Object Oriented Programming aims to implement real world entities like Inheritance, Polymorphism, Encapsulation in programming.
The main aim is to bind together the data and the functions so that other parts of the code cannot access them.
The word polymorphism means having many forms. In simple words, we can define polymorphism as the ability of a message to be displayed in more than one form.
Real Life Example: A Person at the same time can have different characteristics. A man can be a father, a brother, a son, a friend in different situations.
Polymorphism is the ability of OOPs programming languages to differentiate between entities of the same name. Its done in Java with the help of signature and declaration of the entities
Polymorphism is of 2 types:
(source)
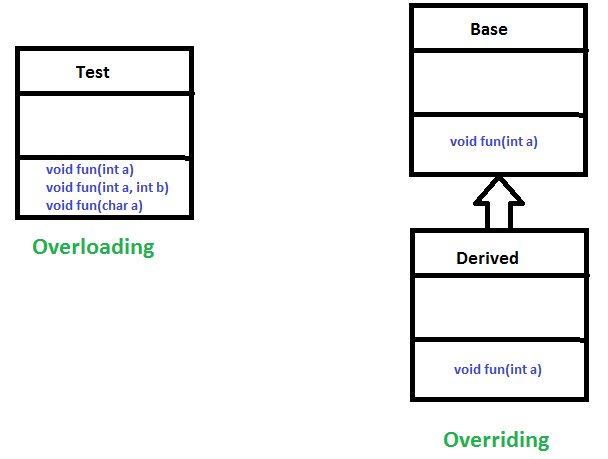
Overloading allows methods to have same name but different signatures where the signature can differ by methods having different types of input parameters or different number of input parameters.
What if the prototype does not match with arguments?
Priority wise, compiler take these steps:
- Type Conversion but to higher type (in terms of range) in same family.
- Type conversion to next higher family (suppose if there is no long data type available for an int data type, then it will search for float data type).
Advantage
We don't have to create redundant method names for similar kind of tasks.
Can we overload static methods?
Yes. We can have two ore more static methods with same name, but differences in input parameters.
Can we overload methods that differ only by static keyword?
We cannot overload two methods in Java if they differ only by static keyword. (Source)
Can we overload main() in Java?
Like other static methods, we can overload main() in Java.
What is the difference between Overloading and Overriding?
- Overloading is about same function have different signatures. Overriding is about same function, same signature but different classes connected through inheritance.
- Overloading is an example of compiler time polymorphism and overriding is an example of run time polymorphism.
Method overloading and null error in Java
In Object oriented programming, overriding is a feature that allows a subclass or a child class to provide a specific implementation of a method which already provided by its parent class or super class.
The method in the subclass is said to Override the method in the superclass
The version of a method that is executed will be determined by the object that is used to invoke it.
If an object of a parent class is used to invoke the method, then the version in the parent class will be executed, but if an object of the subclass is used to invoke the method, then the version in the child class will be executed.
In other words, it is the type of the object being referred to (not the type of the reference variable) that determines which version of an overridden method will be executed.
- Overriding and access modifiers.
- Final methods cannot be overridden.
- Static methods cannot be overridden.
- Private methods cannot be overridden.
- The overriding method must return the same subtype.
- Invoking overridden methods from subclass.
- Overriding and constructor.
- Overriding and Exception-Handling.
- Overriding and abstract method.
- Overriding and synchronized/strictfp method.
Multi-Level method overriding
Employee manager example
The access modifier for an overriding method can allow more access than its overridden method but not less access.
For example: A method with Protected instance can be provided with a public access modifier but not private
If we do not want a method to be overridden, we declare it as a final.
Static methods of the base class cannot be overridden by the child class.
So when we define a static method with the same signature as in the base class it is called Method hiding.
Private methods cannot be overridden as they are bonded during compile time. We get the compiler error that the "fun() has private access in Base."
An inner class can access private members of its outer class. fun() of Inner accesses private data member msg which is fine by the compiler.
From Java 5.0 onwards it is possible to have different return type for a overriding method in child class, but child’s return type should be sub-type of parent’s return type.
This phenomena is known as covariant return type.
We can call parent class method in overriding method using super keyword.
We can not override constructor as parent and child class can never have constructor with same name(Constructor name must always be same as Class name).
Below are two rules to note when overriding methods related to exception-handling.
If the super-class overridden method does not throws an exception, subclass overriding method can only throws the unchecked exception, throwing checked exception will lead to compile-time error.
If the super-class overridden method does throws an exception, subclass overriding method can only throw same, subclass exception. Throwing parent exception in Exception hierarchy will lead to compile time error.Also there is no issue if subclass overridden method is not throwing any exception.
Abstract methods in an interface or abstract class are meant to be overridden in derived concrete classes otherwise a compile-time error will be thrown.
The presence of synchronized/strictfp modifier with method have no effect on the rules of overriding, i.e. it’s possible that a synchronized/strictfp method can override a non synchronized/strictfp one and vice-versa.
We can have multi-level method overriding
Consider an employee management software for an organization, let the code has a simple base class Employee, the class has methods like raiseSalary(), transfer(), promote(), .. etc. Different types of employees like Manager, Engineer, ..etc may have their implementations of the methods present in base class Employee. In our complete software, we just need to pass a list of employees everywhere and call appropriate methods without even knowing the type of employee.
It binds together data and code it manipulates. It is a protective shield that prevents the data from being accessed outside the class scope.
- The variables of a class are hidden from other classes and can be accessed by member functions of the class in which they are declared.
- The data of the class are hidden so it is also called Data-Hiding
- Encapsulation can be achieved by declaring all the variables private and creating public setter and getter methods.
- Data Hiding: The user will have no idea about the inner implementation of the class. It will not be visible to the user that how the class is storing values in the variables.
- Increased Flexibility: We can make the variables of the class as read-only or write-only depending on our requirement. If we wish to make the variables as read-only then we have to omit the setter methods like setName(), setAge() etc. from the above program
- Re-usability: Encapsulation also improves the re-usability and easy to change with new requirements.
- Testing code is easy: Encapsulated code is easy to test for unit testing.
Data Abstraction is the property by virtue of which only the essential details are displayed to the user.The trivial or the non-essentials units are not displayed to the user. Ex: A car is viewed as a car rather than its individual components.
In java, abstraction is achieved by
Some important topics in abstraction
We can achieve 100% abstraction using interfaces.
Interfaces have methods and variables like classes, but the methods declared in the interface are abstract by default. (only method signatures not body).
- It is the blueprint of the class
- It specifies the set of methods a class has to implement.
- A class should implement all the methods in the interface.
- If a class implements an interface and it does not provide all the methods of the interface then the class must be declared abstract.
- Interface cannot be instantiated, but we can make reference of it that refers to the Object of its implementing class.
- A class can implement more than one interface.
- An interface can extend another interface.
- All the methods are public and abstract in an interface.
- All the fields are public, static and final in an interface.
- Its used to achieve multiple inheritance.
- Its used to achieve loose coupling.
A comparator interface is implemented by Collection which helps to sort the collection
A class containing its methods but not its declaration is supposed to be an abstract class with an abstract function. An abstract may contain both abstract and normal methods.
- It is declared with abstract keyword.
- An abstract method is a method that is declared without an implementation.
- It may or may not have all abstract methods. Some of them can be concrete methods
- A method defined abstract must always be redefined in the subclass, thus making overriding compulsory OR either make subclass itself abstract.
- Any class that contains one or more abstract methods must also be declared with abstract keyword.
- There can be no object of an abstract class. That is, an abstract class can not be directly instantiated with the new operator.
- An abstract class can have parametrized constructors and default constructor is always present in an abstract class
- Encapsulation is data hiding(information hiding) while Abstraction is detail hiding(implementation hiding).
- While encapsulation groups together data and methods that act upon the data, data abstraction deals with exposing the interface to the user and hiding the details of implementation.
- It reduces the complexity of viewing the things.
- Avoids code duplication and increases re-usability.
- Helps to increase security of an application or program as only important details are provided to the user.
- Type of methods: Interface can have only abstract methods. Abstract class can have abstract and non-abstract methods.
- Final Variables: Variables declared in a Java interface are by default final. An abstract class may contain non-final variables.
- Type of variables: Abstract class can have final, non-final, static and non-static variables. Interface has only static and final variables.
- Implementation: Abstract class can provide the implementation of interface. Interface can’t provide the implementation of abstract class.
- Inheritance vs Abstraction: A Java interface can be implemented using keyword “implements” and abstract class can be extended using keyword “extends”.
- Multiple implementation: An interface can extend another Java interface only, an abstract class can extend another Java class and implement multiple Java interfaces.
- Accessibility of Data Members: Members of a Java interface are public by default. A Java abstract class can have class members like private, protected, etc.
Its the mechanism in java by which one class is allowed to inherit the properties of another class
- Super Class: The class whose features are inherited are known as super class, parent class or base class.
- Sub Class: The class which inherits the other class is called the sub class or derived class or extended class. The subclass can add its own methods and variables in addition to the inherited features of its parent class.
- Re-usability: One class can reuse the methods and variables of its parent class without writing redundant code.
We use the keyword extends for inheritance
In practise inheritance and polymorphism are used for fast performance and readability of code.
- Single Inheritance
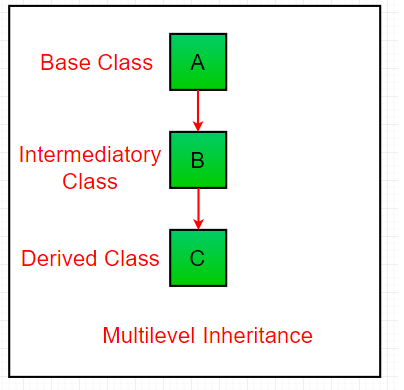
- Multilevel Inheritance
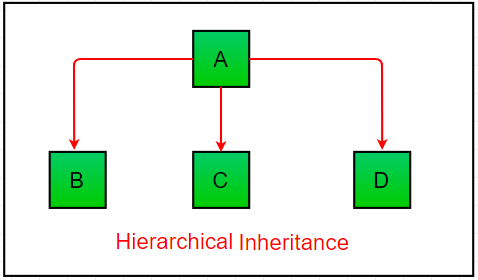
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
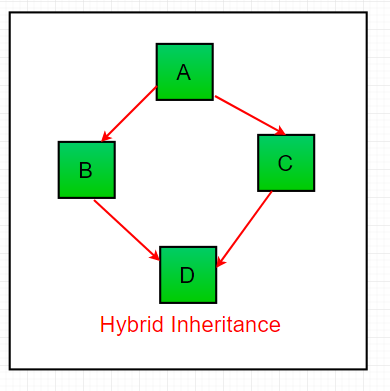
- Hybrid Inheritance
In single inheritance the subclass inherits the feature of one superclass. Class A serves as a base class for class B
In multilevel inheritance a derived class will be inheriting a base class as well as acting as the base class to another class. Class A serves as a base class for B which in turn serves as a base class for C
In Hierarchical Inheritance, one class serves as a superclass (base class) for more than one sub class. The class A serves as a base class for the derived class B,C and D.
In multiple inheritance, one class is derived from more than one superclass and inherit features from all superclasses. Java does not support multiple inheritance. We achieve multiple inheritance through interfaces.
It is a mix of hierarchical and multiple inheritance. It cannot be achieved with classes. It can only be achieved in java through inheritance.
- Default superclass: Except Object class, which has no superclass, every class has one and only one direct superclass (single inheritance). In the absence of any other explicit superclass, every class is implicitly a subclass of Object class.
- Superclass can only be one: A superclass can have any number of subclasses. But a subclass can have only one superclass. This is because Java does not support multiple inheritance with classes. Although with interfaces, multiple inheritance is supported by java.
- Inheriting Constructors: A subclass inherits all the members (fields, methods, and nested classes) from its superclass. Constructors are not members, so they are not inherited by subclasses, but the constructor of the superclass can be invoked from the subclass.
- Private member inheritance: A subclass does not inherit the private members of its parent class. However, if the superclass has public or protected methods(like getters and setters) for accessing its private fields, these can also be used by the subclass.
In sub-classes we can inherit members as is, replace them, hide them, or supplement them with new members:
- The inherited fields can be used directly, just like any other fields.
- We can declare new fields in the subclass that are not in the superclass.
- The inherited methods can be used directly as they are.
- We can write a new instance method in the subclass that has the same signature as the one in the superclass, thus overriding it (as in example above, toString() method is overridden).
- We can write a new static method in the subclass that has the same signature as the one in the superclass, thus hiding it.
- We can declare new methods in the subclass that are not in the superclass.
- We can write a subclass constructor that invokes the constructor of the superclass, either implicitly or by using the keyword super.
A class is a user defined prototype or blueprint from which objects are created. It defines the objects and methods common to all the objects of one type.
Class declarations can include the following type:
- Access Modifiers: It generally defines the accessibility or scope of a class, method, constructor or variables.
- Class Name: It is a name by which the class is defined. The objects of the class are generally created with a new operator before class name. The class name is generally capital by default.
- Superclass: It is the parent class from which the current class inherits all the properties. A class can only inherit one class.
- Interface: It is basically a blueprint of a class contains abstract methods that the class has to override if it implements the interface.
- Body: The body of the class contains the methods, variables and constructor that the class has to define.
It generally defines the accessibility or scope of a class, method, constructor or variables.
- Private: The access level of a private modifier is within the scope of the class.
- Default: The access level of a default modifier is within the scope of the package. It cannot be accessed from outside the package. If we define no access modifiers then the class, method or constructor is said to have a default modifier.
- Protected: The access level of a protected modifier is within the scope of the package and a subclass which is defined anywhere outside the package. Without the subclass it cannot be accessed outside the package.
- Public: The access level of a public modifier is everywhere. It can be accessed from inside the class, outside the class, inside the package, outside the package.
| Access Modifier | within class | within package | outside package by subclass | outside package |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Private | Y | N | N | N |
| Default | Y | Y | N | N |
| Protected | Y | Y | Y | N |
| Public | Y | Y | Y | Y |
When declared outside a class the classes and interfaces have:
- Public
- Default
But for inner class and constructors we can have all the modifiers
Inner class means than a class which is a member of another class. There are 4 types of inner classes:
-
Nested Inner class: It has access to the private instance variables of the outer class. Like any other instance variable, we can have the private and protected as the access modifiers of the class. Instance can also be nested and have all the access variables. Example of Nested Inner Class
A constant is a variable whose value cannot change once it has been assigned. Java doesn't have built-in support for constants, but the variable modifiers static and final can be used to effectively create one.
We can’t have static method in a nested inner class because an inner class is implicitly associated with an object of its outer class so it cannot define any static method for itself. Example
-
Method Local Inner class: Inner class can be declared within a method of an outer class. Example
Method Local inner classes can’t use local variable of outer method until that local variable is not declared as final. Local inner class cannot access non-final local variable till JDK 1.7. Since JDK 1.8, it is possible to access the non-final local variable in method local inner class.
-
Static Nested Inner class: Static nested classes are not technically an inner class. They are like a static member of outer class. Example
-
Anonymous Inner class: It is an inner class without a name and for which only a single object is created. Example
An anonymous inner class can be useful when making an instance of an object with certain “extras” such as overloading methods of a class or interface, without having to actually subclass a class.
we declare and instantiate them at the same time. Generally, they are used whenever you need to override the method of a class or an interface.
Anonymous inner classes are useful in writing implementation classes for listener interfaces in Android etc.
Types of Anonymous Inner class:
-
Anonymous Inner class that extends a class: We can have an anonymous inner class that extends a class.
We know that we can create a thread by extending a Thread class. Suppose we need an immediate thread but we don’t want to create a class that extend Thread class all the time. By the help of this type of Anonymous Inner class we can define a ready thread
-
Anonymous Inner class that implements a interface: We can also have an anonymous inner class that implements an interface.
We also know that by implementing Runnable interface we can create a Thread. Here we use anonymous Inner class that implements an interface.
-
Anonymous Inner class that defines inside method/constructor argument : Anonymous inner classes in method/constructor arguments are often used in graphical user interface (GUI) applications like android.
-
Difference between Normal/Regular class and Anonymous Inner class:
- A normal class can implement any number of interfaces but anonymous inner class can implement only one interface at a time.
- A regular class can extend a class and implement any number of interface simultaneously. But anonymous Inner class can extend a class or can implement an interface but not both at a time.
- For regular/normal class, we can write any number of constructors but we cant write any constructor for anonymous Inner class because anonymous class does not have any name and while defining constructor class name and constructor name must be same.