This repository contains documentation and scripts to setup a RaspberryPi as a WiFi access point, including DHCP and DNS services.
A corresponding subnet is created for connected devices; by default the subnet is based on the host IP address.
- Host IP:
192.168.1.93 - Subnet
192.168.93.1/24 - Range
(1-3) - Duration
24h
Only TCP/IP version 4 traffic is routed on the host to and from the subnet.
The MIT Man-in-the-Middle proxy may be enabled to intercept HTTP/S traffic (i.e. ports 80 and 443).
RPI.mdto setup a RaspberryPiHASSIO.mdto optionally install Home Assistantuhubctl/README.mdto optionally installuhubctl
Setting up a RaspberryPi as a WiFi access point is documented in many places, including the ThePi and official specifications. IMHO the existing instructions were insufficient for successful replication.
Your device will require both an Ethernet cable connection as well as WiFi adapter. You will need to install the latest Raspbian Buster release; documentation is provided in this repository.
Other sources include the official specification.
Depending on the age of the device you may need to update the firmware. The rpi-update program will update the firmware for your RaspberryPi; for example:
sudo rpi-update
The download is often large (e.g. > 100 MB) and sometimes fails; to avoid failures when attempting to update, include the update on the flashed SD card prior to installation in the device (see RPI.md); for example:
curl -sSL https://github.com/Hexxeh/rpi-firmware/archive/master.tar.gz -o master.tar.gz
sudo cp master.tar.gz /Volumes/boot
After the machine has booted, use sudo -s to become root and
- make the directory
- move the included archive
- unpack the archive
- run
rpi-update-- skipping the download rebootthe device
For example:
sudo -s
mkdir -p /root/.rpi-firmware
cd /root/.rpi-firmware
tar xzf /master.tar.gz .
SKIP_DOWNLOAD=1 rpi-update
reboot
When rpi-update is complete, reboot the device and update the system again; invariably the device will require another reboot command; for example:
sudo apt update -qq -y
sudo apt full-upgrade -qq -y
sudo reboot
After successfully installing Raspbian and accessing the device, the rpi-bridge.sh script will configure the system to provide
a WiFi access point. The access point has the following options:
SSID- The identifier used for the WiFi network; default:TESTWPA_PASSPHRASE- The password for access to the WiFi network minimum of eight (8) characters; default:0123456789HW_MODE- The type of WiFi network; options aregandamodeamay not work on all devices; default:gCHANNEL- The network channel used for the WiFi network; default:8
These values may be changed using the bash command-line, for example:
export SSID="MyNetwork"
export WPA_PASSPHRASE="MyNetworkPassword"
export CHANNEL=6
Executing the script configures the WiFi adapter (n.b. wlan0 by default) to provide a subnet of the parent network with both a DNS and DHCP server.
Devices connecting to the WiFi network using the specified SSID and WPA_PASSPHRASE will be assigned IP addresses on the subnet and have traffic routed from the WiFi network to the Ethernet network.
✋ For example, from a bash command prompt:
sudo -s
export SSID="TEST" WPA_PASSPHRASE="0123456789" CHANNEL=8
./sh/rpi-bridge
exit
If the script successfully executes it outputs a JSON structure with the configuration applied; record that information for review.
USAGE: ./sh/rpi-bridge.sh [ br0 ]
SSID: TEST, WPA_PASSPHRASE: 0123456789, CHANNEL: 8, HW_MODE: g; DNS_NAMESERVERS: 9.9.9.9 1.1.1.1
--- INFO ./sh/rpi-bridge.sh 27414 -- DNSMASQ version: 2.80
Synchronizing state of dnsmasq.service with SysV service script with /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install.
Executing: /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable dnsmasq
Synchronizing state of dhcpcd.service with SysV service script with /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install.
Executing: /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable dhcpcd
Synchronizing state of hostapd.service with SysV service script with /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install.
Executing: /lib/systemd/systemd-sysv-install enable hostapd
{
"date": "2020-01-31T17:52:35Z",
"interface": "wlan0",
"dnsmasq": {
"version": "2.80",
"dhcp": {
"ip": "192.168.93.1",
"netsize": 24,
"netmask": "255.255.255.0",
"start": "192.168.93.2",
"finish": "192.168.93.254",
"duration": "24h"
},
"options": [
"bind-dynamic",
"domain-needed",
"bogus-priv"
]
},
"iptables": {
"script": "/etc/iptables.sh",
"service": "/etc/systemd/system/iptables.service"
},
"hostapd": {
"interface": "wlan0",
"channel": 8,
"bridge": "null",
"hw_mode": "g",
"wpa": 2,
"ssid": "TEST",
"wpa_passphrase": "0123456789"
}
}
✅ After success, reboot the device.
sudo reboot
To find RTSP camera(s) attached to the WiFi access point, use the sh/find-rtsp.sh
shell script to find devices on the subnet and attempt RTSP connections; for example:
sudo ./sh/find-rtsp.sh
The WiFi network and TCP/IP subnetwork may be used in conjunction with other systems. Please see below for further information.
Home Assistant motion add-on
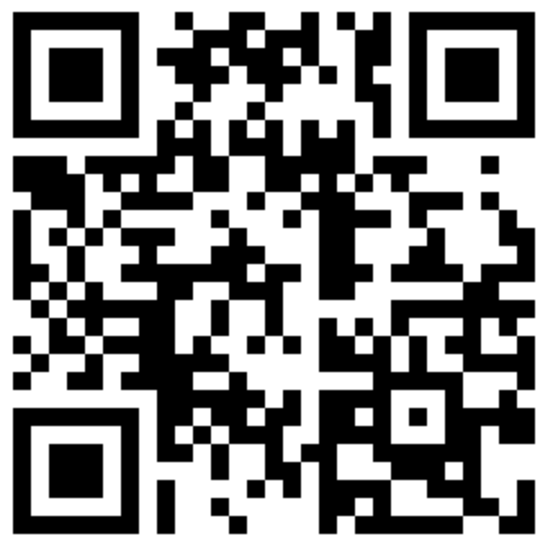
For devices running Home Assistant and the motion add-on, when using WiFi as the primary network, the configuration is completed by generating a QR code which is displayed to the device's camera to provide setup information. The QR code may be generated on-line using the provided Wifi network template.
For testing purposes, using the WiFi SSID=TEST and the WPA_PASSPHRASE=0123456789 the following QR code may be used:
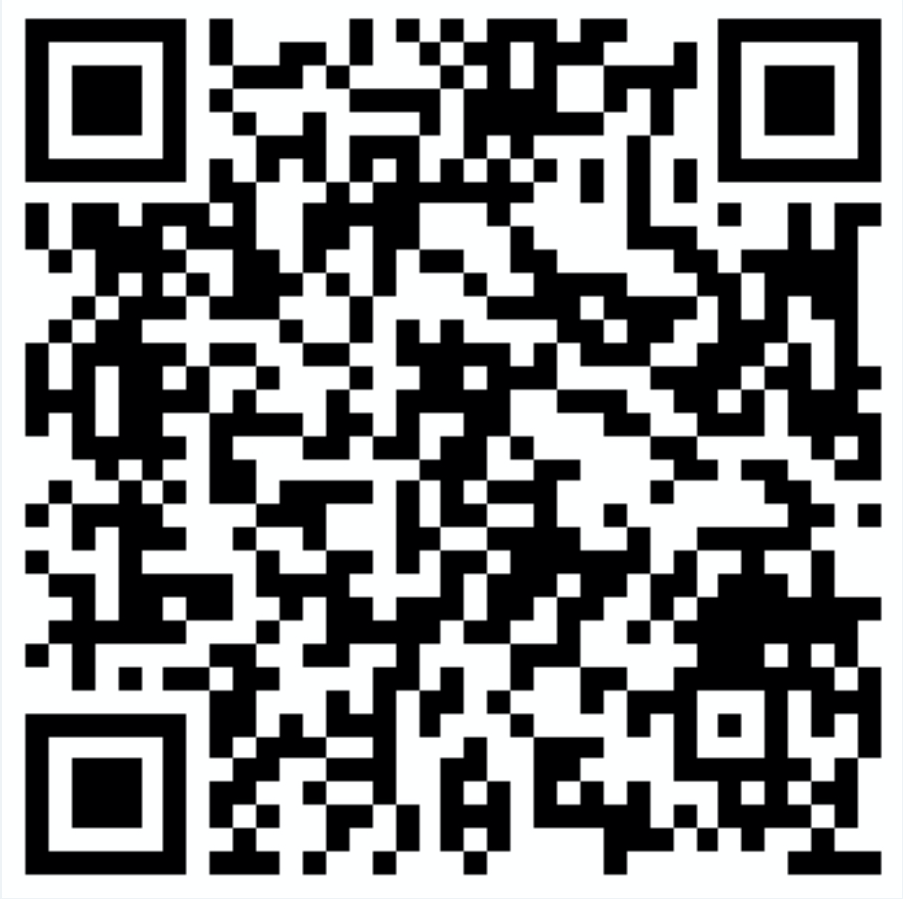
For WyzeCam devices whether being used as an RTSP source by the motion add-on or not, the configuration is completed by connecting a mobile device (e.g. iOS or Android) to the RaspberryPi provided WiFi SSID (and TCP/IP subnet) and running the Wyze application to add a device. The application generates a QR code which is then displayed to the camera to provide setup information.
For testing purposes, using the WiFi SSID=TEST and the WPA_PASSPHRASE=0123456789 the following QR code may be used:
Releases are based on Semantic Versioning, and use the format
of MAJOR.MINOR.PATCH. In a nutshell, the version will be incremented
based on the following:
MAJOR: Incompatible or major changes.MINOR: Backwards-compatible new features and enhancements.PATCH: Backwards-compatible bugfixes and package updates.
David C Martin (github@dcmartin.com)