[TOC]
Djinni目前有两个github版本
- Dropbox版本
- Snapchat版本。该版本是继承自Dropbox版本,增加使用Bazel工具
由于对Bazel不了解,并简化一些依赖问题,本文采用原始版本来使用Djinni。
这里有个官方网站1用于介绍Djinni,本文优先参考这个网站的内容。
在官方网站1上,定义Djinni是一个简单IDL,如下
The Djinni Interface Definition Language provides a simple, yet powerful way to design your interfaces.
可以理解为Djinni是一门IDL语言,使用配套工具生成平台(Android/iOS等)特性的接口,方便调用C++的实现。
官方文档1描述,如下
With Djinni you can implement interfaces in any target language and call the implementation from C++!
官方文档1使用下面这个图,比较形象描述Djinni用于桥接C++到各个平台的语言。
使用Dropbox版本的git源码,在src文件下找到run文件。这个可执行文件是djinni命令行工具。
查看帮助信息,如下
$ src/run --help
Already up to date: Djinni
Usage: djinni [options]
--help
...说明
首次执行命令会下载依赖库,编译scala源码
为了方便在其他地方使用,可以设置run的别名,并将所在文件夹导入到环境变量PATH中
$ cd src $ ln -s run djinni这里以使用zsh为例,添加下行代码
export PATH="$PATH:$HOME/GitHub_Projects/HelloDjinni/djinni/src"在新开Terminal中,执行
djinni --help$ djinni --help Already up to date: Djinni Usage: djinni [options] ...run命令实际是bash脚本
执行src/run --help命令,输出的帮助信息,大致分为下面几个部分
- 输出java接口
- 输出C++接口
- 输出JNI接口
- 输出Objective-C接口
- 输出Objective-C++接口
- 输出yaml接口
输出java接口的选项,如下
--java-out <out-folder>
The output for the Java files (Generator disabled if unspecified).
--java-package ...
The package name to use for generated Java classes.
--java-class-access-modifier <public/package>
The access modifier to use for generated Java classes (default: public).
--java-cpp-exception <exception-class>
The type for translated C++ exceptions in Java (default: java.lang.RuntimeException that is not checked)
--java-annotation <annotation-class>
Java annotation (@Foo) to place on all generated Java classes
--java-generate-interfaces <true/false>
Whether Java interfaces should be used instead of abstract classes where possible (default: false).
--java-nullable-annotation <nullable-annotation-class>
Java annotation (@Nullable) to place on all fields and return values that are optional
--java-nonnull-annotation <nonnull-annotation-class>
Java annotation (@Nonnull) to place on all fields and return values that are not optional
--java-implement-android-os-parcelable <true/false>
all generated java classes will implement the interface android.os.Parcelable
--java-use-final-for-record <use-final-for-record>
Whether generated Java classes for records should be marked 'final' (default: true). 输出C++接口的选项,如下
--cpp-out <out-folder>
The output folder for C++ files (Generator disabled if unspecified).
--cpp-header-out <out-folder>
The output folder for C++ header files (default: the same as --cpp-out).
--cpp-include-prefix <prefix>
The prefix for #includes of header files from C++ files.
--cpp-namespace ...
The namespace name to use for generated C++ classes.
--cpp-ext <ext>
The filename extension for C++ files (default: "cpp").
--hpp-ext <ext>
The filename extension for C++ header files (default: "hpp").
--cpp-optional-template <template>
The template to use for optional values (default: "std::optional")
--cpp-optional-header <header>
The header to use for optional values (default: "<optional>")
--cpp-enum-hash-workaround <true/false>
Work around LWG-2148 by generating std::hash specializations for C++ enums (default: true)
--cpp-nn-header <header>
The header to use for non-nullable pointers
--cpp-nn-type <header>
The type to use for non-nullable pointers (as a substitute for std::shared_ptr)
--cpp-nn-check-expression <header>
The expression to use for building non-nullable pointers
--cpp-use-wide-strings <true/false>
Use wide strings in C++ code (default: false)输出JNI接口的选项,如下
--jni-out <out-folder>
The folder for the JNI C++ output files (Generator disabled if unspecified).
--jni-header-out <out-folder>
The folder for the JNI C++ header files (default: the same as --jni-out).
--jni-include-prefix <prefix>
The prefix for #includes of JNI header files from JNI C++ files.
--jni-include-cpp-prefix <prefix>
The prefix for #includes of the main header files from JNI C++ files.
--jni-namespace ...
The namespace name to use for generated JNI C++ classes.
--jni-base-lib-include-prefix ...
The JNI base library's include path, relative to the JNI C++ classes.输出Objective-C接口的选项,如下
--objc-out <out-folder>
The output folder for Objective-C files (Generator disabled if unspecified).
--objc-h-ext <ext>
The filename extension for Objective-C[++] header files (default: "h")
--objc-type-prefix <pre>
The prefix for Objective-C data types (usually two or three letters)
--objc-include-prefix <prefix>
The prefix for #import of header files from Objective-C files.
--objc-swift-bridging-header <name>
The name of Objective-C Bridging Header used in XCode's Swift projects.
--objc-closed-enums <true/false>
All generated Objective-C enums will be NS_CLOSED_ENUM (default: false). 输出Objective-C++接口的选项,如下
--objcpp-out <out-folder>
The output folder for private Objective-C++ files (Generator disabled if unspecified).
--objcpp-ext <ext>
The filename extension for Objective-C++ files (default: "mm")
--objcpp-include-prefix <prefix>
The prefix for #import of Objective-C++ header files from Objective-C++ files.
--objcpp-include-cpp-prefix <prefix>
The prefix for #include of the main C++ header files from Objective-C++ files.
--objcpp-include-objc-prefix <prefix>
The prefix for #import of the Objective-C header files from Objective-C++ files (default: the same as --objcpp-include-prefix)
--cpp-extended-record-include-prefix <prefix>
The prefix path for #include of the extended record C++ header (.hpp) files
--objc-extended-record-include-prefix <prefix>
The prefix path for #import of the extended record Objective-C header (.h) files
--objcpp-namespace <prefix>
The namespace name to use for generated Objective-C++ classes.
--objc-base-lib-include-prefix ...
The Objective-C++ base library's include path, relative to the Objective-C++ classes.输出yaml接口的选项,如下
--yaml-out <out-folder>
The output folder for YAML files (Generator disabled if unspecified).
--yaml-out-file <out-file>
If specified all types are merged into a single YAML file instead of generating one file per type (relative to --yaml-out).
--yaml-prefix <pre>
The prefix to add to type names stored in YAML files (default: "").创建一个支持多平台的C++工程,实际包含两个部分
- C++库的提供者,包括接口文件以及C++产物
- C++库的使用者,即各个平台(Android/iOS等)的工程
说明
如果C++库的使用者的代码,不在这个C++工程中,C++工程也应该包括各个平台的测试工程
这里以HelloWorld示例,介绍一个完整的跨平台工程的搭建过程。
生成接口文件的步骤,参考这篇文章的步骤2
- 准备好接口生成工具和编译工具
- 创建工程结构
- 创建djinni文件
- 创建shell文件
- 执行shell文件,生成接口文件
接口生成工具,即djinni命令行工具,在上面已经在环境变量PATH中配置好djinni命令。
这里的编译工具采用GN,同样gn命令也在shell中已配置好。
$ which djinni
~/GitHub_Projects/HelloDjinni/djinni/src/djinni
$ which gn
~/GitHub_Projects/HelloGN/gn/out/gnHelloWorld工程,包含两部分内容
- 生成HelloWorld库,包含头文件等
- 使用HelloWorld库的各个平台的工程
目前列出生成HelloWorld库所需要的目录结构,如下
$ tree .
.
├── generated
├── idl
│ └── HelloWorld.djinni
├── run_djinni.sh
└── src
└── hello_world_impl.cpp- generated是接口文件生成的地方
- idl是放djinni文件的地方
- run_djinni.sh是运行djinni命令的脚本
- src是放C++代码的地方
以HelloWorld.djinni文件为例,如下
HelloWorld = interface +c {
static create(): HelloWorld;
fromCpp(): string;
}由于run命令的参数很多,需要配置各个平台的对应参数,一般会写driver脚本(驱动脚本)。
举个例子,如下
#! /usr/bin/env bash
# base config
base_dir=$(cd $(dirname 0) && pwd)
# idl config
# CONFIG start---
idl_folder="idl"
idl_file="HelloWorld.djinni"
# CONFIG end---
djinni_file="$base_dir/$idl_folder/$idl_file"
# cpp config
cpp_out="$base_dir/generated/cpp"
namespace="HelloDjinni"
# java config
jni_out="$base_dir/generated/jni"
java_out="$base_dir/generated/java/com/mycompany/hellodjinni"
java_package="com.mycompany.hellodjinni"
# oc config
objc_out="$base_dir/generated/objc"
objc_prefix="WC"
djinni \
--java-out $java_out \
--java-package $java_package \
--ident-java-field mFooBar \
\
--cpp-out $cpp_out \
--cpp-namespace $namespace \
\
--jni-out $jni_out \
--ident-jni-class NativeFooBar \
--ident-jni-file NativeFooBar \
\
--objc-out $objc_out \
--objc-type-prefix $objc_prefix \
\
--objcpp-out $objc_out \
\
--idl $djinni_file
上面生成cpp、java、jni和oc的接口文件。
$ ./run_djinni.sh
Already up to date: Djinni
Parsing...
Resolving...
Generating...如果djinni执行成功,应该是上面的输出提示。
在src文件夹下,创建hello_world_impl.cpp,内容如下
#include "../generated/cpp/HelloWorld.hpp"
using namespace HelloDjinni;
class HelloWorldImpl : public HelloWorld {
public:
static std::shared_ptr<HelloWorld> create();
std::string helloFromCpp();
};
std::shared_ptr<HelloWorld> HelloWorldImpl::create() {
return std::make_shared<HelloWorldImpl>();
}
std::string HelloWorldImpl::helloFromCpp() {
return "Hello From C++!";
}HelloWorldImpl类是实现Djinni生成的cpp接口,这个接口文件位于generated/cpp文件夹下,内容如下
// AUTOGENERATED FILE - DO NOT MODIFY!
// This file generated by Djinni from HelloWorld.djinni
#pragma once
#include <memory>
#include <string>
namespace HelloDjinni {
class HelloWorld {
public:
virtual ~HelloWorld() {}
static std::shared_ptr<HelloWorld> create();
virtual std::string helloFromCpp() = 0;
};
} // namespace HelloDjinni这里使用GN,将src中的源码编译成静态库。实际还有其他C++编译工具。
添加GN的配置文件,工程结构,如下
$ tree .
.
├── BUILD.gn
├── build
│ ├── BUILD.gn
│ ├── BUILDCONFIG.gn
│ └── toolchain
│ └── BUILD.gn
├── generated
│ ├── cpp
│ │ └── HelloWorld.hpp
│ ├── java
│ │ └── com
│ │ └── mycompany
│ │ └── hellodjinni
│ │ └── HelloWorld.java
│ ├── jni
│ │ ├── NativeHelloWorld.cpp
│ │ └── NativeHelloWorld.hpp
│ └── objc
│ ├── WCHelloWorld+Private.h
│ ├── WCHelloWorld+Private.mm
│ └── WCHelloWorld.h
├── idl
│ └── HelloWorld.djinni
├── run_djinni.sh
└── src
└── hello_world_impl.cpp运行下面命令
$ gn gen out
$ ninja -C out
ninja: Entering directory `out'
[2/2] AR libhello_static_cpp.a会在out/obj下面,生成产物libHelloWorld.a。这个静态库是要提供iOS/Android等工程使用的。
说明
GN配置文件,这里不展开介绍。参考HelloGN的README.md
由于移动平台(Android/iOS),存在模拟器和真机调试两种,因此使用GN编译需要多种CPU架构的二进制文件。
这里以iOS为例,编译支持x64和arm64的静态库。
libName="libHelloWorld.a"
if [[ $1 = "device" ]]; then
gn gen ios_out/arm64 --args='is_debug=true target_os="ios" target_cpu="arm64" ios_enable_code_signing=false'
ninja -C ios_out/arm64
elif [[ $1 = "simulator" ]]; then
gn gen ios_out/x64 --args='is_debug=true target_os="ios" target_cpu="x64" ios_enable_code_signing=false'
ninja -C ios_out/x64
elif [[ $1 = "all" ]]; then
gn gen ios_out/arm64 --args='is_debug=true target_os="ios" target_cpu="arm64" ios_enable_code_signing=false'
ninja -C ios_out/arm64
gn gen ios_out/x64 --args='is_debug=true target_os="ios" target_cpu="x64" ios_enable_code_signing=false'
ninja -C ios_out/x64
mkdir -p ./ios_out/all/obj
lipo -create ./ios_out/arm64/obj/${libName} ./ios_out/x64/obj/${libName} -o ./ios_out/all/obj/${libName}
echo "create static library ($1) successfully!"
else
echo "Must support a parameter"
fi示例代码,见build_ios.sh
上面执行./build_ios.sh all,通过lipo工具得到两种CPU架构的静态库libHelloWorld.a,这个库将在“iOS适配C++库”中使用。
在工程根目录创建ios_project,用于存放iOS工程相关文件。使用CocoaPod后,ios_project工程结构,如下
$ tree ios_project
ios_project
├── HelloDjinni
├── HelloDjinni.xcodeproj
├── HelloDjinni.xcworkspace
├── Podfile
├── Podfile.lock
└── Pods如果要使用上面编译好的C++库,这里以libHelloWorld.a为例,需要下面几个步骤
-
Xcode添加C++静态库
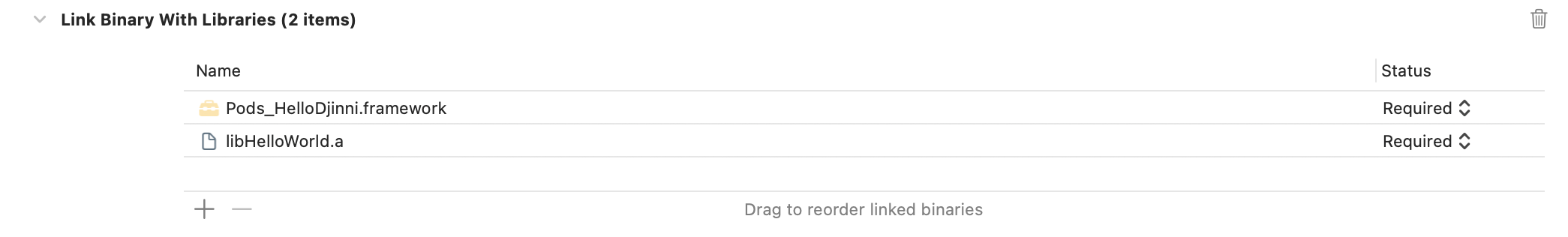
- Link Binrary with Libraries添加libHelloWorld.a
-
Xcode添加Djinni的支持库,有两种方式:源码引入,或者添加djinni_support_lib
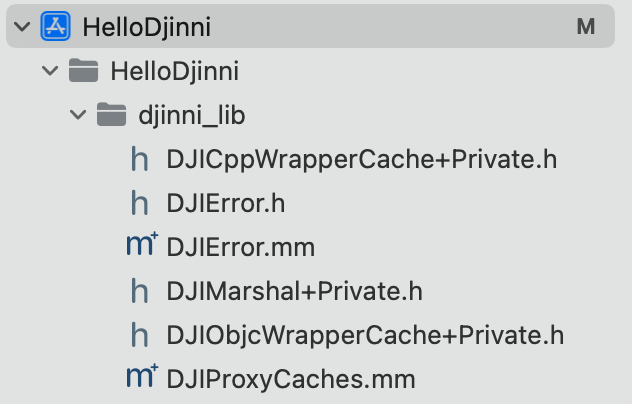
- 源码引入:在Djinni源码仓库的根目录下找到support-lib/objc,有一些.h和.mm文件,它们是Djinni支持iOS使用Djinni生成接口的胶水代码。
- 添加djinni_support_lib:在support-lib/objc下面,有ios-build-support-lib.sh脚本,执行这个脚本可以编译出djinni_support_lib库。使用djinni_support_lib库,还需要djinni_support_lib库的头文件,这个头文件也在support-lib/objc中
-
Xcode添加Djinni生成接口文件
-
Xcode的Build Settings配置头文件和静态库的搜索路径
这里采用源码引入方式,在Djinni源码仓库的根目录下找到support-lib/objc,直接将下面的所有文件拖入到Xcode中,如下
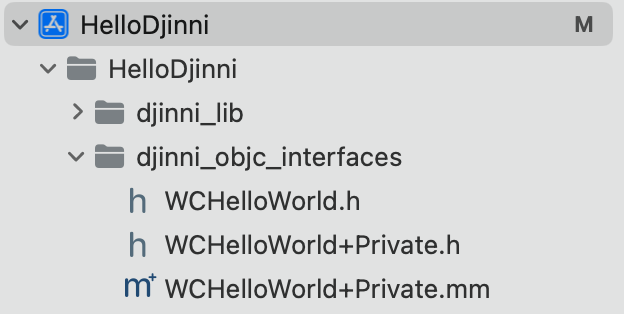
在Djinni工程HelloWorld下面,找到之前Djinni生成的objc接口文件,位置在generated/objc,同样也拖入到Xcode工程中,如下
这里objc接口文件,实际是Objective-C使用C++的胶水代码。
Xcode的Build Settings,配置下面的路径,如下
HEADER_SEARCH_PATHS=$(SRCROOT)/../generated/cpp/
LIBRARY_SEARCH_PATHS=$(SRCROOT)/../ios_out/all/obj上面cpp文件夹是提供给上面Djinni生成接口文件的C++头文件,而ios_out/all/obj是之前编译好的libHelloWorld.a所在文件夹。
在使用Djinni的OC接口之前,可以编译下Xcode,确认上面的胶水代码和静态库是否正确。
示例代码,如下
#import "WCHelloWorld.h"
- (void)test {
WCHelloWorld *helloDjinniInterface = [WCHelloWorld create];
NSString *helloDjinni = [helloDjinniInterface helloFromCpp];
NSLog(@"%@", helloDjinni);
}可以看到Djinni的OC接口,完全屏蔽了C++接口调用,而且这部分胶水代码也是Djinni自动生成的,我们不用自己手写。
示例代码,见UseDjinniOCInterfaceViewController
在上面两节中,可以看到如何向一个iOS工程添加Djinni相关库和接口文件。这里再总结下,Djinni部分的构成,用下面示意图表示。
iOS project
|- Djinni Support Lib(可以是源码或者静态库集成)
|- 用户自己的C++静态库(例如上面的libHelloWorld.a) (1)
|- 用户通过Djinni生成的OC接口文件 (2)
|- 使用OC接口文件的代码 (3)当Djinni的IDL文件更新时,则需要通过上面(1)(2)(3)部分,而(1)和(2)不需要手动调整。
按照开发者角色划分开发任务,如下
- CPP开发,负责开发C++代码,维护IDL文件,并提供C++静态库
- iOS开发,集成和更新C++静态库,调用Djinni生成的OC接口
support-lib/proxy_cache_interface.hpp
template <typename T, typename TagType = T>
class Handle {
public:
template <typename... Args> Handle(Args &&... args)
: m_cache(get_base()), m_obj(std::forward<Args>(args)...) {}
Handle(const Handle &) = delete;
Handle & operator=(const Handle &) = delete;
~Handle() { if (m_obj) cleanup(m_cache, typeid(TagType), get_unowning(m_obj)); }
void assign(const T & obj) { m_obj = obj; }
const T & get() const & noexcept { return m_obj; }
private:
const std::shared_ptr<Pimpl> m_cache;
T m_obj;
};