SLAM implemented by a robot in a abandoned underground cave in Pennsylvania.
In this project, I have implemented Graph SLAM in a 2D grid world where the robot tracks it's movements and detects the surrounding landmarks such as building, trees, rocks etc using its distance measurement sensors and motion poses.
First we define variables with respect to the world and the robot. The variables that I have used are the following:
N: time steps for which we want our robot to have a random walknum_landmarks: number of landmarks in the worldworld_size: the grid size of the world (Here I have taken it as 100 units (10x10))measurement_range: the range in which the robot measures a landmarkmotion_noise: noise or uncertanity present in the robot motion.measurement_noise: noise or uncertanity present in the robot's distance measurement sensor. These two moise variables are introduced to mimick real-life sceanrios.distance: distance by which a robot can move during a particular time step.
All of the above variables go into the make_data() function and out comes the true landmark locations and the robots final pose co-ordinates.
Here data[time_step][0] is the measurement values given by the robot sensor with respect to each landmark and data[time_step][1] is the motion co-ordinates of the robot. Please see the helpers.py file for more info
Here I have instantiated the robot at the center of the grid.
Also, the function sense() in the 1st notebook measures the distance from the robot to the landmarks around it in it's range. This funtion acts as the distance measuring sensor of the robot.
Please go thorugh the 2nd notebook to understand the concept before you go further. It is very important.
The concept in the 2nd notebook explains the motion of the robot in 1D and gives an overview of how it can be done it 2D. Accordingly I have coded the workflow in 2D which defined in the slam() function in the 3rd notebook.
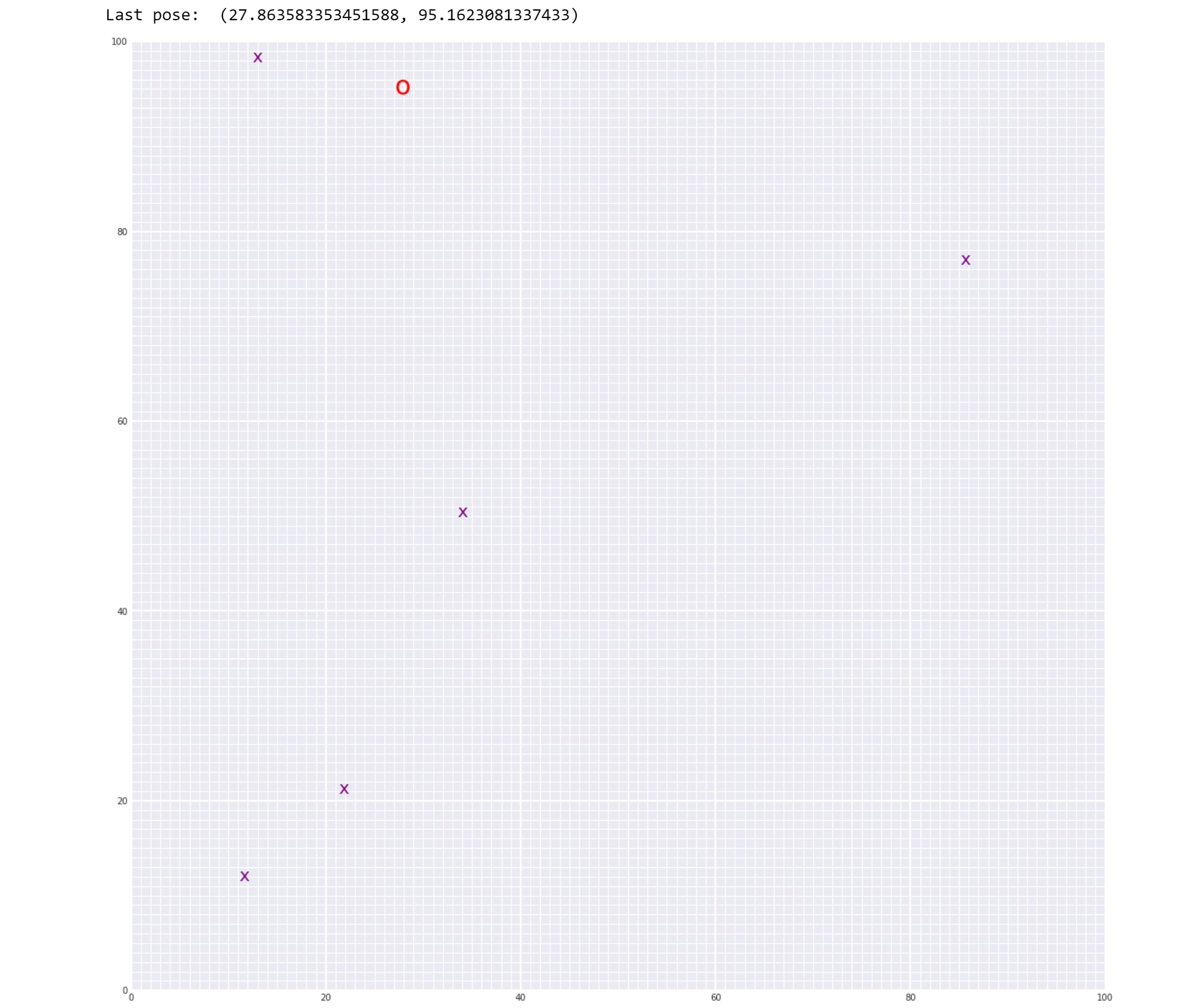
As you can see the red circle is the robot and the purple cross marks are the landmarks. The co-orindates of the last pose of the robot are mentioned after N time steps. We can compare this value with the output robot position value of the data and can see the they are not exactly they same. The error is due to the noise that I have introduced in the robot motion and the sensor.