End-to-End Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) Deployment using Terraform
This is an end-to-end sample on how to deploy the Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) using Terraform.
Overview
This diagram provides a rough overview of the deployed infrastructure:
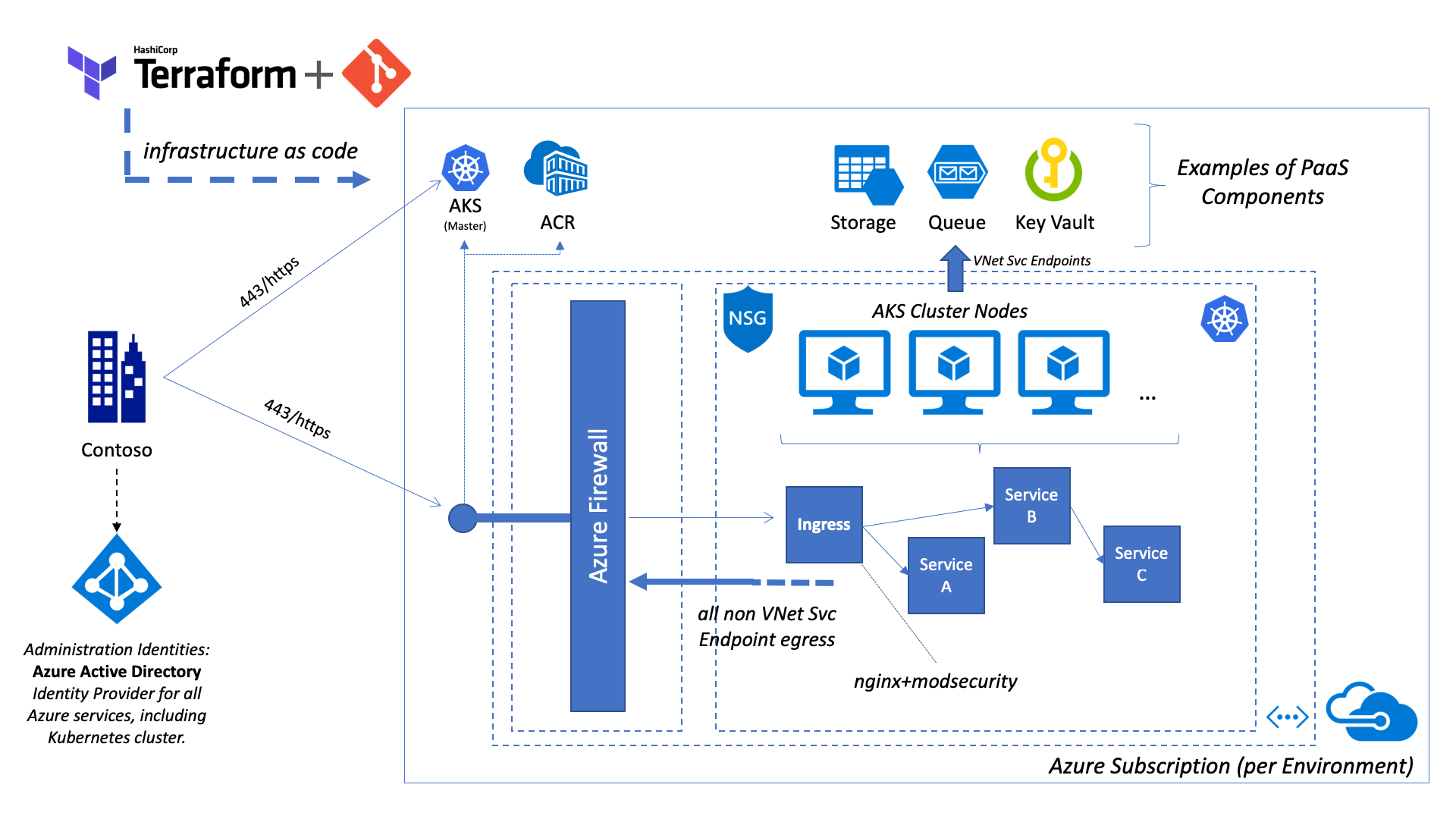
Please note that the additional services like Azure Key Vault and Azure Storage depicted here and just example on PaaS components that can be integrated into the solution.
Getting Started
The easiest way, to start get the whole environment setup and deployed is by running the apply_all.sh script. However, first you have to ensure the following preconditions:
- Terraform is installed in the latest version. Check via
terraform version. - Kubectl is installed in the latest version. Check via
kubectl version. - Helm is installed in the latest version. Check via
helm version. - Azure CLI (az) is installed in the latest version and points to the correct subscription. Check via
az account listwhat is configured as"isDefault": true. This is important as due to one missing feature in the Terraform Azure Firewall resource provider, we have to fallback to invokeazfrom Terraform. - [Azure CLI extension for Azure Firewall]
az extension add --name azure-firewall. - Create a client and server application registration in Azure Active Directory to support Kubernetes OIDC integration. In short, this allows you to use Azure AD as your identity provider to manage cluster access. Follow these steps and retrieve the required setting information. Hint: You do not need to create multiple of these registration in your environment, but you should hand out individual secrets.
- Enable the AKS Audit Log feature flag in your subscription as described in the Note field in the official documentation. Only register the flag, all actual diagnostic configuration is fully automated during the deployment.
- Creating Storage for the Terraform state
az group create \
--name <todo> \
--location westeurope
az storage account create \
--name <todo> \
--resource-group <todo> \
--location westeurope \
--sku Standard_LRS \
--encryption blob file \
--https-only
az storage account keys list \
--account-name <todo> \
--resource-group <todo> \
--output table
# manually set env vars
export AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT="<todo>"
export AZURE_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY="<todo>"
az storage container create --name tf-statesee: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/storage/blobs/storage-quickstart-blobs-cli
Environment Management
When all preconditions are met, you need to gather the required input variables in a file, e.g. secrets.dev.tfvars. The following variables are mandatory to provide:
aad_client_app_id="00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
aad_tenant_id="00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000"
resource_group_name = "<TODO>"
storage_account_name = "<TODO>"
storage_container_name = "tf-state"
storage_account_primary_access_key = "<TODO>"
aks_cluster_admins = ["john@contoso.com", "jane@contoso.com"]Finally you can execute the complete deployment process. -e denotes an environment like DEV, QA or PROD. -p denotes a prefix like your project name. -v points to the context.tfvars file discussed earlier:
./apply_all.sh -e dev -p contoso -v ./context.tfvarsIf you would like to run the deployments individually instead of using the apply_all.sh script, feel free to look into the script file and take out the bits and pieces which are useful to you.
Deployment Structure
The deployment structure is basically divided into two parts. The first part takes care of the Azure Resources, the second part takes care of the Kubernetes side.
-
00-tf-backendConfigures the terraform azure backend state provider. It generates a local set of tfvars files
{envName}_backend.tfvarsthat defines the Azure Storage account backend location for the terraform state.Required rights for execution: Allowance to create Azure Service Principals in your Azure AD tenant, see Azure Docs.
-
01-aksThe actual deployment of an AKS cluster, an Azure Firewall, and the baseline network infrastructure.Required Azure RBAC: Subscription Owner. Requires that the executing entity has the Azure RBAC permission Owner on the target subscription.
-
03-aks-post-deployAfter completing the Azure resource deployment, the post deploy step configures the Kubernetes cluster role bindings and prepares the helm service account.
Requires cluster-admin rights on Kubernetes.
-
04-aks-post-deploy-ingress(optional)This post deploy step configures the Kubernetes environment to support Azure Pod Identity and the Azure nginx Ingress option. Please note, that this step is completely optional. Feel free to setup a manual integration.
Requires cluster-admin rights on Kubernetes.
-
10-deployment-sample(optional)An optional example to verify the deployment. It exposes an echo service.
Requires cluster-admin rights on Kubernetes.
-
99-externals(ignore for the moment)Git sub-module which currently links to the aad-pod-identity GitHub repository. As soon as the aad-pod-identity project issues a proper remote Helm chart, the reference can be removed.
Disclaimer
This sample deploys AKS in combination with Azure Firewall and nginx ingress. Please note, that Microsoft does not officially support an AKS setup in combination with Azure Firewall.
Misc
Getting AKS Admin credentials
az aks get-credentials --resource-group <TODO> --name <TODO> --admin --overwrite-existingGetting AKS User credentials
az aks get-credentials --resource-group <TODO> --name <TODO> --overwrite-existing