: [
'["", {})',
'[/al/i, /al/i]'
]
},
keysExamined: 1000,
seeks: 1,
dupsTested: 0,
dupsDropped: 0
}
}
},
command: {
find: 'persons',
filter: {
name: BSONRegExp('al', 'i')
},
'$db': 'MyDB'
},
serverInfo: {
host: 'LAPTOP-JSB53U7K',
port: 27017,
version: '6.0.6',
gitVersion: '26b4851a412cc8b9b4a18cdb6cd0f9f642e06aa7'
},
serverParameters: {
internalQueryFacetBufferSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryFacetMaxOutputDocSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalLookupStageIntermediateDocumentMaxSizeBytes: 104857600,
internalDocumentSourceGroupMaxMemoryBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryMaxBlockingSortMemoryUsageBytes: 104857600,
internalQueryProhibitBlockingMergeOnMongoS: 0,
internalQueryMaxAddToSetBytes: 104857600,
internalDocumentSourceSetWindowFieldsMaxMemoryBytes: 104857600
},
ok: 1
}
*/db.persons.getIndexes()
/*OUTPUT
[
{ v: 2, key: { _id: 1 }, name: '_id_' },
{ v: 2, key: { index: 1 }, name: 'index_1', unique: true },
{ v: 2, key: { name: 1 }, name: 'name_1', background: true },
{ v: 2, key: { age: 1 }, name: 'customAgeIndex' }
]
*/
//Delete indexes on the field index in the person collection
db.persons.dropIndex(
{
index: 1
}
)
/*
{ nIndexesWas: 4, ok: 1 }
*/
db.persons.getIndexes()
/*OUTPUT
[
{ v: 2, key: { _id: 1 }, name: '_id_' },
{ v: 2, key: { name: 1 }, name: 'name_1', background: true },
{ v: 2, key: { age: 1 }, name: 'customAgeIndex' }
]
*/These utilities are not part of MongoDB Shell. They are independent and separated from MongoDB Shell
winget search --name mongodb
/*
Name Id Version Source
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
MongoDB MongoDB.Server 6.0.6 winget
NoSQLBooster for MongoDB NoSQLBooster.NoSQLBooster 8.1.7 winget
MongoDB Shell MongoDB.Shell 1.10.1 winget
MongoDB CLI MongoDB.MongoDBCLI 1.30.0 winget
MongoDB Atlas CLI MongoDB.MongoDBAtlasCLI 1.5.1 winget
MongoDB Tools MongoDB.DatabaseTools 100.7.3 winget
MongoDB Compass Readonly MongoDB.Compass.Readonly 1.42.2.0 winget
MongoDB Compass Isolated Edition MongoDB.Compass.Isolated 1.42.2.0 winget
MongoDB Compass MongoDB.Compass.Full 1.42.2.0 winget
MongoDB Compass Community MongoDB.Compass.Community 1.41.0 winget
*/
winget install --id MongoDB.DatabaseTools --exact --source winget --silent
/*
Found MongoDB Tools [MongoDB.DatabaseTools] Version 100.7.3
This application is licensed to you by its owner.
Microsoft is not responsible for, nor does it grant any licenses to, third-party packages.
Downloading https://fastdl.mongodb.org/tools/db/mongodb-database-tools-windows-x86_64-100.7.3.msi
██████████████████████████████ 58.0 MB / 58.0 MB
Successfully verified installer hash
Starting package install...
Successfully installed
*/Add the path: C:\Program Files\MongoDB\Tools\100\bin to the Windows environment variables
Open a Powershell and run:
mongoexport --version
<#>
mongoexport version: 100.7.3
git version: ad89a1c6dbe283012012cf0e5f4cb7fb1fcdf75d
Go version: go1.19.10
os: windows
arch: amd64
compiler: gc
#>mongoexport - mongoimport (1/4): used to export or import collection data in extended JSON format.
mongoexport
- exports MongoDB collection data in JSON or CSV format
- uses the strict mode extended JSON format. It means type information will be preserved using key-value pairs.
Syntaxes
/*EXPORT DATA
--host: hostname of the remote server
--db: database where you want to export data from
--collection: collection where you want to export data from
--out: name of the file that will be created on your local system and where exported data will be written to
--jsonArray option wil export data as array of JSON objects. This option doesn't require any argument.
*/
//(REMOTE)
mongoexport --host \<hostname\> --username \<username\> --password \<password\> --authenticationDatabase \<authDb\> --db \<database\> --collection \<collection\> --out \<filename\>
//(LOCAL)
mongoexport --db \<database\> --collection \<collection\> --out \<filename\>
//(LOCAL jsonArray)
mongoexport --db \<database\> --collection \<collection\> --out \<filename\> --jsonArray
//(LOCAL CSV)
mongoexport --db \<database\> --collection \<collection\> --out \<filename\> --type=csv
//(LOCAL with Query)
mongoexport --db \<database\> --collection \<collection\> --out \<filename\> --query '{\<query\>}'
/*IMPORT DATA
--host: hostname of the remote server
--db: database where you want to import data to
--NewCollectionName: collection where data will be stored
--file: name of the file that contains data to import
--jsonArray option wil export data as array of JSON objects. This option doesn't require any argument.
Note: MongoDB wil produce error if you will try to insert document with duplicate unique index value.
*/
//(REMOTE)
mongoimport --host \<hostname\> --username \<username\> --password \<password\> --authenticationDatabase \<authDb\> --db \<database\> --collection \<collection\> --file \<filename\>
//(LOCAL)
mongoimport --db \<database\> --collection \<collection\> --file \<filename\>
//(LOCAL jsonArray)
mongoimport --db \<database\> --collection \<collection\> --file \<filename\> --jsonArray
//(LOCAL CSV)
mongoimport --db \<database\> --collection \<collection\> --file \<filename\> --type=csv Examples
mongoexport --uri 'mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017'
//Export data from the persons collection located in the local MyDB database and store those data in the file persons.json created on the local computer.
mongoexport --uri 'mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017' --authenticationDatabase admin --db MyDB --collection persons --out PersonsExported.json
mongoexport --uri 'mongodb://root:root@localhost:27017' --authenticationDatabase admin --db MyDB --collection persons --out PersonsExported.json --query '{index: 3}'mongodump - mongorestore (2/4): used to dump or restore collection data in BSON format.
mongodump
- exports data in binary format. It exports all indexes along with collections.
- wihout --db option, all databases except 'local' will be dumped
mongorestore
- Binary import of the MongoDB backup
- indexes will be re-created
Syntax
/*DUMP DATA
--host: hostname of the remote server
--db: specific database to dump
--collection: sepecific collection to dump
argument.
--out: directory name where dump result will be stored. If you omit this option, a dump directory named 'dump' will be automatically created
--archive and --gzip to export to a compressed archived
*/
//(LOCAL) dump all databases on the local mongodb server
mongodump
//(REMOTE)
mongodump --host \<hostname\> --username \<username\> --password \<password\> --authenticationDatabase \<authDb\>
//(REMOTE specific DB and Collection) dump specific databases and specific collections
mongodump --host \<hostname\> --username \<username\> --password \<password\> --authenticationDatabase \<authDb\> --db \<dumpDatabase\> --collection \<dumpCollection\> --out \<directoryName\>
//(REMOTE to Archive)
mongodump --host \<hostname\> --username \<username\> --password \<password\> --authenticationDatabase \<authDb\> --db \<dumpDatabase\> --collection \<dumpCollection\> --archive=\<fileName\> --gzip
/*DRESTORE DATA
--host: hostname of the remote server
--dir: directory containing dump data. If omitted MongoDB will look for the folder named 'dump'
--archive and --gzip to export to a compressed archived
*/
//(LOCAL) retore data from the dump folder to the local MongoDB server.
mongorestore
//(REMOTE)
mongorestore --host \<hostname\> --username \<username\> --password \<password\> --authenticationDatabase \<authDb\>
//(REMOTE from specific directory)
mongorestore --host \<hostname\> --username \<username\> --password \<password\> --authenticationDatabase \<authDb\> --dir \<directoryName\>
//(REMOTE from Archive)
mongorestore --host \<hostname\> --username \<username\> --password \<password\> --authenticationDatabase \<authDb\> --archive=\<fileName\> --gzip
~~
`mongostat` (3/4): MongoDB real-time statistics. Easily monitor mongodb performance in real time.
~~~js
//(LOCAL)
mongostat
//(REMOTE)
mongostat --host \<hostname\> --username \<username\> --password \<password\> --authenticationDatabase \<authDb\>mongotop (4/4): Top MongoDB current read and write operations
//(LOCAL)
mongostop
mongotop \<NumberOfSeconds\>
//(REMOTE)
mongotop --host \<hostname\> --username \<username\> --password \<password\> --authenticationDatabase \<authDb\>