Project owner: Jorge J. Barroso (Karumi)
This sample stands on the principles of Clean Architecture.
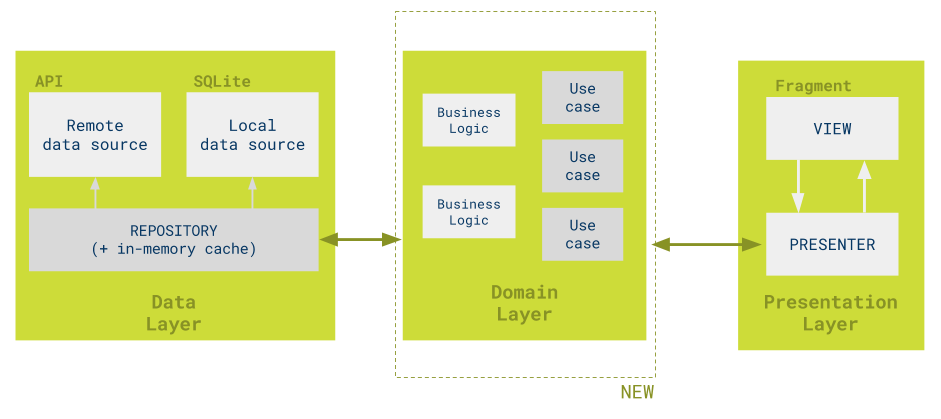
It's based on the MVP sample, adding a domain layer between the presentation layer and repositories, splitting the app in three layers:
- MVP: Model View Presenter pattern from the base sample.
- Domain: Holds all business logic. The domain layer starts with classes named use cases or interactors used by the application presenters. These use cases represent all the possible actions a developer can perform from the presentation layer.
- Repository: Repository pattern from the base sample.
The big difference with base MVP sample is the use of the Domain layer and use cases. Moving the domain layer from the presenters will help to avoid code repetition on presenters (e.g. Task filters).
Use cases define the operations that the app needs. This increases readability since the names of the classes make the purpose obvious (see tasks/domain/usecase/).
Use cases are good for operation reuse over our domain code. [CompleteTask] (https://github.com/googlesamples/android-architecture/blob/todo-mvp-clean/todoapp/app/src/main/java/com/example/android/architecture/blueprints/todoapp/tasks/domain/usecase/CompleteTask.java) is a good example of this as it's used from both the TaskDetailPresenter and the TasksPresenter.
The execution of these use cases is done in a background thread using the command pattern. The domain layer is completely decoupled from the Android SDK or other third party libraries.
Use cases run off the main thread, which is a good solution for Android apps. This is done as soon as possible to avoid blocking the UI thread. We decided to use a command pattern and execute each use case with a thread pool, but we can implement the same with RxJava or Promises.
We are using asynchronous repositories, but there's no need to do this any more because use cases execute off the main thread. This is kept to maintain the sample as similar as possible to the original one.
We recommend using different models for View, domain and API layers, but in this case all models are immutable so there's no need to duplicate them. If View models contained any Android-related fields, we would use two models, one for domain and other for View and a mapper class that converts between them.
Callbacks have an onError method that in a real app should contain information about the problem.
With this approach, all domain code is tested with unit tests. This can be extended with integration tests, that cover from Use Cases to the boundaries of the view and repository.
Apart from support and testing libraries, none.
None
Medium-Low, it's an MVP approach with a new layer that handles domain logic.
Adding a domain layer produces more classes and Java code.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Language files blank comment code
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Java 64 1278 1777 4121 (3450 in MVP)
XML 34 97 337 601
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
SUM: 98 1375 2114 4722
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Very easy. This approach is more verbose, making the maintenance tasks more obvious.
todo-mvp-clean